Dizziness is one of the main symptoms of cervical osteochondrosis. The causes of this serious disease are most often injuries, chronic infections, deficiency of vitamins B and C and, of course, age. The cartilages of the intervertebral discs affected by the disease lose their elasticity, become deformed, the vertebrae wear out, and bone spines grow. All these processes have a negative effect on the vertebral arteries - the vessels are compressed and spasm occurs. As a result, oxygen starvation occurs in the vestibular apparatus and brain. The body reacts to all the changes that occur with dizziness and other unpleasant consequences.
How does dizziness occur?
If the cause is osteochondrosis, then the symptom will not be the only one.
Osteochondrosis changes the structure and shape of the vertebrae - they become deformed and cease to perform their main function.
As the disease progresses, the cartilage layers between the vertebrae become thinner and completely destroyed, which normally prevent contact with bone structures. This is how the vertebrae move closer to each other, their friction causing pain.
Further, the vertebrae themselves begin to lose their bone density, becoming thinner and thinner. Multiple microfractures occur that do not have the opportunity to heal properly.
The orderly row of vertebrae disappears, their shape is changed, and growths appear at the sites of fractures.
Nerves, blood vessels, and in severe cases, the spinal cord can be pinched
All this leads to the fact that the spine fails to cope with its main task - protecting blood vessels, nerves and the spinal cord.
Changes in the vertebrae lead to pinching of the artery that supplies the brain - this is how dizziness occurs, that is, a lack of blood supply rich in fresh oxygen. The vestibular apparatus, not receiving the necessary oxygen and other substances, begins to experience pathological changes.
The photos and videos in this article will tell you about the mechanisms of dizziness due to problems with the spine.
The picture is the main diagnostic method
We need to figure out how this symptom manifests itself specifically in osteochondrosis. Here are some features of dizziness:
- Most often, the symptom appears in the morning, right upon waking up.
- During the day, you may also feel dizzy due to sudden movements of the neck. At the same time, you will hear a slight crunch in the vertebrae.
- In the first stages of osteochondrosis, dizziness occurs quite rarely. If the disease worsens, then the symptom occurs every day.
- When you feel dizzy, your vision begins to darken. Patients often complain of tinnitus.
Dizziness may cause the patient to faint. When symptoms first appear, you need to lie on your back and relax as much as possible.
Consequences and complications
Cervical osteochondrosis cannot be ignored. Many nerves and blood vessels pass through the cervical vertebrae, and in case of any pathologies of the vertebrae or discs, they are compressed, resulting in insufficient nutrition of the brain and the occurrence of pain.
Oxygen starvation can lead to nervous system disorders, dizziness, insomnia, disruptions in the functioning of the heart, hypertension, severe headaches, etc.
In the absence of necessary therapy, the risk of developing vertebral artery syndrome (insufficient blood supply to certain areas of the brain), cerebral ischemia (oxygen starvation), spinal stroke and other diseases increases.
On this topic
- Dizziness
9 reasons that cause dizziness from changing body position
- Natalia Sergeevna Pershina
- March 26, 2020
Radiculopathy is considered a serious complication of cervical osteochondrosis - the formation of growths on the vertebrae, which sometimes leads to paralysis and decreased sensitivity of the body.
The most dangerous complication is compression of the spinal cord, which can be fatal. For this reason, treatment should begin when the first signs appear.
Pathological condition syndromes
Along with dizziness, the patient may experience other symptoms. Let's highlight the most common ones:
- The person loses coordination of movements.
- The eyeballs begin to involuntarily move horizontally.
- There is a feeling of nausea and sometimes even vomiting.
- A person begins to remember information worse.
- Vision and hearing decline.
- The patient becomes irritable and depressed.
- There is ringing in the ears.
- Feels very weak throughout the whole body.
Experts noted that this unpleasant symptom often occurs along with entire syndromes. The patient may experience hypothalamic syndrome. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Blood pressure surges.
- Frequent desire to go to the toilet.
- The heart rate becomes too fast.
