0
Author of the article: Marina Dmitrievna
2017.10.27
1 499
Vessels
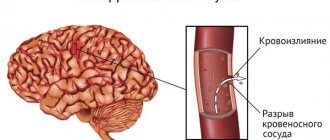
Stroke, or acute disturbance of blood flow in the brain, is a pathology that occurs 3-4 times out of 1000 cases. 80% of the total is ischemic, about 20 is hemorrhagic. Often, a stroke comes as a surprise to both the patient and his loved ones. A painful wait for the result of the operation, after which the patient is transferred to the intensive care unit, and relatives are left asking the question: “How many days do they stay in intensive care after a stroke?”
How long do you stay in hospital after a stroke?
Saratov State Medical University named after.
IN AND. Razumovsky (SSMU, media) Level of education - Specialist
1990 - Ryazan Medical Institute named after Academician I.P. Pavlova
The length of time a patient will need to undergo treatment in a hospital setting after a stroke has occurred directly depends on the severity and subsequent dynamics of the disease. There is little point in keeping someone in a hospital ward for too long after a stroke, since everything is determined by the first hours and days, as well as how well the patient’s condition then improves. If the situation is stabilized and there is no need to put in IVs, then the patient can be discharged in a few weeks. Therefore, everything will depend on the person’s condition and what plan he had for the stroke.
Effective treatment of stroke: innovative technologies to protect your health
Therefore, the global medical community has developed not only a program whose goal is to prevent stroke, treating the consequences and restoring the body takes a large part in their research. Our specialists take an active part in scientific research and have created their own effective program that literally gets patients back on their feet.
We are able to bring an atmosphere of home comfort into a hospital environment and provide psychological comfort to the patient. The stroke treatment center ensures that the patient will be provided with everything necessary, including equipment for rehabilitation and examination, the involvement of outside specialists and studies will not be needed anywhere else.
Stroke treatment is carried out in Moscow; convenient transportation simplifies contact between relatives and patients, and gives them the opportunity to visit the patient as much as possible and necessary.
About the timing and stages of treatment for stroke in an inpatient setting
Nowadays, stroke has become a fairly common disease. On average, 3-4 people have seizures per 1000 people. Most of the cases are patients suffering from ischemic stroke, others are people with the hemorrhagic type of the disease. All relatives are always interested in the question of how much time the victim needs to spend in intensive care and in the hospital for the condition to completely stabilize.
How long you stay in the hospital after a stroke will depend on how each stage of the disease progresses. Namely:
- Period before hospitalization;
- Treatment in the intensive care unit, as well as in the intensive care unit;
- Inpatient placement in a general ward.
How long a patient will have to stay in hospital after a stroke is regulated by the Ministry of Health based on established standards of treatment.
Mom has a stroke. Treatment and rehabilitation after stroke.
758. Guest
| 17.07.2010, 17:24:07 [3907468991]
IROLYA
like this in the presence of the head physician and a notary. Is this a power of attorney to receive a pension? Our power of attorney is simply expiring. and no one *notarizes it, because mom can’t answer the simplest questions. forgets who I am. and cannot name the place where she is. but the doctors say it’s not our concern.
On January 4, I had an ischemic stroke with paralysis of the left side, this became a terrible tragedy for me. I led an active lifestyle, I am an avid fisherman. As a result, I drove myself into post-stroke depression, from which I still cannot get out. 8 months have passed already. the leg has recovered completely, the arm has not yet recovered. I am very worried that for some reason the arm has not recovered
Standard situations and with complications
On average, the length of a person's stay in hospital after a stroke is 21 days. This is provided that there are no failures of body systems that fall under the category of life-critical ones. Those who have been found to have serious violations are kept for 30 days.
When the established 30 days are still too short for the condition of the person being treated, a medical and social examination is scheduled to consider the question of how to continue treatment and whether an individual rehabilitation course is necessary. Doctors try to prevent a person from spending too much time in the intensive care unit with complications - the situation is usually stabilized within 3 weeks.
During this period, the patient's vital signs are checked and prognoses are made. Most often, disorders and complications occur due to inadequate functioning of the brain. When an ischemic stroke occurs and paralyzes an arm or leg, but the person can take care of himself, speech is not impaired - doctors consider spending 2 weeks in a hospital to be sufficient time.
