General description of the pathology
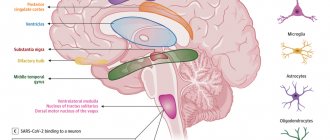
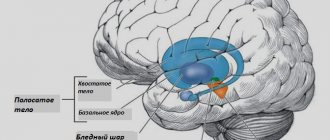
The cerebellum is a special structure of the brain located in the posterior cranial fossa of the occipital and temporal lobes. The organ performs one of the main functions - maintaining balance and coordinating movements. It contains about 50% of the brain's neurons. In order to simply stand up or sit down, you need to use many muscles, the cerebellum is responsible for the coordinated work of them.
Cerebellar ataxia is a syndrome related to neurological disorders. The disease occurs quite often and is almost always associated with various injuries and diseases. Recently, specialists most often diagnose a hereditary form of pathology, and in more rare cases, an acquired form.
Characteristics of the cerebellum
It is important! Evolutionarily, the cerebellum has always been located at the end of the brain. This is largely due to its main function as a coordinator of motor reactions. In humans, the cerebellum is also located in the posterior regions of the brain.
But due to the specific nature of man, this section began to be located under the occipital lobes and only about 1/5 of its part protrudes from under the edges of these lobes. This happened due to the fact that the base of the human brain is directed at an angle to the hemispheres. And the cerebellum has a close connection with it.
The second name for the cerebellum is “little brain.” It occurs due to the presence of essential functions that it possesses. In addition, the cerebellum, like the cerebral hemispheres, has a convoluted cortex and gray matter nuclei. This allows a relatively small (130−160 grams) part of the brain to perform significant functions. Gray matter and nuclei form the basis of functioning and contain the cell bodies of neurons. And, as you know, the main neurophysiological processes occur in nerve cells. The processes are assigned only the role of transmitters.
Due to its structure, the cerebellum plays the role of the main coordinator due to the following:
- Close connections with all parts of the central nervous system.
- Autonomy of work due to the presence of its own gray matter.
The neurophysiology of the cerebellum is briefly as follows:
- The impulse from the musculoskeletal system enters the spinal cord through afferent fibers, where it enters the cerebellar tissue along the nerve tracts and reaches the gray matter.
- Here this information is instantly processed.
- After its processing, a response nerve impulse is formed, which reaches the musculoskeletal system along efferent fibers through the spinal cord.
- The slightest deviation from a certain body position or pattern of movement is recorded by the cerebellum, which causes responses for recovery.
In the example, everything looks less trivial. A person does not need to strain his consciousness in order to maintain balance in a standing position. Or there is no need to think about how the joints of the legs will move when moving. The cerebellum is responsible for all this. That is why humans and higher animals are characterized by the presence of gray matter in this part of the brain.
Reasons for development
The disease is a symptom complex that consists of disorders of dynamic and static human motor skills. The acquired form of pathology develops in the presence of the following factors:
- head injury;
- multiple sclerosis;
- cerebral stroke (ischemic, hypertensive);
- viral or infectious diseases;
- heavy metal intoxication;
- brain tumors;
- obstructive hydrocephalus;
- Guillain–Barre syndrome;
- acute vitamin B12 deficiency.
The listed syndromes lead to the development of cerebellar ataxia with an acute onset. The disease, the symptoms of which begin to appear within a few weeks, has a subacute onset. The main causes of the development of pathology are endocrine disorders, metabolic disorders, malignant tumors, and toxic poisoning.
Progressive chronic ataxia occurs against the background of chronic alcoholism and atrophic processes affecting the cerebellum.
Forms
Focusing on the area of damage to the cerebellum, the following is distinguished:
- Static-locomotor ataxia, which occurs when the cerebellar vermis is damaged. The disorders that develop with this lesion manifest themselves mainly in impaired stability and gait.
- Dynamic ataxia, which is observed with damage to the cerebellar hemispheres. With such lesions, the function of performing voluntary movements of the limbs is impaired.
Depending on the course of the disease, cerebellar ataxia is distinguished:
- Acute, which develops suddenly as a result of infectious diseases (disseminated encephalomyelitis, encephalitis), intoxication resulting from the use of lithium or anticonvulsants, cerebellar stroke, obstructive hydrocephalus.
- I'll sharpen it up. Occurs with tumors located in the cerebellum, with Wernicke encephalopathy (in most cases develops with alcoholism), with Guillain-Barre syndrome, with poisoning with certain substances (mercury, gasoline, cytostatics, organic solvents and synthetic glue), with multiple sclerosis and arising from traumatic brain injury, subdural hematoma. It can also develop with endocrine disorders, vitamin deficiency and in the presence of a malignant tumor process of extracerebral localization.
- Chronically progressive, which develops with primary and secondary cerebellar degenerations. Primary cerebellar degenerations include hereditary ataxias (Pierre-Marie ataxia, Friedreich's ataxia, olivopontocerebellar atrophy, Nefriedreich's spinocerebellar ataxia, etc.), parkinsonism (multiple system atrophy) and idiopathic cerebellar degeneration. Secondary cerebellar degeneration develops with gluten ataxia, paraneoplastic cerebellar degeneration, hypothyroidism, chronic intestinal disease, which is accompanied by impaired absorption of vitamin E, hepatolenticular degeneration, Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease, craniovertebral anomalies, multiple sclerosis and tumors in the area of the cerebellopontine angle and posterior cranial fossa.
Separately, paroxysmal episodic ataxia is distinguished, which is characterized by repeated acute episodes of coordination disorders.
