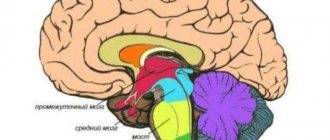
The pineal body, which is also called the epiphysis (epiphysis cerebri), is a small formation that resembles the shape of a pine cone and has a glandular consistency. The color of the gland ranges from red to brown. One end of the epiphysis is located in the region of the midbrain, between the quadrigeminal colliculi (superior), and its end is adjacent to the third ventricle (posterior). Connected by leashes to the visual tubercles. The size of the pineal body in an adult reaches up to 15 mm in length and up to 10 mm in width. The weight of the pineal gland is about 0.2 g. The final size and weight of the gland is formed by the age of 10. The gland receives blood supply by connecting to the branches of the cerebral arteries (posterior, middle and anterior branches).
The pineal body is covered with a membrane consisting of blood vessels tightly connected to each other. The parenchyma consists of the following cells: gliocytes and pineocytes. Vertical layers are separated from the capsule covering the pineal body, which go deep into the gland, thereby dividing it into lobules. Pineocytes are involved in the production of serotonin, from which melatonin is produced through synthesis. Also in the structure of the pineal gland there are neurons, perivascular phagocytes and endocrinocytes.
For a long time, scientists could not understand what functions this gland performs. And even today medicine has not fully revealed the potential of the pineal gland and its role in the human body. To date, the following definition of the functions of the pineal gland has been established. The pineal gland, as an endocrine gland, produces a number of hormones. Among them are melatonin, serotonin, histamine and norepinephrine, peptide hormones.
The basic function of the pineal gland is the regulation of circadian rhythms. With the onset of darkness, the process of melatonin production begins. When exposed to daylight, the pineal gland produces serotonin. With excessive and intense light, serotonin cannot be converted into melatonin, which causes insomnia, mild and severe nervous diseases. The gland is classified as part of the endocrine system, but some connections with the pituitary gland are not yet clear. How does melatonin affect the development and function of the hypothalamus? The connection with the hypothalamus + gonads + pituitary gland complex is more transparent. Hormones secreted by the pineal gland are involved in the normalization of reproductive processes in women and the duration of the menstrual cycle.
An important function of the pineal gland is to inhibit the growth of the pituitary gland until a person reaches puberty. If at this stage of development of the body the pineal gland ceases to act as a restraining factor, then this threatens the premature development of the skeleton and the rapid growth of secondary sexual characteristics.
A set of pineal gland hormones regulates the functioning of the nervous system. With insufficient melatonin secretion, patients experience mental disorders, depression, and a depressed state. Therefore, observing the biological clock and natural changes in light are the key to good health and the prevention of nervous diseases.
In general, the activity of the pineal gland affects all processes of the body. In addition to the endocrine system, it is involved in the functioning of metabolism and the functioning of the central nervous system.
If the pineal gland (tumor) malfunctions, the patient experiences disturbances in sexual development, sexual disorders, and hypertrophied genitals. Often cases of extensive tumors that have grown into nearby tissues are inoperable.
Between the hemispheres of the brain there is a formation similar to a gray-red pine cone - the pineal gland. The hormones produced by this organ inhibit many endocrine glands - the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland and the reproductive glands. Main Feature
– change in the functional activity of the pineal gland depending on the degree of illumination. The pineal gland cannot perceive objects, but does respond to light.
The pineal gland has the ability to respond to the earth's magnetic field. This feature is a kind of built-in compass.
, allowing you to navigate in space.
In general, the pineal gland is capable of changing hormonal levels and the body's reactions to changes in the external environment
, helping a person adapt to new conditions.
The gland is covered with a sheath of connective tissue, which is a continuation of the choroid. Partitions extend from it inward, dividing it into lobes. Therefore, the organ externally resembles a lump
. The cellular composition is represented by light and dark pineocytes (pinea - pine cone). They contain many different vials with hormones and biologically active substances.
The main function of the pineal gland
– formation of hormones (melatonin, adrenoglomerulotropin, serotonin) and coordination of the work of the endocrine system. Features of the hormone:
- is formed in the dark. When you rest at night in a lighted room, and regularly lack sleep at night, the formation of melatonin decreases, the nervous system is not fully restored, manifests itself in the form of apathy, depression, and severe mental disorders are possible with chronic lack of sleep.