What you need to understand after leaving hospital
Treatment after a stroke should be comprehensive. It is usually built as follows:
- The patient takes prescribed medications that improve blood circulation, as well as eliminate spasms and swelling;
- Electrical stimulation is performed;
- Physical therapy training is provided;
- Massage sessions are scheduled.
It is important that a person understands that after the end of a hospital stay due to a stroke, a number of treatment measures will be required and it does not end with discharge from the hospital. At home you will need to continue to do physical exercises, carefully monitor your blood pressure and your regimen. Alcohol and smoking will be strictly contraindicated. You need to move as much as possible, it is best to take walks in the fresh air.
What determines the length of hospitalization?
All patients with signs of ischemia affecting the brain or hemorrhagic stroke are required to be admitted to the hospital. The length of time a patient will be assigned to the department will depend primarily on the following factors:
- Size and location of the lesion - in the case of a major stroke, the length of stay in hospital will be significantly longer;
- How severe are the clinical symptoms;
- Is the patient in depressed consciousness? When the patient is in a coma, it will be impossible to transfer him to the general ward; he can be discharged from the intensive care unit only if the changes in his condition are positive;
- What is the state of the body’s key and vital functions;
- Is constant monitoring required and is there a risk of stroke recurrence?
- Whether the patient has or does not have serious concomitant diseases.
Treatment in intensive care conditions will be aimed at eliminating all disturbances in vital functions. It will be differentiated, basic or undifferentiated depending on what plan the violation occurred.
When and where does rehabilitation begin?
After an ischemic stroke has occurred, rehabilitation will be required, starting on days 4-5. But from the first hours when the patient arrives at the hospital, he will need passive gymnastics. This is not so much gymnastic exercises as it is giving the body a certain position in which the condition will stabilize and improve.
To do this, the patient’s arms and legs are positioned correctly, and the body is positioned in a special way. To do this, use bolsters or pillows, seating the patient in a semi-sitting position. Once every 2 hours, the position of the body will change. Already on the 4-5th day, the patient should begin to be turned into a lateral position. You cannot stay in one position for too long, so as not to cause stagnation, pneumonia or bedsores.
Is it possible for relatives to stay in hospital during the rehabilitation process?
It will be of great help to the patient if one of the relatives is in the room as often as possible. In this way, the relatives themselves have the opportunity to learn how to care for the patient before he is discharged, in order to alleviate possible difficulties later. After discharge home, relatives must dress the patient, feed, give medications and jointly perform the exercises necessary for recovery.
It is important to know many points, such as the fact that you should start putting on a shirt with the hand that was injured, and take it off with the healthy one. Even after hospitalization, you will need to communicate with the person on a regular basis, in a very calm and patient tone. The most intensive recovery of the patient occurs in the first 3-4 months after the stroke occurred.
Frequency of treatment
Often, the patient’s relatives believe that the course of treatment prescribed is very long and frequent. But this is due to the specific nature of the patient’s recovery process. Everything happens priority in the first months. At the same time, everything must be done to reduce the risk of a recurrent stroke.
The initial course is prescribed to be taken immediately after the stroke occurs. The subsequent course is carried out after 2-3 weeks. After which you will need to take about 3-4 more courses during the first 6-8 months. After this, a break of 2-3 months is taken and the course of treatment is repeated. The favorable time for rehabilitation should be used as efficiently as possible.
Duration of sick leave
So, sick leave is issued only when the threat to life has passed, the person has left intensive care after a stroke and has undergone a course of treatment. There is no single standard for setting deadlines. It all depends on the disorder, the amount of skills lost and the recovery process:
- in case of micro-stroke and minor violations, sick leave is issued for 3 months;
- moderate stroke is treated for at least 3 months, it can be increased without commission to 4 months;
- with a severe stroke, rehabilitation is often required for 6-8 months, and the person is given temporary disability.
If during rehabilitation, while on sick leave, a repeated relapse occurs, then treatment is extended for 2.5 months.
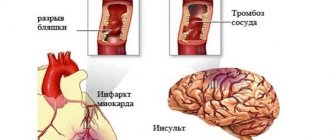
The incidence of strokes in Russia is very high, and out of every ten stroke patients, eight people end up in the clinic with an ischemic stroke, and two people with hemorrhage. Both types of damage provoke serious consequences, and they usually happen unforeseen. In this case, the question becomes relevant: how long are stroke patients treated, how long do they stay in the hospital after a stroke, and what are the prognoses for home treatment.