Hereditary type of disease
Cerebellar ataxia of Pierre Marie is a hereditary disease that is dominant in nature. That is, it develops when receiving a defective gene from one of the parents. Skipping generations is extremely rare. It is one of the forms of a hereditary type of disease. Various factors can provoke the appearance of the first signs of pathology: severe infections (diphtheria, salmonellosis, typhoid fever), injuries, pregnancy, intoxication. Appears after age 20.
The symptoms of a hereditary disease constantly increase and progress. There are no periods of exacerbation and remission in such cases. Some diseases can change the course of the pathology, which significantly complicates timely diagnosis.
Hereditary cerebellar ataxia is divided into several forms:
- Friedreich's ataxia;
- non-progressive congenital ataxia;
- Holmes cerebellar atrophy;
- spinocerebellar ataxia;
- late cerebellar atrophy;
- Machado–Joseph disease.
Treatment methods for ataxia
The choice of treatment method is influenced by the diagnosis of the causes.
For congenital anomalies, symptomatic treatment methods are mainly applicable. Since in this case it is almost impossible to eliminate the cause.
Acquired ataxias are more favorable in this regard, since they can often be completely cured. The choice of conservative or surgical treatment depends on the immediate cause.
Rate this article:
(No votes yet)
Loading...
Related posts:
- Possible types of ataxia: causes and manifestations during their development
- gymnastics for ataxia: its benefits and possible exercises
- How does vestibular ataxia develop and progress?
- Ataxia telangiectasia disease: main manifestations, pathogenesis and treatment tactics
- What is sensitive ataxia and why does it affect the human body?
- How does spinocerebellar ataxia manifest?
Symptoms
The pathology has quite specific symptoms that are immediately noticeable. Patients make sweeping movements while walking. At the same time, their gait is shaky and uncertain. The legs are spread wide apart and practically do not bend at the knees when moving. Therefore, during the movement, the patient seems to sway from side to side (cerebellar gait). The symptoms are especially pronounced when the patient tries to stand up suddenly and start moving.
Involuntary stopping of movement even before reaching the goal is another characteristic symptom of the pathology. Patients with cerebellar ataxia are unable to quickly perform contralateral movements. When trying to turn, the patient “goes” to the side and may even fall. Speech with ataxia loses fluency and becomes scanned.
Dynamic cerebellar ataxia in humans is associated with damage to the cerebellar hemispheres. The main signs of the disease include tremors in the limbs at the end of any action, impaired handwriting, involuntary movement of the eyeballs (reminiscent of trembling), and movement disorders during multidirectional movements.
Etiology
The cause of the disease is a mutated gene. It is transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner. It is important that just one copy of the parental gene causes the disease. The diagnosis is made based on the study of the genotype. Spinocerebellar degeneration has about 20 forms.
The exact mechanism of neuron death has not been established. It is known that complexes of protein molecules (ubiquitin, poly-Q protein) are found in the cell. As it turned out, similar aggregates are found in neurons in Alzheimer's disease. All degenerative brain diseases appear to have a common origin.
Fact! According to ICD 10, all SCA are coded G 11.
Causes
Scientists were unable to identify the causative factor. Perhaps the development of ataxia is influenced by:
- Alcohol;
- Decreased thyroid function;
- Brain tumors;
- “Cancers” of other organs;
- Autoimmune problems;
- Inflammation.
Alcohol is highly toxic. Large doses of alcohol destroy cerebellar cells. As neurons die, this area of the brain atrophies. As a result, ataxia occurs. In other words, the patient seems to be constantly drunk.
Addition! It is known that ataxia is a loss of balance control and impaired coordination of movements.
Thyroid hormones influence myelin synthesis. Hypothyroidism is known to interfere with neuronal repair. In addition, they affect the division of cerebellar cells. Typically, tumors press on tissue as they grow. The cerebellum does not receive nutrients and oxygen. Cells begin to die.
Vestibular ataxia
The development of cancer probably also leads to changes in immunity. After the attack, the body's cells begin to destroy their neurons. Obviously, they mistake them for a “foreign” substance. Sometimes the cerebellum becomes inflamed. It is caused by viruses or bacteria. As a result, acute cerebellitis turns into atrophy. It is known to be caused by:
- Chicken pox;
- "Brain" syphilis;
- HIV;
- Rotavirus.
Classification
It is customary to distinguish between congenital and acquired lesions of the cerebellum. Congenital ataxias are classified according to the type of inheritance.
| Ataxia group | Syndrome | Inheritance type |
| Congenital cerebellar ataxias | Norman's disease Sideroblastic anemia with SCA | Autosomal recessive Sex-linked recessive (SR) |
| SCA caused by dynamic mutations | SCA 1,2,3,6,7,8, 12 | Autosomal dominant |
| Chronic progressive ataxias | For example, Friedreich's ataxia | Autosomal recessive |
Ataxic syndrome appears as a result of damage to:
- Posterior columns of the spinal cord (sensitive);
- Cerebellum;
- Bark;
- Brain stem (vestibular).
Symptoms
All types of the disease are characterized by the following symptoms:
This is impaired, unclear speech. Increased work of the oral muscles.
Chanting phrases. Change sound.
The patient cannot determine the distance to an object.
It occurs both at rest and during movement. As a rule, this differs from Parkinson's disease.
The eyes move chaotically. Motor skills do not go away even at rest, when a person is sleeping.
You cannot look clearly at a specific object.
- Postural instability;
The patient cannot maintain the position. Falls often occur.