- o
has an activating effect, improves mood, relieves pain, inflammation, and reduces the manifestations of allergic reactions. With his participation, the eggs mature and are released from the ovaries. At night, the pineal gland produces melatonin. - Adrenoglomerulotropin
is obtained by processing melatonin. It acts on the glomeruli in the adrenal glands, which produce aldosterone. Thanks to this interaction, the pineal gland can influence blood pressure and water-salt metabolism, but the degree and direction of its action have not been fully established.
Dimensions
in a newborn they are 7-10 mg, and the size is about 1 mm. In an adult, the length is slightly more than 1 cm and the thickness is about 4 mm. The weight of the pineal gland does not exceed 175 mg.
In childhood, the pineal gland exhibits maximum activity
. Not only sleep, but also memory, learning ability, and intellectual development depend on the work of this organ.
When the pineal gland malfunctions, sleep disorders occur.
. This is accompanied by insomnia at night, frequent awakenings, shallow sleep, daytime sleepiness and a lack of alertness in the morning. Such conditions are called biological disorders. They appear under stressful conditions, disruption of the nervous system, passion for gadgets, and the use of stimulants and drinks in the evening.
- developmental anomalies;
- accumulation of fats and calcium salts in elderly patients;
- replacement of cells with non-functioning ones during age-related changes, rheumatism, kidney diseases, strokes, intoxications;
- hemorrhages in the epiphysis;
- pineal cyst;
- pineal tumor.
Read more in our article about the pineal gland in the brain.
Read in this article
What is the pineal gland of the brain
Between the hemispheres of the brain there is a formation similar to a gray-red pine cone - the pineal gland. The gland is located behind the third ventricle of the brain next to the canal connecting its cavity with the fourth ventricle. Anatomically, this region is superior to the thalamus, and is therefore called epithalamic. The pineal gland belongs to the endocrine glands, although given its functions it is closer to the diffuse endocrine system, the cells of which are found throughout the body.
The hormones produced by this organ inhibit many endocrine glands - the pituitary gland, the thyroid gland and the reproductive glands. The main feature is the change in the functional activity of the pineal gland depending on the degree of illumination. This happens because light impulses from the eyes are sent along nerve fibers to the epiphyseal cells.
The pineal gland cannot perceive objects, but does respond to light. Thanks to this feature, esotericists attribute to it the functions of the third eye. Previously, it was considered the container of the human soul.
The pineal gland has the ability to respond to the earth's magnetic field. This feature is a kind of built-in compass that allows you to navigate in space. In general, the pineal gland is capable of changing hormonal levels and the body's reactions to changes in the external environment, helping a person adapt to new conditions.
Serotonin
This hormone has an activating effect, improves mood, relieves pain, inflammation, and reduces the manifestations of allergic reactions. With his participation, the eggs mature and are released from the ovaries.
The pineal gland is not the only organ that produces serotonin. During the daytime, it ensures that it enters the bloodstream along with other cells of the nervous system, and at night, the pineal gland produces melatonin from it.
Adrenoglomerulotropin
The third hormone of epiphyseal cells is obtained during the processing of melatonin. It acts on the glomeruli in the adrenal glands, which produce aldosterone. Thanks to this interaction, the pineal gland can influence blood pressure and water-salt metabolism, but the degree and direction of its action have not been fully established.
What is pineocytoma
Pineocytoma is a benign tumor that develops from the cells of the pineal gland. The disease is characterized by slow growth. However, the tumor can degenerate into malignant. This is a fairly rare disease of the central nervous system that affects young people - 25-30 years old.
Symptoms of the tumor process can be varied, since they depend on the location and size of the tumor. They are associated with an increase in the size of the tumor tissue and compression of adjacent brain structures. Due to the anatomical features of the location of the pineal gland, its increase in size leads to disruption of the outflow of intracerebral fluid and the development of hydrocephalus.
Symptoms of the tumor process:
- Constant bursting headaches that are not associated with changes in blood pressure and stress.
- Nausea and vomiting, dizziness.
- Gait disturbance due to impaired coordination of movement and balance (indicates damage to the cerebellum).
- Changing handwriting.
- General weakness, decreased performance, daytime sleepiness (impaired melatonin production).
- Problems with the construction of speech.
- Changes in weight in one direction or another.
Features in children
In childhood, the pineal gland exhibits maximum activity. In children under 5 years of age, its structure is represented mainly by functioning tissue and a small amount of fibrous fibers. Not only sleep, but also memory, learning, and intellectual development depend on the work of this organ.