Main stages of therapy: timing and features
In case of stroke, assistance to patients can be divided into several stages:
- prehospital care – provided by others or a team of doctors before admission to a medical facility,
- providing assistance in the clinic - performing an operation or treatment in the intensive care unit, intensive care unit,
- the patient's stay in the general ward.
If we can say about the first two stages that the length of stay there is unpredictable and depends on the health of the patient and his condition after the operation, then the third stage is regulated by law. There are instructions from the Ministry of Health, according to which stroke patients, after passing through the acute period, are transferred to a general ward, the duration of stay in it is from 21 to 30 days.
Patients whose vital functions are not impaired are kept in an intensive care ward for three weeks. Simply put, these are those patients with a mild form of stroke whose body has found the strength to restore activities that were not seriously affected.
Stroke patients with more serious disorders, whose body was unable to overcome the abnormalities caused by the stroke, remain in a stable and serious condition for 30 days. If even after thirty days in the clinic the patient’s condition does not improve, a medical and social examination is carried out, recording the condition of the stroke patient after the end of the expected recovery, the extent of the remaining disorders, and their threat to human life. The conclusion of the medical and social examination is a decision on the advisability of the patient’s continued stay in the clinic, drawing up a plan for the patient’s recovery.
Duration of resuscitation depending on the type of stroke
Treatment depends on the type of pathology. Stroke is divided into 2 types:
The patient may stay in the intensive care unit longer, but only after undergoing an examination. On the 21st or 22nd day of his stay in intensive care, a commission meets to assess the person’s physical condition. If one of the delay factors is detected, the period of stay in intensive care is increased to 30 days. In rare cases, it can be extended, but only on the basis of delay factors that are identified at the consultation.
Features of resuscitation and its timing
The ICU will maintain vital signs for three weeks in most cases. All this time, doctors support the body’s activity as much as possible and do everything to prevent the situation from worsening. The main problem at this time is the inadequate activity of parts of the brain and those structures where the consequences of an ischemic stroke remain.
When undergoing surgery due to hemorrhagic stroke, cerebral edema becomes a threatening condition, which can lead to death. The main indicators of the patient’s body and his brain are recorded by devices; if the situation worsens, doctors in the department urgently carry out resuscitation measures. Usually, within three weeks in intensive care, it is possible to avoid threatening conditions and stabilize the patients’ vital signs. In the future, care for a bedridden patient is carried out in the general ward.
Features of hospitalization for stroke are manifested in the volume of disorders that formed in the patient after acute oxygen deprivation of the brain or hemorrhage. The following factors influence how long treatment lasts:
- the location of the focus of ischemia or hemorrhage and its size - the greater the volume of damage, the longer the patient remains under treatment,
- severity of clinical signs of pathology,
- degree of depression of consciousness - for example, in a comatose state, a stroke patient is placed in intensive care and will not be placed in the intensive care ward until consciousness returns to him,
- level of preservation of vital functions,
- monitoring blood pressure readings to avoid relapse of an attack,
- presence of additional complications.
Treatment for stroke in intensive care has two directions: patients are given basic therapy, as well as specific therapy, depending on the needs of each patient.
Basic therapy includes respiratory and hemodynamic support. It is very important to combat possible cerebral edema, which can cause death, to prevent vomiting and psychomotor overexcitement. At the same time, the patient’s nutrition is adjusted and hygienic care is provided.
Specialized care for hemorrhagic stroke depends on the patient’s condition; at the initial stage, pressure correction is achieved and surgical intervention is performed. For ischemic stroke, help is aimed at reducing hypoxia and activating metabolic processes. If help was provided in a timely manner, the length of stay in the clinic is reduced. It is difficult to talk about how long intensive care will take and when the patient will be transferred to the department. It all depends on the extent of the damage and the body’s recovery capabilities. Typically, recovery is faster in younger people.
Factors for prolonging intensive care
A patient with an ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke may remain in intensive care for long-term treatment if:
- a relapse occurred (repeated damage to various parts of the brain);
- human life and health are still under serious threat;
- the person did not come out of the coma;
- the affected parts of the brain did not recover during rehabilitation;
- there are signs indicating an imminent recurrence of the attack.
