Neurologist
Despite the association with nerves that shake and quiver, a neurologist has a very indirect relationship with a person’s psychological state. It is in charge of the nervous system of the body.
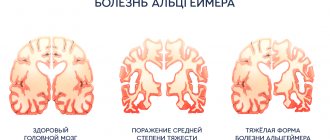
A neurologist graduated from a higher medical institution with two years of residency in his field and knows everything about the structure of the spinal cord and brain, the mechanism of operation of nerve fibers, and pathological conditions resulting from their disorders.
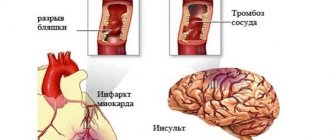
Due to his specialty, this doctor is faced with strokes, encephalitis, brain tumors, neuralgia and osteochondrosis. Rehabilitation courses after brain surgery and spinal fractures are indispensable without it. If a person complains of causeless dizziness, he will definitely be referred to a neurologist, but they will help him cope with depression or neurosis in another office.
Characteristic symptoms of depression
Below we list some manifestations and symptoms, observing which, you need to consult a psychotherapist:
- Incessant panic attacks.
- The presence of apathy and loss of interest in favorite hobbies.
- Uncontrollable bouts of crying or laughing.
- Lost appetite completely or has a craving for overeating.
- Feeling of increased unmotivated anxiety.
- Frequent outbursts of anger.
- A person is dominated by obsessive thoughts or automatically performs ritual actions.
- New phobias appear.
- Physical pain of a psychogenic nature.
- A person is endlessly tormented by insomnia.
- Continued state of acute grief and lack of interest in life.
View gallery
Psychiatrist
Most encounter this doctor only when obtaining permission to engage in some activity, for example, driving a car.
The main work of a psychiatrist is related to severe mental disorders, often requiring regular hospitalization in special institutions . His main patients are people who in the old days were called mentally ill, but in modern realities they are, as a rule, recognized as incompetent and have a disability group.
Schizophrenia, mental retardation, dementia of various natures - for the average person these terms sound scary, but for a psychiatrist they are professional routine. Also in the area of his observations are people suffering from epilepsy or who have attempted suicide. This specialist deals with the psychophysiological causes of such conditions; his medication prescriptions are aimed at suppressing the disease, often they cannot be obtained without a prescription.
Long-term education and continuous development
However, in order to become a psychoanalyst in our country, it is not enough to have a basic humanitarian education. Additional education in the chosen method of psychoanalysis is required. A university graduate can choose the opportunity to study under European programs. But that's not all. Such a specialist must constantly develop and choose a supervisor-mentor from among existing psychoanalysts. And after just a few years, having gone through this entire thorny path, an ordinary psychologist can become a psychoanalyst.
A psychotherapist can also become one. Only for this he will also need to receive additional education and actively interact with a practicing psychoanalyst-supervisor for a long time. To summarize the above, this specialist must be fluent in the chosen method of psychological analysis.
View gallery
Psychologist
The main difference between a psychologist and the other specialists listed above is that he does not have a higher medical education . This feature is expressed in the absence of the right to prescribe any medications. Having become the holder of a humanitarian diploma, a psychologist can consult, work in a helpline, test and conduct training.
But his abilities should not be underestimated. When it comes to mental problems, step-by-step work on yourself sometimes helps better than a miracle pill for depression. The psychologist’s task is to set the right direction for this difficult path. Sometimes support and the right advice are enough to overcome a crisis situation that seems insoluble. If the problem cannot be solved by verbal methods alone, a person should consult a psychotherapist.
What is the difference between neurological and mental illnesses?
Some neurologists believe that a "neurological disorder" is a kind of "commentary" on the "physical" (structural) and functional signs (symptoms) of damage to the "brain" rather than the "mental domain", such as thinking.
Definitions of what constitutes signs (symptoms) of a mental disorder have changed much more frequently in the history of psychiatry than in any other medical discipline. on the subject of semiotics of a particular disease. “Mental illness” is essentially a “cultural judgment,” and individual “labels” such as “schizophrenia” or “bipolar affective disorder” describe a variety of phenomena that are sometimes different from each other or even directly opposed to each other. and sometimes they have a common biological (genetic) base. From time to time it seems that "Mental illness" is not a scientific term, and claims to this paradigm (term criteria) cannot be objectively verified. The definition of “mental illness” takes a completely different approach and evaluates phenomena based on psychosocial criteria. The "mental illness" paradigm completely excludes signs of brain damage as a defining feature of how to classify or label a mental disorder, prohibiting the use of medical criteria, and effectively states that these labels have no "physical" consistency with them. Additionally, the "mental illness" model suggests that there are no medical or psychological differences between "mental illness" and "non-mental illness".
