MedStroke -> Types ->
This article aims to explain the concepts of heart attack and stroke and find out if they have anything in common. It’s not for nothing that people often confuse them with each other, although, in fact, one follows from the other.
Unfortunately, these days, disease statistics clearly do not speak in favor of humanity: in just 5 years, the number of registered heart attacks has increased by 20%. This is due not only to environmental degradation and poor heredity, but, alas, to our way of life.
- The nature of heart attack and stroke
- Main Differences
- Comparison of heart attack and stroke disease
Main differences between heart attack and stroke
Cardiological diseases affect not only people of retirement age, but also patients under 45 years of age. A polluted environment, excessive emotional and physical stress, neglect of one's health - all this contributes to the development of the syndrome.
A heart attack is a disease of the cardiovascular system that occurs against the background of vascular damage due to a lack of nutrients. The main cause of the disease is thrombosis. After the onset of a pathological condition, necrosis of the problem organ develops: kidneys, intestines, heart muscles, liver, brain.
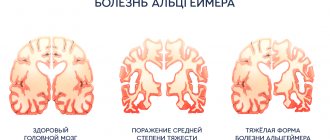
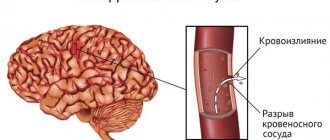
Stroke is a change in the blood circulation of the central nervous system, occurring in an acute form in the form of thrombosis or rupture of a vessel and hemorrhage. Sometimes the syndrome, in its symptoms, resembles a “gray matter” infarction.
The main difference between the pathological conditions is that during a stroke there is still a chance to restore the lost functions of the affected cells. Their work is performed by healthy tissues, which, if all the doctor’s recommendations are followed, return a person to normal life activities.
Heart attack and stroke have different origins
Stroke and heart attack, first of all, differ in their origin and the reasons that provoked the attack. In addition to the main factors that can provoke the onset of a crisis - atherosclerosis and thrombosis, there are other external and internal stimuli.
The most common causes of the syndrome are:
- Hypertension (very high blood pressure).
- Systematic use of certain groups of drugs and alcoholic beverages.
- Constant stress.
- Disproportionate loads.
- Genetic predisposition.
- Chronic, acute infections.
It is especially dangerous for a person when a heart attack and stroke are combined at the same time; in this situation, the patient faces coma or death. At the first sign of an attack, you must immediately call an ambulance.
Treatment
The differences between a cerebral infarction and a stroke also lie in the treatment methods. Its implementation begins after first aid is provided in a hospital and an accurate diagnosis is made.
Treatment of heart attack
Treatment of cerebral infarction begins with the administration of thrombolytics to the patient. Their action is aimed at dissolving the blood clot that has blocked the vessel and restoring blood circulation in the affected organ. With timely assistance, the patient becomes much better almost immediately.
Important! If, for one reason or another, the use of thrombolytic drugs was not carried out in the first 3 hours after the attack, irreversible destruction develops in the tissues.
Subsequent treatment consists of taking medications:
- stabilizing pressure;
- anticoagulants and antiplatelet agents to prevent thrombosis;
- improving cerebral blood supply.
As additional means, vitamin and mineral supplements are used with the obligatory inclusion of B vitamins.
Surgical treatment is prescribed strictly according to indications. It is used when it is necessary to mechanically remove a blood clot that does not resolve with medication.
Stroke treatment
A stroke is much more dangerous than a cerebral infarction, since after a hemorrhage, the cost of saving a person’s life is counted in hours. An important role is played by the timely provision of assistance, which consists of the administration of the following groups of drugs:
- To stabilize blood pressure - Clonidine, Captopril.
- To relieve psychomotor agitation - Relanium, Sibazon, Flunitrazepam.
- To prevent vomiting - Reglan, Cerucal.
- To eliminate headaches - Analgin, Ketonal, Tramal.
Causes of cardiovascular disorders
Predisposition to crises is caused by the influence of the same external and internal stimuli. A heart attack, like a stroke, occurs as a result of impaired blood flow. Changes in blood circulation lead to:
- vasospasm;
- closure of arterial lumens with a thrombus;
- blockage of a vessel by an embolus.