The purpose of a patient's stay in the intensive care unit is to preserve life and restore nervous functions at the brain level. If the patient still needs reconstructive surgery, he is kept in intensive care, where care is provided for recently operated patients.
The recovery period depends on resuscitation treatment. The period of time during which the basic procedures will be prepared and performed directly affects the speed of the patient’s rehabilitation.
When a person is admitted to the intensive care unit, the following steps must be taken:
- correction of respiratory system dysfunction;
- reduction of unreasonable psychomotor agitation;
- restoration of the normal state of the body (combat hyperthermia);
- compensation for brain swelling.
After an emergency examination, surgery is prescribed or special equipment is used. In case of hemorrhagic stroke, surgery is required to eliminate life-threatening edema, during which the edematous fluid is removed and the pressure of the edema on important parts of the nerve center is compensated. Surgical intervention is urgent and should be carried out no later than the second day of the patient’s admission to the hospital. If the operation was delayed by 3–4 days, rehabilitation will be delayed.
Ischemic stroke does not always require surgery. Its clinical symptoms are compensated by the work of special life support units, outpatient and resuscitation procedures. The recovery period is several days shorter than with surgery.
Stay in the ward
Patients can be transferred to a general ward if the health criteria meet the established ones:
- The patient’s blood pressure level has stabilized, heart function has normalized,
- the patient can breathe independently without the support of devices,
- the doctor and attendants can communicate with the patient - understanding simple requests, performing movements, if possible,
- the patient’s ability to ask for help independently,
- if the risk of rebleeding has subsided.
As soon as the patient's condition begins to meet these criteria and the patient gets better, he is transferred to the general ward in the stroke department. Recovery and treatment continue in the general ward, where stroke patients begin to resume their lost functions. To do this, specialist doctors work with them.
Loss of ability to work: features, timing
If a patient has a stroke, he becomes temporarily disabled. The official diagnosis is called “acute cerebrovascular accident.” The recovery period after illness varies from person to person. It depends both on the amount of damage received and on the rate of recovery of the patient.
If a patient is diagnosed with a subarachnoid hemorrhage or a small-volume stroke, recovery will take an average of about three months. At the same time, he will spend three weeks of this time in the hospital, and the rest of the treatment with a microstroke is carried out on an outpatient basis. For a moderate stroke, hospitalization will take thirty days, and overall treatment will take three to four months. In case of severe damage, the chances of a quick recovery are significantly reduced, so the stay in the clinic is extended - in addition to the usual period of treatment, a medical and social examination is carried out, based on the results of which the therapy is extended. The patient can be assigned a disability group, a recovery plan for the patient is drawn up, after which he is discharged. Relatives have to care for the sick.
In case of a stroke due to a rupture of a blood vessel aneurysm, the recovery time for patients is different. If the hemorrhage is small and surgery is not performed, then a person can stay in the clinic for about two months, and the same amount of time is given for outpatient treatment. In total, incapacity for work lasts about four months. If there is a relapse, the sick leave is extended for another six weeks, and if the dynamics are positive, the patient’s full recovery can take up to eight months.
When an aneurysm is operated on, people remain in the hospital for at least four months. If complications arise, the patient stays in the hospital longer after a stroke. In the future, sick leave is extended taking into account the patient’s recovery rate.
STROKE. Caring for a Bedridden Patient After a Stroke (important doctor’s advice). ISCHEMIC STROKE. BRAIN HEMORRHAGE (How to live after a stroke? Doctor's advice) Stroke. Rehabilitation after a stroke. Complex treatment. Where? How?
How to recover after a stroke?
Doctors report that they have only 5 hours to save the life of a person affected by this disease. How long do people stay in hospital with a stroke? Treatment and recovery period depend entirely on how timely first aid was provided. Unfortunately, a person may not realize that they are having a stroke, so those around them should pay attention to the following signs:
- If you ask a person to smile, one side of the face will remain motionless and the corner of the mouth will turn down.
- When trying to raise both arms up, a person will be able to fulfill the request only partially - only one limb will rise.
- Speech may also be sluggish, and you may notice a feeling of "mush in the mouth" or the person's inability to say simple sentences or their own name.
In this case, you need to immediately call an ambulance.
Treatment
We remind you that transient ischemic attack requires hospitalization. It allows you to find out the reason why the attack occurred. If you do not seek help in time, the attack may recur. Some patients experience several attacks per day. And each of them can end fatally.