. Therefore, it is important that young children have a strict daily routine with sleep duration appropriate for their age.
As you grow older, septa appear in the epiphysis, and in older people it looks like small lobules. The volume of connective tissue in adults increases significantly compared to children, and functional activity decreases.
Major diseases you may encounter
When the pineal gland malfunctions, sleep disorders occur. This is accompanied by insomnia at night, frequent awakenings, shallow sleep, daytime sleepiness and a lack of alertness in the morning.
Such conditions are called a violation of biological (circadian rhythms). They appear under stressful conditions, disruption of the nervous system, passion for gadgets (light sources at night), and the use of stimulants and drinks in the evening.
The causes of dysfunction can also be:
- developmental anomalies – absence, displacement into the deep layers of the brain. This malformation is not life-threatening, since the functions of the pineal gland are transferred to the pituitary gland;
- deposition of amyloid protein in common amyloidosis, hypertension;
- accumulation of fats and calcium salts (brain sand) in elderly patients (fatty degeneration and calcinosis);
- replacement of cells with non-functioning ones (gliosis) due to age-related changes, rheumatism, kidney diseases, strokes, intoxications;
- circulatory disorders due to infections, intoxications, hemorrhagic diathesis;
- hemorrhages in the epiphysis;
- thrombosis of the vessels supplying the gland in atherosclerosis, purulent meningitis, sepsis;
- inflammation in tuberculosis and syphilis;
- pineal cyst;
- pineal tumor.
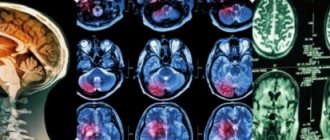
MRI examination (pineal gland cyst)
Manifestations of all these conditions are the following symptom complexes:
- hyperpinealism
- the activity of the thyroid gland and gonads decreases, libido decreases, the development of secondary sexual characteristics in adolescents is disrupted, and menopausal syndrome develops; - hypopinealism
- the synthesis of lutropin, follitropin increases, the production of estrogen increases with the growth of the inner layer of the uterus, polycystic ovaries, menstrual irregularities with heavy bleeding. With tumors, premature puberty and enlargement of the external genitalia occur; - dyspinealism
occurs with protein starvation, deficiency of B vitamins, manifested by ovarian dysfunction, disruption of the rhythm of sleep and wakefulness;
And more about the disease and Itsenko-Cushing syndrome.
The pineal gland produces a number of hormonal compounds, of which the most studied are melatonin, serotonin, and adrenoglomerulotropin. Melatonin is responsible for the onset of sleep in the dark, and also inhibits the activity of the pituitary gland and endocrine glands. It has an immunostimulating, antitumor effect, and prevents early aging of the body.
In children, it suppresses the activity of the gonads, improves memory and learning. If the pineal gland malfunctions, insomnia, menstrual cycle disruption, an increase in the volume of the pituitary gland and its excessive activity occur.
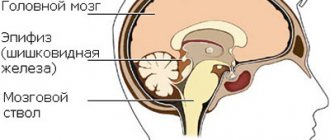
Epiphysis, or pineal body (pineal gland). This is the medical name for a section of the human diencephalon, shaped like a pine cone. The pineal body is located in the region of the midbrain and has a grayish-red color (Fig. 1). Being very small in size (8–15 mm in length), it is also divided into small lobules by trabeculae (septa). The pineal gland reaches its final size at the age of 10 years.
The influence of pineal gland hormones on the human body
The most important function of the pineal gland in the brain is to produce the hormones melatonin, serotonin, histamine and norepinephrine. The healthy functioning of the organ in childhood ensures the child’s intellectual development and his ability to learn.
The effect of hormones on the body as a whole:
- Supports stress resistance of the central nervous system;
- Control blood pressure;
- Regulate sleep starting from embryonic development;
- Supports carbohydrate and fat metabolism in the body.
Malfunction of the pineal gland affects the biological rhythms of the body: insomnia, shallow sleep and feeling tired in the morning.
Causes of pineal gland dysfunction:
- Cystic formation in the epiphysis of the brain;
- Degeneration of cellular composition with age-related changes in the body;
- Amyloidosis;
- Accumulation of calcifications;
- Neoplasm in the pineal gland;
- Blockage of a vessel providing blood supply to an organ by a thrombus;
- Stroke;
- Inflammation and lack of blood supply (with intoxication, infectious diseases, hemorrhagic diathesis);
- Hypertension.
