Pathologies of the cervical spine
Shooting pains in the head are characterized by a special development mechanism, although they are not independent diseases.
Simply put, this is a severe symptom indicating the presence of some disease in the human nervous system (pathological pulsation of fibers). Shooting pain, in almost all cases, occurs with a clear localization. Pain can manifest itself multiple times and locally. By considering in which area of the head the pathological nerve is located, the doctor can determine the location of the source of pain and its depth.
Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is a fairly common cause of occipital pain. This disease is especially common in people over 50 years of age and is caused by the degenerative destruction of intervertebral cartilage, and sometimes by displacement of the vertebrae themselves. The main causes of the disease: physical inactivity, alcohol abuse, excess weight, hereditary predisposition, some diseases of other internal organs. In the initial stage, the disease manifests itself as heaviness in the occipital area, which is usually incorrectly attributed to overwork.
Cervical spondylosis is a chronic disease of the spine and also often causes. The disease is characterized by the growth of osteophytes on the edges of the vertebrae, caused by degeneration of ligamentous tissues. The most common cause of spondylosis is age-related changes, but the disease can also appear in young people with a sedentary lifestyle. Pain in the occipital area is combined with pain in the ear and shoulder area. The pain increases noticeably when turning the head.
Cervical myositis (myogelosis) is an inflammatory process in the muscles of the cervical spine. The disease occurs from frequent drafts, prolonged exposure to an uncomfortable position, incorrect posture and nervous stress. At first, the painful sensation concerns only the neck, but gradually moves to the back of the head and here responds with sensitive shooting pains. Other symptoms of the disease are difficulty moving the shoulders and dizziness.
Hypertension is a common disease of the cardiovascular system and can cause neck pain. Hypertension is manifested by increased blood pressure and, in addition to such pain, may not manifest itself with other symptoms. Sometimes you feel a little dizzy and weak. The disease progresses significantly against the background of stressful situations and physical overload.
A very dangerous cause of shooting pain can be increased intracranial pressure. Such pain does not stop for a long time, intensifying in the morning and at night. Additional symptoms are nausea and vomiting; As the disease progresses, a pre-fainting state may occur.
Neuralgia of the occipital nerve can develop when signs of osteochondrosis or spondyloarthrosis appear. Pain in the back of the head is especially severe when sneezing. Pain sensations are observed in the neck area, radiating to the eyes, jaws, and ears. In cold and windy weather, the complication progresses noticeably.
Migraine (cervical migraine) is very common and often causes pain. At the same time, pain is felt in the temples, frontal part; blurred vision, tinnitus, and concentration are impaired.
Main reasons
Migraine
The most common causes of shooting pains in the head include the following conditions:
- Neuritis and neuralgia are nerve lesions that manifest as sharp shooting pains. Their occurrence is based on compression of nerve endings and roots, which leads to a sharp deterioration in the patient’s condition.
- Spinal pathologies (osteochondrosis, vertebral hernia) are conditions that are accompanied by compression of the arteries that supply blood and nutrients to the brain tissue. Against the background of this process, ischemia of the organ occurs, which manifests itself as pain in the head.
- Arthritis of the temporomandibular joint is another lesion of the bone structure, which also provokes circulatory disorders in the brain and contributes to the occurrence of pain.
- A concussion is a condition characterized by a shooting headache combined with nausea, vomiting and other signs of damage to the nervous system.
- Migraine is a special type of disorder that is more common in women. This condition is manifested by a sharp one-sided headache that lasts for several hours or even several days.
- Otitis is a common disease manifested by inflammation of the inner and middle ear. One of the symptoms of this pathology is severe pain in the ear canal area, which shoots to the head.
- Dental lesions - pulpitis and other serious diseases that provoke severe pain. In this case, sensations can be localized not only in the area of the changed tooth, but also radiate to the head, which makes diagnosing the disease difficult.
Much less often, shooting headaches occur due to more severe damage to the head and nervous system. Among them are vascular pathologies (stroke and transient ischemic attacks), as well as cysts and neoplasms in brain tissue.
Characteristic
Shooting pain in the head, or cranialgia, occurs suddenly, without any obvious trigger. It is not an idiopathic disease; it manifests itself as a sign of one or another pathology. It is characterized by the following features:
- An unexpected sudden appearance in the form of a painful impulse. The duration of the attack ranges from a couple of seconds to 10 hours. Shooting in the head is constant.