A microstroke suffered on the legs usually leads to ischemic-type ONCM, severe arrhythmia. In addition, TIA leads to decompensation of coronary heart disease.
Men
The stronger sex is more likely to experience micro-stroke. And this group has the highest number of refusals from hospitalization. This is why a transient attack is dangerous. The affected vessels are so small that they do not cause severe damage. Or the symptoms disappear altogether. This imaginary well-being usually leads to severe strokes. And the most common reason is the lack of timely medical care.
Remember about the risk group:
- Age over 60 years;
- Drinking alcohol;
- Smoking;
- Obesity;
- Diabetes;
- Arterial hypertension;
- Systemic atherosclerosis.
It is known that blood vessels are additionally affected in this disease. Their walls become thinner, and atherosclerosis progresses. An additional risk factor is increased diuresis in diabetes. This creates additional conditions for blood thickening. Therefore, strokes with diabetes occur 2.5 times more often.
In an elderly patient with this disease, the risk of having a stroke after a TIA increases several times. And the main role in this is played by collateral circulation. When a blood clot closes a major vessel, blood rushes around the blockage. At the same time, diabetes turns small capillaries into hard “glass” tubes that are not able to compensate for such blood flow. Ischemia intensifies.
Women
Micro-stroke “on your feet” is experienced by 30-40% of the population in developed countries. In Russia there are no adequate statistics. However, these numbers will be higher. What follows an ischemic attack in a woman?
Firstly, any brain hypoxia leads to unusual fatigue, depression and headaches. If the patient has not experienced them before, this is a reason for examination. Secondly, after a TIA, performance and cognitive functions are significantly reduced. This affects the quality of work, especially if a woman holds a leadership position.
So, any attack occurs as an ischemic type of stroke. There are two types of TIA based on the location of the lesion:
- Vertebro-basilar basin;
- Carotid basin.
So, the first option occurs in 70% of cases. What symptoms accompany the event?
- Dizziness with occipital pain;
- Nystagmus;
- Diplopia (double vision);
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Loss of half the visual field (usually bilateral);
- Flashing “flies” before the eyes;
- Damage to the muscles of the face, pharynx, tongue, soft palate;
- Sudden fall without loss of consciousness;
- Short-term loss of memory and orientation.
TIA in the carotid region behaves like this:
- Loss of sensation in one or more limbs;
- There is no movement in one or more limbs;
- Speech is partially or completely lost;
- Vision disappears in one eye, paralysis of half the body develops on the other side.
TIA lesions resolve within 10 minutes to 1 hour. If the symptoms do not go away within a day, a diagnosis of acute cerebrovascular accident is made. And this is a completely different disease. It has a high mortality rate and a long rehabilitation period.
How to treat ischemic stroke?
- Correction of blood pressure at numbers above 200/110 mmHg. You cannot reduce the pressure at lower numbers, otherwise the blood supply to the brain will stop altogether. You should also not use medications that give a quick effect (nifidipine). Preference should be given to captopril, enalapril;
- Fighting cerebral edema (mannitol);
- Diazepam is administered to relieve seizures.
When treated in a hospital, the patient is given neuroprotective therapy. These are glycine, emoxypine, cytoflavin, cerebrolysin.
The main danger of a transient attack is the high risk of subsequent stroke. 25% of patients develop serious complications within the next 3 months. In rare cases, cardiac problems appear: arrhythmia, heart failure, angina.
There is a TIA severity rating scale. It can be used to assess the risk of developing a recurrent vascular accident.
| Age | Over 60 years old |
| Anamnesis | Repeated attack or diabetes |
| Arterial hypertension | Over 140/90 |
| Clinic | Unilateral upper limb paresis or isolated speech loss or symptoms lasting more than 10 minutes |
| Neuroimaging | Changes on CT and MRI |
| Etiology | Atherosclerosis of large great vessels |
Each feature from the table is scored one point. The more there are, the higher the likelihood of developing a second attack or stroke. There are no reliable ways to reduce this risk. As modern research shows, correction of the lipid spectrum, arterial hypertension, and sugar does not provide guarantees. The possibility of relapse remains high.
What recommendations does the attending physician give after a transient attack? A person with a TIA is discharged from the hospital within 3-4 days. But only if there is a low risk of a recurrent attack. What is needed for full recovery?
