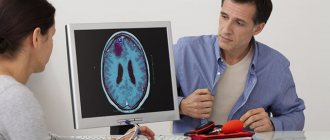
This article describes the symptoms of dementia in children that every parent should be aware of. If they appear, you should immediately consult a doctor.
Does your child have trouble remembering simple everyday things? Is your daughter or son sometimes unable to communicate effectively? Does your child have trouble recognizing family members? Even though you think these behaviors may simply indicate personality traits, these symptoms may indicate something much more serious. This article describes the symptoms of dementia in children. Such dementia is dangerous, and if it is not recognized in time, the child will develop poorly and will not be able to think and reason normally. Read on.
What is dementia and dementia in children: definition
Dementia and dementia in children
Childhood dementia, or dementia, is an umbrella term for a range of conditions that cause a gradual decline in cognitive abilities. Simply put, it is a loss of mental capacity that leaves a person unable to perform daily activities. It impairs memory and the ability to think, reason and plan. The effects of dementia worsen over time.
- For some babies, symptoms remain the same for many years.
- For others, the loss of skills occurs very quickly.
- Not everyone suffers from dementia, but your chances of developing the disease increase as you age.
- People with dementia are unable to care for themselves in the later stages of the disease and need help.
The damage caused by dementia is not only limited to the patient, but also takes a huge toll on family and friends. Some types of dementia include:
- Alzheimer's disease
- Vascular dementia
- Dementia with Lewy bodies
- Mixed dementia
- Parkinson's disease
- Frontotemporal dementia
- Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease
- Hydrocephalus
- Huntington's disease
- Wernicke-Korsakoff syndrome
There are many reasons causing this pathology. Read about them below.
Detection of pathology and methods of therapy
Organic dementia is characterized by a distortion of the individual’s development process, but not a complete stop. Fortunately, the pathology is treatable. Therapy for this disease is a long process in which specialists and the patient’s parents must be involved. First of all, if the dementia was caused by another disorder, the symptoms of that disease should be addressed first. The diagnosis of “organic dementia” should be made after consulting several doctors (psychiatrist, neurologist) and conducting brain examinations. Therapy for this pathology includes:
- The use of medications that help improve metabolism in nerve cells and blood flow in tissues. These medications include nootropics and psychostimulants.
- Classes with specialists in the field of psychology. They are aimed at improving the ability to think.
In the case of well-chosen therapy and compliance with all doctor’s instructions, patients, as a rule, have a good prognosis. Such children go to a regular school and study normally.
Dementia in children: causes
Dementia and dementia in children
There are various health conditions and disorders that can cause dementia in children. Various types of genetic diseases, head injuries and infections can negatively affect a child's brain. Below are some of the reasons:
Heavy metal poisoning:
- Chronic exposure to heavy metals such as lead can cause symptoms of dementia in children.
- These toxic substances are present everywhere, including food and air.
- The adverse effects of heavy metal poisoning are more common in children and may not lead to problems until adulthood.
Hypothyroidism:
- This pathology in children is caused by insufficient activity of the thyroid gland, which is unable to satisfy the body's needs for thyroxine hormones.
- There are two types of hypothyroidism, which include congenital and acquired.
- Congenital hypothyroidism is present in infancy, while acquired hypothyroidism develops later in childhood.
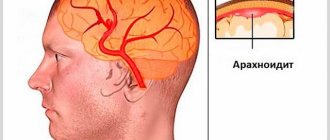
Encephalitis:
- This is an inflammation of the brain caused by a viral infection.
- Children under one year of age have a higher risk of developing this pathology.
- Additionally, this infection is more common in areas with large populations of ticks and mosquitoes.
Batten disease:
- This is a form of neuroceroid lipofuscinosis that affects children.
- Batten disease is an inherited disorder caused by a defective gene that causes lipofuscin to accumulate in the brain.
- Symptoms usually appear between the ages of 5 and 10 with the onset of vision problems.
Niemann-Pick disease:
- It is a rare inherited neurodegenerative disease that leads to progressive dementia in children.
- The disease causes excessive accumulation of cholesterol and glycosphingolipids in the brain.
Lafora's disease:
- This is a neurodegenerative disease that is inherited in an autosomal recessive manner.
- The disease is characterized by the appearance of epileptic seizures, which worsen over time.
Children with Lafora disease experience decreased cognitive abilities and eventually develop dementia.
Symptoms of dementia as a form of mental retardation in children
Symptoms of dementia as a form of mental retardation in children
Most of the disorders that cause dementia in children are rare and incurable. It is vital to identify symptoms early so that your child can receive appropriate medical care and support. Rates of childhood dementia, a form of mental retardation in children, vary individually, depending on the type and cause of dementia. However, there are some common symptoms to be aware of:
Memory loss:
- One of the most common symptoms of dementia in children is memory loss.