First view. Spinocerebellar ataxia type 1 is severe. Typically, symptoms include tremor, ataxia, and vision loss. Later, problems with swallowing appear.
It is known that it begins at the age of 30-70 years. The defective ATXN1 gene is located on chromosome 6. The disease is common among the peoples of Yakutia. Siberian scientists propose a method for treating the disease.
At the testing stage.
Second view. SCA type 2 is common in young people. However, late cases of development of the disease are also possible. In addition to ataxia, patients develop abnormal eye movements. They are called saccades. The mutation is located in the ATXN2 gene on chromosome 12. Pathology has no cure.
Third type . The third type appears after 30 years. The disease also occurs in old people. Coordination suffers first of all. In addition, muscle fasciculations are characteristic. This is an involuntary trembling and contraction of the muscles of the tongue and face. In rare cases, the phenomenon of “bulging” eyes occurs. The ATXN3 gene mutation is located on chromosome 14. According to the author, the disease is called Machado-Joseph.
Fifth and sixth views. SCA 6 is transmitted in an autosomal dominant manner. Mutant CACNA 1A gene on chromosome 19. During illness, gait disturbances predominate. The patient loses the ability to walk after a few years. Other signs appear rarely. For SCA 5, a defect in cell enzyme systems appears.
Seventh view. The disease manifests itself as ataxia and loss of vision. It is known that active symptoms appear in adulthood (over 30 years). There is active death of macular cells. The mutated ATXN 7 gene lies on chromosome 3.
Hereditary spinocerebellar ataxias
Hereditary ataxia due to vitamin E deficiency
This is a rare form of hereditary disease. It appears at an early age (from 4-18 years). As a rule, this type of ataxia is detected in North Africa and Mediterranean countries. Symptoms include impairment of facial expressions and speech. Later, changes in the skeleton and heart occur. Friedreich's ataxia occurs in a similar way. The gene defect is located on the long arm of chromosome 8.
Autosomal dominant spinocerebellar ataxias
This group includes 12 forms of the disease (SCA 1,2,3,6,7,8,10,12,17, 31,36 and DRPLA). This type of inheritance gives 50% transmission of the disease from parents to children.
Of course, provided that both have the defective gene. Otherwise, only one of the ancestors is capable of transmitting the disease in 25% of cases.
In addition to ataxia, signs of visual impairment and abnormal eye movements dominate. Saccades and tremor also appear.
Friedreich's disease
The disease appears at an early age. In addition to neurology, other organs are involved in the process. So, the spine is bent. Sometimes the foot becomes deformed. In rare cases, the disease affects the heart muscle. Hormones suffer from Friedreich's pathology. The gonads are often affected. At the end of the disease, the patient becomes diabetic.
Other forms of hereditary spinocerebellar ataxias
There are quite a few types of ataxia (Verelley's disease, Pierre-Marie's ataxia, Foix-Alajouanine syndrome). And the following signs help to distinguish forms:
- Age of debut;
- The nature of the manifestations;
- Course of the disease.
For example, Pierre-Marie's ataxia resembles Friedreich's disease. It was separated into a separate form at the beginning of the last century. The disease begins late. As a rule, the first signs are noticeable at 30-40 years of age. For example, in pathology there are no bone deformities. Signs of dysphagia and dementia dominate.
Marie-Foy-Alajouanine syndrome is extremely rare. It is known that the onset of the disease is later (average age 47 years). As a rule, the cells of the cerebellar vermis and Purkinje fibers die. Characterized by a slow flow. Thus, complete paralysis occurs only after 15-20 years from the onset of symptoms.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of ataxia is based on:
- Clinical examination;
- Genealogy;
- Results of genetic diagnostics;
- Visualization.
Differential diagnosis is difficult. Therefore, the patient’s clinic is assessed by at least three specialists. This is a neurologist, otolaryngologist and ophthalmologist. Large clinics have more specialized professionals. For example, otoneurologists and neuro-ophthalmologists.
The disease is familial. The types of inheritance are varied. It is a sex-linked, recessive and dominant species. Genealogical analysis will help establish the form of inheritance.
A genetic test is the most informative. It will help identify mutated genes. Set the number of CAG repeats in ATXN. As a rule, a scraping is taken from the inner surface of the cheek for analysis. But you can use any bio-material.
Diagnosis of spinocerebellar ataxia
Does the disease occur in children?
Improper coordination of movements in children can be caused by genetic predisposition, birth injuries, hepatitis, infectious pathologies, cerebral palsy, and brain hernias. In pediatric practice, both static and dynamic types of the disease are encountered. Diagnosing ataxia in the first year of a baby’s life is quite problematic, because during this period the development of gait occurs.
If you notice characteristic symptoms, you should definitely show your baby to a specialist and undergo an MRI of the brain. A puncture will also help diagnose the disease, during which the fluid surrounding the brain and spinal cord will be taken. Cerebellar ataxia in children due to another disease responds well to treatment.
Types of ataxia
Cerebellar
Cerebellar ataxia occurs more often as an independent disease transmitted through generations. An unpleasant feature is the late triggering of the disease mechanism: mature, five- to six-year-old animals suddenly begin to show signs. Often such animals have already been allowed for breeding, therefore, ataxia will inevitably manifest itself in future generations. Recent genetic engineering studies have made it possible to isolate the gene responsible for the development of ataxia. Therefore, it has become possible to conduct a specialized DNA test to determine predisposition. Competent, responsible breeders are required to do such tests.