- Unexplained fatigue appears.
- Nervous breakdowns begin.
- The skin becomes overdried.
- The patient begins to sweat.
- Increases body temperature.
Synclinal syndrome may begin with dizziness. It occurs with osteochondrosis at the time of vascular spasm and irritation of the nerves in the vertebrae. Often at the time of the syndrome, a person may lose consciousness. It is accompanied by additional symptoms:
- Noise and discomfort in the ears.
- The patient's speech is impaired for 1 day.
- Black spots before eyes
Often patients may experience visual syndrome due to dizziness. It occurs with osteochondrosis due to compression of the arteries: carotid or vertebral. At the time of this syndrome, fog appears before the eyes and vision is greatly reduced.
It is worth highlighting the pharyngo-laryngeal syndrome. It is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- I feel a small object in my throat.
- It becomes more difficult for the patient to swallow.
- Itching and soreness begins in the throat.
- The person's voice becomes weak and quiet.
All these syndromes appear with dizziness for a certain time. The syndrome subsides and all symptoms recede. However, if treatment for osteochondrosis is not started, all manifestations can cause serious complications.
To get rid of this unpleasant symptom, you need to start comprehensive treatment for osteochondrosis. The main goal of therapy is to relieve pressure from the vertebral artery, restore damaged discs and relax nerve endings.
The doctor is obliged to prescribe a certain course of drugs for the treatment of osteochondrosis:
- Anti-inflammatory. Analgin, vitamin B, Movalis and Ibuprofen are often prescribed.
- Novocaine blockades. They are used to relieve spasm, severe pain and inflammation.
- Muscle relaxants. Baclofen, Botox and Sirdalud injections are prescribed. The drugs will relieve severe muscle tension.
- Retinol. Will supply oxygen to brain tissue.
If you start taking a course of medications, dizziness, nausea and other unpleasant symptoms will immediately go away. It will take more time to completely get rid of osteochondrosis.
Dizziness from cervical osteochondrosis can only be cured by eliminating the primary problem – the osteochondrosis itself.
Treatment for such a serious pathology in the neck area will depend on the results of the study. They will give an idea of the condition of the cartilage and bone structures of the spine.
Medicines for dizziness in cervical osteochondrosis solve most of the problems
With degenerative disorders of the intervertebral discs in the neck, a person may feel dizzy at any time of the day, including morning, evening, night hours, as well as during performance of work duties. The pathological condition is accompanied by various signs. These include:
- the appearance of noise and ringing in the ears;
- loss of balance while walking or standing;
- severe pain in the head;
- the appearance of nausea, vomiting;
- increased sweating;
- pale or reddened appearance of the skin on the face;
- deterioration of vision caused by a change in the position of the eyeballs along a horizontal line;
- numbness of the upper extremities, most often occurring at night;
- increased pain when turning or sudden movements of the head;
- rapid pulse and discomfort in the cardiac region;
- darkening in the eyes, the appearance of colored circles, white and black spots or bright flashes.
Dizziness with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine causes sensations of the ground running away from under the feet, rotational turns of the room in front of the eyes, and right-hand movement of surrounding objects. The pathological condition has a different duration. With cervical osteochondrosis, you may feel dizzy for a minute or several hours.
Spend just a little time doing neck exercises to avoid dizziness!
When diagnosing cervical osteochondrosis, dizziness is of a vegetative nature, caused by the constant interaction of all systems of the human body. Its pronounced symptoms may indicate the need to urgently seek qualified help from a neurologist or vertebroneurologist.
To know how to deal with dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis, it is necessary to determine the form of its development and the type of syndrome. Doctors highlight:
- vestibular-stem syndrome, characterized by impaired blood supply to the brain and accompanied by swaying while walking, the appearance of nausea, vomiting with sudden movements of the head, pictures of moving floors, walls, pieces of furniture;
- cochlear-trunk syndrome, accompanied by dysfunction of the hearing aid, congestion, ringing, whistling in the ears, problems with balance;
- hypothalamic syndrome, the main symptoms of which include: severe sweating, fatigue, heart rhythm disturbances, a decrease or increase in the reading of the patient’s body thermal state;
- syncopal syndrome caused by damage to the spinal nerve and spasm of blood vessels, characterized by the appearance of floating spots in front of the eyes and tinnitus.