- The pain is very intense and intensifies with eye movement. It is similar to the feeling that a bell is beating in the skull; on the contrary, it can be superficial. It is impossible to touch the painful area. Painkillers don't help.
- The lumbago is localized mainly in the temporo-occipital part, sometimes radiating to the neck. When trigger points are pressed, new attacks occur.
- The pain is accompanied by vomiting. Temperature may rise to 37.5°C and nausea may occur.
- Acute pain in the cervical region, upper back.
- Feeling as if something is shooting in the ears, twitching, loud sounds cause irritation.
- Laughter, coughing, even chewing food or a woman removing makeup leads to the feeling that something is hitting or shooting inside the head.
- Numbness of the limbs. My arms and legs feel tight and ache.
- Rocking gait.
- Changes in personal qualities. A person often becomes nervous, irritable, and tense. Nothing touches him, he pays attention only to his feelings.
- With frequent occurrences, intelligence and memory suffer, sometimes the patient cannot remember the PIN code or phone numbers.
Prevention
The use of certain preventive measures will reduce the intensity, reduce the frequency of painful manifestations, and eliminate the need for constant treatment:
- You need to take a break from any activity for a few minutes to do a light massage or exercise.
- Living spaces and workplaces should be regularly ventilated.
- It is important to follow the principles of proper nutrition, eat vegetables and fruits.
- In cold weather, try to avoid hypothermia, make sure that there is no air in the ears and neck area, and avoid colds.
Shooting pains are not an independent pathology. A thorough diagnosis will allow the doctor to identify what prompted its appearance and determine treatment tactics. With self-treatment, there is a high probability of developing complications. Simple preventive measures will help avoid shooting headaches.
Etiological factors
It usually shoots after applying compression to the spinal nerves. It hurts, as a rule, on one side in the back of the head, moving to the temple and further to the forehead. The main causative manifestation of this type of cranialgia is considered to be diseases of the spine:
- Osteochondrosis of the neck.
- Hernias between the vertebrae.
- Disc protrusion.
- Spondylosis.
Patients feel a feeling of pain at the site of the affected nerve (unilaterally), which is characterized by an acute attack lasting from a couple of seconds to an hour. This condition manifests itself especially often during:
- Trigeminal neuritis.
- Neuralgia of post-traumatic nature.
- Toxic polyneuropathy.
- Neuralgia of the glossopharyngeal nerve processes.
Soreness develops after inflammation or infection of certain nerve fibers, which indicates the presence of pathology of various forms:
- Otitis with purulent complications.
- Sinusitis.
- Sinusitis.
- Inflammation of the orbits, in which a purulent complication is observed with the transition of the process to the nerve processes passing nearby.
- Aneurysms.
- Tumors in the head, which include hematomas, abscesses, cysts, cancer.
- Osteomyelitis of the jaw joint or facial bones.
Diagnosis of cranialgia
To prevent a part of the head from shooting through acute pain, it is necessary to accurately determine the reasons for its occurrence. To do this, you often have to undergo an extensive examination.
After being examined by a therapist and passing the necessary tests, the patient is referred to specialists:
- The ENT doctor will check the hearing organs and examine the nasal cavity to rule out infectious diseases;
- a vertebrologist will check the condition of the spine to exclude cervical osteochondrosis;
- A neurologist performs brain diagnostics to exclude dangerous pathologies and inflammatory processes.
If one of these diseases is detected, a thorough examination of the head and cervical spine is prescribed: MRI, X-ray, ultrasound.
Diagnostics
Shooting cranialgia is a complex illness that requires mandatory treatment of the causes that caused it. You should undergo an examination by a neurologist and other specialists, which will allow you to diagnose the causes and prescribe treatment based on the results of the examination. It is dangerous to treat shooting pains on your own, as this can lead to worsening of the condition and progression of the disease.
The choice of how to treat the disease depends on the cause of the pain and its intensity. Since the most common source of cranialgia is osteochondrosis, you need to be examined to identify degenerative changes in the spine. If there is a shooting in the head due to cervical osteochondrosis, a comprehensive intake of medications that have an analgesic, anti-inflammatory and muscle relaxant effect (NSAIDs, muscle relaxants) will help relieve pain.
