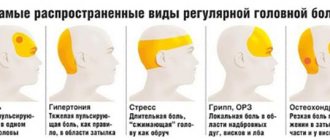
Causes of pain in the forehead
The following diseases can cause headaches in the forehead:
Sinusitis is an inflammatory disease in the nasal cavity that occurs due to infections or problems with the nerves of the upper and back teeth. Signs of sinusitis are regular discharge, runny nose, nasal congestion and pain in the forehead and bridge of the nose.
Frontal sinusitis is a form of sinusitis - an infectious lesion of the frontal sections of the nasal sinus by viruses, bacteria or fungi. The disease is characterized by acute pain in the forehead and nasal congestion with discharge.
Pharyngitis is an infectious disease of the pharyngeal mucosa, occurring in acute or chronic form. Symptoms of pharyngitis are sore throat, cough and redness of the throat. Sudden inhalation of cold or polluted air is the cause of pharyngitis.
High blood pressure is a consequence of stress, weather changes, mental overstrain, and lack of sleep. A headache with blood pressure can cover the entire head from the forehead and temples to the back of the head and is of a pressing nature.
Migraine is a predominantly hereditary disease, common in women, which causes sharp throbbing pain in one of the areas of the forehead or temples. Characterized by pressure on the eyes, loss of energy and regular headaches.
Headache in the forehead can be caused by infectious diseases :
- Meningitis;
- Flu;
- Angina;
- Chickenpox;
- ARVI;
- and etc.
Pain also occurs during hormonal imbalance - the menstrual cycle in women or during adolescence in children.
Folk remedies for headaches in the forehead
Traditional medicine helps relieve pain in the frontal area: lotions, compresses, teas, inhalations. For frequent attacks, they are combined with drug therapy. Popular recipes:
- Mix 15 ml of vinegar and 200 ml of water. Make a compress on the forehead and back of the head, change it when the fabric dries. Carry out the procedure until the pain disappears.
- Mash the cabbage leaf well in your hands until the juice releases, then apply to your forehead.
- Squeeze the juice out of the garlic. Lubricate the temples and bridge of the nose with it in case of sharp, severe pain.
- Massage of the frontal and temporal areas using lavender and grapefruit oil.
- Pour 5 g of chamomile into 220 ml of boiling water, simmer over low heat for 5 minutes, let steep for 30 minutes. Strain the broth and drink 70 ml after meals.
Pain in the forehead and eyes
Simultaneous pain in the eyes and forehead indicates an overload of the sensory organs - the eyes and nervous system. The pain appears after work, severe mental, physical or emotional stress, as well as due to sitting at the computer for a long time.
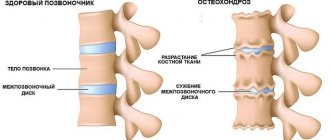
Headache in the eyes also occurs due to cervical osteochondrosis, mainly in people leading a sedentary lifestyle. The cervical vertebrae compress the blood vessels, preventing the delivery of oxygen to the brain, which leads to pressing pain in the eyes and forehead.
You will learn more about eye pain in the following video.
Pain in the forehead and temples
Pain in the forehead and temples is an unpleasant and oppressive pain that can spread to the occipital region. In healthy people, such pain occurs due to excessive stress on the nervous system. But there are other reasons
- Intoxication of the body;
- Infections;
- Poor nutrition;
- Head injuries;
- Disorders in the nervous system - disruption of the functioning of internal organs.
Headaches in the forehead and temples may occur due to a hereditary predisposition to migraines and poor blood flow. Stagnation in the blood flow and disruption of the integrity of blood vessels provoke the development of hypertension.
What is in the frontal part of the head?
The frontal bone is immovably connected to numerous bones of the skull. Its periosteum is strong, growing at the sutures and areas of muscle attachment. The area of this part of the head has a rectangular shape: The frontal bone belongs to the group of integumentary bones of the skull.
In the anterior region of the outer ear there are lymph nodes through which lymph flows from the frontal part of the head. The sinuses are located behind the brow ridges. They are filled with air and separated by partitions. The subcutaneous layer contains processes of the facial, frontal, and supraorbital nerves. The supraorbital vein and supratrochlear blood vessels are located in the frontal part.
The skin on the forehead is thick and devoid of hair. Some hair and numerous sebaceous glands are characteristic of the superolateral part. The forehead skin moves in different directions. Subcutaneous adipose tissue contains numerous sweat glands and dense cords.
Why is inflammation of the structures in the forehead dangerous?
The occurrence of dangerous pathological conditions is a consequence of inflammatory processes that occur in the frontal region:
- frontal sinuses - accumulation of pus and mucus;
- blood vessels of the brain - the development of thrombosis, then strokes;
- brain – inflammation of the cerebral cortex, edema, plethora;
- meninges – production of excess cerebrospinal fluid, edema, increased intracranial pressure.
What do we have to do
- Analgin;
- Baralgin;
- Pentalgin;
- Tempalgin.
- Moment;
- Nurofen;
- Ibuprom;
- Has
Due to the strong stimulation of the nervous system and stress on the liver, the tablets should be taken no more than 2 times in a row.
Drugs that can only be taken after a doctor’s prescription:
Drug treatment negatively affects the functioning of the kidneys and liver due to the long-term cleansing of industrial chemicals.
Home treatment. If pain in the forehead and eyes is caused by osteochondrosis or poor circulation, then self-massage of the cervical spine can help.
For more information about massage for headaches, see the following video.