Each hormone produced by the pineal gland is responsible for certain conditions of the human body.
Serotonin is synthesized from tryptophan; the body obtains the amino acid when processing food. The hormone is synthesized in the pineal gland of the brain. The intake of light carbohydrates from food (confectionery) and sufficient sunlight increase the production of serotonin, which directly affects a person’s mood.
The hormone is produced only in conditions of complete darkness and helps restore the body, relieving the feeling of fatigue and toning the entire body. Age-related changes affect this hormone - the production of melatonin decreases, which leads to damage to hormonal DNA and withering of the body.
Functions of the hormone in the body:
- Stimulates memory function;
- Reduces pain;
- Prevents obesity;
- Helps produce immune cells;
- Controls blood pressure;
- Regulates the sleep-wake cycle.
The hormone is a biogenic amine and is synthesized from tyrosine (an amino acid), which the body receives from food. The process of norepinephrine synthesis occurs in the pineal gland of the brain and adrenal glands.
The hormone improves the functioning of brain structures and promotes the absorption of glucose in muscle fibers.
The hormone is an organic compound formed from histidine (the chemical structure of a protein) and is a mediator of allergic reactions.
We recommend watching an educational film and learning more about the pineal gland.
Histology of the pineal gland
This pineal gland (another name for the organ) consists of polygonal parenchymal cells (pinealocytes) and astrocytes (glial cells).
Rice. 1. Brain structure
Pinealocytes have the form of processes; they cover about 90% of parenchyma cells (photo, Fig. 2). Pinealocytes are divided into dark and light, differing in size and density of the cytoplasm. Glial cells take on the function of support.
Rice. 2. 1 – pinealocytes; 2 – deposits of silicon compounds and calcium salts
The pineal gland and its functions
To date, it is not completely clear why exactly a person needs the pineal gland, but the influence of the pineal gland on the endocrine system, which it regulates, is known. At night, the pineal gland is activated, releasing a significant amount of hormones. First of all, it produces melatonin, which is responsible for the frequency of sleep and slows down the aging process, as well as adrenoglomerulotropin, which stimulates the synthesis of aldosterone (a hormone of the adrenal cortex). In addition, the influence of the pineal gland on the pituitary gland and hypothalamus has been established: the pineal body suspends their activity, and is also responsible for reducing nervous excitement and providing a hypnotic effect, strengthens the immune system, and prevents the appearance and development of tumors. In addition, the influence of the pineal gland on human sexual functions is also known: it inhibits them.
During the day, the pineal gland produces serotonin. Due to excessive light at night, serotonin cannot be converted into melatonin, which causes insomnia and various nervous diseases in humans.
Treatment of pathologies in the pineal gland
The pineal gland is a rather small organ and its size does not allow one diagnostic test to determine the type and severity of the pathology. Even magnetic resonance imaging does not reflect the nature of the tumor if it is detected. Therefore, for an accurate diagnosis, a biopsy is performed during which it is determined whether it is a cancerous tumor or whether it is benign.
The tumor does not go away on its own, and it cannot be treated with medication either, so the only treatment method in this situation is surgery. After removal of the cyst or tumor, the patient’s condition continues to be monitored for many more months. After all, the source of tumor development is still unknown, and therefore there is a high risk of its reappearance.
The functions of the pineal gland after removal of a cyst or tumor are usually completely restored, despite the fact that its structure is damaged. After the recovery period, the patient must be examined every 6 months using magnetic tomography and a series of blood tests.
Pineal body: diseases and treatment methods
The modern way of life is far from the regime established by nature: we often work at night, sleeping during the day. This schedule helps reduce the level of melatonin production by the human pineal gland, which can trigger the development of pineal gland diseases. According to some experts, the pineal gland, when its functionality is impaired, causes diseases such as obesity, diabetes mellitus (type 2), hypertension, as well as insomnia and depression.
A decrease in the activity of the pineal gland is associated with several reasons:
When large tumors (more than 3 cm in length) appear, patients suffer from constant severe headaches, accompanied by blurred vision. The tumor is removed surgically. If, according to the diagnostic results, it turns out to be malignant, the patient is prescribed chemotherapy (or radiation therapy).