It seems that neuroscience is “necessarily objective” while psychiatry is “necessarily subjective,” even though both disciplines are about how we interpret human experience.
Essentially, “mental illness” is a psychiatrist’s way of telling a patient “we don’t know why this is happening” and “there is no need for an objective diagnosis of a mental disorder.” So, the psychiatrist argues that there is no medical explanation that can be found for a mental disorder, and one must look elsewhere for the definition of “mental disorder”, just not in the area of neurology. "Mental illness" is a diagnosis of exclusion - all other explanations must fail here, and professionals generally refuse and assign a logically convenient "label" in order to avoid confusion about the diagnosis of this or that mental disorder.
Some doctors say that neurology and psychiatry are either “twins” who want but cannot separate, or are actually two manifestations of the same “subject” (brain disease). There is no doubt that psychiatry is limited from neurology in a completely arbitrary line, and there is a large degree of overlap between these specialties.
Psychotherapist
Having received a diploma in psychiatry, not all newly minted specialists bravely set out to meet with delusional disorders. By adding a psychotherapist certificate to his education, the doctor gains the right to deal with more subtle cases.
Depression, neuroses, panic attacks, and some phobias do not turn a person into a socially dangerous creature, but they cause many problems and interfere with leading a full life. It is precisely these conditions that a psychotherapist helps to cope with. As a medically trained person, he has the right to make specific diagnoses and prescribe medications , such as antidepressants, and his in-depth knowledge of the psyche allows him to use non-drug therapies.
This combination makes it possible to effectively deal with a wide range of problems and achieve their complete disappearance.
Working with healthy people
Well, we briefly figured out what the difference is between a psychologist and a psychotherapist. The first specialist works exclusively with healthy people who find themselves in certain life difficulties. He helps people find a way out of their current situation. Not everyone pays attention to the importance of professional help when trying to overcome difficulties alone. But in vain. Timely, qualified work by a specialist will help avoid complications and will not lead to serious advanced clinical cases.
View gallery
Learning differences
Having dealt with each specialist separately, it is worth paying attention, finally, to the main question: what is the difference between a psychologist and a psychiatrist and psychotherapist? There are really a lot of differences here, and therefore they should be divided into two main groups: according to the form of training and according to the form of work activity.
How are psychologists trained? At the moment in Russia there are a number of branches in the field of psychology. Here it is necessary to highlight the following types of psychologists:
- educational psychologist - focused on working with children and their parents;
- social psychologist - focused on working with adults;
- legal psychologist - works in the field of committing offenses and crimes;
- clinical psychologist - works with seriously ill people in hospitals.
What is the difference between a psychiatrist and a psychologist? In the field of education, a psychiatrist goes through a fairly large number of disciplines, including medical treatment, psychoanalysis, psychodrama, the basics of behaviorism, cognitive therapy and many other branches of science. However, the practical activities of a psychiatrist seem to be much more important. It is worth talking about it further.
What diseases can a psychiatrist treat?
It is impossible to describe all cases in which a psychiatrist is competent. However, there are the most common mental disorders that cannot be treated without the intervention of a psychiatrist:
- Schizophrenia
is a mental disorder associated with suppression of thinking processes and emotional reactions. The psychiatrist prescribes medication to slow down the degradation process. - A psychiatrist helps with depressive disorders
, for example: postpartum. A serious consequence of the disorder is suicide. The psychiatrist identifies the causes of the disorder, prescribing the necessary medications and psychotherapeutic agents. - The treatment of neuroses
also falls under the competence of a psychiatrist. Neurosis develops in cases of prolonged emotional stress and trauma. It manifests itself in the form of deterioration in well-being, disorders of mental processes (memory, attention, thinking, etc.). - Suicidal disorders.
When considering the question of who a psychologist and a psychiatrist are, what is their difference, it is worth noting the treatment methods used in psychiatry. The basis of treatment is medications combined with patient education and psychotherapy.