The types of syndromes and their signs suggest how to treat dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis.
Dizziness does not always accompany cervical osteochondrosis and may indicate serious degenerative changes in the cervical spine. Dizziness, caused by cervical osteochondrosis, usually feels like mild alcohol intoxication. Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis can be either episodic or constant.
Dizziness is a very unpleasant symptom that can unsettle the patient for a long time. Especially when it is accompanied by other manifestations of osteochondrosis.
The most common symptom of cervical osteochondrosis is neck pain, stiffness and headaches. Less commonly, symptoms caused by pinched nerve roots of the cervical spine may occur, such as:
- pain radiating to the shoulder;
- pain radiating to the arm;
- pain radiating to the fingers;
- tingling in the hand;
- numbness in the hand and fingers;
- arm muscle weakness;
- dizziness.
Many people with mild cervical osteochondrosis experience no symptoms, while others suffer from severe pain. Headaches with cervical osteochondrosis usually begin in the back of the head, right above the neck, and then move to the forehead. However, headaches can occur anywhere in the head.
The pain usually comes and goes. Exacerbations alternate with the absence of any symptoms.
About 1 in 10 people develop long-term, chronic symptoms.
Other, more severe symptoms are usually manifestations of:
- cervical radiculopathy - when an intervertebral hernia or bone growth compresses nearby nerve roots;
- cervical myelopathy - when the cervical spinal canal (the bones that surround and protect the nerves) narrows, compressing the spinal cord.
The most common symptom of cervical radiculopathy is acute pain radiating to the arm (also known as brachialgia).
Also, with cervical radiculopathy, you may experience numbness or tingling in your arm. Turning the head and stretching the neck can aggravate pain symptoms.
Cervical myelopathy
Cervical myelopathy occurs when severe cervical spondylosis or a large herniated disc causes a narrowing of the spinal canal, resulting in compression of the spinal cord.
When the spinal cord is compressed, it prevents signals from passing from the brain to the spinal cord and vice versa. Symptoms may include:
- poor coordination—for example, it may be difficult to button a shirt;
- heaviness or weakness in the arms or legs;
- problems walking;
- less often - urinary incontinence;
- fecal incontinence.
If you experience symptoms of cervical myelopathy, consult a doctor immediately.
Untreated cervical myelopathy can lead to permanent spinal cord damage and disability.
Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis is aimed at reducing pain symptoms and preventing permanent nerve damage. Treatment of cervical osteochondrosis can be either conservative or surgical. Surgical methods are used only in extreme cases.
May include:
- taking over-the-counter pain relievers;
- taking over-the-counter anti-inflammatory drugs;
- lifestyle changes, including visiting the pool, performing physical therapy, walking and posture correction;
- physiotherapy;
- spinal traction;
- massage.
- hirudotherapy
Prolonged wearing of cervical collars is not recommended, as this can lead to increased pain symptoms.
Surgical treatment
Surgical treatment methods can only be recommended for:
- compression of the nerve by an intervertebral hernia or bone growth (cervical radiculopathy), as well as compression of the spinal cord (cervical myelopathy);
- there is serious nerve damage that may become permanent unless emergency surgery is performed.
What is vertigo?
Dizziness, or vertigo, is a pathological condition in which a person has a feeling of incorrect perception of the position of the body in the surrounding space. It begins to seem to him that objects begin to rotate around him or, conversely, his body rotates around objects.
During an attack of vertigo, the patient loses confidence in his actions and his movements become awkward. In addition, he may experience vegetative and neurological symptoms:
- nausea, vomiting;
- unstable blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- hyperhidrosis of the face and upper extremities.