In the presence of inflammatory processes, special attention should be paid to the ears. Infections that affect them often cause lumbago in the head.
The appearance of impulsive shooting pains can be associated with various factors, and if they are not detected and the necessary measures are not taken, the patient’s condition can rapidly deteriorate. Therefore, at the first occurrence of such pain, you should consult a therapist. He will clarify the characteristic features of pain, location, additional signs, and conditions of occurrence. Depending on the symptoms, he will give you a referral to visit a specialist in order to determine exactly why the pain occurred.
The otolaryngologist will conduct a thorough examination of the nasal cavity and hearing organs for the presence of sinusitis, sinusitis, and otitis media.
The neurologist will clarify the symptoms and check the reflexes. Prescribes a brain examination to exclude tumors, including malignant ones, cysts, and hematomas.
A verterbrologist examines the cervical spine and, if osteochondrosis, hernia, protrusion or displacement of the vertebrae is suspected, he will prescribe appropriate examinations.
In most cases, the patient additionally undergoes ultrasound diagnostics, radiography, magnetic resonance or computed tomography. In situations where there is a suspicion of vascular pathology, angiography is prescribed.
Shooting pain in the back of the head can have different causes, so before starting treatment, it is necessary to diagnose the disease. The diagnosis is made after examinations such as ultrasound of the vessels of the head and cervical spine, cervical muscles and tissues, and the thyroid gland; X-ray with functional test, neuromyography, MRI of the cervical spine, ECG and other studies aimed at identifying specific diseases.
Treatment
No specialist can prescribe treatment without a preliminary examination. First, you should rule out possible otolaryngological problems and undergo an examination by a neurologist. If there is a shooting in the head due to inflammation of the nerve endings, then the patient will be prescribed thermal, physiotherapeutic or water treatments, massage of pain points, and drug treatment. The last point includes taking non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, vitamins belonging to group B, and blocking pain points with anesthetics.
Location of pain
Often, shooting pain in the head appears on one side, but given the location of the affected nerve, it can begin in any area. Based on intensity and localization, cranialgia is divided into the following types:
- Frontal cranialgia - most often has a right-sided location and appears due to pathology in the processes of the facial or trigeminal nerve. The impetus for the formation of such problems can be a long stay in the cold, which provokes hypothermia of the entire body. Painful impulses appear unexpectedly or after squeezing the area located above the right eyebrow.
- Shooting in the temples - due to the large number of bundles of nerve endings located in this area, lumbago can develop for various reasons. The main pathologies are the temporal arteries, jaw joint or trigeminal nerve. Attacks of pain are typical for both sides, but on the left they are recorded much less frequently. Cranialgia is unexpected, often appears with weak pressure on the location of the nerve or during chewing, however, it is not associated with hypothermia. Sometimes, forceful compression of the pain points leads to relief.
- The parietal zone is the point of passage of a large number of nerve fibers, due to which shooting pains have an uncertain character: an unexpected appearance with immediate subsidence after the onset, or developing into prolonged attacks, with repeated impulses of pain. A typical cause of pain in the crown of the head is considered to be any pathology in the neck.
- The back of the head develops due to pathological changes in the nerves or injuries to the cervical vertebrae. Often appears due to hypothermia or sleeping in an atypical position. The pain becomes unbearable, worsens when moving the head, radiating behind the ear, to the back of the head, to the neck and shoulders.
- Facial pain – occurs in all parts of the face except the forehead due to inflammation of the trigeminal nerve. In some cases, an attack causes numbness in the areas innervated by the affected nerve.
- Internal cranialgia is one of the most severe symptoms, which indicates significant inflammation affecting the eyes and ear nerves.
Shooting pains, regardless of their location, are only a warning signal that there is an inflammatory process in the body, and the patient should take urgent measures to eliminate them.
Treatment effectiveness
Having not noticed a positive result from therapy in the first days, patients become disappointed in both the doctor and the treatment methods prescribed to them. However, many people do not want to think that chronic problems cannot be eliminated in 2-3 days. Their treatment must be comprehensive and long enough. But if you consult a doctor in the very first days of the onset of unpleasant sensations, when the acute stage of the inflammatory process in the nerve endings is still in progress, the effect of therapy will be noticeable almost immediately. In addition, getting rid of the problem with early treatment will be much easier, and treatment will take much less time.
