Other diseases
Why does the head hurt behind the ears if no pathologies are found in the hearing organs? The reasons are as follows:
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical muscles - occurs if nerves are pinched during deformation of the cervical vertebrae, which causes poor circulation and throbbing pain.
- Caries - with improper oral care, the inflammatory processes occurring in the teeth spread to the surrounding tissues, causing pain in the head behind the ear on the right or left. This is especially true for caries of the upper teeth.
- Brain tumor - its growth leads not only to severe headache in the area where the tumor is located, but also provokes pain in the ears.
- Meningitis is an inflammation of the brain caused by bacteria or viruses. Accompanied by severe headaches, high fever, and often convulsions. If symptoms of meningitis appear, urgent hospitalization is required.
- Mumps (another name is “mumps”) is caused by a virus, leads to damage to the parotid salivary glands, possibly involving the submandibular or sublingual glands, which causes painful areas on the head in the ear area. The disease is accompanied by fever, fever and enlarged salivary glands. The disease leads to serious complications, so treatment should not be neglected.
- Sinusitis, rhinitis - these diseases are localized in the upper part of the respiratory tract - in the nose and sinuses. The main symptoms are nasal discharge, loss of smell and pain, sometimes radiating to the ears.
- Lymphadenitis is a disease in which the lymph nodes become inflamed. It is often a consequence of previous infectious diseases. When the parotid lymph nodes are inflamed, headaches often occur above the ears.
- Herpes. Its main characteristic feature is rashes on various parts of the body. When a rash appears on the head, the pain may be concentrated in the ear area.
- Shingles is caused by a virus; when it worsens, itching, rash, throbbing pain inside the ear and loss of hearing are possible.
- Trigeminal neuralgia - leads to headaches affecting the temple, the area above the ear on the left or right, and the lower jaw.
- Migraine is pain in the temporal part of the head and in the ear area. Exacerbation is provoked by stress, regular lack of sleep, and physical overload. For some people, it is caused by changes in weather or climate when moving.
- Inflammation of the temporomandibular joints, which connect the lower jaw to the base of the skull. This disease is often caused by stress, arthritis, trauma, teeth grinding and is accompanied by pain in the jaw and ears.
- A boil in the ear canal leads to pain and unpleasant itching inside the ear. It is necessary to open the boil to remove the pus, which leads to an improvement in the condition. It is better to carry out this manipulation in a hospital.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with the Norms and timing of teething in infants: symptoms and methods of relief
Noise in the ears and dizziness due to osteochondrosis
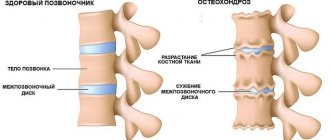
A lack of blood flow in the brain also occurs with external compression of the vertebral arteries. They arise from the subclavian arteries in the transverse processes of the cervical vertebrae, in the bone canal in the occipital region. Each transverse process from the sixth to the second cervical vertebrae has an opening through which the vertebral artery passes. This structure of the cervical spine provides it with protection from adverse influences. But from above, the artery extends over the first vertebra, forming a bend. In this vulnerable place, under certain conditions, it can become bent, which causes vertebrobasilar insufficiency.
The cervical spine changes over time under the influence of osteochondrosis. Various growths appear, the height of the intervertebral discs decreases, the distance between the vertebrae decreases, and it also decreases between the openings of the bone canal. Therefore, the vertebral artery begins to be irritated by bone growths. With each irritation, the artery spasms, that is, it contracts, resulting in decreased blood flow. When repeated frequently, this compression becomes chronic. The artery no longer allows the required amount of blood to pass through. Ringing in the ears and dizziness, blurred vision, nausea, gait becomes unsteady, and fainting is possible.
It is necessary to know the dangerous head positions that provoke vertebrobasilar syndrome with tinnitus and dizziness. This is throwing it back and the favorite sleeping position on the stomach, when the head is turned as far as possible to the side.
Therapy for osteochondrosis includes two main areas. First of all, this is drug treatment with non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, chondroprotectors to restore cartilage tissue, muscle relaxants that relieve muscle spasms, and drugs that improve blood flow, which helps avoid dizziness and loss of consciousness. Physiotherapy (electrophoresis, ultrasound), manual therapy, magnetic therapy, laser therapy and therapeutic exercises are indicated. Exercises are performed in an amplitude that does not cause pain.
Which doctor should I contact?
We look for the root cause of pain at the otolaryngologist
If you experience a headache, you should consult a neurologist. The fact is that pain is the result of the reaction of nerve endings to one or another irritation. You can also go to an otolaryngologist if you suspect that the cause lies in otitis, sinusitis and other pathologies.
