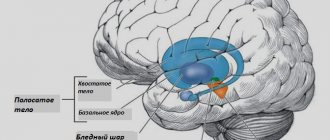
Involutional paranoid is a complex mental disorder that classically would only apply to patients aged 45 to 60 years, but in practice, the age range for diagnosis increases to 65 years. It is distinguished from late schizophrenia and dementia. The first disorder is richer in symptoms and the severity of their manifestation, increasing pathogenesis, increasing separation from reality, and the second is associated with a decrease in mental abilities. Involutional melancholia and psychoorganic syndrome are also excluded. Paranoid, one way or another, indicates that patients have delusions, sometimes complicated by pseudohallucinations, but the condition does not reach schizophrenia. All this made it possible to isolate the disorder into a separate nosological unit. We owe the appearance of the term to S. G. Zhislin, who introduced it into the medical lexicon in 1965. It should be noted that the group of presenile psychoses was described by Kraepelin in 1896.
Involutional paranoid according to ICD 10 has code F22.81 and belongs to the block “Other chronic delusional disorders”.
Involutional paranoid is a complex mental disorder characteristic of people between 45 and 65 years of age.
What does the disorder look like?
Involutionary paranoid is characterized mainly by the presence of delusions, which are associated with reality at the level of “in principle possible.” For example, it is known that the military of different countries, when creating bacteriological weapons, are trying to use insects as spreaders of infections. But world criminology knows only isolated cases where domestic murder attempts were made in this way. Patients boldly and with full confidence in their rightness claim that their neighbors send flies and cockroaches to them, having previously infected them with various exotic infections. It is possible that one of the relatives disposed of the patient’s clothes that had become unusable. The same one sees in this a fact confirming the intention to bring him to the grave, to drive him away from the world. This is how sockets arise, with the help of which the sick are illuminated with the rays of death, sorcerers-villains, and utility workers who have installed their infernal installations in heating pipes, having previously entered into a conspiracy with their enemies.
Worth seeing: Paranoid personality disorder
Delirium has persistent features. Over time, the plot does not change. If neighbors let in the gas, then they may also enter into an agreement with relatives, but no aliens are expected. The technologies for causing damage do not change either - if there is gas, then no death rays; if poisonous powder is added to food, then no evil spirits.
One of the main plots of nonsense is the transformation of health problems that are natural for older people into “proof” of someone’s malicious intent. I feel dizzy because of the gas that the neighbors pump in through the ventilation. My stomach hurts because of the poisons that homemade borscht is insidiously poured into. In particularly mystical individuals, the cause of illness is magical influence. But confirmation is the real presence of some somatic problems that are included in the original packaging.
One of the main plots of nonsense is the transformation of health problems that are natural for older people into “proof” of someone’s malicious intent.
The behavioral response is also not very diverse. This is an accusation against someone - neighbors, relatives, representatives of various and very real structures. It may be limited to oral statements or go as far as writing complaints to various authorities, including courts. Almost never such patients have physical altercations. In the world they are no different from all other people. Even with villain neighbors it’s dry on the landing, but they can say hello.
Sometimes it goes to clinic doctors. Patients often actually suffer from various somatic diseases, sometimes dysfunction of the autonomic nervous system. And of course, radiculitis, gastritis, colitis and other diseases that only occur in the elderly. But patients see in the actions of doctors both criminal negligence and even malicious intent. Well, the knee doesn’t go away. Means what? And the fact that the doctor deliberately does not treat, or specifically prescribes the wrong treatment. Of course, this may be accompanied by a variety of official complaints.
Alcohol paranoid
If a person abuses alcohol for a long time, he may develop alcoholic paranoia. This is the occurrence of a delusional state with mania of persecution, in which symptoms of withdrawal syndrome develop.
With alcoholic paranoia, a person suspects his family and friends of constant persecution. He believes that they want to harm him, so he constantly hides and runs away from them. A person, under the influence of his thoughts, begins to look for confirmation of his ideas in every little thing. Any situation, the presence of sharp objects, the appearance of incomprehensible things may indicate that the sick person is right in his suspicions.
Of all mental disorders, this is one of the mildest
The patients are well adapted for life. Hatred towards one’s own children occurs somewhere in a parallel world and does not interfere with picking up one’s grandchildren from kindergarten. Transmission of rays through sockets does not interfere with their use in everyday life - turning on the iron or TV.
Patients can control themselves. So, in a conversation with a local police officer, after sending a dozen complaints, a person can say that he was misunderstood, that he suspects, but does not claim anything, which, from his point of view, is not excluded, but he cannot get to the bottom of it, because :
- old;
- is ill;
- delegates everything to the competent authorities.
Sometimes involutionary paranoid drives a person to hate his loved ones
Involutionary paranoid does not provide grounds for recognition as incompetent. Practice shows that if such people get a job, they cope with their responsibilities quite well. They are fully aware of who they are, where they are, what is happening, and are able to draw sound conclusions about everything in the world that is not directly related to their delirium. Such patients should not also think about the fact that they will be assigned a disability group. It is given when patients lose the ability to support life. And all the elderly people, whose enemies add poison to their soup, do not forget to eat. Moreover, many of them can live well alone if:
- such is fate;
- there are no relatives nearby.