Blockage of a vessel by an embolus leads to circulatory impairment
Oxygen stops reaching healthy tissues, cells gradually die, and necrosis occurs. The syndrome develops depending on the location of the lesion. Blockage, as well as vascular spasms, is possible for certain reasons. Problems with blood flow are observed against the background of certain pathologies:
- Atherosclerosis. Cholesterol particles cause blockage of arteries, leading to heart attack or stroke.
- Diabetes. The disease changes the structure of blood vessels - they lose elasticity and are susceptible to sudden ruptures.
- Excess weight. Obesity is the result of an unhealthy diet and systematic consumption of fatty foods. Plaques gradually accumulate on the walls of the arteries.
- Hypertension. The vessels can withstand high pressure, but if it is observed in the patient not constantly, but periodically. The pathological condition is especially dangerous for the blood vessels of the brain; the risk of hemorrhages increases.
- Changes in blood plasma coagulability. Thrombosis is possible - the appearance of bloody clots that can move through the arteries and block them.
- Diseases of the heart muscle. Rhythm interruptions can provoke the appearance and separation of blood clots.
- Aneurysms of the arteries of the heart and “gray matter”. The thinned part of the vessel protrudes under the pressure of blood, putting pressure on nearby tissues.
Patients over 35 years of age who have been diagnosed with one of the listed pathologies are at risk. They need to constantly visit the doctor, undergo examinations, and lead a healthy lifestyle.
What are the symptoms of a stroke?
When a stroke occurs, massive damage to areas of the brain occurs due to the lack of adequate blood supply. The first signs of a stroke are a temporary or permanent disruption of the functioning of organs and systems (speech apparatus, motor activity, loss of cognitive functions, etc.). Precursors of a stroke can manifest themselves in increased blood pressure, deterioration in well-being, coordination, the appearance of causeless fatigue and short-term loss of consciousness, which indicates hypoxia of brain tissue. This is a bad picture of a stroke.
Brain dysfunction
Many people wonder at what pressure a stroke can occur. To obtain more detailed information about the occurrence, pathogenesis and symptoms of stroke, it is best to watch a video in which all the necessary information is laid out in detail.
When identifying the usual signs of a stroke, you need to pay attention not only to the patient’s behavior, but also to his subjective feelings. With the development of ischemia of a certain area of the brain, disruption of the body's functioning is observed, associated with the functions controlled by this area. For example, in some situations, the following signs of a stroke occur: the corners of the lips may droop on one side, the movements of the arms and legs become sluggish, the patient cannot shake hands, he has problems with speech, etc.
Many people wonder what is more dangerous – an acute heart attack or a stroke. It is impossible to answer this unequivocally, since each case is individual and depends on the reactivity of the body’s protective functions. One thing can be said: the development of a stroke is accompanied by the loss of certain skills and less compensation for the resulting disorders than with myocardial infarction.
General symptoms and additional differences
There are not only differences between a heart attack and a stroke, but there are also some similarities. The main symptoms inherent in pathological conditions sometimes make it difficult to determine the type of attack, which makes it difficult to provide first aid:
- high pressure;
- pallor of the skin;
- numbness of the facial muscles;
- shortness of breath, breathing problems;
- pain in the heart, head;
- loss of consciousness.
Ischemic stroke often causes complete or partial paralysis - the systems responsible for spatial orientation and movement are affected. A heart attack is characterized by characteristic symptoms: darkening of the tips of the ears and the entire face, blue lips, which indicates serious disturbances in heart rhythm.
Differences in therapy for heart attack
In the first minutes, all therapy is reduced to eliminating pain and restoring the patency of the coronary vessels. To eliminate pain in the pericardial region and behind the sternum, it is advisable to use narcotic analgesics (morphine) in doses. In addition to this pain relief technique, neuroleptanalgesia can be used to locally reduce pain in the affected area of the heart (a combination of droperidol, fentanyl and thalamonal).
For patients with severe nervous agitation, tranquilizers can be used to reduce anxiety, fear of death, etc. When transporting a patient to a hospital, it is necessary to carry out simultaneous antiplatelet and thrombolytic therapy that can eliminate the manifestations of vessel occlusion.