If the patient has no idea what caused the pain in the head on the left above the ear, then the best decision would be to visit a therapist. He will prescribe a series of tests and, depending on the results, will be able to issue a referral to a specialist for further examination and treatment.
Among the main diagnostic methods are the following:
- examination by a specialist (ENT specialist, ophthalmologist, neurologist)
- a general blood test, which is needed to determine the overall clinical picture
- urine test to identify pathogens in the body
- examination of the vessels of the head allows us to determine the quality of blood supply to the cerebral cortex
- Computed tomography of the brain makes it possible to determine the presence of tumors, brain abnormalities and other pathologies
- MRI – allows you to determine the condition of the brain, bones, blood vessels and soft tissues
Upon completion of all diagnostic methods, the doctor makes a diagnosis or, if necessary, refers to other specialists - oncologist, psychiatrist, and so on.
Accumulation of sulfur is the cause of pain
The reason why both the head and the ear hurt is the accumulation of earwax. The substance is formed in large quantities due to certain disorders. The hole in the ear canal will be blocked, and the plug will put strong pressure on the nearest nerves.
The patient experiences pain on the left or right, depending on where exactly the problem is. Many people note hearing impairment, the timbre of the voice changes, vomiting and coughing appear.
What to do
If your ear hurts for this reason, you need to rinse the ear canal using a Zhanne syringe. Manipulations should not be performed by patients with diabetes mellitus.
Another method of solving the problem is electric suction. This type of intervention can be carried out by professionals. To solve the problem at home, you can use drops that ensure hearing hygiene. Dead tissue will be able to come out, and the outer ear will be cleansed. The measures will help avoid the development of the inflammatory process.
Neurological causes
Nature created the human brain as a complex system that controls all, even the smallest, processes in the rest of the body. That is why, if you notice pain in your head, deterioration of vision, hearing, persistent dizziness, it is not recommended to delay a diagnostic examination.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with a blood test for teething in infants
The symptom - pain on one side of the head above the ear - can be one of the signs of many neurological pathologies. A highly qualified specialist can carry out an adequate differential diagnosis. Self-diagnosis and self-medication are absolutely prohibited.
A headache above the ear can occur with the following neurological pathologies:
- Pulsating, one-sided pain in the head, accompanied by visual, auditory, and olfactory disorders is a sign of a disease such as migraine. The right side of the head is most often affected. Pathology can strike at any age, but is usually detected in childhood. Patients describe pain as a sudden attack of deterioration in well-being; unpleasant sensations are localized in the eye area, above the ear, in the back of the head, on the right or left. Discomfort increases with sudden movements, tilting the head, and attempts to perform work duties.
- Today, many professions are interconnected with the fact that a person is forced to spend the entire working day in one position, for example, at the computer. The shoulder area of the body suffers first, the muscle fibers are pinched and the vessels that deliver nutrients to the brain are compressed - a tension headache is formed. The discomfort intensifies in the evening, when bending over, awkward turns in the neck. It may be slightly stronger on the right side if the person is right-handed. Accompanied by dizziness, flashing spots before the eyes.
- Trigeminal neuralgia - a person experiences severe pain on the left and right when that branch of the nerve fiber that is responsible for innervation of the face in the area of the ear and jaw on the affected side is damaged.
Therapeutic measures should be prescribed only by a specialist - self-medication is absolutely prohibited, the risk of severe complications is extremely high.
Unilateral/bilateral pain on the right/left
Unilateral pain on the right or left side of the face can signal dental and neuralgic diseases. Discomfort on the right or left often occurs due to a diseased tooth located in these parts. Similar symptoms are observed with pulpitis, periodontitis, caries.
Also, one-sided discomfort can indicate heart disease or the growth of wisdom teeth, inflammation of the ternary nerve. Bilateral pain is typical for bruises, dislocations, and malocclusion.
Otitis
The clinical picture depends on the severity of the process and the depth at which the inflammation is located. In some cases, the patient’s ears burn (usually one), the temperature rises slightly, and the headache becomes the result of intoxication of the body.
An advanced process in the middle or inner ear is accompanied by severe pain, which spreads to the entire half of the skull and shoots into the hearing organ. At the same time, many patients are unable to do their usual activities, sleep, or even eat. This condition is often accompanied by fever and a general deterioration in the patient’s well-being.
We invite you to check out 15 great ways to deal with toothache in seconds.
Pathologies of the hearing organs
Pain in the head behind the ear on the right, left, or above it indicates the following problems with the auditory organ:
- Otitis is an inflammation that can affect both the outer, middle and inner ear. Often occurs after an infectious disease. It can also be an independent pathology: the cause is injuries, improper hygiene of the auricle. The disease occurs with high fever and severe pain; shooting in the ear and bursting sensations are possible. On the 3rd - 4th day, purulent discharge may appear from the ear cavity.
