Catalepsy after hypnosis
All vital functions of a person are suspended, so much so that to a non-specialist it may seem that the person is dead. A cataleptic seizure is characterized by a state of so-called waxy flexibility - a person in a state of seizure can be placed in the most uncomfortable and unnatural position, without making any special effort, and this position will remain motionless until the very end of the seizure.
A cataleptic seizure is one of the manifestations of a number of mental illnesses, sometimes occurring in hypnotic sleep (but in this case it is not associated with mental illnesses).
Catalepsy during hypnosis is not a pathology and does not require special therapy. Hypnotic catalepsy itself does not have negative consequences, but it is important to carry out hypnosis carefully, professionally, without resorting to it unless clearly necessary.
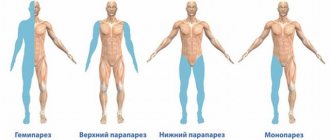
A cataleptic seizure does not occur all at once; it develops sequentially from top to bottom - from the muscles of the neck and upper limbs to the lower limbs.
Reverse development, recovery from a seizure, occurs in the opposite direction. The seizure usually lasts from several minutes to several days, but in medical practice there have been cases of being in a cataleptic seizure for several weeks and even several months.
With catalepsy, inhibition reaches such a degree that the person seems to be in a coma. He may be in an uncomfortable and sometimes unnatural position, without movement, without putting any effort into it. This condition after a cataleptic attack is called “waxy flexibility.”
A seizure may occur as a symptom of mental illness or associated with hypnosis. In the latter case, it is not pathological and does not require treatment. Hypnotic catalepsy leaves no consequences. However, hypnosis itself, as a method of therapy, is dangerous and should be performed exclusively by a specialist.
The development of a cataleptic seizure is sequential in direction: from the muscles of the arms and neck to the muscles of the legs. The exit from it flows in the opposite direction. The duration of such a seizure can be a couple of minutes or several days. There are known cases of being in a state of catalepsy for several months.
Physiological catalepsy is a condition that occurs when a person is immersed in a hypnotic state. In the past it was used to test how deeply a person had fallen into hypnosis. It is also used for some procedures: suggestion, deepening the state, guidance and others.
To induce a state of catalepsy, verbal suggestion is not required; it can occur with non-verbal methods of influence (developed by Dr. Erickson). Such methods can be used to demonstrate the possibilities of hypnosis and to carry out influence techniques.
Types of catalepsy
Despite the fact that in science there is no clear classification of this pathology, in practical psychiatry it is customary to distinguish:
- Simple – a condition in which patients hear and see everything, but cannot move.
- Rigid - a disorder in which pronounced muscle rigidity is manifested - resistance to any deformation of the position of the body or its parts.
- Pharmacological – a condition caused by the action of drugs.
- Hypnotic catalepsy is a phenomenon created under the influence of suggestion (hypnosis). A characteristic symptom is hand catalepsy.
Astral catalepsy is a separate group - trance, which occurs mainly at night. The term was coined by S. Muldoon, a paranormal researcher, who defines it as a short-term disturbance caused by erroneous beliefs in the mind.
Astral catalepsy is an exoteric category. Its occurrence is explained by the action of ghosts, aliens or the tricks of witches. It is believed that at this time the soul is outside the body and receives additional nourishment from world energy. Experienced exotericists claim that the condition can be controlled and induced as needed. Despite the fact that official medicine does not recognize its existence, its manifestations may indicate the occurrence of mental disorders.
General information
The term “catalepsy” is of Greek origin and literally means “grasping”, “holding”. Another common name for the syndrome is waxy flexibility. Epidemiological indicators are low, amounting to 0.018-0.02% in a population with an approximately equal ratio of men and women. The cataleptic state is observed not only in humans, but also in all vertebrates, and therefore can be considered as a biologically appropriate reaction.
In animals, it occurs in life-threatening situations and is a common form of passive-defensive behavior - freezing, suppression of vegetative functions is an imitation of death, which reduces the likelihood of an enemy attack, and also prepares the body for possible real death.