It is important not to miss the symptoms at the beginning of the disease, because seeking help earlier can prevent a rapid deterioration of the condition. First, there is a condition defined by the dog owner as awkwardness. A gradual swaying of the body begins, the animal’s inability to maintain balance. The dog begins to starve because it has difficulty eating and loses weight. Muscle tone weakens and atrophy occurs.
There are two types of this type of ataxia: static and dynamic. The first is characterized by weakening specifically the muscles of the animal’s body. It is difficult for the dog to maintain a certain position. The second most often manifests itself during movements.
Early diagnosis of a dog’s condition will help to overcome tumor and traumatic factors in time. If a genetic cause is established, then all that remains is to maintain the dog’s condition, protect the pet as much as possible, and try to keep it from causing damage. Severe damage to the cerebellum cannot be cured. It is more humane to euthanize the animal.
Sensitive
Sensitive ataxia occurs with lesions of the spinal cord. Then the dog cannot bend and straighten its joints correctly. The ability to determine the correct movement is lost. Severe lesions lead to the inability to move. Occasionally, such a condition can be cured, especially if partial brain damage occurs and the disease is caught at the very beginning.
Vestibular
Vestibular ataxia is manifested by a pronounced tilt of the animal’s body in a certain direction. All movements of the injured animal are careful and slow. Constant dizziness causes vomiting and movement in a circle.
Other types of canine ataxia occur due to exposure to infectious diseases and various injuries. Therefore, it is so important to cure any inflammatory processes in the head area in a timely manner. The close location of the brain to the organs of vision, hearing, and oral cavity contributes to the rapid crawling of pathogenic microorganisms.
Diagnostics
To make an accurate diagnosis, a specialist usually only needs to perform a few simple tests. One of them is an attempt to stand in the Romberg pose. To do this, the patient is asked to stand with his toes and heels together and his arms extended forward with palms facing down and fingers spread. This position is difficult for the patient - severe unsteadiness is observed. In a more complex version, the patient is asked to place one leg forward so that the toe touches the heel.
Babinsky asynergy helps to identify cerebellar ataxia syndrome. In a standing position, the patient is asked to bend back and throw back his head. Normally, to perform this action, a person will need to straighten at the hip joint and slightly bend his knees. With cerebellar ataxia, such an attempt ends in a fall.
Vestibular-cerebellar syndrome: Believed to be vestibular vertigo and imbalance
It is believed that vestibular vertigo and imbalance are the most common symptoms in patients with vertebrobasilar insufficiency. This is confirmed by our research: vestibulo-cerebellar syndrome occurred in 75.38% of cases.
Submitted by N. M. Zhulev et al. (2001), vestibulocerebellar disorders in the form of dizziness and unsteadiness of gait occurred in 84% and 49% of cases, respectively.
With a decrease or cessation of blood flow in the arteries of the vertebral-basilar basin (stenosis, occlusion), the greatest changes develop in the microvessels, neurocytes and neuropil of the cerebellum and the central parts of the balance analyzer [Burak G. G., Samsonova I. V., Kobets G. G., 2000].
Vestibulocerebellar syndrome includes a number of characteristic symptoms: dizziness, instability in the Romberg position, unsteadiness of gait, intention tremor, nystagmus, muscle
in
hypotension [Skoromets A. A., Skoromets T. A., 1993; Novoseltsev S.V., 2004]. Vestibular disorders in vertebrobasilar insufficiency can be peripheral and central in nature [Worlow C.P., Denis M.S., Van Geyn J.
et al., 1998; Zgshty A., Ki$1e1 M., Rapsge! O. e1 a1., 2001]. Almost a quarter of patients with vascular risk factors and isolated severe dizziness, nystagmus and ataxia have cerebellar infarction [Horrson I.K.., Ba1oN K.XV., 1998].
In our study, a subjective feeling of dizziness among 164 examined patients was noted in 87 (53.05%). Systemic dizziness in the form of rotation of surrounding objects was detected in 49 (56.32%), non-systemic dizziness in the form of instability, a feeling of sinking in 31 patients (35.63%). Associated dizziness was noted in 7 patients (8.04%).
Instability in the Romberg position was observed in 72 patients (43.90%), staggering when walking - in 91 (55.49%).
Along with the above symptoms, a decrease in muscle tone in the arms was noted in 79 patients (48.17%); spontaneous nystagmus - in 88 (53.66%); intention tremor - in 17 (10.37%).
An example of vestibulo-cerebellar disorders in vertebrobasilar insufficiency is the following observation.
Patient Ch., 30 years old. Complaints of dizziness in the form of a feeling of “sinking through”, aggravated by sudden turns of the head; instability, unsteadiness of gait, loss of coordination of movements.
Restricted mobility of the cervical spine, pain in the upper cervical spine, and headaches in the occipital region were periodically noted. These complaints appeared 2 years ago.
The drug treatment carried out at that time did not lead to an improvement in the condition. Recently, complaints have become constant.
During a manual (osteopathic) examination: craniosacral rhythm - 6 cycles per minute, right-sided torsion of the sphenobasilar symphysis, extension pattern of the sacrum; functional blockade
Co-C|, C|-C„, Tsg-3,; dysfunction of the right ilium a
anterior rotation; dysfunction of the first rib on inspiration (high position) on the left; dysfunction of the right dome of the diaphragm during inspiration (low position); limited mobility of the pelvic diaphragm, more on the left, limited mobility of the liver and stomach.
On radiographs of the cervical spine: straightening of physiological lordosis, limited flexion in the Co-C segment, instability of the C-Cy segment.