A headache always gives a person some discomfort, especially if the pain is localized and on the right side. Very often, not paying attention to this condition, the patient simply washes down the pain with painkillers and that’s where it all ends, but you should understand that they do not go away without leaving a trace and develop into a chronic stage.
Pain at this stage occurs more and more often, becomes more severe, but what is typical is that it disappears as unexpectedly as it appeared. Attacks can be unexpected, at any time of the day.
Whatever pains and lumbago a patient has in medicine, they are called cranialgia. The occurrence of these painful sensations in the head on the right side can occur for various reasons, in most cases it is a symptom of minor injuries or even hypothermia.
To make a correct diagnosis of the patient, studies are sent. It is also necessary to remember that if pain of this nature begins to bother you very often, you should immediately seek advice from a specialist in order not only to establish the cause, but to begin treatment.
Diagnostic measures
Shooting pains, which occur extremely rarely, are unlikely to force the patient to consult a doctor. In order to determine the exact cause of the deviations and undergo an examination, it is necessary that the unpleasant sensations become permanent and interfere with the normal functioning of a person. After an initial examination and consultation with a specialist, the patient will need to undergo the following procedures:
- Examination by an otolaryngologist and some neurological tests. The doctor should tell you exactly what factors cause the shooting pains, how long they last and when they stop. It is important to remember the exact frequency of attacks. If the etiology is hidden behind the common disease osteochondrosis, then a vertebrologist should be involved in its identification and treatment.
- MRI and CT of the brain.
- Angiography of blood vessels using special contrast agents.
- X-ray of the cervical spine.
The patient must undergo a full range of diagnostic procedures so that the doctor receives maximum information and can accurately determine the cause of the shooting pain.
Use of medications
Pharmaceuticals are used in almost all situations where headaches occur. They are prescribed in the same way as they are taken according to the doctor’s recommendations. In this case, and, in general, under no circumstances should you engage in independent selection of medications if you have health problems.
Such an attitude can only worsen the patient's condition. For example, in case of severe pain, the doctor may prescribe local anesthetics to the patient. For chronic symptoms, Baclofen, Gabapentin or Carbamazepine.
First aid
What can you do on your own in case of an unexpected attack?
- If symptoms appear, anesthetics can be used. Doctors recommend Lidocaine or Novocaine, which block trigger zones.
- Warm compress. Heat will help if cranialgia is caused by neuralgia or cold nerves in the neck.
- Aspirin. In your personal first aid kit there is always this medicine that relieves inflammation.
- Warming ointments. Areas of the head that pulsate are treated with anti-inflammatory ointments.
- If lumbago is caused by otitis media, then vasoconstrictor drops should be introduced into the nasal cavity, which will improve the condition and relieve swelling.
- Inhalations using decoctions of medicinal herbs or aromatic tea tree oil will help.
Cranialgia must be treated in any case. But if the attack began spontaneously, the patient should know how to help himself at home.
- Warm compress - it is best to use dry heat, especially if the cause of the pain is associated with an inflamed nerve in the ear or neck, as well as with various neuritis and neuralgia.
- Anesthetics - drugs are indicated for pain that appears for the first time or shooting pain of moderate severity. Doctors advise using drugs that block trigger points: Novocaine, Lidocaine.
- Aspirin - these tablets are available in every home medicine cabinet for their pronounced anti-inflammatory properties. To relieve intense pain, 1 tablet should be enough.
- Gargling - when the etiology of attacks is related to an infection in the respiratory system, you need to gargle with a decoction of oak bark, sage or calendula.
- Warming ointments - painful areas are treated with certain ointments with the effect of relieving inflammation and the area is wrapped in a warm scarf.
- If your head is shooting due to otitis, you need to instill vasoconstrictor nasal drops, which can relieve swelling and improve your general condition.
- Inhalations with medicinal herbs.
- Acupressure may be effective for mild pain.
Drug treatment
If a patient has an ear infection, the doctor may prescribe:
- Antibiotics.