Catalepsy
Pull-pull
Most often, with this syndrome, the first complaints occur during the period of most intensive growth, that is, at approximately the age of 14–18 years. “Gutta-percha” teenagers begin to be bothered by pain in the joints (usually the knees, ankles, small joints of the hands) or in the spine. The pain can range from moderate to very severe. Often, such teenagers have scoliosis, chronic foot fatigue, and flat feet. Patients with this syndrome have a high tendency to frequent injuries (sprains, subluxations of joints). By the way, these symptoms (especially if they appeared at a young age) can disappear as spontaneously as they appear. Therefore, they were previously mistakenly classified as “growing pains.”
A simple screening test using the Beighton method helps the doctor determine whether a teenager has joint hypermobility syndrome. The doctor asks the young patient to do 5 different types of movements and evaluates their performance. But there are 9 exercises in total (since our limbs are paired).
Each movement that demonstrates increased flexibility is worth 1 point. We can talk about the presence of the syndrome if, in addition to joint pain, young people score 4 points or higher, and those over 50 score from 1 to 3 points. And here are the test exercises (all except the last one are performed for both right and left limbs):
1. Bend the little finger back (1 point – if the angle of deviation is more than 90°). 2. Bend the thumb of the hand (1 point - if it easily touches the inside of the forearm). 3. Straighten the arm (1 point – for hyperextension at the elbow joint by more than 10°). 4. Straighten the leg (1 point – for hyperextension in the knee joint by more than 10°). 5. Bend the torso forward with straight legs (1 point for touching the palms to the floor).
However, in the absence of complaints from the musculoskeletal system, excessive joint mobility in comparison with the average can be considered as a constitutional feature and even an age norm. Before prescribing treatment, it is necessary to carry out a differential diagnosis, its purpose is to exclude other diseases that may also affect the joints (arthrosis deformans, rheumatoid arthritis, etc.). The patient will have to take an x-ray of the joints (necessarily symmetrical, on both arms or legs), CT or MRI and take a general clinical blood test.
Treatment options
In the process of treating the disease, attention is paid to the developmental features and nature of the course of catalepsy. It must be taken into account that
waxy flexibility is similar to certain types of movement disorders that manifest themselves in some organic brain lesions. Often such disorders progress in Parkinson's disease.
The treatment method used is interactive imagogy, which is essentially conscious work with the individual internal forces of the human body. In psychotherapeutic practice, such exercises are called imago-image.
The main principle of using this technique is the possibility of visual perception of one’s diseased organs, after which, based on the resulting picture, a certain positive image is transformed, which has a beneficial effect.
The waxy flexibility state can be used in situations where there is a need to significantly limit the patient's motor capabilities to speed up the treatment process. All procedures must be carried out exclusively with the participation of a qualified specialist in specially equipped psychological centers.
Causes of the disease
What can cause cataleptic stupor? The mechanisms of occurrence are not completely clear. Spontaneous short-term catalepsy is a kind of psychoneurological short circuit. There are several theories why the causes of a painful condition should be sought either in psychology or in the activity of the nervous system. A number of key factors in the development of cataleptic stupor can be identified:
- mental disorders (schizophrenia, hysteria, etc.);
- diseases of the nervous system, for example, narcolepsy, parkinsonism;
- organic damage to brain structures (encephalitis, for example), especially damage to the cerebellum, causing disruption of connections with the frontal lobes;
- overdose of drugs, most often antipsychotics;
- a trance state caused by hypnosis or deep meditation;
- pathological lack of will and increased suggestibility.
With catalepsy, symptoms such as uncontrolled repetition of what is heard (echolalia), involuntary imitation of seen movements (echopraxia) can be observed simultaneously. A cataleptic attack in narcolepsy is often accompanied by hallucinatory phenomena upon recovery from stupor. Catalepsy develops within the framework of narcolepsy, as a consequence of a sharp transition from a wakeful state to the REM sleep phase. In catatonic schizophrenia, along with cataleptic stupor, other symptoms of psychomotor disorders are observed: impulsive agitation, negativism (resistance to attempts to change posture), numbness.