- However, if your child forgets things more often or asks the same questions more than once, this could be a sign of dementia.
- Memory loss alone does not mean a child has dementia.
- To make a full diagnosis, doctors look for at least two cognitive impairments that are present without loss of consciousness.
Language problems:
- Children with dementia may have problems forming words and expressive and receptive language skills in general.
- You may notice deviations in verbal and nonverbal communication.
Loss of intellectual skills:
- Children with dementia may exhibit a lack of problem-solving ability.
- Because the symptoms of dementia tend to be progressive, intellectual impairment gradually worsens over time.
- This can lead to an inability to learn new things.
The child cannot learn, remember, or communicate normally with adults. There is also a personality change. Read on.
Characteristics of a sick child
Developmental defects of a mentally retarded child affect all parameters of the individual and the person as a whole. Organic defects result in diseases such as hydrocephalus and cerebral palsy. Intellectual disabilities are associated with damage to certain cortical brain processes. Difficulties with cognitive activity take on different forms, leading to the impossibility of learning for mentally retarded children. Physiological disorders lead to decreased vision, hearing, and underdeveloped speech.
Psychology defines three criteria:
- clinical – associated with organic brain damage;
- psychological – expressed in disorders of cognitive activity;
- pedagogical – indicates a low level of learning ability.
Problems of perception
The perception of the information received occurs in an incomplete volume. It is difficult for kids to analyze and describe the image they see. Having memorized one subject, they do not strive to independently learn other things; they need to be pushed to action. It is impossible to educate mentally retarded children in a regular school.
A child with such a deviation does not understand the simplest things and cannot attend a regular school.
Understanding the world should occur in stages, but in sick children this mechanism is disrupted. There is no systematic analysis of objects; the baby is hardly able to notice the connection between parts of the whole. Such absent-mindedness leads to the loss of the initial idea of the thing he is studying. Weak mental activity prevents you from correctly assessing your actions and actions.
Delays in speech and mental functions represent serious differences between sick children and normal children. Sick children have great difficulty mastering writing and reading, they are inattentive, and cannot bring what they start to the required competent completion.
Underdevelopment, as psychology shows, is also noticeable in emotional terms. Children do not outwardly show their feelings, their volitional mechanisms do not work well, and their activity is poorly developed. They lag behind in physical development, being delayed in mastering basic skills: they begin to crawl, hold their head up, and walk poorly and late.
The games of such children, even at school age, remain very primitive
Problems of perception
Personality changes: how does attention develop in children with dementia?
Development of attention in childhood dementia
Most children with dementia experience behavioral personality changes over the course of the disease, including:
- Mood swings and lack of emotional control
- Displaying anxiety and anger
- Confusion about people and places
- Frequent screams and panic
- Lack of personal hygiene
- Clumsiness
The development of attention in children with dementia is weak. The child is constantly capricious and even throws tantrums. Can't say exactly who his grandparents or other relatives are.
Important: At the first manifestations of dementia, you should consult a pediatrician. He will make a preliminary diagnosis and refer you to a specialized specialist.
It is critical for parents to develop an effective support structure for managing dementia in children. Understanding symptoms in detail and reducing or eliminating triggers can help manage behavioral problems associated with dementia. But all prescriptions should be made only by a doctor.
Treatment tactics
Symptomatic therapy can prevent further weakening of intelligence and maintain its existing level.
For the symptomatic treatment of dementia, antipsychotics, anticonvulsants, tonics, vitamins and biogenic stimulants are used.
Neuroleptics
If a small patient suffers from tension, aggression, a pronounced feeling of fear, mental disinhibition, mood swings, apathy, lethargy or poor sleep, he is prescribed antipsychotics Azaleptin, Clozapine, Nootropil, Noocetam, Olanzapine, Piracetam, Reserpine, Cerebrolysin , etc.
Anticonvulsants
For convulsions, the child is prescribed anticonvulsants, which reduce hyperkinesis, contribute to partial compensation of personality disorders and reduce emotional tension.
In parallel, children are prescribed diuretics, complexes of vitamins and microelements, as well as medications that reduce intracranial pressure.
Biogenic stimulants
The program for the treatment of dementia in children includes biogenic stimulants Actovegin, Cortexin, Mexidol, Albumin, Apilak , etc.
The listed drugs stimulate cellular metabolism due to the accumulation of oxygen and glucose in the brain tissue.
B vitamins
B vitamins stop the processes of excitation of the nervous system , help improve memory and increase concentration.
The intake of B vitamins should be supplemented with iodine-containing products, amino acids and hormonal drugs.