Warts themselves bring certain inconveniences to the lives of their owners. This is not only a cosmetic defect, but also a constant risk of unnecessary skin injury due to scratching or touching growths. When a wart appears on the head under the hair, an additional number of inconveniences arise, especially for men: it is impossible to get a normal haircut due to the protrusion of the papilloma above the surface of the skin, inadequate or uncomfortable use of hats, glasses, and many other accessories.
Who is at risk
According to statistics, ¾ of all people have encountered warts on their skin at least once in their lives.
However, most of them (approximately 50%) resolve successfully within one year from the start of active treatment.
Risk groups have been identified that are most likely to develop warts, including on the head:
- young children whose immunity is severely weakened;
- teenagers before puberty;
- patients undergoing immunosuppressive therapy;
- patients with atopic dermatitis;
- people who have a severely weakened immune system: patients with AIDS, lymphoma, etc.
Of course, warts can appear in anyone at any age, but according to statistics, the largest percentage of HPV patients with typical tumors on the body are in older children.
Varieties
A wart on the head can be:
- simple is a keratinized papule, the diameter of which does not exceed 7 mm. As soon as a simple papilloma appears on the skin, it is flesh-colored, but over time its color changes to brown or gray. Usually, daughter growths grow next to such a formation. Should such a papilloma be removed or not? Definitely yes, since after frequent injury it can not only grow into a large wart, but also degenerate into a malignant tumor;
- flat papillomas have a smooth, contoured surface, can rise above the skin no more than 2 mm and be up to 5 mm in diameter. In appearance, such warts resemble flat nodules; they most often appear on the skin of the face. The color of the wart can be pink, flesh-colored or brown. The shape of such formations is round, but when several papillomas merge, the result is irregular;
- condylomas are a papillary growth on a stalk of soft consistency. The color of such formations is pink, reddish or flesh-colored. They most often appear on the eyelids and near the lips, and can also grow under the hair. If such a wart is not treated, it will become quite large and cause pain and visual discomfort;
- Keratomas are warts that appear only in older people. They can reach 3 centimeters in size. In appearance, keratomas resemble loose plaques, the surface of which is covered with sebaceous and horny masses. They are usually dark in color and may itch. Such warts appear on the head under the hair or on the temples, but can also affect other parts of the head.
The first three types of papillomas under unfavorable conditions, for example, with frequent trauma, can degenerate into a malignant tumor.
Only keratomas will never cause skin cancer.
How to distinguish viral warts?
One or more benign lesions appear after infection with the human papillomavirus (HPV). In the initial stages, the growths are flesh-colored or pinkish-pearl in color. They change with age and acquire a grayish-yellow or brown color. The diameter is up to 10 mm, and larger tumors are formed by the fusion of several growths.
Externally, it is difficult to distinguish a harmless wart from a malignant neoplasm. But an experienced doctor can easily do this based on several signs.
In most cases, simple or flat warts grow on the scalp. They are small in size (5-10 mm), hair can grow through them, and this fact allows the growths to be well camouflaged.
They can only be detected when the wart grows to a large size and when a person cuts his hair short. Simple warts have a stalk; frequent combing of hair with a comb leads to injury to it.
Constant violation of the integrity of the wart increases the risk of malignancy.
A simple wart is different from genital warts. Condylomas look like multiple growths, shaped like pyramids. They are flesh-colored or brown and grow up to 5 mm in height.
Flat warts are single neoplasms, in their structure they resemble low platforms rising above the skin by 1-2 mm; in structure, flat warts are similar to neoplasms assembled from many lobules.
If a wart grows slowly, if it reaches a certain size and stops growing, if hair grows through it, there is no need to worry. Uniform color and structure, the absence of purulent discharge from the growth allows us to make positive prognoses.
The shape and size of warts of infectious origin depend on the type of virus (more than 100 different HPVs are known).