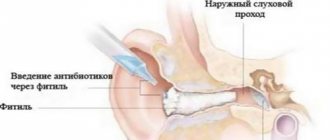
Prescribed for severe inflammation. The use of aminoglycoside antibiotics is prohibited, as they can cause deafness. For diseases of the middle ear, medications in this group are not used. Main drugs: , Spiramycin, Netilmicin, Fugentin, . The dosage is determined by the doctor based on the degree of the disease, age and weight of the patient. - Drops.
They have an antiseptic and anti-inflammatory effect. Before use, you need to warm it up in warm water. Drops are administered using a syringe without a needle or pipette. Recommended drugs: , .
Hydrogen peroxide is often used as rinsing drops. The product helps get rid of earwax and clean the ear canal. Dosage – 10 drops
in each ear
2-3 times a day.
The mechanism of the appearance of shooting pain in the head
Nerve fibers, or simply nerves, are responsible for the appearance of all sensations in the human body, whether they are sensations associated with external conditions (temperature, light, touch, air movement) or internal processes. On the surface of the body and in the thickness of the internal organs, nerve fibers end in nerve endings that contain receptors.
- Sensitive nerve fibers are responsible for the perception of external and internal signals.
- Motor nerve fibers are responsible for the body’s response to received signals (muscle contraction, changes in the functioning of internal organs).
A nerve impulse is a small charge of electric current that travels along a nerve fiber isolated from the rest of the body to its destination (special areas of the brain and spinal cord). This organization of the system allows nerve impulses to move as quickly as possible from the place of formation to the place of “decoding” in the brain. After “deciphering” the impulses in the brain, the body can adequately respond to the changes that have occurred.
Shooting pain in the head appears in cases where, for any reason, changes occur such as:
- there is a violation of the “isolation” of nerve fibers as a result of damage and the impulse does not reach its destination in full, being partially lost along the way (in case of mechanical damage or disruption of the structure of the nerve fiber as a result of a demyelinating disease);
- there is an increased, excessive formation of impulses in pathological foci (in case of injury, inflammation, autoimmune damage);
- The sensitivity of the brain and spinal cord to normal nerve impulses increases.
At the same time, it shoots in the head with the following features:
- the sensation is short-lived, lasts a few seconds, but can be repeated several times in a row;
- the pain is intense, bright; dull and aching pain is absolutely not typical for such situations;
- the sensation has a clear localization. Usually a person indicates a specific place that begins to hurt;
- There are special actions or situations that provoke the appearance of shooting pains in different parts of the head.
When you know the mechanism of the appearance of shooting pain, it becomes clear that most often shootings in the head appear when large nerves that provide innervation to the head and neck are damaged. However, there are no other signs of damage to the nervous system in humans. There is no dizziness or unsteadiness when walking, noise or ringing in the ears, pathological eye movements, trembling in the hands or throughout the body, or difficulty performing movements. In most cases, the following nerves are affected:
- Trigeminal. As shown in photo 3, the innervation zone of this nerve is extensive and covers the chin, lower jaw, lips, nose and cheekbones, cheeks, temples, area around the eye and partly the forehead. Most often, the first branch of the trigeminal nerve is affected, which is responsible for the innervation of the forehead, temple and eye area. At the moment when there is a shooting in the head, salivation and lacrimation also appear, and the skin of the face turns red. An attack is provoked by irritation of trigger zones - areas of the skin closely connected to the nerve ending. In the case of the trigeminal nerve, trigger zones are located on the face and head, rarely behind the ear. An attack of pain occurs when chewing, especially hard food, smiling or having an emotional conversation, shaving, and in women, during cosmetic procedures or applying makeup. The disease develops against the background of an inflammatory process in the nerve ending (for example, with hypothermia) or its damage during a systemic disease (for example, with multiple sclerosis). In older people, trigeminal neuralgia may be a consequence of impaired blood circulation and, accordingly, the nutrition of the nerve fiber. Also, similar symptoms develop after a herpetic lesion in the trigeminal nerve area. In this situation, the pain is intense, but longer lasting.