Causes
Manifestations of spinal pathology are diverse, many of them are caused by chronic processes occurring in the body. Osteochondrosis and dizziness are interconnected, which makes it necessary to have an idea of the reasons that cause deviations in health.
The mechanism of occurrence of the disease is as follows: with a normal column structure, the vertebrae are tightly connected to each other by cartilaginous discs with the help of ligaments and muscles. The impact of certain factors causes parts of the spine to move closer to each other, they are incorrectly installed and infringe on the nerve roots.
Cervical osteochondrosis can occur due to the following factors:
- The impact of vibration waves on a person (work as a driver of heavy vehicles, work on a corresponding machine).
- Incorrect body position, which leads to scoliosis, and then to osteochondrosis.
- Low physical activity.
- Incorrect sleeping place (it is necessary to choose orthopedic mattresses that evenly distribute the load on the spine).
It is not always possible to avoid the influence of these factors, so it is necessary to take preventive measures.
Before you start treatment, you need to find out why your head starts to feel dizzy with osteochondrosis. Doctors noted that the main reason is poor blood supply to the brain tissue. This causes too little oxygen to reach the brain and makes you feel dizzy. Blood circulation slows down for the following reasons:
- The vertebrae put a lot of pressure on the arteries.
- The vertebral artery is pinched from osteophytes or from an intervertebral hernia.
- If the patient has a dislocation of the superior process, it can also compress the artery.
Doctors noted that after 50 years, people are more likely to experience dizziness. This occurs due to changes in the vascular channels.
What factors contribute to the development of dizziness from cervical osteochondrosis, why does it develop?
The segments of the spinal column are small, but they are constantly under enormous load. The cervical spine is especially active; the area is responsible for turning and tilting the head, holding it, which is why cervical osteochondrosis is most common.
Dizziness, otherwise known as vertigo, becomes a consequence of degenerative processes in this part of the spine. Why is this happening?
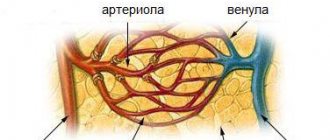
- There are openings in the cervical spine through which arteries and nerves pass into the skull. The vessel directs blood to the back parts of the brain, supplying them with nutrition and oxygen.
- The vertebral artery comes into contact with the hard tissues of the spine. When osteochondrosis of the cervical spine develops, deformation of its segments occurs. They shrink, and growths appear on the affected vertebrae - osteophytes, which steadily leads to a change in the shape of the canal and compression of the vessels.
- As a result of changes in the lumen of the artery, its stenosis, the normal flow of blood is disrupted, and its quantity also changes. This impairs the functioning of parts of the brain, and dizziness indicates a change in the functionality of the vestibular apparatus and hypoxia.
Sometimes a slight tension in the neck muscles or displacement of a vertebra causes compression of the vascular walls and affects the nerve endings and impairs blood circulation. Therefore, people with osteochondrosis feel dizzy.
It is easier to treat dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis at the initial stage, while VAS (vertebral artery syndrome) is weakly expressed. If you do not pay attention to the symptoms for a long time, in addition to constant pain in the back and heart, fainting is possible.
Dizziness is a sign not only of osteochondrosis of the neck, the group of people who are susceptible to this syndrome is quite wide: from 25 years of age and older, so self-diagnosis is inappropriate here, the symptom may indicate other disorders. Therefore, only a doctor knows how to treat dizziness. What other factors cause dizziness:
- vestibular neuronitis;
- disorders in the inner ear due to age-related changes, inflammatory processes, damage and toxic effects;
- consequences of brain injuries;
- presence of a tumor;
- pathologies of blood vessels and heart;
- neurological problems;
- psychogenic factor.
Often the signs of pathologies are very similar, so if symptoms of dizziness appear, you should consult your doctor.
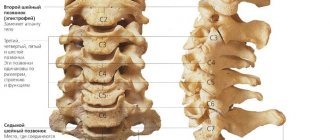
Cervical osteochondrosis is caused by age-related wear and tear of the spine.