Wart on the head in the hair causes of appearance
Warts are a round, nodule-shaped formation on the skin, under the hair, dense to the touch, protruding above the surface of the skin under the hair. The cause of these formations is papillomaviruses, which can be infected through contact with a sick person or with objects used by a viral carrier. That is, you can “catch” the virus, for example, by using someone else’s comb. But not everyone develops skin nodules when they come into contact with the virus, and the disease begins. The immune system of many people successfully copes with papillomavirus.
Photo of growth in hair.
What is a growth on the scalp and why does it appear?
The cause of warts under the hair on the head is the excessive growth of changed, virus-infected skin cells. The size of the nodules can vary from a pinhead to 2-3 cm in diameter. The places where growths occur on the head are the face, neck (in places of contact with the collar, skin folds, growths arise from friction).
An unpleasant neoplasm in the form of a skin nodule, what risks does it carry if not removed?
Doctors advise removing and getting rid of warts on the head in the following cases:
- The location of the wart on the head is subject to constant friction (for example, in contact with the collar). If you do not get rid of it, including at home, the risk of malignant cells appears increases.
- A sharp increase in size of the skin nodule (growing rapidly), a change in its color, shape (the wart has grown and expanded at the base). In such cases, you MUST show the keratotic growth to a doctor in order to get rid of the diagnosis of squamous cell carcinoma or melanoma of the skin. The treatment is carried out by a doctor.
- Nodules are also removed at home for aesthetic reasons. For example, hanging formations, including under the hair on the head, can cause psychological discomfort, reduce self-esteem, and ruin life. This is an unpleasant symptom, especially for women with long hair. A child scratching such a growth, injuring the skin, thereby increases the risk of malignant cells.
This is interesting: Celandine against condylomas
Does the growth pose a danger of infection?
If you do not injure the nodule or comb it, it does not pose a risk of infecting others. Warts on the head should not be confused with moles; getting rid of them, especially at home, on your own, is very dangerous. Moles are not difficult to distinguish: a person has them from birth, their color is darker than the surrounding skin, moles, as a rule, do not grow and are flat in shape, they are invisible in the hair on the head.
About neoplasms
In one of our articles, “Skin growths: benign, malignant and borderline,” we already talked about skin growths and classified them according to their danger to human health.
Today we will look at those that are most often found on the head and are sometimes invisible under the hair. Experts recommend regularly palpating and, if possible, examining the head for the presence of tumors, since the proximity of a malignant tumor to the brain can lead to irreparable consequences. If you notice a strange growth on your head, immediately consult a dermatologist or oncologist. The scalp is also the most traumatized and exposed area. Many people use combs with hard teeth, which can easily tear off the growth. In addition, we wash our hair, dye it, apply masks that can corrode the tumor and provoke its degeneration into a malignant tumor.
You need to urgently contact a specialist.
First, let's look at malignant neoplasms on the scalp.
First of all, malignant neoplasms include melanoma - skin cancer. You can find out more about it in our special article “Skin cancer: melanoma.” The neoplasm looks like a small plaque of light brown or black color with a rough surface. Melanoma is dangerous, it metastasizes and can lead to irreparable consequences.
Skin epithelioma is a tumor that develops on the surface layer of the epidermis. Also distinguished is epithelioma of the sebaceous gland - a neoplasm that occurs on the scalp, with inflammation of the sebaceous glands. Epithelioma looks like a pink or light brown growth and can reach 5 cm in diameter.
Scalp keratosis is a keratinization of the top layer of skin. Most often found on the face and scalp, it can be located either on a small area of the skin or affect the entire surface of the head. The neoplasm looks like multiple warts, ranging from light to dark brown in color. Experts also identify seborrheic keratosis of the scalp; its appearance indicates pathologies occurring in the body.
With this diagnosis, a thorough examination is necessary, since this may be evidence of cancer of the internal organs. Treatment for keratosis of the scalp is prescribed by an oncologist or dermatologist after receiving all the tests. Treatment methods may include medications and peeling procedures, massage, and laser therapy.