- Glossopharyngeal nerve. This nerve innervates not only the skin, but also the organs of the oral cavity and pharynx. The pain is localized in the pharynx, tonsils, and spreads to the area behind the ear and head. An attack of glossopharyngeal neuralgia develops during chewing and swallowing, gargling, coughing, talking and is accompanied by increased salivation, interruptions in heart function and increased blood pressure.
In the treatment of neuralgia, the use of painkillers is ineffective. After consultation with a neurologist, anticonvulsants (Finlepsin, Tegretol, Carbamazepine) are prescribed for neuralgia.
With osteochondrosis of the cervical spine, various pathological changes simultaneously occur:
- the bodies and processes of the cervical vertebrae, in which the vessels and nerves pass, are deformed;
- intervertebral discs that provide shock absorption to the vertebrae become deformed and become thinner;
- the ligamentous apparatus changes its properties, which helps ensure the correct relative position of the organs of the neck;
- the work of the muscles that provide both active movements and the normal position of the neck in a calm state is disrupted.
Because of this, osteochondrosis of the cervical spine combines several pathophysiological causes of shooting pain in the head, described below.
- Direct damage to nerve fibers due to injury from bone formations or muscle compression.
- Deterioration of blood supply to nerve fibers due to compression of the arteries passing through the neck.
With cervical osteochondrosis, headache develops when the head remains in an uncomfortable position for a long time; stress, emotionally caused headaches also occur. An attack of pain can be isolated or accompanied by:
- increased blood pressure;
- sharp fluctuations in blood pressure levels;
- nausea, even vomiting;
- feeling of “failure”;
- discomfort in the heart and a feeling of interruptions in the functioning of the heart;
- chills, depressed mood.
What to do to effectively eliminate an attack of shooting headaches with osteochondrosis of the cervical spine is described below.
- Take a comfortable position, ensure maximum rest for the cervical spine.
- Provide free access of oxygen to the room, remove clothing that makes breathing difficult.
- Take a pain reliever from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (Indomethacin, Nimesulide, Meloxicam).
- Outside of an acute attack: undergo a massage course, do therapeutic exercises, undergo a course of physiotherapeutic procedures, and, as prescribed by a doctor, take chondroprotectors (Aflutop, Teraflex, Adgelon).
Shooting pains in the head develop in diseases that are indirectly related to damage to nerve fibers. Such diseases include:
- Ophthalmological pathology:
- with astigmatism, a shooting headache occurs in the forehead or bridge of the nose;
- with myopia and farsightedness there are “lumbago” in the projection of the eyebrows;
- Optic neuritis leads to discomfort deep in the orbit, behind the eyeball.
- Pathology of ENT organs: purulent otitis, mesotympanitis, frontal sinusitis, ethmoiditis. In this situation, the development of the symptom is provoked by the involvement of nerve fibers passing in the immediate vicinity in the inflammatory process. The headache is similar with vasomotor rhinitis, which causes swelling of the soft tissues of the nose and paranasal sinuses and compression of the nerve fibers by the swollen tissues.
- Dental pathology. Deep caries and pulpitis lead to irritation of the sensitive endings of the I and III branches of the trigeminal nerve, the innervation zones of which are described above, and the corresponding appearance of “lumbago” in the head. A more rare cause of deterioration in health is the appearance of galvanism - the occurrence of microcurrents between crowns and implants made of different metals due to potential differences.
For organic brain damage, constant bursting or dull pain is more typical. When individual branches of nerves are involved in the pathological process, short-term lumbago appears in the head.
The most common development of symptoms with organic brain damage is associated with the following:
- Brain tumors, predominantly of vascular origin. In this case, the receptors of the dura mater, which is innervated by the trigeminal and glossopharyngeal nerves, are irritated, and large cerebral vessels are also compressed.
- Aneurysm of cerebral vessels. The aneurysm compresses the nerve fibers passing in the immediate vicinity, further irritating it during pulsation. As the aneurysm grows, it can disrupt the normal course of the nerve fiber, displacing surrounding tissue.
- Traumatic brain injury. In this situation, the nerve endings are damaged directly by injury or subsequently by bone fragments, and are also compressed by displaced organs or swollen tissues.
Headache is familiar to every person. It varies and can radiate to any part of the skull. A fairly common occurrence is shooting pain in the head on the right or left behind the ear. In medical practice, this condition is called cranialgia.
