FLUVOXAMINE: DOSAGE
Installed individually. At the beginning of treatment, the daily dose is 50-100 mg (recommended to be taken at night). If there is insufficient effectiveness, the daily dose can be increased to 150-200 mg. The maximum daily dose is 300 mg. If the daily dose is more than 100 mg, then it should be divided into 2-3 doses.
According to official WHO recommendations, treatment with antidepressants should be continued for at least 6 months after the depressive episode has resolved.
Instructions for use
For depressive syndrome, the patient is prescribed 50 or 100 mg of the drug for a single dose in the evening.
If necessary, the dose can be gradually increased to 300 mg (150 mg in the morning and evening). Therapy should last at least six months.
For obsessive-compulsive disorder, in the first 3-4 days the patient is prescribed a minimum dose of 50 mg per day. The dosage is gradually increased, but it is unacceptable to take more than 300 mg of Fevarin per day.
If after 3 months of taking the drug no positive results are noted, the patient is selected for another therapy.
The treatment regimen for fevarin depends on the pathology for which it was prescribed.
When treating depression, the initial dosage is 50 mg per day; if the drug is well tolerated, it is increased to 100 mg per day after about 4 days. After this, once a week you can increase the dosage until the desired result is achieved. The maximum recommended dose is 300 mg. To achieve this, the concentration is increased every week by 50 mg per day.
For the treatment of obsessive-compulsive syndrome, an initial daily dosage of 50 mg is also prescribed, and then 100 mg. These numbers are gradually increased until a maximum of 300 mg is reached. The difference is that most patients require a lower dose of fevarin and a shorter duration of use to treat compulsions. As a rule, after 10 weeks of treatment, the drug can be gradually withdrawn, gradually replacing it with psychotherapeutic help.
If the patient takes 50-150 mg of the drug, a single dose is allowed. For example, in the morning during breakfast. If the dose of fevarin is higher, it is better to switch to a two- or three-time dose. For example, take 150 mg of the drug in the morning and evening, or 100 mg in the morning, lunch and evening.
If you abruptly stop taking fevarin, withdrawal syndrome may develop, which you should learn more about.
Drug interactions
When used simultaneously with MAO inhibitors, there is a possibility of developing serotonin syndrome, especially when used simultaneously with irreversible, non-selective MAO inhibitors.
With simultaneous use, the plasma concentration of alprazolam, bromazepam, diazepam increases and their side effects increase due to the fact that fluvoxamine inhibits the metabolic processes of these benzodiazepines.
With simultaneous use, the plasma concentration of amitriptyline, clomipramine, imipramine, maprotiline, trimipramine increases, which is apparently due to the fact that fluvoxamine is a non-competitive inhibitor of the CYP1A2 isoenzyme, with the participation of which the process of N-demethylation of these antidepressants occurs.
When used simultaneously with buspirone, its effectiveness may decrease; with valproic acid - the effects of valproic acid may be enhanced; with warfarin - there may be an increase in the concentration of warfarin in the blood plasma and a risk of bleeding; with galantamine - the likelihood of increased side effects of galantamine increases; with haloperidol - the concentration of lithium in the blood plasma increases.
With simultaneous use, the concentration of carbamazepine in the blood plasma increases, which is due to inhibition of its metabolism in the liver, mainly due to the suppression of the activity of the CYP2D6 isoenzyme under the influence of fluvoxamine.
With simultaneous use, the concentration of clozapine in the blood plasma significantly increases, which in some patients is accompanied by the development of toxic effects of clozapine.
With simultaneous use, caffeine clearance may be reduced and its effects may be enhanced. This interaction is due to the fact that fluvoxamine significantly inhibits the CYP1A2 isoenzyme, which is the main enzyme responsible for the metabolism of caffeine.
When used simultaneously with metoclopramide, a case of the development of extrapyramidal disorders has been described.
When used simultaneously with olanzapine, the concentration of olanzapine in the blood plasma increases; with propranolol - the concentration of propranolol in the blood plasma increases, which is apparently due to the inhibition by fluvoxamine of isoenzymes of the cytochrome P450 system involved in the metabolism of propranolol.
When used simultaneously with theophylline, the concentration of theophylline in the blood plasma increases, which leads to the development of toxic reactions. This interaction is due to the fact that fluvoxamine significantly inhibits the CYP1A2 isoenzyme, which is the main enzyme responsible for the metabolism of theophylline.