Separately, we can note such a phenomenon as catalepsy of the hand, which occurs during hypnosis. Hypnotherapists claim that hanging a hand in the air during a hypnosis session opens the patient's mind to suggestion. The state of waxy flexibility during a trance is designated by a term such as astral catalepsy or sleep paralysis. It is believed that during deep meditation or hypnosis, a person’s consciousness moves from the physical body to the astral (emotional) body. Like narcolepsy, astral catalepsy is accompanied by a number of illusory ideas, such as a feeling of an invisible pressing force, loud noise, body vibration, difficulty breathing.
Pathogenesis
Cataleptic states are different in origin; the trigger can be an emotional state, functional and structural changes in the central nervous system, and signals from the hypnotist. The “common final path” of the development of the syndrome is the activated subcortical systems of modulation of muscle tone with the relative deactivation of the cortex, reticular formation, and basal ganglia.
Muscle tone is maintained, complex innervation of motor acts is disrupted. This is manifested by drowsiness, motor retardation, and freezing in assigned positions. The attack does not develop all at once; pathological changes gradually spread in the upper cervical region, arms, then move to the lower part of the body.
Cataleptic states are different in origin; the trigger can be an emotional state, functional and structural changes in the central nervous system, and signals from the hypnotist. The “common final path” of the development of the syndrome is the activated subcortical systems of modulation of muscle tone with the relative deactivation of the cortex, reticular formation, and basal ganglia. The balance of the body is maintained, but the arbitrariness of movements is lost. According to recent studies, damage to the caudal hypothalamus and tegmentum in the upper midbrain causes a syndrome similar to catalepsy.
Signs of catalepsy
Signs of a cataleptic attack:
- muscle hardening;
- decreased reactions to pain and other irritants;
- decreased activity of movements.
With catalepsy, a person falls into a stupor, in which he cannot control the body, but hears and sees. Symptoms of an attack include changes in body functions: pulse and breathing rhythm.
The duration of the attack, in severe cases, is more than a month. Stupor can occur at any time: during gestures, movements, and conversation. The person freezes in one position, which he maintains until the end of the seizure.
The development of a cataleptic attack begins from above, that is, first the muscles of the shoulders, neck and arms go numb, and then the whole body. Lastly, stupor affects the leg muscles. The process of ending the seizure occurs in the opposite direction.
Complications
Severe cases of catalepsy are complicated by delusional and hallucinatory disorders. During the attack, patients experience confusion, usually oneiroid with an influx of delusional fantastic images and ideas. Hallucinations appear in a certain sequence, creating a holistic, complete picture.
After an acute condition, there is usually amnesia for the events that actually happened, but patients describe their own condition quite accurately. Complications of prolonged cataleptic attacks arise as a result of autonomic disorders. Headaches, dizziness, sleep and digestion disorders develop.
Complications and consequences
One of the main complications is astral catalepsy. This condition usually occurs at night. This condition in most situations is explained by the influence of ghosts and alien life forms on the human body.
Often the cause of this condition is real witchcraft. Experienced specialists in the field of esotericism assure that such a state can be regulated by other people.
Regardless of the fact that doctors are in no hurry to admit the existence of such a disorder, its manifestations may well indicate that the patient has some kind of mental disorder.
Symptoms of catalepsy
In psychiatry, catalepsy is called waxy flexibility, because. the patient can maintain any position assigned to him for a pathologically long time, without making any effort. In other words, the person himself freezes for a long time in a certain position, even a very uncomfortable one, or individual parts of his body (legs, arms, head) maintain a posture typical of catatonic stupor.
Catalepsy can occur both in a number of mental illnesses (for example, schizophrenia and hysteria) and during hypnotic sleep.