Scalp keratoacanthoma is a benign tumor of the hair follicles that most often occurs in older people. It is a spherical dense neoplasm affecting the scalp. Keratoacanthoma and its multiple forms are flesh-colored and can grow rapidly, reaching 2-3 cm.
A mole is a small pigmented formation on the skin that can appear at any age and on any part of the skin, even on the head in the hair. Moles can grow in large numbers during puberty, during hormonal imbalance or pregnancy, which you can read more about in our special article.
Perhaps the most common neoplasms on the scalp are warts and papillomas. They appear due to the human papillomavirus, which is most often activated with reduced immunity, severe stress, infectious diseases, and a lack of vitamins in the body. Find out more about what HPV is and how it manifests itself on the body in our article “Human Papilloma Virus”.
Hemangioma of the scalp is a vascular tumor that appears due to improper development of blood vessels. It appears in infancy and most often forms on the face, neck or scalp. This is a benign neoplasm that does not cause harm to the body, except for aesthetic imperfection.
Hemangioma of the scalp is a racemous hemangioma; it is a lumpy pink, burgundy or red formation, reaching up to 5 cm in size, rising above the skin, and does not cause discomfort or pain when pressed. Removal of a hemangioma can be performed at any age, but first you need to consult a doctor. Since removal of a hemangioma on the head may have a number of contraindications.
When treating any neoplasm on the head and hair, the most important thing is to consult a specialist in time. This will not only help identify a malignant tumor in the early stages, but also save life and health.
How to remove a wart on the head at home - removal methods?
- Chemical methods - various acids and alkalis will help you get rid of skin growths in your hair at home. You can read more about these substances below.
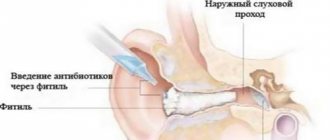
- Thermal methods of cauterization at home - cryotherapy (treatment is carried out by freezing with liquid nitrogen, dimethyl ether). Cryopreparations and chemical pharmaceuticals in various forms (solutions, ointments, creams, gels) are used for treatment.
- Cryotherapy is carried out using products such as “Cryopharma”, Wartner Cryo. Procedures that freeze the tumor are carried out for 10-14 days, after which the warts disappear without a trace, and the site of freezing will not hurt. During treatment, it is necessary to cover the hair on the head to protect it. Cryopreparations are available in the form of a spray. In some cases, if the result is unnoticeable, for the treatment of old nodules on the head, an additional course may be required after 2 weeks.
2. Pharmaceutical solutions for treatment at home (prohibited for use in children):
- Feresol (phenol and metacresol), a caustic substance, to get rid of a neoplasm at home, a single cauterization is usually sufficient (for formations up to 2 mm in size). This product should not remove warts from children or pregnant women.
- Verrucacid, a milder treatment. Will help get rid of the nodule in 2-3 times
- Collomak (salicylic acid solution), used for treatment at home 2 times a day for up to 7 days, no more. With its help you can get rid of the nodule in a week.
- Iodine solution. Cauterize pointwise 1-2 times per day, no more than a week.
Attention! All chemicals at home should be applied pointwise, while protecting the surrounding areas of the skin and hair on the head with a film and lubricating them with Vaseline or greasy cream.
Also read about the beneficial properties of beetroot. More details here:
3. Ointments and gels
- Viferon (immunomodulator), stimulates the production of one’s own antibodies to viruses at the site of application, can be used at home in pregnant women and children. Lubricate the nodules 2 times a day, you can get rid of them after a course of 30 days.
- Imiquimod has a dual effect: it eliminates formations and activates local immunity against the human papillomavirus. Apply spotwise, at night every other day. Course up to 30 days. Panavir gel. Also an immunostimulant, a course of treatment at home for up to 21 days may require several courses to completely get rid of the growth.