The cause of hemorrhage in the pineal gland can be congenital anatomical features, but most often it is associated with atherosclerosis. Diagnosis is carried out using brain tomography. Neurologists and other specialists will provide assistance in this case.
In case of functional impairment, the patient is asked to follow a daily routine and consult a specialist for the treatment of concomitant diseases. First of all, you need long sleep (at night) and a balanced diet.
Congenital malformations of the pineal gland are quite rare. Hypoplasia of the pineal gland (underdevelopment) can cause complaints in children or adults or be completely asymptomatic.
Organ pathologies, their symptoms and treatment
In addition to disruption of daylight hours, other negative factors affect the functioning of the endocrine gland:
- congenital abnormalities of brain development,
- severe neuroendocrine pathologies,
- damage to brain cells.
Hypoplasia of the pineal gland is indicated by the early onset of puberty. Doctors rarely diagnose congenital malformations of the pineal gland.
Functional disorders can be eliminated quite easily; you just need to review your daily routine and treat background pathologies. For the proper production of melatonin and other important substances in the pineal gland, you need to include foods of various categories in your diet. Balancing nutrition is a prerequisite for the normal functioning of the endocrine system.
On a note! Pineal gland diseases occur in men and women. The more provoking factors, the higher the risk of damage to the pineal gland. Lack of attention to the signs of pathological changes can cause severe damage to the nervous system, ischemic stroke, and hypertensive crisis. If problems with the pineal gland occur in children, then against the background of active growth of the tumor, the functioning of the adrenal cortex is disrupted, which provokes a shift in the timing of puberty to an earlier period.
Pineal tumors
Volumetric neoplasms in the tissues of the pineal gland are benign and malignant. Often the cause of development is the influence of ionizing or X-ray radiation.
While the tumor is small, the patient does not suspect the existence of a pathological focus in the pineal gland. If the neoplasm grows, reaches 3 cm, and cell malignancy actively occurs, then negative symptoms appear. Patients complain of headaches that cannot be controlled, and blurred vision.
After examination with a tomograph, the doctor confirms or denies the suspicion of tumor development. Treatment is strictly surgical. If tissue histology shows the presence of atypical cells, then the patient, under the guidance of an oncologist, receives chemotherapy or undergoes a course of radiation to suppress the growth of cancerous structures.
Hemorrhage into the pineal gland tissue
A dangerous process develops in adults against the background of vascular atherosclerosis. In children, a serious condition rarely occurs. Sometimes a stroke occurs due to an aneurysm (congenital abnormality).
Against the background of hemorrhage in the brain, various parts of the nervous system are often affected. An MRI is prescribed to confirm the diagnosis. A neurologist, neurosurgeon, cardiologist, and other specialists are involved in treatment.
Parasitic diseases
Most often, this type of pathological process is detected in residents of regions where livestock farming is developed. In most cases, echinococci penetrate the pineal body. The size of parasites is from 2 to 8 mm. Waste products poison the body, the movement of dangerous tapeworms disrupts the functioning of the pineal gland and provokes the development of tumor-like formations.
With echinococcosis, cysts are prone to active growth. The cavity with a dense capsule must be removed: non-surgical methods and medications do not have any effect. A cyst in the pineal gland is diagnosed using immunological tests and tomography. To eliminate the pathological process, you need the help of a qualified infectious disease specialist and neurosurgeon,
Prevention of pineal gland diseases
To prevent functional disorders of the pineal gland in the body, it is necessary to lead an active lifestyle with an emphasis on healthy eating and be sure to get enough sleep. To reduce the risk of congenital pathologies of the structure of this organ, the expectant mother needs to protect herself from viral diseases, harmful industrial enterprises, and also avoid alcohol and smoking.
As for malignant and benign brain tumors, the reasons for their formation have not yet been fully studied. To prevent tumors of the pineal gland, experts recommend excluding the influence of X-rays on the head and neck areas.
The mystical purpose of the pineal gland
The pineal gland, in comparison with other brain structures, was discovered relatively recently, and its secluded place gave scientists and philosophers reason to talk about the supermission of the pineal gland. He was endowed with the functions of the “third eye”, responsible for extrasensory abilities. Rene Descartes, a French philosopher, considered the pineal gland to be the seat of the human soul.
Quite often in modern medical practice, and even in the scientific literature, you can come across the term “epiphysis”. What it is? What functions does this structure perform? What properties does it have? These questions are of interest to many people, especially considering the fact that this organ is often associated with some esoteric theories.