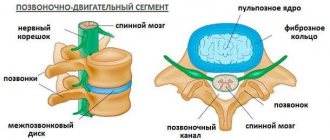
Our spine consists of:
- vertebrae - the bones of the spine that make up its skeleton (vertebral column). The vertebrae protect the nerves from damage;
- intervertebral discs. Intervertebral discs consist of a dense elastic membrane (fibrous ring) and soft contents, the consistency of which resembles toothpaste. Intervertebral discs are located between each pair of vertebrae and act as friction shock absorbers. Also, intervertebral discs provide movement of the spine;
- spinal cord - the main bundle of nerves connecting the brain to the body;
- Nerve roots are the initial sections of nerves emerging from the spinal cord.
As we age, intervertebral discs lose water and nutrients and become more susceptible to damage. Our bodies compensate for wear and tear on the joints by forming small bone spurs to support the neck and stabilize the spine. These growths are called bone spurs or osteophytes.
Osteophytes can lead to loss of spinal mobility, resulting in neck stiffness and pain. Osteophytes can also pinch nearby nerves and the spinal cord. This usually occurs in older patients.
In addition to age, there are other risk factors that increase the chance of developing cervical osteochondrosis. These include:
- sedentary lifestyle and obesity;
- history of neck or spine injuries;
- intervertebral hernia;
- repetitive loads;
- professional sports.
Intervertebral hernia of the cervical spine is the main cause of dizziness in cervical osteochondrosis.
An intervertebral hernia occurs when an intervertebral disc is damaged. A herniated disc can put pressure on the nerves that exit the spinal cord.
If the nucleus pulposus of the disc compresses the nerves of the cervical spine, it can cause severe pain that radiates into the arm (cervical radiculopathy). When the hernia is located in the upper cervical spine, a triad of symptoms occurs - headache, dizziness and surges in blood pressure. Also, these symptoms can exist separately or be combined with pain in the neck, arm, shoulder and under the shoulder blade. A herniated disc can also compress the spinal cord (cervical myelopathy).
Cervical hernias can occur at any age.
There is evidence that people who engage in heavy physical labor have an increased risk of developing cervical osteochondrosis.
Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis is associated with impaired blood flow to the brain due to compression of the cervical arteries. Such dizziness is not associated with pathology of the arteries themselves, therefore it is diagnosed and treated in the same way as the underlying disease. Dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis is just a symptom. There is no specific treatment for such dizziness.
Medicines
Prescription of medications is usually aimed at eliminating several causes that affect dizziness in cervical osteochondrosis. Medicines help solve the following problems:
- normalize blood circulation in the brain;
- restore the structure of cartilage tissue;
- reduce pathological changes in the body;
- neutralize neurosis;
- eliminate pain syndrome;
- normalize metabolism.
The restoration of cartilage tissue is facilitated by chondroprotective drugs of plant origin (“Piaskledin”) or those made on an animal basis (“Arthra”, “Chondroitin”, “Structum”, “Dona”).
Analgesics (“Amidopyrin”, “Analgin”) or muscle relaxants (“Mydocalm”) will relieve pain. The inflammatory process is neutralized by non-steroidal drugs (“Diclofenac sodium”, “Ibuprofen”, “Voltaren” and others).
Soft sedative tablets (valerian, Afobazol, Tenoten) have a beneficial effect on the nervous system, eliminating feelings of anxiety and restlessness.
It is very important to promptly stop the neurological symptoms that characterize cervical osteochondrosis. Dizziness and nausea can quickly stop after taking nootropic drugs (“Picamilon”, “Aminalon”, “Phenibut”), as they help improve blood microcirculation in the brain tissue. In addition, it is imperative to prescribe medications containing all B vitamins (“Neuromultivit”).
Characteristics of dizziness
Symptoms and treatment of pathology are interrelated. Therapy is prescribed after diagnosis by a doctor, but to correctly determine it, you need to know the characteristics of dizziness:
- The man’s position is extremely unstable, he staggers from side to side, the ground disappears from under his feet.
- Objects may “dance” before your eyes.
