In psychology there is no unambiguous definition of the concept of frustration. Some experts call this term the state of “failure of hopes,” in other words, a situation when a person experiences negative emotions due to the fact that he could not achieve a goal, his expectations were not met, and his need was not satisfied. Others believe it is a state when internal tensions and experiences do not allow a person to achieve what he wants.
A person in a state of frustration experiences a diverse range of negative emotions: anxiety, anger, apathy, disappointment, and so on.
Frustration is always traumatic for the psyche. It occurs when the desire to get something is great and the obstacles that arise cause severe disappointment or anger. The situation that has developed in this way takes a person out of a state of internal balance and he strives to restore it by any means.
How are frustration and aggression interconnected?
Frustration provokes aggression, directed either at others or at oneself. In the first case, this is expressed in rudeness, pugnacity, or simply embittered behavior. In the second, a person becomes overly self-critical, blames himself for everything, and engages in self-deprecation.
According to Dollard's theory, frustration always causes aggression, no matter in what form, and aggression is always a consequence of frustration. Based on this theory, we can say that when faced with aggressive behavior, we are faced with a frustrating personality. It is worth noting that a person in a state of frustration does not always show verbal aggression. We can conclude that an individual in such a state will not always be aggressive, but an aggressive person always experiences frustration.
How to get out of frustration
- Try to look at yourself from the outside. If you cannot detach yourself, seek help from someone close to you whom you can trust. Let this person appreciate how unsolvable and difficult your goal is to achieve.
- It is important to think about how valuable your goals were. Perhaps they were dictated by fashion, society, or the influence of someone from the outside. It is possible that you personally do not feel the desire to achieve these goals for your satisfaction.
- If you still want to achieve your goal, make a plan for achieving it. It is necessary to decide on resources and think through the steps to complete the stages to achieve the goal.
- Give yourself a date when you plan to achieve certain results. But you need to approach this issue wisely, so as not to fall further into frustration due to the fact that you have shouldered an unbearable burden.
- Remember to be patient. Sometimes it's worth waiting to achieve what you want.
- If you feel emotional fatigue, constant stress, perhaps it’s time to take a break, for example, do what you love or just relax, and then, with renewed vigor, return to your intended goal.
Now you know what is called frustration in psychology. Failure can break any person, engulfing him in a state of despair. Therefore, it is worth knowing how to react to such situations, and carefully thinking through the goals that are planned in the near future.
Causes
There are many difficulties or minor failures in life, but not all of them lead to frustration. The condition occurs when a person has to deal with stress for a long time or when a certain need is not satisfied for a long time or he himself considers the obstacles to the goal insurmountable. In general, the causes of frustration are divided into:
- biological (health or age, or physical disabilities prevent a person from achieving what they want),
- psychological (a person’s own complexes, fears, pressures stand in the way of a person’s goal),
- physical (being in a situation where several basic needs are not met due to being in a confined space),
- material (lack of money or other material means prevents you from getting what you want),
- sociocultural (rules and norms, stereotypes accepted in society do not allow satisfying the need, or a situation of lack of communication).
What it is
In the psychological literature, frustration is considered as a mental state that arises in a situation of perceived or real impossibility of satisfying one’s desire. Literally, the term can be translated as “deception” or “vain expectation.” Frustration is a normal state in psychology that is inherent in all people.
Important! It is not pathological, but can lead to destructive behavior: suicide, bad habits and others.
Several other terms are also distinguished. A frustrator is an obstacle that prevents you from achieving a goal. A frustrating situation is what provokes the development of negative emotions from dissatisfaction.
Some theories
Scientists do not have a consensus on what exactly is frustration. D. Dollard believed that it is expressed in aggression. The further away the desired goal, the angrier the person becomes. If such a situation is repeated repeatedly, then the individual’s tolerance to it decreases, and his aggression becomes more pronounced.
The theory of K. Lewin, R. Barker and I. Dembo is based on the belief that frustration is regression. When a traumatic situation occurs, a person rolls back to the previous age period.
N. Mayer had a different idea. He assumed that when frustrated, a person becomes pathologically fixated on something and does not pay attention to other goals.
Until now, scientists have not been able to say exactly what frustration is. This condition should not be confused with deprivation, in which a person generally lacks a desired object or goal.
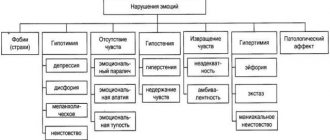
Forms and types
According to Rosenzweig's classification, there are three forms of frustration associated with the manifestation of aggression:
- Extrapunitive,
- Intropunitive,
- Impulsive.