Worth seeing: How to get rid of paranoia
Presenile psychoses
Presenile psychoses
(synonym: presenile psychosis, involutional psychosis) is a group of mental illnesses that usually arise after 50 years. The reason for the isolation was the fact that at this age depressive and delusional psychoses occur, the clinical picture of which differs significantly from that observed in young and middle age.
Follow-up, genealogical and clinical studies have shown that P. p. can be attributed to late manifested schizophrenia
and
manic-depressive psychosis
;
in some cases they (usually presenile delirium of damage) represent the onset of senile dementia
. Therefore, a significant part of domestic psychiatrists and the majority of foreign ones do not classify P. p. into a separate group.
The main forms of P. p. are presenile melancholy and presenile relapse. Presenile, or involutional, melancholia often begins after mental trauma, a change in the usual life pattern (for example, retirement), or somatic illnesses. The clinical picture is characterized by the appearance of anxiety-agitated depression and various delusional ideas - self-accusation, self-abasement, impoverishment, belief in the presence of a serious illness, often replaced by Cotard's delusions (see Depressive syndromes
). The course of presenile melancholia is protracted, and the clinical picture gradually becomes simpler.
Presenile delusions of damage (involutional paranoid, or involutional pair, develops unnoticeably, manifested by paranoid delusions of damage, robbery, less often poisoning or persecution. Delusions are systematized in a general form: always extends to people in the immediate environment (neighbors, cohabiting relatives, co-workers). Delusional statements of patients contain a large number of specific details of an everyday nature (stained, mixed up papers, spilled soup from a pot, shaking rugs under the door, etc.), and therefore such nonsense is often called delirium of everyday relationships, or delirium of “small scope.” In some cases delusion can exist without any complication for many years, sometimes until death.Patients exhibit severe delusional behavior,
characteristic methods of combating committed “hooligan” actions are developed. So, they put additional locks on the doors, lay out objects in a special way in order to identify persons suspected of theft or trying to break into the room by changing their position, do not leave the stove while cooking or tie the lid to the pan, etc. Often patients experience a slightly elevated background mood. In both cases, they often complain about imaginary offenders to various public authorities, and at home or at work they start squabbles and scandals. Many patients with presenile delusions of damage, incl. lonely, well adapted in everyday life; Some of them, despite the illness, maintain professional performance. Only those patients who develop aggressive behavior towards others or whose delusions are complicated by hallucinatory or affective disorders are placed in psychiatric hospitals. The diagnosis is made based on the clinical picture. Treatment is carried out with psychopharmacological agents over a long period. Many patients with presenile delusions of harm are treated on an outpatient basis. The prognosis for recovery is questionable.
Bibliography
.: Involutional psychoses, ed. G.V. Morozova et al., M., 1979, bibliogr.; Rokhlina M.L. Late endogenous psychoses in the light of clinical and genealogical studies, Zhurn. neuropath and psychiatrist, t. 86, v. 9, p. 1367, 1986, bibliogr.; Guide to Psychiatry, ed. G.V. Morozova, vol. 1, p. 591, M., 1988; Sternberg E.Ya. Gerontological psychiatry, p. 167, M., 1977.
Full-width / Middle / Regular Print Version
Reactive paranoid
Reactive paranoid is divided into:
- Acute reaction to stress. It in turn is divided into:
- The hyperkinetic form, when a person loses focus in actions. He rushes about, runs somewhere, gets lost in space, and is subject to fears and anxiety.
- Hypokinetic form, when a person is inhibited or completely immobilized.
- Hysterical psychoses. They in turn are divided into:
- Pseudo-dementia, when a person’s consciousness narrows, he loses his former skills and answers questions incorrectly.
- Hysterical twilight stupefaction, when a person is lost in space, suffers from amnesia, and incorrectly perceives the surrounding reality.
- Puerilism, when a person becomes a child, infantile.
- A syndrome of delusional fantasies, when a person considers himself to be great, the richest, most significant, etc.
- Personality regression syndrome, when a person completely loses his former skills.
- Hysterical stupor - confusion, psychomotor inhibition.
- Psychogenic mania and depression. A depressive state can be acute (develop quickly and manifest itself clearly) or protracted (symptoms develop very slowly). Psychogenic mania manifests itself in the form of irritability, activity, agitation, and fussiness. However, states of grief and inspiration can also be observed.
- Psychogenic paranoid. It happens in 0.8% of cases. Manifests itself in acute, subacute and severe forms.
Reactive paranoid manifests itself in a certain situation due to its incorrect interpretation. A person forms incorrect conclusions and views. The situation must be psychologically traumatic. When a person subsequently finds himself in such conditions, further incorrect conclusions arise.
You can recognize reactive paranoid by:
- Situational occurrence.
- By cure, if a person is taken out of the situation.
- Connections with a traumatic situation.
A person with reactive paranoid becomes suspicious, internally tense, and anxious. This type of paranoid can be easily reversed either independently at the stage of its inception, or with a specialist during its long-term development.