- Undergo additional examination if everything was not completed in the hospital. The scope of the study will be determined by the attending physician;
- To refuse from bad habits. This is an important risk factor that the patient can get rid of on his own;
- Normalize nutrition. Eliminate fatty and processed meats from your diet, add vegetables and fruits. Avoid eating outside the home;
- Add physical activity (daily walks, exercise therapy and gymnastics, gym classes);
- Normalize mental state. If necessary, consult a psychotherapist;
- Learn to cope with stress (yoga, meditation, creativity, communication).
Sports mode is not related to physical health. Therefore, the patient is advised to limit active exercise after an attack. However, you should not prohibit going to the gym and exercising. To do this, it is important to carefully monitor your well-being. It is important to use the help of an instructor or trainer with experience in working with this pathology.
So, the load after a mini-stroke should be light. The exercises are aimed at developing limbs if there has been loss of function. Cardio training is gradually introduced. But the condition is strict monitoring of pulse and blood pressure. Excessive fatigue is unacceptable during classes. After working in the gym, the patient feels pleasantly tired, but not a loss of strength.
In addition to the recovery room, swimming, Nordic walking, and cycling are also suitable. Of course, you should give preference to your favorite type of activity. But before exercising, you should consult with your doctor about the presence of contraindications.
Charger
Exercising is a great way to start the day. If you have suffered a mini-stroke, such activity will bring a lot of benefits. A set of exercises improves blood circulation, promotes quick awakening and lifts your mood. Any standard exercises are suitable for charging. Basic principles:
- Their daily implementation;
- Well-being control;
- Time limit (no more than 10-15 minutes).
Music, joint activities (with loved ones or friends), and long-term evaluation of the result will help you consolidate a healthy habit.
Diet
As a rule, a microstroke is an indicator of poor nutrition. Which foods should be removed from the diet and which should be added? Let's talk about this in more detail.
| Can | Cannot or limited |
| Bread with bran (improves digestion, contains B vitamins) | It is better to minimize the baking |
| Milk and dairy products (source of calcium and protein) | Sweet yoghurts, desserts (high in calories) |
| Fish red and white | Do not get carried away with fatty varieties, use salted fish |
| Vegetables, fruits, berries, greens | Better seasonal, don’t get carried away with potatoes |
| Turkey, rabbit, chicken, veal | Lamb, beef, pork, processed meat (smoked meat, sausages, sausages) - an uncontrolled source of salt |
| Sweets – marshmallows, marshmallows, homemade jams, Lenten cookies | Chocolate, baked goods, confectionery |
| Cereals, peas, lentils, beans |
Menu examples
We will show you how to eat healthy and varied after a mini-stroke.
Breakfast
- Egg
- Porridge with fruit
- Tea with milk
- Cream soup with pumpkin
- Cabbage salad
- Baked turkey breast with gravy
- Dried fruits compote
- Boiled pike perch
- Potato wedges baked with herbs
- Berry juice
- Alcohol, coffee
After a transient ischemic attack, certain restrictions should be followed. But an attack should not make life unbearable. Therefore, giving up your favorite drinks is quite conditional. Coffee and alcohol are substances that can increase blood pressure. In addition, they have a dehydrating effect - they reduce the amount of water in the body.
Should you give up coffee? There is no need to exclude the drink from your diet. But it is necessary to seriously limit it to those who drink 6 cups per day. After a micro-stroke, the principle of “reasonable consumption” applies. One or two glasses of espresso in the morning doesn't hurt anyone. It is important to remember that after coffee you should drink a glass of clean still water.
Folk remedies
In which department and for how long do they stay in the hospital after a stroke?
Stroke is a serious disease, the mildest forms of which require hospitalization, long-term therapy, and recovery. Diagnosis and treatment of pathology are so complex and specific that a good result can only be achieved in a hospital setting of specialized medical centers or departments.
Doctors distinguish 3 stages of medical care:
- prehospital;
- treatment in intensive care unit or intensive care unit;
- treatment in a general ward.
The final stage is rehabilitation, the task of which is to eliminate or minimize the consequences of acute cerebrovascular accident. Let's look at the peculiarities of each of these stages and the length of stay in the hospital after a stroke.