This disorder is usually observed in narcolepsy or catatonic schizophrenia and is combined with other manifestations of increased suggestibility, such as:
- Echolalia and echophrasia - repetition of heard words and phrases, respectively;
- Echopraxia – reproduction of seen gestures;
- Stereotypy – monotonous repetitions of poses and movements;
- Verbigeration - monotonous repetition of phrases and words;
- Negativism: passive - ignoring requests addressed to the patient, active - performing other actions instead of the intended ones, paradoxical - reproducing exactly the opposite actions that the person is asked to do.
The development of symptoms of catalepsy in the vast majority of cases is gradual - they spread in a sequential order: from the neck muscles and arms to the muscles of the lower extremities. It has been clinically established that catalepsy can be a transient disorder, but it can also last quite a long time - weeks or even months.
In some cases, the clinical picture of catalepsy is limited to the listed signs (so-called empty catatonia), but often delusional, hallucinatory and affective disorders are observed in this condition. In some patients, consciousness remains normal (lucid catatonia), while others experience clouding of consciousness, most often oneiroid - clouding with an influx of delusional fantastic ideas that arise, which follow in a certain sequence and form a single whole, i.e.
This disease is characterized by a suspension of vital functions: a person becomes practically insensitive to pain and heat, he experiences a decrease in activity, and hardness occurs in the muscles. The interesting thing is that the patient in this state sees and hears everything, but cannot make movements.
Arising suddenly, stupor finds the patient in a certain position and fixes this position. For example, many cases have been recorded when a person “freezes” during a conversation with his attending physician: he had just been talking and gesticulating, and then he was overtaken by an attack of catalepsy. At the same time, he becomes so flexible that he can be given any new pose.
Cataleptic seizures are characterized by complete immobilization and a strong increase in muscle tone. The patient remains in the position in which the attack caught him for a long time.
This disorder is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- decreased sensitivity to external and internal stimuli;
- echolalia (mechanical repetition of heard words);
- decreased breathing;
- echopraxia (repetition of seen gestures);
- decrease in heart rate.
An attack can last from one minute to several weeks, and sometimes months. Its development occurs suddenly. The disappearance of stupor causes violent emotional manifestations in the patient.
This disease is dangerous because a person is able to lose mobility in a potentially dangerous place where there will be a threat to his health and life.
The development of a disorder such as catalepsy occurs gradually and continues to spread in strict sequence:
- neck muscles;
- hands;
- torso;
- lower limbs.
The reverse development of the disorder is characterized by the opposite direction. In modern medical practice, there are many examples of not only transient catalepsy, but also very protracted disorders, the duration of which ranged from several weeks to 2-3 months.
It will not be possible to detect the development of the disorder during the onset of stupor, since in such a state the patient may resist attempts to change position. Catalepsy will be completely absent when stupor is diagnosed with simultaneous numbness of muscle tissue.
Catalepsy is in fact one of the types of disorders of the functioning of the nervous system, the result of which can be called the suspension of the natural vital functions of the body. As the disorder develops, muscles often begin to harden, activity when moving worsens, and people’s sensitivity to heat and various pain sensations worsens.
Causes of catalepsy
As for the theory of the origin of catalepsy, scientists have two points of view on this matter with significant differences - neurological and psychological. In the first case, experts claim that the disorder is caused by certain formations of the brain. In the second option, the nature of the origin of the disease is explained by purely psychological phenomena. For example, there is an opinion that the cause of catalepsy is increased subordination of the will.
In any case, the basis of catalepsy is a limited “switching off” of the cerebral cortex, but the activity of the nervous motor apparatus remains. Its main task is to ensure balance of the human body in general and its parts in particular. When the patient is in a normal state, this function is masked by voluntary movements of a different nature. When catalepsy occurs, the influence of the cerebral cortex on the reflex, which is responsible for balancing, manifests itself in an open and more dramatic form. The appearance of the disorder may be preceded by anxiety and hysterical attacks, and the disappearance of the attack is accompanied by violent affective manifestations.
How symptoms develop
We recommend
Catalepsy is a pathology characterized by the fact that at the time of an attack a person freezes in a certain position for quite a long time with the suspension of all vital functions. There may even be a feeling that the patient is dead. Doctors call this condition “waxy flexibility,” because a person can be placed in any uncomfortable position without much effort, which will persist until the end of such an attack.