- When looking at an object, rainbow circles, spots, and running dots appear before your eyes.
- Ringing in the ears and hearing loss occurs. Surrounding sounds are heard as if through cotton wool.
- Changes in the color of the skin, and this can be either redness or paleness.
- Increased heart rate.
- If the vertebral artery is involved in the process, then fainting may occur.
- Sweating.
- Severe attacks can lead to vertigo (loss of balance with a feeling of riding on a merry-go-round).
The attending physician can determine at an appointment whether the signs are associated with osteochondrosis or not. One of the criteria for determining the origin of symptoms is that with dizziness from osteochondrosis, the symptoms gradually increase. Can the symptom appear suddenly? It should be understood that this is a gradual process associated with the slow destruction of bone and cartilage tissue.
Unlike osteochondrosis, with a stroke, hemorrhage, or cerebral aneurysm, the symptoms appear abruptly and the person’s condition quickly deteriorates. But if dizziness is left untreated, it can lead to acute cerebrovascular accident.
With osteochondrosis, symptoms can be of various origins:
- With systemic vertigo, a person experiences sensations as if he himself is spinning or the surrounding objects are in motion.
- Unsystematic origin - as if there is no support under your feet, everything is falling through.
- Combined origin - both groups of signs are of concern.
Whatever the nature of the condition, a person wants to know how to relieve headaches, eliminate dizziness and prevent this frequent symptom.
It is with osteochondrosis that the symptom manifests itself in a special way. The head begins to spin due to two main syndromes:
- Vestibular-stem syndrome.
- Cochlear-trunk syndrome.
This syndrome exhibits certain symptoms:
- The eyeballs begin to twitch.
- The floor and walls waver before my eyes.
- All objects around begin to rotate slowly.
- The patient's walking becomes unsteady.
- A feeling of fear arises.
- Nausea and vomiting begins.
This syndrome begins with cervical osteochondrosis due to sudden movements of the head and when getting out of bed.
The second syndrome has its own characteristics:
- Hearing decreases.
- Ringing in the ears begins.
- Pawns ears.
Treatment methods
What medications are prescribed for cervical osteochondrosis? More on this later.
An established diagnosis of “cervical osteochondrosis,” complicated by a depressive mental disorder, requires the immediate initiation of treatment, which includes a whole range of measures. The following groups of drugs are used:
- antidepressants, if necessary - tranquilizers;
- non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs;
- chondroprotectors;
- vasodilators if necessary;
- possibly sleeping pills;
- complex of polyunsaturated fatty acids, vitamins and microelements.
Diagnostics
Cervical osteochondrosis is usually suspected if the typical symptoms of neck pain and stiffness are present. The presence of osteochondrosis can also be assumed if the patient complains of pain in the arm and loss of a number of functions of the arm.
Various tests described below can be used to make a diagnosis.
Medical checkup
Cervical osteochondrosis can limit the range of motion in the neck. The doctor may ask you to turn your head to one side or the other, or tilt your head toward your shoulders.
Your doctor may also check the reflexes in your hands. Problems with reflexes and decreased sensation may indicate nerve damage caused by a narrowing of the spinal canal (cervical myelopathy).
X-ray. An X-ray will help identify any problems with the skeletal system, including bone growths (osteophytes).
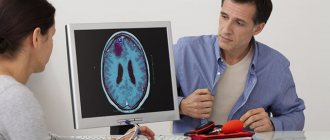
MRI (Magnetic Resonance Imaging) and CT (Computed Tomography) MRI examination is the “gold standard” for examining the spine. During the study, powerful magnets are used to create magnetic fields and radio waves. The result is an image in which you can see not only bones, but also soft tissues, including intervertebral discs and nerves.
A CT scan provides a more detailed picture of your spine than an X-ray. A CT scan is usually only performed if you are unable to have an MRI scan for some reason.
To clarify the diagnosis, the neurologist prescribes a detailed examination:
- Radiography. It will allow you to identify the degree of changes in the spine, the presence of growths on the body of its segments.