Is it possible to carry out treatment using traditional methods?
As noted earlier, drug therapy is aimed at eliminating concomitant symptoms, rather than treating the disease itself. None of the folk remedies can act directly on the disease itself, so one cannot expect an absolute cure with the help of alternative medicine recipes. Thus, it will not be possible to stimulate the functions of the pineal gland using traditional methods, but you can take care of increasing immunity. Next, we will consider the features of treatment of the pineal gland in children.
Epiphysis - what is it?
In fact, there are two structures in the human body that are usually referred to by this term. Surely many have heard about the bony epiphysis, which is the end section of tubular bones.
But the human brain also has a pineal gland. What it is? This is a small structure, which is usually classified as diffuse. By the way, there are other names for this organ, for example, the pineal gland and the pineal gland of the brain is part of the so-called photoendocrine system, and, despite its relatively modest size, its role for the normal functioning of the body is simply enormous.
Epiphysis of bone and its functions
The bony epiphysis is an expanded ridge of the tubular bone. It is this part that represents the articular surface, which forms the joint along with the adjacent bone.
In this section, the bone tissue has a spongy structure. The surface of the epiphysis is covered with articular cartilage, and underneath is the so-called subchondral plate, which contains many nerve endings and capillaries.
Inside, the bony epiphysis is filled. This structure is extremely important for the normal functioning of the human body, since this is where the formation and maturation of red blood cells occurs.
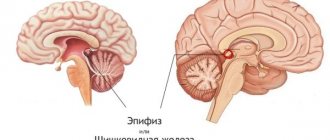
Epiphysis (pineal body) and its location
It is worth noting that the pineal gland is the most recently discovered and least studied part of the human brain. Of course, over the past decades, many discoveries have been made that explain the mechanism of operation of this structure. By the way, in appearance this small organ somewhat resembles a pine cone, which is why it was called the pineal gland.
This organ is located almost in the center of the brain, between the two hemispheres in the region of the interthalamic fusion. It is also attached to both located in the diencephalon.
Therapeutic measures
Treatment of pineal gland pineocytoma is surgical. Microsurgical approaches are used to minimize damage to brain tissue. Radiation therapy is indicated if the tumor is located in an inaccessible place or there are severe concomitant diseases that may affect the course of the operation. Radiation therapy is also prescribed for malignant process.
Modern techniques make it possible to perform operations to remove pineocytoma using a cyber knife or gamma knife on an outpatient basis. This is a painless procedure with minimal side effects, which helps to avoid classic surgery. During the procedure, thin beams of radiation are directed from different directions onto the tumor. In this case, healthy brain tissue is not affected.
Do you know what causes an increase in the size of the pituitary gland? How is Itsenko-Cushing syndrome related to the pituitary gland of the brain?
Find out how pituitary adenoma is treated. Is pituitary microadenoma treated during pregnancy?
Read about the causes of nighttime insomnia. Which doctor should I contact if I have sleep disturbances?
Postoperative follow-up
It should be remembered that any surgery or radiation exposure to the brain can lead to disruption of hormone production. Therefore, all patients who have undergone treatment for a tumor process of the pineal gland need constant monitoring of hormones and regular examination by an endocrinologist. If a violation is observed, hormone replacement therapy is prescribed.
Cellular structure
The pineal gland is a small organ colored grayish-red. On the outside, it is covered with a dense capsule of connective tissue. The capsule forms so-called trabeculae, which penetrate inside the gland and divide it into small lobules. This is exactly what the human pineal gland looks like - its structure can be considered quite simple.
The internal part of the gland consists of parenchyma and connective tissue elements. The main structural elements in the pineal gland are pinealocytes - polygonal parenchymal cells. In addition to them, four more types of cells were discovered: pineal gland neurons, interstitial endocrinocytes, also peptidergic neuron-like structures and perivascular phagocytes.
It is worth noting that at the beginning of a person’s life, the pineal gland grows rapidly, but around the time of puberty, the growth of the pineal gland gradually fades. Moreover, as the human body grows and ages, the gland involution occurs.
Causes of cyst formation
Now it is clear where the pineal gland is located (photo presented).