Such an attack occurs gradually: first, the neck and facial muscles begin to become numb, spreading to the lower extremities, and it ends in the reverse order. This condition can pass quickly, or it can last for weeks or even months.
Quite often it is during a conversation that such stupor occurs. This condition causes such severe muscle tension that the patient can easily be lifted by the heels and the back of the head. At the time of the attack, a disturbance of consciousness occurs. If such a seizure occurs during malignant schizophrenia, then the patient is aware of everything that is happening. With the oneiric form, a person is immersed in a world of illusions, which is supplemented by fantastic phenomena.
Treatment of catalepsy
The first task is to differentiate catalepsy from other movement disorders that can be observed with organic brain lesions, in particular with parkinsonism caused by epidemic encephalitis.
To treat catalepsy, interactive imagogy is used - a method that involves working with the internal forces of the body (in psychiatry it is called the imago-image). The essence of this method is to identify areas of mental problems that are inaccessible to conscious vision, i.e. bringing into motion images of a patient in an unconscious state and bringing them to a conscious level.
During the process of this psychotherapeutic procedure, a person plunges into himself, into his inner world and, through images, begins to understand complex situations and his own problems. He talks about his images to a psychotherapist, who at the same time observes his semantic field (in ontopsychology this is the name for the information and energy interaction of people). If it is absent, it means that the images did not come from the unconscious, but were “fantasized,” i.e. The problem is fake or it has gone away. True images coming from the depths are always accompanied by a semantic field. These images that arise in a person during a session are interpreted by a psychotherapist who has the knowledge to decipher them.
Thus, treatment of catalepsy is a long course, which is carried out only in specialized psychological centers with the participation of experienced specialists.
Diagnostics
This pathological condition is diagnosed based on the collected medical history and a thorough psychiatric and neurological examination.
Diagnosis of catalepsy is carried out by a psychiatrist and a neurologist. Attacks of waxy flexibility can appear when the main diagnosis is established or be the reason for the initial visit to a specialist. Depending on this factor, the volume of diagnostic procedures is determined. A comprehensive examination includes:
- Survey. The conversation is conducted with the patient and relatives. The doctor collects anamnestic data and finds out the symptoms. When communicating with a patient, the specialist determines the ability for productive contact, the preservation of critical abilities, and intellectual functions.
- Observation. Behavioral and emotional abnormalities are assessed during the patient’s consultation and hospital stay. Often the doctor is able to be directly present during the development of an attack.
- Neurological examination. During the initial diagnosis, tests can identify neurological pathology as a possible cause of catalepsy. Examination of the patient during an attack confirms a decrease in pain and temperature sensitivity, inhibition of reflex responses, muscle hypertonicity with preservation of plasticity.
Hypnotic catalepsy
Cataleptic stupor is the main manifestation of hypnosis.
It is used for medicinal purposes to limit the patient’s motor activity if this is necessary to restore the body. The method is used to attract the patient’s attention, that is, it is an inducer. Such manipulations can only be carried out in appropriate clinics under the supervision of specialists, as well as the treatment of catalepsy.
You can clearly see the result of introducing a person into a cataleptic state through hypnosis at a hypnotist show. Risky stunts allow you to observe the degree of muscle hypertonicity in this state. The person is placed on two chairs, with only the head and legs fixed on them. A slab weighing about 200 kg is placed on the stomach of a fragile man or woman and then broken. Although such ideas are widespread, they are extremely dangerous. Hypnotic intervention, without medical indications, negatively affects the psychological state of the hypnotized person and can provoke catalepsy as a pathology.
Regular experiments with introducing a person into a cataleptic state through hypnosis will invariably affect his sleep. Such patients often experience obsessive dreams, where they dream that the hypnotist puts them into a state of catalepsy. As a result, the condition is provoked in reality. In a state of natural sleep, muscular overstrain can last for several hours and it is extremely difficult to bring a person out of it. A relapse will greatly upset the dreamer’s nervous system.