4. Other forms : for example, lapis - silver nitrate, a means for cauterizing warts, is available in a convenient pencil form. Helps get rid of the problem in 3-5 days, the resulting crust should fall off on its own, without mechanical impact. Treatment may cause a dark spot to appear on the skin.
5. Pharmacy analogues of folk remedies, alkaline aqueous solutions of sodium hydroxide. potassium (Super celandine) - celandine extracts have taken first place in the treatment of warts. They, like acid-containing preparations, should be used with caution, protecting nearby areas of skin and hair on the head, no more than 3 times, applying one drop of solution. Otherwise, scars may remain after treatment.
How to prepare a remedy for warts on the head based on celandine
There is no need to introduce celandine as a medicine for treatment at home; it has long been known. You can make preparations based on celandine for free at home to treat warts under the hair on your head, which you can only rejoice at.
The juice from the stems of celandine is used. The time to collect grass is from late spring to late summer. You can simply take fresh juice from a cut plant stem. The juice is a bitter, poisonous, yellow liquid. The finger with which the liquid is applied to the growth must be protected with a fingertip, or it is better to use gloves.
Another way to get rid of the growth at home is to prepare an ointment by crushing a green plant and squeezing the juice out of it. Mix the juice with glycerin, gradually adding it until a thick mass is formed. Use by applying to the wart on the head 1-2 times a day. To get rid of the tumor and remove the wart, it takes up to 2 weeks.
Symptoms and diagnosis
Advice from E. Malysheva.
You don’t need pills to make warts and papillomas disappear from the roots! Write down a simple but effective recipe that will help you get rid of such an unpleasant diagnosis once and for all. You just need to rub in the regular one in the morning.
The etiology of a papilloma can be suspected by visual examination - examination.
Age-related warts look like moles, the color of café au lait, covered with sebum and keratinized skin particles.
Viral papillomas can be of different shapes: flat, in the form of a thread, in the form of a cauliflower inflorescence. Color varies from flesh to brown.
There is no pain, itching or swelling.
A number of research methods have been developed for accurate diagnosis and correct treatment of viral papilloma:
- dermatoscopy – examination of a tumor using a dermatoscope. Allows you to exclude the malignant course of the disease
- histology – wart scraping is examined under a microscope, tissue structure is determined
- polymerase chain reaction (PCR) is a biological method for determining the viral origin of a biosample.
This is interesting: Baths for psoriasis: turpentine, radon, starch, oatmeal, herbal
All additional examinations of papilloma are prescribed by the attending physician, tests are carried out as directed.
Are warts on the head dangerous?
Papilloma located on the head under the hair is subject to frequent mechanical stress when combing, washing the hair and cutting.
These factors can injure the wart and tear it. Inflammation forms and, under the influence of microbes, suppuration occurs.
This causes inconvenience to patients, develops complexes and fears of injuring the papilloma. Keratotic warts are not prone to degeneration.
Viral papillomas, when damaged regularly, can transform into a malignant tumor, which seriously aggravates the patient’s health condition.
If papillomas begin to grow, the first thing to do is give up.
Symptoms and causes
Warts on the head under the hair are classified into special groups . They can appear either due to infection with the papilloma virus, or under the influence of factors such as age, hormonal changes, or malfunctions of individual body systems.
Symptoms of warts on the head:
- formation that visually resembles cauliflower (the size of the growth may vary);
- round or oval growths on the scalp;
- flat formations of a pink or brownish hue.
- increased sweating of the head (sweat accelerates the process of virus penetration and its further development);
- abundant accumulations of bacteria (occurs due to poor head hygiene and infrequent hair washing);
- increased secretion of sebaceous glands (may be a feature of the body);
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract (this group of diseases significantly weakens the body and lowers immunity);
- infectious diseases (can become a complication of this group of diseases);
- constant stressful situations (an unstable emotional state also negatively affects the immunity of the human body);
- abuse of bad habits and lack of a healthy lifestyle (factors lead to a weakening of the body’s protective functions);
- a long course of treatment with potent drugs (a striking example is antibiotics, some of which literally destroy the immune system).