Damage to the heart muscle
In the most severe cases, coronary angiography and stenting are necessary. The first procedure involves injecting a contrast agent into the right and left coronary arteries. In this case, the monitor shows the entire relief of the vessels and displays the location where the thrombus is located. To reduce the degree of vessel occlusion, stenting is performed. This technique involves introducing a special mesh (stent) into the cavity of the affected coronary vessel, which, when expanded, presses the thrombus against the walls of the artery and restores normal blood flow. Over time, the clot dissolves under the influence of drugs applied to the surface of the stent.
Additional differences between the two pathologies
To properly carry out pre-medical actions, you need to know the difference between a heart attack and a stroke. The symptoms of crises are similar to each other, which makes their diagnosis difficult.
Differences in pathological conditions:
- Cerebral infarction is the death of cells due to lack of nutrition of the injured organ. The second form of the disease is an acute form of disruption of the blood flow of the “gray matter” with subsequent tissue necrosis.
- A heart attack is a form of stroke – an ischemic pathology.
- The first type of syndrome is characterized by a lack of nutrition of a specific part of the organ or its entirety. Stroke is a change in cell integrity due to hemorrhage or lack of nutrients.
After an attack, the patient needs urgent assistance before the emergency medical team arrives, this will avoid dangerous complications. A heart attack often causes death. Therefore, this type of syndrome is much more terrible for humans. In the event of a stroke, correct actions before the ambulance arrives will preserve important functions and increase the likelihood of the victim returning to a full-fledged lifestyle.
Differences between the two pathologies
Possible complications during an attack
What is worse than a stroke or heart attack is a question that not only patients, but also doctors are interested in, because both diseases can cause dangerous complications. Despite the fact that a large heart attack more often leads to an “irreparable” outcome, a person can also die as a result of a stroke.
Ischemic crisis often causes:
- disruption of the performance of a separate section of the “gray matter”, its death;
- paralysis, paresis - absence or decrease in activity in muscle tissues: changes in speech, swallowing reflexes, motor skills, movements, writing;
- pneumonia – develops due to a sedentary lifestyle and inflammation in the lungs;
- coma state - prolonged loss of consciousness, lack of reaction to external factors;
- dementia – strangulation of the patient’s intellect;
- memory loss;
- pain in the limbs, body, tingling, numbness, lack of sensitivity.
What is more dangerous for a person is not only the condition itself, but also the lack of timely help. At the first symptoms of a stroke, those around you should take all necessary measures before the emergency hospital arrives.
The salvation of a person depends on timely assistance
Among the serious complications of an extensive heart attack, doctors identify:
- Changes in the rhythm of the heart muscle.
- Arrhythmia, bradycardia, tachycardia.
- Heart failure, asthma, pulmonary edema.
- Cardiogenic shock is a severe pain syndrome, a sharp decrease in pressure to a critical level, and a slowdown in heart rate.
- Rupture of cardiac muscle tissue is a change in integrity when cells wear out and die, leading to death in 10% of patients.
There are some differences and similar signs between a stroke and a major heart attack. The main thing they have in common is a high risk to the health and life of the patient. It is important to notice the first symptoms of the syndrome in time and seek medical help.
Simple tips will help you avoid troubles
What is worse - hemorrhage or ischemia?
It is impossible to say unequivocally what is worse - a cerebral infarction or a stroke. Both diseases are extremely dangerous conditions that very often lead to death. They require emergency medical care, competent treatment and long-term rehabilitation.
If we compare them in terms of survival rate, then for hemorrhagic stroke it is only 20-30%. 60-70% of patients manage to survive a cerebral infarction. In both cases, rapid death (during the first two days) and prolonged coma may occur. Sometimes the patient falls into a vegetative state: he is alive, but immobilized, does not respond to speech and other external stimuli, does not speak, and cannot control urination and bowel movements.
Characteristic consequences of a stroke of any type are paralysis of the limbs and parts of the face, impaired speech functions, memory, changes in behavior, decreased vision, and constant headaches. After a blow, in 30% of cases a relapse of the disease develops, which leaves the person practically no chance of salvation.
If the patient manages to survive the attack, he will most likely experience disability. About half of survivors of a cerebral infarction and 2/3 of those who managed to stay alive after a cerebral hemorrhage remain disabled. Some of them end up bedridden.
Only 11-20% of patients manage to restore their working capacity, but they will never be able to fully regain health and lost functions. The effects of the blow will be felt for the rest of your life. Only 25% of people who have an attack live longer than 10 years.