Manifestations
Catalepsy can catch a person in any position, fixing the body posture. Thus, there are cases when patients suddenly froze during a conversation with their doctor. In this case, the patient’s position can be easily changed. Muscle tension in this condition can be so severe that the patient can easily be lifted by supporting only the back of the head and feet.
The main symptoms of the described disease are as follows:
- muscle hardening;
- almost complete loss of sensitivity to heat and pain;
- inability to move (paralysis).
If astral catalepsy is accompanied only by the above symptoms, we are talking about the so-called empty catatonia. In other cases, patients may also experience affective, delusional disorders and hallucinations. During an attack, a kind of suspension of a person’s vital functions occurs, while he does not lose the ability to see and hear everything that is happening around him, although from the outside he may seem completely dead due to a very slow pulse and heartbeat.
Features of the manifestation of catalepsy
How does this movement disorder manifest itself? The attack always begins from the head and gradually reaches the lower extremities, and ends in the reverse order. After emerging from the stupor, a person usually experiences vivid affective symptoms. There are two forms of cataleptic hardening:
- stupor with waxy flexibility;
- catalepsy with rigidity.
Wax flexibility is an attack of this kind when the body of a frozen person can be given any position, even the most uncomfortable, and he will maintain it until the end of the attack. A person in this state is somewhat reminiscent of a doll, which, no matter how you sit it down, will sit. Rigid catalepsy is characterized by a complete lack of flexibility. The muscle tension during an attack is so strong that a person can be lifted out of bed only by holding his head, and he will still maintain his posture. The duration of an attack of catalepsy can be very variable, from several minutes to many days. An attack can occur with a disturbance of consciousness of the oneiric type, when a person sees illusory phenomena, as during sleep. With clear consciousness (for example, with narcolepsy), the patient after a cataleptic attack is able to describe his feelings and everything that is happening.
Prognosis and prevention
The prognosis for catalepsy is favorable with successful treatment of the underlying pathology, preservation of cognitive functions, and the ability to critically think. Under such conditions, the method of interactive imagogy, which develops the skill of voluntary seizure prevention, turns out to be effective. There are no specific preventive measures; the likelihood of catalepsy can be reduced through timely diagnosis and treatment of mental and neurological diseases on the basis of which it arises.
Symptoms of pathology
Catalepsy is characterized by a group of signs of catatonic stupor, which manifests itself in catatonic and hebephrenic schizophrenia. This phenomenon can also be the result of suggestibility or a consequence of hysteria. However, most often the manifestations of catalepsy indicate the development of schizophrenia, so its signs are considered symptoms of psychosis. The disorder is accompanied by such phenomena as:
- echophrasia - reproduction of phrases,
- echolalia - mechanical repetition of words,
- echopraxia - copying gestures,
- stereotypy - monotonous reproduction of movements and poses,
- verbigeration - monotonous copying of words and phrases,
- negativism - ignoring requests,
- decreased sensitivity,
- muscle stiffness.
Negativism in the development of catatonic schizophrenia can be:
- Passive, the patient ignores calls to him, as if he does not hear.
- Active, the patient performs some other action in response to a request.
- Paradoxically, the patient, when contacted with a request to perform some specific action, does the opposite.
Why does it happen?
The causes of catalepsy are divided into two groups:
- Neurological disorders.
- Psychological problems.
People susceptible to suggestion, stress and hysterics in some situations:
- powerful emotions;
- prolonged experiences;
- depression,
may fall into a state of catalepsy. Taking large doses of such antipsychotic drugs can also cause a seizure.
Catalepsy can develop with the following mental and neurological pathologies:
- Cerebellar diseases. The reason for this syndrome is the blocking of connections between the frontal parts of the brain and the cerebellum, which occurs after a tumor or injury.
- Schizophrenia. A characteristic manifestation is the alternation of phases of excitement and stupor. With the latter, an attack of catalepsy may occur.