Doctors do not consider this condition as an independent disease, but consider it the first sign of a more serious disease.
Shooting cranialgia appears suddenly and also disappears suddenly. There is a feeling in my head as if something has burst. Pain can occur in any area of the skull.
Associated symptoms
In addition to the shooting headache, the patient may experience other characteristic symptoms, based on the spectrum of which doctors assume the diagnosis of the patient.
Helpful information
Most often, discomfort in the head is accompanied by nausea, dizziness and vomiting. These are nonspecific symptoms that indicate a general disturbance in brain activity. Such manifestations are typical for migraines, neuralgia, and concussions.
Nonspecific manifestations also include numbness of the extremities, indicating pathology of the peripheral nervous system.
The presence of articular disorders in the spine is indicated by severe pain in the neck combined with a crunching sound when turning the head. Sometimes patients may experience impaired mobility in the cervical spine; any movement is impossible due to contracture and arthritis.
In the presence of peripheral inflammation, the patient experiences corresponding symptoms. If the cause of the development of the clinical picture is otitis media, then there will be decreased hearing and severe pain in the ear canal. In the case of pulpitis and other dental diseases, the patient experiences severe toothache; other symptoms include increased sensitivity to thermal influences, bleeding gums, etc.
In more severe brain pathologies (tumors, cysts, injuries), headaches are accompanied by a sharp deterioration in the condition of the nervous system, which can manifest itself as the following symptoms:
- Eye symptoms (nystagmus, strabismus, gaze paralysis);
- Violation of facial expressions, spasm of masticatory muscles;
- Convulsions;
- Paresis and paralysis of the limbs;
- Breathing disorders;
- Decreased coordination of movements, changes in gait, inability to make precise muscle movements.
The listed disorders indicate severe damage to the nervous system. When they appear, it is necessary to urgently hospitalize the patient in order to stop the disease before severe irreversible complications develop.
Why do lumbagoes occur in the head?
There are a number of diseases in which this disease can appear.
A lumbago in the head can occur in any part of it.
- If we are talking about the frontal zone, then pain is felt on the right. Most often this occurs after a person has been in a draft.
- There are a large number of nerve endings in the parietal region, which is why the unpleasant symptom occurs in attacks and with frequent repetitions.
- In the back of the head, lumbago occurs both on the right and on the left. As a rule, if a person slept in an uncomfortable position or when turning his head.
- Shooting in the temporal zone can occur for many reasons, since there is a large accumulation of nerves in this area.
The provocateurs of the disease can be:
- loud noise;
- hypothermia;
- chewing;
- cough;
- too bright light;
- physical overload.
The main symptoms of cranialgia:
- paroxysmal occurrence;
- nausea and vomiting that does not provide relief;
- numbness of the limbs, small parts of the neck and face;
- high blood pressure;
- temporary deafness;
- the nature of the pain is sharp, possibly intensifying.
Most often this occurs due to compression of the nerve trunk, inflammation of the nerve process, or some kind of mechanical damage to the nerve.
Usually simple painkillers in such cases do not have the expected effect. And it is not clear when to take them, because carnialgia lasts a matter of seconds and it is not known when a new attack will occur. The only correct solution would be a full examination with an obligatory consultation with an ENT specialist and a neurologist.
Procedures
If a patient complains of shooting in the head, then doctors advise using heat. In a hospital inpatient setting, they can apply paraffin to the problem area, make compresses with dimexide, and apply semi-alcohol lotions. In addition, physiotherapeutic procedures are often prescribed: electrophoresis, laser therapy, UHF, iontophoresis, magnetic influence, galvanic current. The greatest effect from them is observed in cases where one or another nerve has been blown through in a draft. In some situations, with superficial neuralgia, it is recommended to do a light massage of the pain points.
Cleaning the ear canal
| A drug | Photo | Price |
| Otipax | From 254 rub. | |
| Otinum | From 209 rub. | |
| Hydrogen peroxide | From 7 rub. |
If lumbago is felt on the left side, drop it into the left ear. If on the right, the procedure is performed on the right side. The use of these drugs will soften the cerumen plug if the lumbago is associated with its formation. It is carefully removed with a cotton swab. And the procedure itself is carried out for several days until the ear canal is completely cleansed.