Specific therapy for cerebral infarction involves measures aimed at preventing thrombosis. In case of hemorrhagic stroke, it is often necessary to resort to neurosurgical intervention; in some cases it is treated conservatively. As for nonspecific therapy, it is the same - the patient is prescribed drugs to normalize blood circulation, antihypertensive drugs, and drugs that support the heart.
Providing first aid to the victim
During an attack, people near the victim should immediately call an emergency medical team. If a person becomes ill, one should perform the basic steps one by one. What are they:
- lay the victim on a horizontal surface, place a cushion under the head;
- loosen, remove things and accessories that impede the flow of oxygen;
- if you lose consciousness, place your head to one side to prevent mucus and vomit from entering the respiratory tract;
- If the victim has dentures, they must be removed.
The actions themselves when providing first aid also differ; it is important to note the nature of the symptoms. If you have a stroke, you should not give the victim liquid, food, or medications in tablet form. Paralyzed arms and legs can be rubbed with medical alcohol. The main thing is to control the parameters of pressure and breathing. In the absence of experience, it is better not to take other actions on your own.
During a heart attack, the victim can be given nitroglycerin by placing it under the tongue. Taking aspirin will help dilute blood clots in the arteries before the ambulance team arrives. There is no point in dealing with the crisis on your own. Only experienced doctors can save a person’s life.
The main difference between a heart attack and an ischemic stroke is the danger that one of the pathological conditions poses to a person. When the first alarm signals appear, it is necessary to take pre-medical measures and call an ambulance. A competent doctor will help prevent the onset of a stroke or heart attack - in the future this can save the patient’s life.
Manifestations of primary symptoms
Here it is important to find out how a stroke differs from a heart attack, and how to distinguish pathologies when they appear in the initial stages. This can save the victim from death and a wheelchair. Or at least minimize the damage to health.
- During a stroke, pain spreads to the head area. In the case of the second disease, pain is observed in the area of the affected organ and the area of the heart muscle.
- If a person begins to have a stroke, their gait becomes unsteady and severe dizziness occurs. A heart attack does not have such symptoms.
- A heart attack causes a sharp weakening of the entire body, and during a stroke, consciousness is instantly impaired.
- Due to a heart attack, a person becomes more mobile and active, which is caused by severe pain at the site of the lesion. But an ischemic stroke provokes a decrease in activity, increased movement, as the body completely or partially begins to go numb.
These are characteristic differences that make it possible to differentiate the manifestations of two pathologies. Knowing how they differ from each other, you can take competent first aid measures. But the diseases have both differences and similarities.
Common features
Because of them, people are not always able to tell exactly what is happening to the patient. The first signs of the two diseases are similar to each other in the following:
- the skin becomes pale;
- attacks are accompanied by severe pain;
- blood pressure rises sharply;
- the person experiences shortness of breath;
- some people lose consciousness;
- a feeling of heaviness and tightness appears in the chest area.
In addition to the common symptoms of attacks, pathologies have the same causes. These include:
- abuse of bad habits (alcohol and tobacco products);
- consequences of taking narcotic drugs;
- diseases that cause narrowing of blood vessels;
- unhealthy and unbalanced diet;
- minimal physical activity or its complete absence;
- factors that systematically affect the increase in blood pressure;
- ignoring recommendations for preventive diagnostics.
If you have had to deal with the manifestations of attacks of these two diseases, you need to immediately seek qualified help. Some begin to provide first aid with their own hands, doing cardiac massage or artificial respiration. But such an intervention can be harmful if you do not know the exact diagnosis. Therefore, at the first symptoms of a patient, try to lay him on a bed or other soft surface, give maximum access to oxygen (disperse onlookers, open all windows and doors) and leave him alone until the doctors arrive.
Yes, there are significant differences between cerebral stroke and heart attack, if you understand in detail the features of the two pathologies. But at the same time, during treatment, doctors in both cases use medications with a general therapeutic effect.
These are drugs that are aimed at:
- prevention and recovery from complications of a somatic nature;
- creating optimal patency for clogged airways;
- increased activity of the cardiovascular system in a person;
- fight against bacterial infections if the pathology is accompanied by an increase in body temperature.