- Doppler ultrasound. The procedure will help determine the condition of the cerebral vessels and the nature of the blood flow.
- MRI. Tomography of the spine will give an idea of the presence of hernias and compression of the nerve roots.
To make it easier for a specialist to make a diagnosis, all your accompanying sensations about how dizzy you feel should be described in detail, without omitting details.
Passing diagnostics, which is prescribed by the attending physician without fail, is a necessary measure to confirm degenerative disorders of the intervertebral discs in a person’s neck and determine the correct, effective treatment for cervical osteochondrosis. Most often, patients undergo:
- magnetic resonance imaging, the results of which reveal the degree of damage to the intervertebral discs of the neck;
- Doppler ultrasound, designed to study the condition of blood vessels;
- radiography, which provides an opportunity to see the pathological zones of each cervical vertebra.
How to cure dizziness resulting from neck osteochondrosis
Neurologists and vertebroneurologists know how to relieve the symptoms of a patient’s pathological condition, the appearance of which is caused by degenerative disorders of the intervertebral discs in the patient’s neck. After collecting anamnesis and obtaining the results of diagnostic studies, treatment measures are prescribed. These include:
- drug therapy, which involves taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory and psychotropic drugs, chondroprotectors, analgesics, painkillers and vasodilators, complexes of vitamins, minerals, microelements;
- use of traditional medicine recipes;
- physiotherapeutic, water, massage procedures, the action of which is aimed at stopping degenerative processes in the cervical vertebrae, relieving pain, normalizing blood circulation in blood vessels;
- physical therapy, including exercises for dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis;
- sanatorium-resort and balneological treatment;
- organization of a balanced nutritional diet, adherence to work, rest, and nutrition.
Patients who may feel dizzy due to pathology of the cervical vertebrae are recommended to sleep on low pillows with an orthopedic effect. Their use helps relieve symptoms of dizziness, pain and tension in the problem area. It also becomes possible to provide adequate rest to sick people and eliminate the occurrence of dystrophic disorders of the vertebrae down behind the cervical spine.
Treatment tasks
Symptomatic manifestations of dizziness worsen the quality of life and distract a person from everyday activities. In addition, neglect of the condition can lead to loss of self-care. Treatment of dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis must be considered from the point of view of a complex therapeutic task. The treatment process involves a certain scheme:
- Elimination of factors that compress and irritate nerve formations and the vertebral artery.
- Restoration of structural regions of the vertebral cervical system and peripheral tissue structures.
- This goal is achieved through drug therapy, functional methods of treatment, physiotherapy, physical therapy, massage and folk remedies.
Gymnastic exercises in the treatment of osteochondrosis and relief from dizziness cannot be done during an acute attack. Physical activities should be aimed at strengthening the neck muscles, improving vertebral mobility and stimulating blood circulation. It is recommended to perform all exercises calmly and slowly; careless movements can aggravate painful manifestations and increase inflammation. We offer several recommendations to help avoid dizziness attacks:
- Sit comfortably, leaning on the back of a chair, and press on your forehead with the palm of your right hand for 10 seconds. Repeat 5-6 times.
- In a sitting position, press your palm on your right cheek, holding your hand for 10 seconds. After each exercise, take a short break.
- Alternately stretch your neck up and pull it into your shoulders. The back should be straight, forward or sideways movements are not allowed. Repeat at least 10 times.
- Soft turns of the head. You need to do the exercise very slowly, exhaling in each direction, repeating it 6-8 times.
- Tilt the head forward and backward (done slowly and smoothly).
- Tilt the body while sitting on a chair with your arms crossed over your chest: while inhaling, go forward, while exhaling, return to the starting position.
- To complete the complex, it is recommended to try to draw your mobile phone number in the air with your nose.
The proposed set of therapeutic exercises effectively helps to get rid of dizziness. In addition, it can be recommended to all people as a good preventive measure against osteochondrosis of the neck.
