Feel
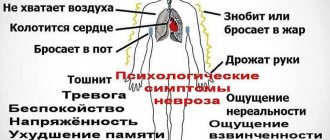
Irritability, constant feeling of fatigue, sharp reactions to simple events, frequent headaches, a feeling as if something is squeezing the head, as if wearing a helmet or hoop, rapid heartbeat, sweating, appetite disturbances, sleep disturbances, problems with bowel movements, short temper, a constant feeling of anger or, conversely, lethargy, a constantly bad mood, tightness of the muscles of the neck, shoulders, back, the inability to breathe fully (take a deep breath in and out) and, finally, a constant feeling of fear, anxiety, causeless restlessness - all these are signs of a disease known among psychologists and psychiatrists, as anxiety neurosis.
Characteristic symptoms
How can you understand that an anxious feeling has gone beyond the norm and it’s time to seek medical help? The complexity of the condition can be determined by characteristic mental and somatovegetative symptoms. The most common symptoms of anxiety neurosis are:
- a feeling of an approaching catastrophe, panic, anxiety and depression;
- sleep disturbance, depersonalization, manifestations of hypochondria, obsessive thoughts, derealization;
- a feeling of disorientation, neurotic shortness of breath, blurred vision, pressing pain in the chest, irregular heartbeat;
- panic attacks with all the characteristic symptoms;
- feeling of lack of air, internal tension, confusion, confusion, dizziness, trembling, restlessness;
- exercise intolerance and hyperventilation, tachycardia, nausea, headaches.
Terminology
Throughout the 20th century, concepts such as neurosis and anxiety disorder were used by doctors in the case of any state of obsessive anxiety and depression and were differentiated from “psychosis.” These two types of mental illness were distinguished only by the fact that in the first case, patients retain contact with reality and rarely exhibit antisocial behavior.
The disorders caused by a disease such as psychosis are much more serious. Here there is an inability to correctly perceive the real world, gross violations of social behavior and an inability to control one’s mental reactions. Symptoms of anxiety neurosis are increased general anxiety, which manifests itself in various physiological symptoms associated with the activity of the autonomic nervous system (regulating the functioning of internal organs, blood vessels, glands).
Treatment methods with folk remedies
Alternative medicine can help cope with attacks of anxiety and fear. Traditional methods are in demand due to their safety, effectiveness and accessibility. Home treatment should also begin with identifying and eliminating the factors that provoke attacks.
Herbal medicine will not completely eliminate mental illness
You should not hope that herbal medicine will completely eliminate psychological distress. This technique allows you to achieve relaxation and relieve tension only for a while.
If you approach the problem thoroughly, therapy with medicinal infusions can be no less effective than taking antidepressants and tranquilizers.
You can prepare the mixtures yourself by mixing different types of medicinal plants. Melissa, valerian, lavender, linden blossom, mint, sweet clover, hop cones, and peony root have a sedative and calming effect. These herbs can be a good alternative to synthetic medications.
Warm baths with the addition of infusions of soothing medicinal plants will help you relax. Juniper, rose hips, oregano, wormwood, and pine buds have a positive effect. The duration of such water procedures should not exceed 20 minutes.
Read: Causes of nausea without vomiting: what they may be associated with
For neurotic disorders, infusions of medicinal herbs promote relaxation, increase stress resistance and the body's defenses.
Differences between neurosis and psychosis
The symptoms of the disease vary quite greatly.
| Neurosis | Psychosis |
| chronic fatigue syndrome | hallucinations |
| irritability | rave |
| a violent, gratuitous reaction to stress | changes in a person's appearance |
| headache, feeling of tightness | indifference |
| sleep disorders (difficulty falling asleep, frequent waking up) | inhibition of reactions |
| hysteria | disturbances in facial expressions |
| seizures | disturbances of perception and sensations |
| fear (independent of circumstances, sudden) | emotional instability |
| obsessive states | disorganization of behavior |
At the end of the twentieth century, after the conference on the revision of the International Classification of Diseases in Geneva, such an independent disease as anxiety neurosis ceased to exist separately and was included in the definition of anxiety disorder (generalized anxiety disorder). Now such a definition as neurotic disorders summarizes various categories of disorders:
- Depressive disorders.