Warts are among the contagious formations . If growths appear on the head, then the risk of spreading them throughout the body increases.
Warts that appear on the head are divided into separate categories. Simple or ordinary types of growths are among the most common types of formations.
In shape they resemble a large mole or genital papilloma.
The color is most often gray-yellow or brown.
Other types of warts on the head include the following:
- Thread-like growths (the name indicates the shape of the growth, and their color is most often pink or flesh-colored).
- Flat types (raise slightly above the skin and have a brownish color).
- Genital condylomas (clearly rise above the surface of the skin; their color can range from flesh-colored to almost black).
- Chicken.
Depending on the type of origin, growths on the head can be keratotic or viral .
The types described above can appear in women, men and children on:
Let's see what a wart looks like on the head in the hair, photo of the formations:
Treatment of warts in children and adolescents.
The appearance of warts on the scalp during adolescence is often caused by hormonal changes occurring in the body and goes away over time. Therefore, there is no need to rush to remove them.
The same applies to growths that appear in young children. The reason for their appearance is weakening of the immune system. The formation of papillomas is caused by dirt getting into scratches, cuts and irritated skin.
Baby warts have the shape of nodules that resemble seaweed. In addition to the head, they appear on the face and hands. Heavy sweating also provokes the appearance of growths on the scalp in children.
However, children's warts should not be removed either, since they disappear without a trace with age. Strengthening the child’s immunity with the help of immunomodulators and vitamin-mineral complexes will help get rid of them. According to the doctor's recommendations, medicinal ointments can be used.
When and which doctor should I contact?
Dermatologists are specialists who specialize in the treatment of warts . Additionally, to identify the causes of growths on the fingers and head, in most cases it is necessary to undergo a full examination, so a visit to a therapist is considered a mandatory step in the diagnosis and treatment of growths.
Factors for immediately contacting a doctor are::
Then how to determine whether it is a wart or not? Find out more here. You should also know what else is similar to a wart and how it differs from papilloma.
Prevention
The course of the described disease, subject to timely treatment, has a favorable prognosis. Removing fibroids allows you to minimize the risk of tumor transformation into a malignant formation. Since the real reasons for the formation of connective tissue formations are not fully understood, there is no specific prevention. Doctors give general recommendations to their patients. They advise eating right, leading an active lifestyle, giving up bad habits, and preventing the possibility of injury to the scalp. If fibroids are detected, there is no need to delay your visit to the doctor. It is important to make sure that there is no threat to life.
Treatment options
There is a wide range of methods for removing formations on the head and other parts of the body. When carrying out such procedures, it is important to additionally eliminate the causes of formations.
The main factor contributing to their development is considered to be a reduced level of immunity, so it is recommended to improve your health by taking interferon-based medications.
Pharmaceutical preparations – ointments, creams, tablets
The principle of using pharmaceutical drugs for warts is not complicated.
Wart ointment and cream are applied to the surface of the wart in accordance with the instructions, and the procedures are repeated until the growth completely disappears. Products based on salicylic acid (Salipod patch, creams, ointments) are especially effective
Additionally, immunostimulating drugs such as Viferon are taken.
Warts on different parts of the body (not just on the head) can be removed using:
Folk remedies
In folk medicine there are many recipes against warts.
Acetic acid is considered one of the most effective folk remedies against warts. The substance should be dripped one drop daily onto the growth and within a few days or weeks it should die off.
Other traditional medicine for warts on the head:
- daily lubrication with fresh juice of cabbage leaves;
- rubbing the wart daily with regular chalk;
- Lubricate the growth with castor oil twice a day;
- applications (daily) based on a decoction of wormwood.
Works well on warts:
By the way, based on the latter, there are many pharmaceutical products for removing papillomas; Super Clean is considered one of the cheapest and most effective.
Medical treatments when visiting the clinic
In clinics, warts are removed with special devices that interact with electric current, liquid nitrogen or ultraviolet rays. Surgery is considered an emergency measure to get rid of the growth .