Traditional medicine for dizziness
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=u84G8RqeUfw
Treatment of dizziness with cervical osteochondrosis sometimes involves the use of folk remedies. Before doing this, you should definitely consult a doctor.
The cost of self-medication is quite high. The clinical picture may worsen and additional treatment will be required.
The best recipes are presented in the table.
Table 6. Folk remedies.
| Means | How to cook | Number of uses |
Potato compress | Grate 1 raw potato on a medium grater and mix with the same amount of fresh honey. Lightly squeeze the prepared pulp, wrap it in gauze, and apply it to the back of the neck. | 1 time/24 hours - before going to bed. |
Aloe mixture | Peel 1 gram of plant leaves, mix with 50 ml of radish juice and the same amount of vodka. | 1 time/24 hours - before the morning meal. |
Hop cone ointment | Mix 1 tablespoon of crushed cones with the same amount of pork fat. | Rub into the cervical vertebra area. The procedure is carried out before lights out. |
Flour cakes | Mix 1 cup of sifted wholemeal flour with 200 ml of water. Knead stiff dough, roll out thinly, bake flat cakes. Cool slightly, wrap in a clean cloth. | The cakes are applied overnight. |
Not only medications prescribed by a doctor, but also proper nutrition will help overcome dizziness with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. To relieve dizziness as a symptom, you need to stop drinking caffeine-containing drinks and minimize your daily salt intake. During an exacerbation, doctors categorically prohibit the use of herbal infusions, lotions and compresses to eliminate dizziness.
They should be used only for preventive purposes, after consulting with a specialist.
Some of the most famous folk recipes are:
- Infusion of celery seeds – 1 tbsp. pour a spoonful of seeds with 1 cup of boiling water, filter, take 1 tbsp 3 times a day. spoon.
- Grinding with radish and honey on vodka - thoroughly mix 3 cups of grated radish, 2 cups of honey, 1 cup of vodka. Rub several times a day into the area of the cervical vertebrae.
- Compress from horseradish leaves - 1 leaf of horseradish is scalded with boiling water, then cooled a little and applied to the neck area overnight. The course of treatment ranges from 6 to 10 days - this is exactly how much is required to normalize blood flow.
Dizziness, pain and other unpleasant sensations caused by cervical osteochondrosis significantly reduce the quality of life of many people. That is why the disease requires careful treatment - its first symptoms cannot be ignored, and if they occur, you should urgently consult a doctor. And it’s even better not to forget about disease prevention and prevent deformation of the cervical vertebrae.
You can use natural, natural remedies to eliminate the symptom. Here are some recipes:
- Pour boiling water over hawthorn and drink it instead of tea every day.
- Mix castor oil, as well as essential oils of fir and juniper. Rub the mixture into the painful area of the cervical spine.
- Mix honey and grated potatoes. Distribute the mixture over your neck and keep as a compress.
Alternative treatment can only be used as an addition to the main therapy.
Useful physical procedures
The doctor will definitely prescribe a course of procedures for osteochondrosis of the cervical spine. After the first sessions, signs of dizziness will disappear and the tinnitus will go away.
- Ultrasound treatment. After the procedure, inflammation is relieved and pain goes away. This light massage with special waves will relieve dizziness and help cure osteochondrosis.
- Magnetotherapy. The doctor sets up a magnetic field that will act on the damaged area of the neck. During the procedure, the blood vessels dilate, and the dizziness immediately goes away. At the same time, metabolic processes are normalized and all toxins are removed from the body.
- Electrophoresis. The doctor applies a special current to the painful area and simultaneously injects a drug. Usually Novocain or Lidaz are used. After the procedure, blood circulation improves and muscle spasms are relieved. After visiting a couple of procedures, you can forget about dizziness.
- Detensor therapy. The spine is stretched under the weight of the human body. For the procedure, a mattress with special recesses is used. After such therapy, muscle tone improves, inflammation decreases and the head stops spinning.
All procedures must be prescribed by the attending physician. You are not allowed to attend therapy sessions on your own. The course is prescribed according to your diagnosis and a certain stage of osteochondrosis.