- Phobic disorders.
- Psychasthenia, obsessive-compulsive disorders.
- Hypochondriacal disorders.
- Neurasthenia.
- Hysteria.
All of them are considered reversible and have a protracted course. And the clinic is characterized by significantly reduced physical and mental activity, as well as obsessive states, hysteria and a state of chronic fatigue.
However, many doctors continue to identify this mental illness as a separate one, since this term is more understandable and does not frighten patients so much. Explaining how to treat anxiety neurosis is much easier than delving into the complex terminology of psychiatry.
Causes and features of the syndrome
Anxiety neurotic disorder is most common in people aged 18–40 years, and twice as often in women. The main cause is either short but intense stress or a prolonged state of mental overstrain. From a genetic point of view, anxiety neurosis is associated with depressive disorder; in half of patients with this diagnosis, immediate relatives suffer from similar depressive neurosis-like syndromes. The course of the syndrome is chronic with alternating periods of remission and exacerbation. Acute periods can vary greatly in intensity and last from a couple of weeks to several years. Periodic exacerbations of anxiety can be so intense that they take the form of panic attacks. In some cases, the patient can recognize an impending period of exacerbation by special warning signs. Symptoms persist in the vast majority of patients, even after long periods of remission. If the course is protracted, this syndrome may transform into agitated depression, hypochondria, or obsessive-compulsive neurosis.
What causes anxiety neurosis
There are no clear reasons for the appearance of this disease, but there are several plausible theories:
- There is a predisposition to developing anxiety and neurosis. In this case, the disease can arise from the slightest stress or from an incorrectly chosen model of behavior.
- Disturbances in the body's hormonal system (excessive releases of the hormone adrenaline) can cause frequent panic attacks, which can further lead to mental illness.
- Uneven distribution of the hormone serotonin in the brain can cause symptoms and subsequently neurosis.
- Sigmund Freud also wrote that if “someone suddenly becomes irritable and moody, or prone to anxiety attacks, you should first ask about his sex life.” Indeed, the symptoms of the state of a person who has not achieved release (orgasm) after arousal during sexual intercourse are very similar to those described in neuroses.
Most likely, anxiety neurosis is caused not by one factor, but by a whole series of psychological problems, biological “errors” and social factors that influence its development.
It is worth noting that relatives and friends may not notice anything unusual in the behavior of a person suffering from phobic neurosis. After all, it will not be surprising that the pulse rises if a person enters for whom there are feelings (positive or strongly negative), that a person sweats if it is hot outside or indoors. Also, many symptoms may be hidden behind signs of diseases that a person already suffers from. After all, it is unlikely that the patient will have only one diagnosis written on his card - anxiety neurosis.
Treatment at home will definitely not help here. In the case of a prolonged course of the disease without medical help, pathological conditions may arise, such as a panic attack, the desire for complete isolation (the desire to protect oneself from the outside world, the fear of going out). Various phobias may appear: fear of public transport, open spaces (agarophobia), riding in an elevator and other forms of claustrophobia. Such people often consciously avoid places where panic attacks occurred, limiting the circle more and more.
Fear neurosis or obsessive-phobic neurosis
Separately, we should highlight such a form as phobic neurosis, in which, among all the symptoms, various fears and anxieties come to the fore. That's why it's called fear neurosis. Most often, people suffering from this syndrome are afraid of getting sick from various diseases, going out, being in a crowd, or traveling by public transport. With too much fear for one’s health, frequent examinations and medical consultations, fear neurosis can develop into a hypochondriacal disorder. Obsessive-phobic neurosis often develops in people with an anxious and suspicious character, prone to introspection. At the same time, a person cannot independently get rid of his own obsessive fears, although he perceives his neurotic state as painful. Fear neurosis is often accompanied by panic attacks when the patient encounters the object of his fears. Such a neurotic disorder can be caused by disruption of a person’s usual activities and the associated state of expectation of failure. Fear neurosis in a severe stage is manifested by a panic reaction even to a word associated with the subject of fear.