Pre-hospital stage
This is the time from the beginning of the arrival of the ambulance until the patient is delivered to the hospital. The duration of the pre-hospital period depends on how quickly the doctor is called by the patient or someone around him, the speed of the ambulance, and the time of delivery of the patient. The optimal term for hospitalization is 3 hours from the moment the first symptoms appear. Doctors will have enough time to conduct a full examination of the patient and begin full treatment, which will ensure the best prognosis.
If the optimal period of hospitalization is missed, it is still advisable. It has been proven that transporting a patient to a hospital has a positive effect on the outcome of the disease during the first 14 days after the onset of an attack (1).
Duration of treatment for severe stroke
The most difficult thing is the prognosis of a severe stroke. The professionalism of doctors and adequate therapy are not the key to a quick recovery. In any case, it all depends on the patient’s body.
Hemorrhagic stroke with aneurysm rupture is considered a serious disease. Rehabilitation takes about 4 months. But often the period is extended based on the opinion of the attending physician.
The duration of treatment for severe forms is determined individually, taking into account the time during which the stroke patient’s condition is stabilized and measures are taken to restore lost functions. Inpatient treatment is carried out for 3-6 months. According to average statistical forecasts, out of 10 cases, only 2-3 people recover. In this case, the rehabilitation period can last up to a year.
Indications and contraindications for hospitalization
Hospitalization is indicated for all patients with suspected stroke, including minor forms of the disease and microstrokes. It is required even if at the time of examination of the patient by the ambulance team, all symptoms of acute cerebrovascular accident have passed. This allows you to prevent the development of more severe forms, episodes of which often occur during the first day after the initial symptoms.
There are two groups of contraindications to hospitalization: relative, absolute.
Relative – conditions in which transporting a patient can lead to a significant deterioration in the patient’s condition or death. The doctor decides whether or not to take the patient to the hospital. Relative contraindications include:
- critical disorders of blood circulation, breathing, heart function until they stabilize;
- epileptic attack, psychomotor agitation until they are eliminated;
- terminal coma;
- senile dementia with severe disability before the onset of stroke;
- last stages of malignant diseases.
Absolute – factors that exclude the possibility of hospitalization. These include a written refusal of the patient or his relatives to be hospitalized.
Is it possible to find out how long people are in the hospital with a stroke?
Any person suspected of having an acute circulatory disorder requires hospitalization. It is impossible to determine in advance how long people stay in the hospital with a stroke.
The timing and conditions of hospitalization, the time spent in intensive care, and in the general ward are influenced by many factors. Sometimes even the attending physician is unable to determine the treatment period.
The legislative framework
The certificate of incapacity for work is drawn up by the attending physician of the hospital where the stroke patient is being treated. While he is in the hospital, the period corresponds to the duration of therapy. Upon discharge, the period can be extended according to the doctor’s decision.
A sick leave certificate is a document confirming the fact of absence from work due to temporary disability. It is issued exclusively by institutions that have passed state accreditation.
The procedure for issuing a certificate of incapacity for work is regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation (Article 183). The rights of institutions to issue documents are controlled by Order of the Ministry of Health and Social Development of the Russian Federation dated No. 624n. Payment for sick leave is made in accordance with the requirements of Federal Law No. 255-FZ.
Factors determining length of hospitalization
It is impossible to determine how long a person will spend in the hospital. This is difficult for doctors and relatives to do.
Several factors are decisive for understanding the length of treatment for a stroke in a hospital:
- Features of damage. The volume, nature of development, and complications that have arisen are considered. An extensive, hemorrhagic stroke is an indication for a long stay in the hospital.
- Manifestation of symptoms. Signs of a stroke and their severity can destabilize the patient’s condition over a long period of time. It is not advisable to prescribe it when deterioration may occur. Lack of stability increases the likelihood of another stroke, severe consequences, or the development of complications.
- Coma . In a comatose state, the risk of deterioration of the patient's condition is high. The person is in the hospital until consciousness and key indicators normalize.
- Stabilization of functions important for the life of the body. The work of the heart, respiratory system, and the degree of damage to other organs are analyzed.
- Treatment being carried out. After complex surgery, people usually spend more time in the hospital.
- Dynamics. Before making a decision on discharge, doctors clarify how the process of stabilizing the patient is going.
- Concomitant pathologies of the cardiovascular system. A common complication after a stroke is exacerbation of heart disease. Patients are often transferred from the neurology department to the cardiology department.
For reference. Discharge from the hospital should occur only after the heart rhythm has stabilized and there are no complications.