With Doppler ultrasound (Fig.
3, a): in the carotid system, hemodynamics are not impaired, a decrease in the linear velocity of blood flow in the right vertebral artery with an asymmetry coefficient of up to 40%, a compensatory increase in blood flow in the left vertebral artery (pPA = 40 cm/s, lPA = 62 cm/s), increased linear velocity of blood flow in the main artery (OA = 110 cm/s), decreased blood flow in the right posterior cerebral artery, difficulty in venous outflow through the right internal jugular and vertebral veins.
Electroencephalographic examination reveals signs of irritation of brain stem structures.
| '-*/С KGtsCHCHSH— "■- o" -rgo" |
Hggch"1 2 Teach
Rice. 3. Ultrasound Dopplerography of the vertebral and basilar arteries of patient Ch.: a — before treatment (extravasal compression of the right VA, compensatory increase in blood flow in the left VA, spasm of the basilar artery); b — after manual (osteopathic) treatment (normalization of blood flow in the vertebral arteries, decrease in BFV in the basilar artery)
The use of manual (osteopathic) therapy in the treatment of this patient (correction of dysfunctions of the sphenobasilar symphysis, sacrum using craniosacral techniques, myofascial release of blocked cervical SMS, correction of pelvic dysfunction using myoenergetic techniques, improvement of mobility of the pelvic and thoracoabdominal diaphragms using fascial techniques, correction of dysfunction of the first rib, restoration of liver mobility) led to the disappearance of dizziness, improved coordination of movements (gait became more confident), improved neck mobility, and the disappearance of cervicocranialgia. The course of manual (osteopathic) treatment consisted of 5 procedures with an interval of 7 days, after which control Doppler ultrasound was performed (Fig. 3, b).
Source: https://zakon.today/nevrologiya_1068/vestibulo-mozjechkovyiy-sindrom-105640.html
Cerebellar ataxia in humans. How to treat?
In cases where ataxia manifests itself as a secondary disease, treatment should begin with eliminating the underlying disease. Infectious and inflammatory processes require antibacterial and antiviral therapy. If the etiology of the pathology lies in vascular disorders, normalization of blood circulation will be required. For this purpose, drugs from the category of anticoagulants, thrombolytics, vasodilators, and angioprotectors are prescribed.
It will not be possible to completely get rid of the hereditary form of the disease. With this type of disease, the only help will be metabolic therapy - the use of B vitamins, preparations based on ginkgo biloba, nootropics.
A mandatory part of the treatment process is massage and physical therapy. A properly selected set of exercises will normalize the condition of muscle tissue, restore tone, and coordinate movements.
Ataxia in dogs: symptoms
In Greek, the word ataxia means “without order.” This description speaks volumes about the symptoms of the disease. With progressive ataxia, the dog looks “drunk”: falls, stumbles, turns its head, crouches when turning. At the same time, moving in a straight line is quite easy for sick dogs, but the pet is not able to climb the stairs, walk along a winding corridor, or change the trajectory of movement.
Dogs with ataxia may even bump into large objects, are unable to jump, make a turn, are unable to chase a person or other animal, or play with their relatives. Animals with a damaged cerebellum move with small “goose steps”, and at the same time they can walk too wide, placing their paw much further than necessary.
Some owners confuse the manifestations of ataxia with epilepsy, as animals often shudder, suffer from dizziness, their head shakes, their eyelids and chin tremble. Convulsive jerks and movements usually occur in a situation where the animal is concentrated, for example, eating or trying to plot a route.
Video - Ataxia in dogs
Drug therapy
Treatment of cerebellar ataxia requires the mandatory use of the following categories of medications:
- muscle relaxants (help eliminate muscle spasms);
- nootropics (improves brain activity);
- drugs that help cope with vestibular disorders;
- antidepressants;
- B vitamins, vitamin C and PP;
- anticonvulsant medications.
For cerebellar ataxia, drugs such as Betaserc, Betagistin, Tagista, Betaver, Westinorm, Phenibut, Piracetam, Cerebrolysin, Mexidol, Sermion, Cavinton are used ", "Neurobeks", "Milgamma", "Mydocalm", "Pregabalin".
Ataxia
“Ataxia” literally translated from Greek means “disorder.” However, our current understanding of the term is poorly coordinated movements associated primarily with damage to the cerebellum and/or cerebellar connections.
In addition to cerebellar ataxia (which accounts for most cases of ataxia in clinical practice), there are also cases of so-called sensory and vestibular ataxia, caused respectively by damage to the spinal proprioceptive pathways and the vestibular system.
Clinical manifestations of various types of ataxias
Cerebellar ataxia
Clinically, cerebellar ataxia manifests itself as an unstable and unsteady gait with an extended base, as well as incoordination and clumsiness of movements, dysarthria (chanted, jerky speech), dysmetria of saccades and oscillations.
Patients usually stand with their feet wide apart; when they try to put their feet closer together, they begin to sway or even fall; due to unstable balance, support or support is required from surrounding objects.
Even minor manifestations of walking ataxia can be detected during so-called tandem walking in a straight line. Ataxia can be generalized or primarily affect walking, movements of the arms, legs, speech, and eye movements; may be one-sided or involve both parties.