- Mastoiditis is an inflammation of the process of the temporal bone caused by injury or viral infection. The main symptoms are high fever, weakness, poor sleep and appetite, and the appearance of pus in the ear. When you press on the ear, the pain increases and radiates to the head. The disease occurs mainly in children; it is rare in adults.
- A plug is an accumulation of wax that occurs when the ear canals are not properly cared for. It often causes pain and leads to hearing loss. Removing it requires the help of a specialist.
- Labyrinthitis is inflammation in the inner ear. It manifests itself as pain behind the right or left ear. It occurs with nausea, dizziness, and possible vomiting.
- Meniere's disease is non-infectious. It is characterized by an increase in the volume of endolymph in the inner ear. It occurs with dizziness, constant nausea, pain and noise in the problem ear.
- Otomycosis is an inflammation caused by a fungal infection, usually affecting the outer ear. At the initial stage, pain, congestion and itching are felt in the ear. If the disease is advanced, pus appears.
- Cochlear neuritis is a non-infectious disease that damages the auditory nerve. The person feels pain in the head, and hearing loss may occur.
Prevention
To avoid pain in the ears and head, you need to follow very simple recommendations that everyone can follow.
- Rejection of bad habits;
- Adequate sleep and rest;
- Regular moderate physical activity;
- Healthy eating;
- During the cold season, dress appropriately for the weather;
- When bathing, do not allow water to get into your ears - this will protect them from otitis media;
- Compliance with treatment regimens for the underlying disease.
With timely treatment, attacks will be minimized. Therefore, it is important to closely monitor your health and visit specialists on time. An annual comprehensive examination of the body will help you not to miss the onset of the disease.
To prevent pain in the temples and back of the head, accompanied by tinnitus, you must follow a few simple rules:
- Don't get too cold and lead a healthy lifestyle;
- When working at the monitor, take 15-minute breaks every hour;
- Hypertensive patients should always monitor their blood pressure;
- Avoid stressful situations, learn to control yourself;
- Ventilate your premises regularly and spend more time in the fresh air.
By following all these recommendations and excluding serious diseases, you can not only temporarily improve your condition, but also relieve pain in the temporal and occipital region for a long time. In this case, it is very important to pay attention in time and take into account the location and type of pain.
Causes of inflammation of lymphadenitis
Since there are lymph nodes nearby, pain around the ear can be caused by their inflammation. They are aching in nature and intensify when pressed. Localization occurs slightly above the neck. Diagnosis of lymphadenitis can be made by palpating the lymph nodes. The fact is that when you press on the lymph nodes, you can feel a ball, which indicates that they are inflamed, thickened, enlarged and cause pain.
In addition, pain behind the ear can radiate to the jaw. In some cases it causes itching. If the inflammatory process is accompanied by suppuration, the temperature may rise, intoxication and headache may appear, irritation intensifies and becomes pulsating. The manifestation of these types of symptoms indicates the presence of a serious illness and requires treatment under the supervision of a doctor.
Features of ear treatment at home
Folk remedies are an auxiliary therapy for squelching in the ears.
- 1 tbsp. ammonia diluted with 20 ml of boiled water. Then moisten a cotton cloth in the resulting solution and apply it as a compress on the forehead. Keep for 45 minutes. Course - 6 days.
- Take equal parts of crushed currant leaves, leaves and flowers of lilac and black elderberry. The resulting collection in the amount of 2 tbsp. pour 400 g of water, keep in a water bath for 20 minutes, stir constantly. Then let it brew for a while. Strain the finished broth and take 1.5 tbsp. 3 times a day half an hour before meals.
- Fill the onion with caraway seeds and bake in the oven. Squeeze out the juice and instill 3 drops 2 times a day in each ear.
- Dip 2 small pieces of peeled potatoes in honey and place in each ear. Tie a warm scarf on top.
- 4 tbsp. crushed lemon balm, pour 1 liter of boiling water, hold for 1 hour. Then strain and take as tea for 4 weeks.
- Pour 1 part of chopped lemon balm into 3 parts of vodka. Leave for 7 days. Strain the resulting tincture, instill it warmed into each ear, 3 drops. Plug your ears with cotton swabs and tie a woolen scarf around your head.
- 3 tbsp. overnight rice, pour 400 g of water. In the morning, drain the water and add 400 g of fresh water. Cook without adding salt for 3 minutes after boiling, skimming off any foam that forms. You will get porridge, add 3 cloves of garlic to it. It is advisable to eat the porridge hot.
- Mix viburnum with honey. Wrap the resulting mass in gauze or any natural fabric in several layers and place it in each ear overnight.
It must be remembered that any treatment, medicinal or using traditional recipes, should be used only after diagnosis and recommendations of the attending physician. You need to be especially careful with your hearing organs.