The resulting cyst is often detected by chance; as a rule, it is identified during a magnetic resonance imaging study. At the initial stage there is no clinical manifestation. The cause of cystic formation is a failure in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, which occurs due to the following changes:
- The appearance of blockage of the excretory lumen. This usually happens due to injury or surgery. The resulting scars can obstruct the passage of cerebrospinal fluid, which accumulates in the lumen between the meninges and soft tissues.
- The presence of infectious lesions of the membranes. For example, most often echinococcus acts as a catalyst for inflammatory processes. Taking an anamnesis along with clinical collection of cerebrospinal fluid through puncture will help doctors identify the pathogen.
Canal blockages tend to occur among patients who have a genetic predisposition to it. Cystic transformations of the pineal gland occur due to deviations in the anatomical structures of the lumen that removes the cerebrospinal fluid; the increased viscosity of the cerebrospinal fluid can also have an effect.
Main functions
Of course, the functions of the pineal gland have not yet been fully studied. However, it is known that the main hormone of the pineal gland is melatonin, which is responsible for the formation of so-called circadian rhythms (sleep and wakefulness patterns). This hormone is responsible not only for the frequency of sleep, but also helps the body adapt to changing time zones. It also acts as an antioxidant and slows down the aging process.
Of course, the pineal gland also produces some other hormonal substances. For example, the gland secretes adrenoglomerulotropin, which stimulates the processes of aldosterone synthesis. In addition, the pineal gland performs some other important functions. For example, it inhibits the release of growth hormones and sexual development, prevents the formation and growth of tumors, and strengthens the immune system. It is believed that pineal gland hormones, to one degree or another, control the functioning of the hypothalamic-pituitary system, thereby influencing the functioning of all endocrine glands of the body.
Regulation of functioning
It is worth noting that the features of the work and regulation of the pineal gland have not yet been studied enough. Research is difficult due to the small size of the gland and its location. However, it has been proven that the pineal gland is controlled not only by nerve endings, but is also receptive to light.
Of course, light does not penetrate directly to the pineal gland. However, photons stimulate specific ganglion cells in the retina. From here it is transmitted to the suprachiasmatic nucleus of the hypothalamus, from where it is sent through the paraventricular nucleus to the upper segments of the thoracic spinal cord. From here, excitation is transmitted to the pineal gland through the superior cervical ganglion. It is worth noting that the impulse arising in the suprachiasmatic nucleus does not stimulate, but, on the contrary, inhibits the functioning of the pineal gland. Thus, in light, melatonin secretion decreases, and in darkness (at night) it increases. As for the stimulation of the pineal gland, the neurotransmitter in this case is norepinephrine.
Pineal gland diseases
Of course, some diseases can also affect this part of the brain. For example, often during examinations various neoplasms are discovered in a structure called the pineal gland. What it is? Yes, sometimes malignant degeneration of cells occurs in the tissues of the pineal gland. A benign tumor or cyst appears.
Since the pineal gland is an endocrine gland, naturally the hormones it produces affect the functioning of the entire endocrine system. Even a small epiphysis cyst can lead to severe hormonal imbalance and the development of a disease called macrogenitosomia. This disease is accompanied by changes in the level of certain hormones, which entails premature physical and sexual development (the appearance of menstruation at an early age, etc.). Mental retardation is often observed.
Pathologies of the pineal gland
Despite the fact that the pineal gland itself is small, its location allows it to protect the organ from physical influences, it is still susceptible to various pathologies. And any non-standard state of the endocrine chain hypothalamus-pituitary-epiphysis can lead to deadly hormonal imbalances in the body.
The pineal gland as an organ of the brain has not been fully studied, but the list of its pathologies is already quite extensive:
- Deviations in the functioning of an organ that are genetically transmitted from parents to children.
- A secretory disorder within the pineal gland, which leads to a general imbalance of the substances it secretes.
- Formation of tumors of various types in the glandular body of the pineal gland. Tumors and cysts can be either single or group, and of any size. In this case, histology is performed to determine the malignancy of the tumor.
- The function of the pineal gland can be impaired by the action of any medication, especially in combination with psychological overload.
- Infectious lesion of the glandular body. It can be caused by tuberculosis, meningitis, brain infection or local sepsis.
- The anatomy of the pineal gland shows that a disruption in the blood supply to the organ can cause a malfunction in its functioning. This can be caused by trauma, cerebral thrombosis, or arterial hypertension.