Ataxia is often accompanied by muscle hypotonia, slowness of movement, intention tremor (action tremor that increases in amplitude when approaching a target), impaired control of complex multi-joint movements (asynergy), increased postural reflexes, nystagmus (usually horizontal in cerebellar ataxia), and some cognitive and affective symptoms. changes (the so-called “cerebellar cognitive-affective syndrome”, usually caused by acute, fairly large ischemic damage to the posterior lobe of the cerebellum). It should be emphasized that motor disorders in ataxia are usually not associated with muscle weakness, hyperkinesis, spasticity, etc., however, all of them, as well as other additional symptoms, can complicate the clinical picture of the disease. In turn, severe ataxia can be the main cause of disability and social maladjustment.
Relatively isolated trunk ataxia with impairment of standing and walking is observed with limited lesions of the cerebellar vermis (patients deviate or fall forward with rotal lesions of the vermis and backward with caudal lesions).
Ataxia in the limbs is usually attributed to damage to the cerebellar hemispheres, saccadic dysmetria to dysfunction of the dorsal parts of the vermis.
Unilateral damage to the cerebellum is manifested by disturbances on the side of the same name: such patients stand with a lowered ipsilateral shoulder, stagger and deviate when walking in the direction of damage, coordination tests also reveal ataxia in the involved arm and leg.
Although in humans there is no strict correspondence between specific body parts and cerebellar hemisphere regions, lesions of the anterosuperior hemispheres are thought to result predominantly in ataxia in the legs (a similar pattern seen in alcoholic cerebellar degeneration), while the posterolateral hemispheres are associated with movements in the arms , face and speech. Ataxia may also be associated with damage to the cerebellar pathways; sometimes it manifests with quite characteristic clinical symptoms, such as rough, high-amplitude “rubral” tremor when stretching the arms in front of oneself (typical of damage to the dentato-rubral loop, for example, in multiple sclerosis or Wilson-Konovalov disease).
Sensitive ataxia
Compared with cerebellar sensory ataxia, it is quite rare.
It is usually a consequence of damage to the posterior columns and, accordingly, a violation of proprioceptive afferentation (for example, with Friedreich's disease, deficiency of vitamins E and B12, neurosyphilis).
Sensitive ataxia can be diagnosed by a distinct proprioceptive deficit and a significant increase in symptoms with eye closure. Sometimes in such cases you can notice the phenomenon of “pseudoathetosis” in the affected limb.
Vestibular ataxia
Vestibular dysfunction can cause a syndrome called vestibular (or labyrinthine) ataxia. In fact, this syndrome can be considered a specific subtype of sensitive ataxia.
Patients with vestibular ataxia demonstrate gross impairment of walking and standing (vestibular balance disorder), but without involvement of the limbs or speech. With unilateral lesions of the labyrinth, the “flanking gait” in the direction of damage is significantly impaired.
This type of ataxia is often accompanied by dizziness, vomiting, and hearing loss.
Pathophysiology
Pathophysiologically, cerebellar ataxia is a failure of the normal anti-inertial mechanisms that are responsible for the smoothness, uniformity and precision of movements.
Under physiological conditions, any voluntary movement is the result of precisely coordinated and organized activity of many antagonistic and synergistic muscles.
Coordinated in space and time, the interaction between various muscles is realized through bilateral connections of the cerebellum with various levels of the central nervous system involved in the performance of motor functions (motor areas of the cortex, basal ganglia, brainstem nuclei, reticular formation, spinal cord motor neurons, proprioceptive neurons and pathways ).
Being the main coordinating center of movements, the cerebellum proactively receives information about any changes in muscle tone and the positions of body parts, as well as about any planned actions. Using this anticipatory information, the cerebellum corrects muscle activity, exercises fine motor control, and ensures precise execution of movements.
Medicine "Betaserc"
The French drug Betaserc is used for disorders of the vestibular apparatus and is a synthetic histamine substitute. The active ingredient in the medication is betagestin, a substance that can activate H-1 and H-3 histamine receptors in the central nervous system. The component affects blood flow, improves microcirculation, and stabilizes endolymph pressure.
With regular use of the drug, the frequency of dizziness is significantly reduced, ringing and tinnitus are reduced, and hearing is restored. The duration of the therapeutic effect of the drug ranges from several minutes to 24 hours.
An adult patient can take no more than 48 mg of betagestin per day. The dose of the drug is divided into 3 doses. A more precise dosage is determined by a specialist individually.
It should also be remembered that the drug can cause side effects: nausea, vomiting, dyspepsia, bloating, severe headache, allergic reactions.
Special Recommendations
Loving your pet will help you learn to cope with illness!
A sick animal must be protected from injury. To do this, he is given a separate room, in which there is practically no furniture and no sharp corners. The disease gradually progresses, so the risk of injury increases.
The pet's condition can be satisfactory, even if the disease is hereditary. Therefore, you should not panic ahead of time and try to euthanize the animal. Many pets cope well with the disease. The body simply adapts to the lack of coordination.
Of course, it will be noticeable that the dog walks strangely: it places its legs incorrectly or raises its paws too high and lingers on every step. But this is not a reason to get rid of your pet. Good care, good nutrition and love for your pet can work wonders.
The drug "Tagista"
The Russian analogue of Betaserk is the drug Tagista, which differs from the original only in cost. The price of the substitute is 80-90 rubles per package. While an imported product will cost the buyer 640-690 rubles.
The medication is often prescribed for cerebellar ataxia. Treatment is carried out only under the supervision of a specialist. Tablets are available in dosages of 8, 16 and 24 mg of betahistine.
Indications for the appointment of "Tagist" are such pathological conditions as Meniere's syndrome, vestibular vertigo, vestibular neuritis, hydrocele of the inner ear. It is forbidden to use the product if you have pheochromocytoma or hypersensitivity to the components in the composition. The medication is not prescribed to children under 18 years of age.