Warts on the head can be removed in the following ways:
- Cryotherapy (exposure to liquid nitrogen).
- Laser (the procedure is performed under local anesthesia).
- Radio waves (the wart is removed by electric current).
- Surgical removal (using a scalpel under anesthesia).
If you want to know which is better: removal with nitrogen or laser, then read the article at the link.
A wart on the head, like other types of growths in this category, should not be treated uncontrolled . There are ways to remove warts at home that are almost identical to clinical procedures.
However, before using any product, it is better to consult your doctor in advance . A wart can be not only benign, but also malignant.
Removal
- Laser. A modern effective method for removing skin tumors, performed under local anesthesia. Read more about the method here
- Cryodestruction. This is the removal of growths using liquid nitrogen. The skin around them is not damaged and no scars remain.
- Electrocoagulation. The growth is burned out by high-frequency current, which causes the death of viruses. This is a bloodless method of removing tumors.
- Extensive, fused growths on the scalp are removed surgically.
Instead of traumatic surgical removal, more gentle methods are usually used.
Many people are interested in how to remove a wart on the head. Currently, there are many methods that involve the most gentle procedure possible. Modern techniques have virtually no contraindications, and undesirable consequences occur extremely rarely. The following methods are used:
- Laser wart removal. It is the most popular and effective way. The laser beam instantly excises the growth, cauterizes all capillaries and vessels at the site of its impact. One procedure is enough to completely get rid of the wart. For such manipulations, local anesthesia is used. During the procedure, the patient does not feel pain or discomfort. After this, no scar remains.
- Cryodestruction. Liquid nitrogen is used for this manipulation. The action is based on complete freezing of the growth, which completely kills its cells. After some time, the wart disappears on its own. The disadvantage of this technique is that in most cases one procedure is not enough; a whole course is required. There is also a possibility of injury to surrounding tissues.
- Electrocoagulation. The technique is based on the effect of electric current on the wart. After cauterization, a small stain remains, which subsequently disappears completely. The procedure is completely painless as local anesthesia is used. This technique, when performed correctly, significantly reduces the likelihood of wart re-formation.
- Removal using a scalpel. It is an outdated method and is used extremely rarely. It is only advisable if the growths are localized over a large area. Excision occurs with a small area of healthy skin. The rehabilitation period after such manipulation takes a long period and requires the patient to follow special wound care rules.
It is necessary to choose a method for removing warts from the scalp only after consultation with a specialist. The right method will help you get rid of warts and also avoid possible complications. All manipulations should be carried out only after diagnostic measures and a thorough personal examination.
Growth on the scalp
Growths are visible skin defects that occur in almost every person. The peculiarity of growths is that they can appear on any part of the body in the form of dots or vesicles (this could be a papilloma, wart or nevus), as well as formations and tumors (atheroma, hemangioma). Often the growth appears in the hair on the head. Each formation is characterized by its own symptoms, which make it possible to determine the type of growth, identify the causes of its occurrence and methods of treatment.
Periungual, plantar, filiform warts
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=LQvnHaI4TpU
Periungual warts are classified as flat and juvenile neoplasms. They appear on the periungual bed. There is a version that the cause of the neoplasm may be associated with damage to the skin when visiting a manicure and pedicure specialist. This disease contributes to the destruction of the nail structure.
Plantar warts, unlike corns, are located in those areas of the foot that have minimal contact with the support. Over time they harden. May cause pain when walking.
Growths on the skin (photos and names of which can be found on the Internet), characterized by a thin stalk, are filiform warts. Their color completely matches their skin tone. The shape resembles a small olive. Most often they are located on the face.
The main types of growths on the head and the causes of their occurrence
The growths become noticeable only after they have reached a significant size, so they become a serious cause for concern. Such formations are divided into those that are safe for human health and those that are dangerous.