In the first case, a person sees the cause of failure in external factors (circumstances, people). He stubbornly strives for what he wants, no matter what, while experiencing embitterment and irritability. A person’s behavior in such a state becomes patterned and not flexible.
In the case of the intropunitive form of frustration, the opposite is true: the individual blames himself for failure, experiencing anxiety. A person begins to deny himself the satisfaction of personal needs, becomes withdrawn, and limits his activities. These changes in behavior are accompanied by increased anxiety and excessive feelings of guilt.
There is an excellent webinar on the topic of anxiety from Denis Burkhaev.
The impulsive form of frustration is manifested by the fact that a person does not blame anyone or anything for failure; he either simply does not notice it or considers it inevitable.
Personal life
When breaking up, a person may experience negative emotions. He becomes obsessed with recovery, and it seems to him that there will be no life without the return of his partner.
Important! Frustration manifests itself in obsession, aggression, and anxiety.
This condition can be briefly characterized as pathological dependence. Moreover, it often happens when a person strives with all his might to obtain a certain object of passion, but, having achieved this, he is disappointed in the idol.
Symptoms and behaviors
A prolonged stay in a state of frustration leads to a breakdown in communication, a lack of faith in oneself and the success of one’s actions, and motivation disappears. A person finds himself in a vicious circle: strong feelings due to failure or obstacles on the way to a goal become the reason for passive behavior, which further distances a person from what he wants.
A state of frustration leads to a revaluation of values and ideals. At this point, a person may experience:
- disappointment mixed with anxiety
- despair and readiness to take active steps to change the situation, but the state of frustration remains,
- irritability, aggression.
When you remain in this state for a long time, the protective mechanisms of the psyche begin to work, for example, denial, repression.
The behavior of a frustrated person can be different:
- Aggressive. Moreover, aggression can be directed at external objects (people) or at oneself (self-accusation, remorse, excessive guilt);
- Apathetic. Passive inert behavior, general physical lethargy. For example, instead of working, a person looks out the window;
- Psychological escape from difficulties, attempts to ignore them;
- Fixation. An individual in a state of frustration becomes fixated on a goal (need). For example, attempts to achieve the favor of a specific person, get a promotion at work, enter a certain university;
- Additive behavior. Alcohol abuse, drug addiction, overeating or starvation. These are self-destructive attempts to get out of a state of frustration;
- Inconsistent, actions are not coordinated and may contradict each other, a person strives in every possible way to get what he wants.
Prolonged frustration can lead to depression.
Application in psychology
In psychotherapy, a specialist can intentionally cause frustration in a person. This is necessary in order to show him the problem with true needs. This state often leads to the release of negative emotions.
For example, at a reception a client says that his mother annoys him. The psychotherapist suggests playing the role of a mother. Together they act out a conflict situation, and the specialist deliberately provokes the client. As a result, he shows aggression and other bad emotions. With the help of frustration, it is possible to release hidden feelings and begin to achieve real goals.
Such techniques are quite traumatic and should only be used by experienced people.
Frustration is a natural reaction from the psyche. It is important that it does not drag on.
How to diagnose?
To identify the state of frustration in psychotherapy, the Rosenzweig frustration reaction test is used. This is a set of cards depicting different life situations: accusatory or with obstructive circumstances. The patient is asked to give an answer for one of the characters in the picture and continue the dialogue. He selects answers from several options. Based on this choice, the psychotherapist can assess his condition and determine the degree of conflict.
Examples
The state of frustration is provoked by various life phenomena (critical statements from friends, colleagues, categorical refusal to help, etc.). Little things like this can ruin your mood, but often only for a short time. Examples of frustration in real life:
- The worker completed an order assigned to him, for which he was paid little and was not praised for his good performance. A person feels bad because his need for self-affirmation, respect from his boss and finances is ignored or not fully satisfied.
- A girl was invited to a wedding, and she cannot buy the dress she likes in her size in any stores, for some time she is overcome by despair, her plans are ruined, she cannot think clearly, and an obsessive thought about the impossibility of fulfilling her plans is spinning in her head.
- Betrayal by husband/wife. General plans for life, vacation, acquisition of property - all this collapses due to the betrayal of a loved one. Devoted people are tormented by resentment, anger and disappointment, and in the end all these emotions go away and apathy sets in. This condition lasts much longer than the unpleasant sensations from the examples above.
Convinced fatalist - who is this?