Depending on the severity of the condition, Tagista tablets may be prescribed in 1-2 pieces. (at a dosage of 8 mg) three times a day. An improvement in the condition is observed after the first dose of the drug.
Prevention
To prevent the development of a terrible pathology in a pet, it is recommended to follow simple preventive measures:
- Buy a dog from breeders who do not allow individuals with symptoms of ataxia to be bred;
- Treat non-contagious and infectious diseases of the dog in a timely manner;
- Feed your pet a balanced diet with vitamin and mineral supplements.
Ataxia in dogs is not always automatically a death sentence. With superficial lesions, the animal only needs emergency measures, and thinking about euthanasia is too hasty. This is confirmed by the long-term life of a significant percentage of dogs surrounded by the necessary care.
"Phenibut" for cerebellar ataxia
Medicines from the category of nootropics are able to influence the higher functions of the brain and increase its resistance to the influence of negative external factors. They stimulate the brain, improving mental activity and memory.
One of the effective representatives of the group of nootropics is the drug “Phenibut”. In its structure, the drug is a derivative of gamma-aminobutyric acid.
The drug has a corrective effect on impaired cortical functions of the brain, eliminates symptoms of physical and mental asthenia, has antidepressant properties, has a positive effect on memory, and reduces increased emotional excitability.
It is recommended to take the drug for dizziness caused by cerebellar ataxia, skull injuries, and infectious pathologies. Indications for use include pathologies such as memory disorders, anxiety disorders, insomnia, Meniere's syndrome, alcohol dependence, and increased anxiety.
The medicine should be taken in long courses to achieve positive dynamics. The daily dose of medication for adults is 0.75-1.5 g.
Diagnosis and treatment
There are no specific tests or diagnostic methods to detect ataxia. The diagnosis is made after a series of examinations and the exclusion of other, less serious diseases with similar symptoms. The most informative will be a magnetic resonance or computed tomography scan. In the absence of the necessary equipment, they are limited to radiography.
In the case of hereditary ataxia, a DNA test is performed for diagnostic purposes. A complete genetic treatment for a disease of this nature has not been developed. Over time, a sick dog becomes practically incapacitated. The veterinarian prescribes maintenance therapy to alleviate the condition and maintain normal living conditions for the pet. Most often this is symptomatic therapy in the form of sedatives, sedatives and vitamins.
It is important to create the most comfortable living conditions for a sick dog, because it will no longer be able to cope without the participation and care of its owner. It is better to provide your pet with a separate room without traumatic objects, sharp corners and interior items.
If the disease arose for another reason, then treatment of ataxia in dogs is aimed primarily at eliminating it.
The animal body is able to partially compensate for existing disorders. When one part of the brain is damaged, another area of the brain takes over a share of its functions. In addition, dogs are taught to control the strength, speed and range of movements using their visual abilities. In this regard, manifestations of the disorder are noticeable only when the animal is tired or excited.
These body abilities can not only prolong the dog’s life, but also make it close to normal, despite the disorder.
Consequences of the disease and prevention
Treatment of cerebellar ataxia will be successful only if the true cause of the development of the disease is correctly established. The disease can be completely cured only in rare cases. Most often, patients remain with symptoms characteristic of the disease, which periodically worsen. In cases where it was possible to start therapy for the underlying disease in a timely manner, the prognosis will be as positive as possible. The patient’s age, general health, and the form of manifestation of cerebellar ataxia have a significant influence.
There is no specific prevention against the development of ataxia. Experts recommend timely treatment of infectious and viral pathologies, vaccination against serious diseases, and monitoring the functioning of the thyroid gland and cardiovascular system. Before planning a pregnancy, you should definitely consult a geneticist if there are cases of this disease in the family.
Cerebellar degeneration causes, symptoms, treatment and prevention methods
Cerebellar degeneration (cerebellar ataxia) is a disorder of the cerebellum, located in the occipital region of the brain and responsible for the coordination of movements.
The disease develops in the form of necrosis of brain neurons and provokes disruption of many body functions, from mental and speech to human motor abilities.
It occurs as a result of pathological abnormalities in neurology, as well as chronic diseases of the nervous system and brain, tumor formation, intoxication and alcoholism. To cure a pathology or alleviate the patient’s condition, you should contact a neurologist, narcologist, or psychiatrist.
Symptoms of cerebellar degeneration
Cerebellar degeneration manifests itself in the form of various symptoms:
- fast and sudden uncontrolled rotational movements of the eyes;
- various forms of nystagmus (involuntary rotation of the eyeballs) and saccades (rotation of the eyes in one direction);
- disturbances in focusing the gaze on moving objects;
- disorders of coordination of movements when walking;
- muscle atrophy, tremor of the upper and lower extremities;
- exacerbation of neurodegenerative diseases;
- disorders of speech, memory, attention and thinking;
- the appearance of cerebellar ataxia of a dynamic or static-locomotor type;
- violations of fine motor skills of the hands.
Prevention of cerebellar degeneration
- Avoid injury, infection, poisoning, follow safety precautions.
- Go swimming, exercise, and dose your physical activity correctly.
- When planning a pregnancy, make an appointment with a geneticist.
Diagnostic accuracy and quality service are the main priorities of our work. We value every review our patients leave us.
Panina Valentina Viktorovna
Actress, Honored Artist of the RSFSR
I found out about you on the Internet - I urgently need an MRI.
And after the performance I’m with you. I really liked your staff. Thank you for your attention, kindness and accuracy.