- Hysterical neurosis. A seizure occurs after a hysteria and is more common in women.
- Narcolepsy. In the second year of the disease, attacks of hypersomnia, or sleep disturbances, begin.
Causes
Existing nervous diseases contribute to the development of catalepsy, for example, the catatonic type of schizophrenia, narcolepsy. This deviation is usually characteristic of persons with increased suggestibility. An experienced hypnotist can easily provoke a cataleptic attack in such a person.
This pathology can also develop as a result of a hysterical trance. Many researchers regard catalepsy as one of the types of narcolepsy. The patient loses control over his body position due to relaxation of the skeletal muscles. The likely cause of weakening muscle tone is the transition from the waking phase to a state of paradoxical sleep, bypassing the “slow” and “fast” phases.
It is reliably known that if such stupor occurs, this indicates damage to the cerebellum associated with a violation of the frontal lobe of the brain. The provoking factor can also be an infectious disease such as paralytic poliomyelitis.
Excerpt characterizing Catalepsy
Meanwhile, Nesvitsky, Zherkov and the retinue officer stood together outside the shots and looked either at this small group of people in yellow shakos, dark green jackets embroidered with strings, and blue leggings, swarming near the bridge, then at the other side, at the blue hoods and groups approaching in the distance with horses, which could easily be recognized as tools.
“Will the bridge be lit or not? Who came first? Will they run up and set fire to the bridge, or will the French drive up with grapeshot and kill them? These questions, with a sinking heart, were involuntarily asked by each of the large number of troops who stood over the bridge and, in the bright evening light, looked at the bridge and the hussars and on the other side, at the moving blue hoods with bayonets and guns. - Oh! will go to the hussars! - said Nesvitsky, - no further than a grape shot now. “It was in vain that he led so many people,” said the retinue officer. “Indeed,” said Nesvitsky. “If only we had sent two young men here, it would have been all the same.” “Oh, your Excellency,” Zherkov intervened, not taking his eyes off the hussars, but all with his naive manner, due to which it was impossible to guess whether what he was saying was serious or not. - Oh, your Excellency! How do you judge! Send two people, but who will give us Vladimir with a bow? Otherwise, even if they beat you up, you can represent the squadron and receive a bow yourself. Our Bogdanich knows the rules. “Well,” said the retinue officer, “this is buckshot!” He pointed to the French guns, which were being removed from their limbers and hastily driving away. On the French side, in those groups where there were guns, smoke appeared, another, a third, almost at the same time, and at the very minute the sound of the first shot reached, a fourth appeared. Two sounds, one after the other, and a third. - Oh, oh! - Nesvitsky gasped, as if from burning pain, grabbing the retinue officer’s hand. - Look, one fell, fell, fell! - Two, it seems? “If I were a king, I would never fight,” Nesvitsky said, turning away. The French guns again hastily loaded. The infantry in blue hoods ran toward the bridge. Again, but at different intervals, smoke appeared, and buckshot clicked and crackled across the bridge. But this time Nesvitsky could not see what was happening on the bridge. Thick smoke rose from the bridge. The hussars managed to set fire to the bridge, and the French batteries fired at them no longer to interfere, but so that the guns were aimed and there was someone to shoot at. “The French managed to fire three grape shots before the hussars returned to the horse handlers. Two volleys were fired incorrectly, and all the buckshot was carried over, but the last shot hit the middle of a group of hussars and knocked down three. Rostov, preoccupied with his relationship with Bogdanich, stopped on the bridge, not knowing what to do. There was no one to cut down (as he always imagined a battle), and he also could not help in lighting the bridge, because he did not take with him, like other soldiers, a bundle of straw. He stood and looked around, when suddenly there was a crackling sound across the bridge, like scattered nuts, and one of the hussars, who was closest to him, fell on the railing with a groan. Rostov ran towards him along with others. Someone shouted again: “Stretcher!” The hussar was picked up by four people and began to be lifted. Catalepsy is a state resembling sleep, since during this period a person experiences a decrease in sensitivity to internal and external stimuli.