Types of growths that do not pose a threat to human health
Birth tumor. This term refers to swelling of the soft tissue in the place of the head that first passed through the birth canal. Edema is formed due to prolonged contact of the child’s head and the mother’s pelvic bones, which leads to stagnation of blood and lymph. In addition, rupture of blood vessels often occurs due to a pressure difference in the external and internal environments. A tumor acquired during childbirth is not dangerous and goes away without intervention. Its structure does not have clear boundaries, it is soft and elastic to the touch. Most often, a tumor can form on the back of the head, crown and forehead.
This is interesting: Psoriasis: what the disease is afraid of
Papillomas and warts. The formations are caused by infection with the human papillomavirus. Infection occurs as a result of contact with a person who is a carrier of the virus. Growths signal a weakening of the immune defense and most often appear on the skin as a consequence of stress, infectious diseases and problems in the gastrointestinal tract. Hair papilloma is formed under the influence of several types of viruses (about 100 of them are known). Particularly prolific types of the virus are those that provoke the appearance of common warts on the skin (HPV 2, 4, 26, 27, 29, 57). These growths do not pose any danger to human health, since they are not formations that can transform into cancer cells. The formations are only a cosmetic defect, but due to the fact that papillomas and warts form on the back of the head in the hair, they are easily injured in the process of caring for the head. A child can become infected with HPV from an infected mother in the womb or during movement through the birth canal; self-infection often occurs in weakened children through abrasions, scratches and neglect of personal hygiene rules.
Fibroma. This is a benign tumor. It is formed in the dermis. Most often, the growth is not dangerous to health and is an aesthetic defect. Fibroma appears on the head in the hair, back of the head. Several versions of tumor formation have been put forward:
- diabetes;
- heredity;
- injuries; disruption of the endocrine system.
Skin growths are divided into two types - hard and soft. They differ in their structure and color. Hard fibroma has the same color as the skin, dense and smooth to the touch. Soft fibroma is not common; it looks like a mushroom with a thin stalk. Due to its location on the head, fibroids can be subject to injury.
Atheroma. Atheroma is a benign neoplasm in the form of a ball on the head - a cyst. Most often, atheroma is called an epidermal cyst due to its location in the skin and formation from the layers of the epidermis. Atheroma can increase in size, but is not a tumor, and therefore cannot degenerate into malignant formations. This is due to the fact that the mechanism of formation of tumors and cysts is fundamentally different. An epidermal cyst on the head is a fairly common problem; it is located shallowly and has clear boundaries. Atheroma forms both on the skin and in the subcutaneous fat layer. It is customary to divide epidermal cysts into two types - congenital and acquired. Congenital atheroma is characterized by constancy in size and shape throughout life. An acquired cyst forms on the back of the head as a result of a malfunction of the sebaceous glands on the skin and neglect of personal hygiene rules.
Hemangioma. This is a congenital disease, it is also called a vascular tumor. The cause most often cited is maternal illness during the 1st trimester of pregnancy due to colds. Hemangioma does not degenerate into cancer. Education on the back of the head goes away on its own in only 7% of cases (by 5-10 years). The most common hemangioma is simple, arising from small vessels - capillaries. In appearance, it resembles a red or burgundy mole. Less common is cavernous hemangioma, consisting of cavities filled with blood. Cavernous tumor does not go away on its own.
Ringworm
This is one of the few contagious diseases that affects the scalp. The causative agent is a microscopic fungus. The manifestations are encoded in the very name of the scalp disease - areas with lost hair appear on it, as if it had been cut. The skin in these places is red and inflamed. People of all ages are affected, but most often 3-7 year old children. This is partly because ringworm can be contracted from dogs and cats.
To kill the fungus, simple treatments on the head will not be enough. You will have to take medications prescribed by a dermatologist orally. Infection occurs only through close contact. Children who are being treated for ringworm are allowed to attend school without having to cut their hair completely. It is only important not to use personal hygiene items that are used by an infected person. First of all, these are combs, towels, and bedding.