May everything be as good in your soul as I am now, despite all the problems...
Be!!! We're happy! Your Panina V.V.
Open review scan
Array( [ID] => 107 [~ID] => 107 [CODE] => [~CODE] => [XML_ID] => 107 [~XML_ID] => 107 [NAME] => Panina Valentina Viktorovna [~NAME ] => Panina Valentina Viktorovna [TAGS] => [~TAGS] => [SORT] => 100 [~SORT] => 100 [PREVIEW_TEXT] =>
I found out about you on the Internet - I urgently need an MRI.
And after the performance I’m with you. I really liked your staff. Thank you for your attention, kindness and accuracy.
May everything be as good in your soul as I am now, despite all the problems...
Be!!! We're happy! Your Panina V.V.
[~PREVIEW_TEXT] =>
I found out about you on the Internet - I urgently need an MRI.
And after the performance I’m with you. I really liked your staff. Thank you for your attention, kindness and accuracy.
May everything be as good in your soul as I am now, despite all the problems...
Be!!! We're happy! Your Panina V.V.
Source: //cmrt.ru/zabolevaniya/golovnogo-mozga/mozzhechkovaya-degeneratsiya/
Virtual tour
Operating mode of the Elitevet central air transport center. At Pobeda we are now open from 8.00 to 21.00. In Pridneprovsk we now work from 9.00 to 20.00. On Topol, reception is available 24 hours a day.
Emergency animals are prioritized during the morning and night hours. Please take this fact into account when planning a routine visit to the doctor during these hours.
I would like to express my deep gratitude to the staff of the Elitvet clinic. Administrators - for their responsiveness, they always give you directions over the phone, they are very friendly. And first of all, doctors, for their caring at any time of the day, competent differential diagnosis and desire to help. My cat Izyum has improved thanks to your recommendations and prompt assistance!
We would like to express our deep gratitude to the medical staff of the clinic for saving our pet and family member, the cat Marky. In particular, for high professionalism, efficiency, warm attitude, sensitivity and attentiveness. The cat was brought in with blood in the stool, thinking it was the gastrointestinal tract, but diagnostics showed purulent inflammation of the uterus. On the same day the cat was successfully operated on. We left her in the hospital for a day for observation. During the period of antibiotic and antimicrobial therapy, our doctors took us for follow-up examinations and provided consultations by telephone. Your work is a shining example of hard work and integrity.
Good day everyone. I want to thank you for saving the life of our beloved pet. Our Chihuahua named Eura was promptly diagnosed and operated on for pyometra. Despite the risks associated with our age (8.5 years), all manipulations were carried out to reduce the risk. The veterinarian approached the treatment of our Eurusya very carefully and professionally. We sincerely thank her for her professionalism and kind heart and would like to wish more such sensitive, responsive and professional doctors in your clinic. Once again THANK YOU SO MUCH.
Has your dog started to lose balance when turning and falling? , but not at all from the cold? Such symptoms are characteristic of ataxia.
Ataxia refers to genetic diseases in animals. For the disease to appear in a puppy, the recessive gene must be present in both parents.
Modern research methods make it possible to identify a hereditary mutation, therefore such dogs are not allowed to breed. But ataxia can occur against the background of other pathologies in the body. Let's try to figure out what factors contribute to the development of the disease, how cerebellar ataxia manifests itself and how to treat it.
Currently, there are methods to detect ataxia in dogs.
Causes of the disease
An animal can get the disease from its parents, but more often the pathology is acquired in the process of life. The appearance of signs of cerebellar ataxia is influenced by the following factors:
- Previously suffered infectious diseases in which the cerebellum was damaged.
- Trauma to the skull with the formation of hematomas.
- Brain tumor.
- Damage to the cranial nerve.
Otitis media can cause the disease.
Symptoms of ataxia
Before making a turn, a dog with ataxia may crouch for balance.
Cerebellar ataxia is the most severe of other forms of the disease, and also difficult to cure. The cerebellum is the part of the brain that is responsible for the ability to move and coordinate in space.
- Damage to the cerebellum caused by injury or disease leads to problems with coordination and the ability to move and balance
. Sometimes the disease causes the dog to lose spatial orientation. She ceases to navigate the area and does not even recognize her native places. - With ataxia, changes in the dog's movement become immediately noticeable
. A “drunk” gait appears. The animal moves quite normally along a straight path, but when trying to turn, problems arise. When turning, the dog crouches, trying to maintain balance. If you turn quickly, you may not calculate the opportunity and fall. - The disease tends to progress
. Coordination problems get worse over time. A sick animal begins to bump into objects. The gait becomes like that of a goose. - With ataxia, the pet suffers from attacks of dizziness
. He may fall, and his eyelids will tremble. Many owners perceive the manifestation of nystagmus as. Even veterinarians sometimes misdiagnose the disease after seeing the animal's convulsive shudders. - The dog trembles when trying to turn sharply or keep attention on a certain object
. Very often this problem occurs during feeding. The pet cannot eat normally, as it begins to tremble and hit its face on the plate. - The animal may panic, try to hide in the far corner and not go anywhere
. Constant malnutrition, dizziness and panic attacks worsen the dog’s condition, and progressive weakness appears. The animal is fading away before our eyes.
What should a dog owner be wary of? All of the above symptoms are difficult to miss; in addition, the pet has a constant tilt of the head, hearing may deteriorate, behavior and gait change. Difficulties arise when climbing stairs.
The pet requires a thorough examination to exclude the presence of other diseases.