- Despite the fact that the pineal gland is located deep in the brain, it is susceptible to atrophy caused by diabetes mellitus, general intoxication, cirrhosis of the liver or leukemia. That is, it will suffer like any other organ in this situation.
- The condition of the pineal gland can be impaired by physiological calcification. This is a situation where undissolved calcium ions accumulate in the body.
Pineal gland in modern esotericism
It's no secret that a lot of mystical stories and esoteric theories are associated with the pineal gland. The fact is that this organ was discovered relatively late, and hidden deep in the brain structures, which prompted some scientists and philosophers to think about the extreme importance of the pineal gland. For example, Rene Descartes in his works called the pineal gland “the saddle of the soul.” And indeed, it was this structure that for decades and even centuries was perceived as a kind of container for the human soul.
There are also more ancient beliefs about the mystical “third eye,” which allows a person to see the invisible and is responsible for various extrasensory abilities. For example, in the 19th century, a theory was put forward that a mysterious third eye actually exists. But if in some animals it is located on the surface of the body (for example, in some cyclostomes the pineal gland actually comes to the surface and serves as a photosensor), then in people the eye “hides” inside the skull.
EPIPHYSUS (pineal, or pineal, gland), a small formation located in vertebrates under the scalp or deep in the brain; functions either as a light-sensing organ or as an endocrine gland, the activity of which depends on illumination. In some vertebrate species both functions are combined. In humans, this formation is shaped like a pine cone, which is where it got its name (Greek epiphysis - cone, growth). The pineal gland develops in embryogenesis from the fornix (epithalamus) of the posterior part (diencephalon) of the forebrain. Lower vertebrates, such as lampreys, may develop two similar structures. One, located on the right side of the brain, is called the pineal gland, and the second, on the left, is the parapineal gland. The pineal gland is present in all vertebrates, with the exception of crocodiles and some mammals, such as anteaters and armadillos. The parapineal gland as a mature structure is present only in certain groups of vertebrates, such as lampreys, lizards and frogs. Function.
Where the pineal and parapineal glands function as a light-sensing organ, or "third eye", they are only able to distinguish between different degrees of illumination, and not visual images. In this capacity, they can determine certain forms of behavior, for example, the vertical migration of deep-sea fish depending on the change of day and night. In amphibians, the pineal gland performs a secretory function: it produces the hormone melatonin, which lightens the skin of these animals, reducing the area occupied by pigment in melanophores (pigment cells). Melatonin is also found in birds and mammals; it is believed that in them it usually has an inhibitory effect, in particular, it reduces the secretion of pituitary hormones. In birds and mammals, the pineal gland plays the role of a neuroendocrine transducer, responding to nerve impulses by producing hormones. Thus, light entering the eyes stimulates the retina, impulses from which travel along the optic nerves to the sympathetic nervous system and pineal gland; these nerve signals cause inhibition of the activity of the epiphyseal enzyme necessary for the synthesis of melatonin; as a result, the latter's production ceases. On the contrary, in the dark, melatonin begins to be produced again. Thus, cycles of light and dark, or day and night, affect melatonin secretion. The resulting rhythmic changes in its level - high at night and low during the day - determine the daily, or circadian, biological rhythm in animals, including the frequency of sleep and fluctuations in body temperature. In addition, by responding to changes in night length by changing the amount of melatonin secreted, the pineal gland likely influences seasonal responses such as hibernation, migration, molting, and reproduction. In humans, the activity of the pineal gland is associated with such phenomena as disruption of the body’s circadian rhythm due to flying across several time zones, sleep disorders and, probably, “winter depression.”
Collier's Encyclopedia.
— Open Society. 2000. Synonyms
:
Anatomy of the pineal gland
The gland is located between the hemispheres of the brain and is fixed by wires to the visual thalamus. Its weight in an adult is only about 0.2 g, its dimensions do not exceed 1-1.5 cm. The structure of the organ is composed of parenchymal and neuroglial cells, folded into small lobules. It is covered by a connective tissue capsule, from which connective tissue trabeculae radiate inwards. Blood vessels and nerve fibers pass through the gland; its blood supply is quite intense.
The development of the pineal gland begins in the 2nd month of embryogenesis; it is formed from the epithalamus of the posterior forebrain. The size of the organ varies depending on the age of the person. Its growth stops during puberty. Over time, a reverse process of development (involution) occurs.
The pineal gland is also called the “third eye”. It has long been considered a portal between the spiritual and physical body.