Anxiety neurosis. Simple form
The simple form of fear neurosis is distinguished by the fact that it occurs abruptly, after a trauma (accident, loss of a loved one, disappointing medical diagnosis, etc.). A person with a simple form of the disease eats poorly, has difficulty falling asleep and often wakes up, his hands and knees tremble, he feels low blood pressure, he often goes to the toilet, breathing is incomplete, dry mucous membranes are noted, he cannot collect his thoughts when talking and is confused in answers . In this case, anxiety neurosis treatment involves only symptomatic treatment. Over time, all functions will restore themselves. To speed up the process, you can use herbal medicine, physical therapy, massage, and sessions with a psychotherapist.
What's happened
In modern psychotherapy, there is a concept of three types of neuroses - obsessive-compulsive neurosis, neurasthenia and hysteria. In this article we will talk about fear neurosis, one of the forms of obsessive-compulsive neurosis. With this type of neurosis, the experience of fear and anxiety becomes a priority. Against the background of general anxiety when faced with real or imaginary danger, phobias develop. A phobia is an obsessive fear of objects, situations or activities that interferes with an individual’s social life.
A person with increased anxiety may hear on TV that an earthquake has occurred somewhere in the world, and begins to experience obsessive fear, is afraid to live on the floor above the second and cannot fall asleep, imagining terrible pictures of natural disasters. Phobias tend to expand their “sphere of influence.” So, if a dog frightens a person while walking, he will first be afraid to walk in the same place, then of all dogs, even small ones, and finally, he will begin to experience panic fear even when leaving the house to go to the nearest store.
The most common types of phobias in anxiety neurosis:
- agoraphobia (fear of open spaces);
- social phobias (fear of public speaking, “disgracing yourself” in public);
- fear of germs (plus an obsessive state of frequent hand washing, wiping door handles);
- cancerophobia (fear of getting cancer);
- claustrophobia;
- fear of going crazy;
- fear that something will happen to relatives.
Anxiety neurosis: symptoms and treatment in children
In young children, neurosis can be caused by anything. If a child is just beginning to learn about the world, if he is naturally closed and irritable, if there are any congenital or acquired (for example, birth injuries) diseases, then such a child can easily develop fear neurosis. A sharp, unusual sound (especially at those moments when the child is sleeping or in a calm state), bright light, a strange face that appears unexpectedly, a new pet - all can cause severe fright. Older children will definitely remember the scene of a fight, an aggressive person or an accident.
In seconds of fright, the child will most likely freeze and become numb or begin to tremble. If the fear remains in the memory, then the child may temporarily stop talking, “forget” that he can walk, eat himself with a spoon, wipe his nose, and much more. Often children begin to stutter, bite their nails, and wet the bed. This is how anxiety neurosis manifests itself in children. The symptoms and treatment of this disease are well known to any child psychologist. In most clinical cases, the prognosis of therapy is favorable. All functions that were impaired are gradually restored, and the child forgets about the fear.
Children should never be frightened by scary fairy tales, films or characters. If a child over five years old is frightened, then he should be watched more closely. There is a high probability that various phobias (obsessive states) can develop from anxiety neurosis.
Treatment
If, after several visits to a doctor, psychiatrist or psychotherapist, an anxiety neurosis is diagnosed, the treatment that the doctor will prescribe will most likely be medicinal. It is impossible to cure such a disease on your own at home, with herbs, compresses, hot baths or with the help of healers who remove damage. If the problem brings the patient to the doctor, then it’s time to entrust treatment and diagnosis to specialists. Taking pharmacological drugs prescribed by your doctor and psychotherapy sessions over a few months can make life wonderful. Resolving your internal conflicts, changing your attitude towards the world around you and yourself, searching for internal problems and ways to solve them in your mind, along with the help of antidepressants, will help prevent possible complications and find harmony.