You can also warm up the cervical spine at home, which helps relieve pain and discomfort.
For cervical chondrosis, you can use warming ointments:
- Virapin;
- Ketonal;
- Nurofen;
- Atrevin;
- Viprosal.
A cold compress can relieve sharp and throbbing pain - moisten gauze or a towel with cold water and apply it to the forehead without pressure for 10 minutes.
The cause of migraines can be an insufficient amount of vitamin magnesium, so headaches can be weakened by a diet of foods containing magnesium:
- Nuts;
- Beans;
- Broccoli;
- Spinach;
- Soy milk.
A hot shower, a calm environment, relaxation, proper rest and bed rest can relieve or ease pain.
What to do if your eyes and head hurt
If your head and eyes hurt systematically and your unwellness lasts a long time and is accompanied by other symptoms (fever, nausea, vomiting), you should consult a therapist and ophthalmologist. Specialists will help you choose the right treatment. First of all, therapy for this condition is aimed at eliminating the cause of the symptoms. For inflammatory pathologies, the prescription of antibiotics, antiviral medications, and decongestants is indicated.
If you have a headache and pressure on your eyes due to migraine, medications from the triptan group are prescribed. High blood pressure or hypertensive crisis is treated with antihypertensive pharmacological drugs and diuretics. For injuries and concussions, neuroprotective agents are indicated. If there are hematomas or hemorrhages due to injuries, surgical intervention may be required.
- Vegetable rice in the oven step by step
- Gift tax
- How to put cans on your back
Drugs
In addition to etiotropic treatment, symptomatic therapy is carried out. Headaches are treated with analgesics, antispasmodics and nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs). In addition, medications are prescribed to improve blood supply and trophism of the brain. Consider the main characteristics of popular medications that are indicated for use for headaches and pressure on the eyes:
| Name of the drug | Active substance | pharmachologic effect | Indications for use | Contraindications | Side effect | Cost in rubles |
| Aspirin |
|
|
|
|
| 50 |
| Indomethacin |
|
|
|
|
| 180 |
| Sedalgin |
|
|
|
|
| 220 |
| Pentalgin |
|
|
|
|
| 270 |
| Paracetamol |
|
|
|
|
| 15 |
| Spasmalgon |
|
|
|
|
| 150 |
| No-shpa |
|
|
|
|
| 80 |
| Tempalgin |
|
|
|
|
| 250 |
| Sumatriptan |
|
|
|
|
| 130 |
| Zomig |
|
|
|
|
| 780 |
| Naramig |
|
|
|
|
| 360 |
| Imigran |
|
|
|
|
| 560 |
How to eliminate pain syndrome at home
If your forehead hurts and puts pressure on your eyes during the day, the following home remedies will help:
- Rub the temple area with Zvezdochka balm and lie down for 15-20 minutes.
- Take a warm bath with sea salt and 2-3 drops of pine or lavender essential oil.
- Take a contrast shower: alternate cool and warm water at intervals of 1 minute.
- Drink a glass of hot black tea with mint, honey and lemon.
Traditional treatment
The use of alternative medicine methods is a good addition to drug treatment. Remember that some folk remedies have contraindications for use or may have a negative effect on the effects of medications, so you should consult your doctor before using decoctions or infusions. The following folk methods will help eliminate pain in the forehead and eyes:
- St. John's wort decoction with mint. Take 2 tbsp. l. dry herb St. John's wort and 2-3 leaves of fresh mint, pour 0.5 liters of water, put on fire, bring to a boil. Then cover with a lid, leave to infuse for 30-40 minutes, strain. Take 1/3 cup 2 times a day for two weeks.
- Infusion of rose hips and hawthorn. Take 20 g of dried rose hips and hawthorn, pour 1 liter of hot boiling water. Leave to infuse for 2-3 hours. Take 0.5 cups 2 times a day after meals.
- Honey with garlic and lemon zest. Finely chop 2-3 small cloves of garlic, mix with the zest of one medium lemon and 50 g of fresh flower honey. Leave the mixture in the refrigerator for a day. Use 1 tsp. in the morning after breakfast.
- Plantain tincture. Collect 7-10 plantain leaves, wash thoroughly and chop. Pour in 50 ml of vodka and leave to steep for 5-7 days. Take 10 drops daily in the morning for a month.
BEST RECIPES FOR HEADACHES
What to remember
- A headache in the forehead is a symptom that signals a disease or independent disorder in the nervous system.
- Pain in the forehead and eyes is caused by excessive strain on vision. The reason for eye strain is fixation of the eyes on one object (TV, monitor).
- Pain in the forehead, temples, and back of the head is hypertension.
- Forehead pain and nausea are concussions.
- Drug treatment is an effective way to relieve pain, but it is not the most beneficial. Proper rest and daily routine are usually sufficient.
See you in the next article!
Share with your friends!
Prevention
Proven measures to prevent headache recurrences:
- regular daily routine with sufficient sleep,
- reduction of stressful situations,
- reduction of mental and physical burden,
- avoiding significant pressure changes (mountain environment),
- to give up smoking,
- restrictions on salt and spices, foods and drinks that cause painful attacks,
- consumption of vegetables, fish oil, foods rich in copper (nuts, seeds, olives, wheat bran),
- movement - running, swimming, cycling (do not exercise during acute attacks!),
- Do not use perfumes with strong odors.
Proper drinking regime is a good way to prevent headaches. A spicy drink made from 1 tbsp works well. l. fresh chopped ginger, filled with 1 tbsp. boiling water Leave to cool and drink.