With simultaneous use, the clearance of tolbutamide and its metabolites decreases, which is due to inhibition of the CYP2C9 isoenzyme.
There are isolated reports of increased side effects of phenytoin when used simultaneously with fluvoxamine.
With simultaneous use, metabolism slows down and clearance of quinidine decreases.
Analogs
Fevarin is one of the most expensive antidepressants. For long-term treatment of mental disorders, therapy with budget antidepressants looks more attractive.
The best among them include:
- Fluoxetine. The price for 20 tablets (20 mg each) is about 35 rubles.
- Amitriptyline. The cost of 50 tablets (25 mg each) is around 30 rubles.
- Citalopram. A more expensive analogue, 30 tablets of 10 mg each, can be purchased for about 150 rubles.
The presented analogues are used in the treatment of depressive syndrome, panic attacks, obsessive-compulsive disorders, and neuroses. Just like Fevarin, its analogues are serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
Antidepressants are sold from pharmacies only with a doctor's prescription.
The antidepressant Fevarin is a leader among drugs used in psychiatry.
When used correctly, it can cope with a severe form of mental disorder; if the dose is exceeded, it is dangerous due to adverse reactions, overdose and death.
There are a number of drugs whose main active ingredient is fluvoxamine. Such drugs include:
- Avoxin;
- Luvox;
- Faverine;
- Favoxil;
- Fluvoxamine-Sandoz.
All of the drugs listed are produced by different companies, and therefore have different trade names. They differ in excipients, absorption and distribution in the body. It is not recommended to replace one drug with another.
FLUVOXAMINE: SIDE EFFECTS
From the digestive system: often - nausea, sometimes accompanied by vomiting (usually disappears in the first 2 weeks of treatment); possible - constipation, anorexia, dyspepsia, diarrhea, discomfort in the epigastric region, dry mouth, discomfort; rarely - increased activity of liver enzymes, mainly in elderly patients - transient hyponatremia (in some cases caused by the syndrome of inappropriate ADH secretion, disappears after discontinuation of fluvoxamine).
From the side of the central nervous system: possible drowsiness, dizziness, headache, insomnia, anxiety, psychomotor agitation, fear, tremor, discomfort, asthenia; After abrupt withdrawal of fluvoxamine, headache, nausea, dizziness, and a feeling of fear were observed in rare cases.
From the cardiovascular system: a slight decrease in heart rate (by 2-6 beats/min), a feeling of palpitations, tachycardia is possible.
Other: possible increased sweating, changes in body weight.
Some of the side effects listed above may be symptoms of depression and are not caused by fluvoxamine.
Contraindications
Hypersensitivity, liver failure, simultaneous use of astemizole, cisapride, terfenadine, MAO inhibitors (including furazolidone, procarbazine, selegiline), breastfeeding, children under 8 years of age.
Prescribed in the treatment of depression and obsessive-compulsive disorders.
Can be used in the complex treatment of panic attacks, neuroses associated with schizophrenia.
The use of fevarin is justified in the following cases:
- Recurrent depressive disorder, mild or moderate episode of depression;
- Single episode of depression;
- Bipolar affective disorder, current episode of depression;
- Decreased mood in old age or with diseases of various organs and systems;
- Obsessive thoughts and/or movements;
- Somatoform and functional disorders in complex treatment.
Fevarin has a mild anti-anxiety effect, so it can be prescribed in cases where depressive or obsessive-compulsive syndrome is accompanied by anxiety, fear, and agitation.
There are a number of conditions for which fevarin cannot be prescribed, as well as conditions that require careful use. Strict contraindications to the use of this drug include:
- Hypersensitivity to any components of the drug. First of all, we are talking about intolerance to fluvoxamine, since this is the main substance. However, a strong reaction to auxiliary components is also a contraindication.
- Bipolar affective disorder, current episode manic. Relatively speaking, mania is an antidepressant, an absolutely opposite direction of affect. Treating her with any antidepressants is contraindicated.
- Concomitant use with monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Combining different groups of antidepressants is contraindicated, since in this case their side effects overlap and intensify. Fluvoxamine can be used no less than 14 days after discontinuation of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. Conversely, after discontinuation of fluvoxamine, MAOIs can be prescribed only after 2 weeks.
In addition to absolute ones, there are a number of relative contraindications. These include:
- Liver and/or renal failure in the stage of decompensation;
- Anamnesis aggravated by cardiovascular diseases, severe atherosclerosis, myocardial infarction, strokes;
- Epilepsy and convulsive syndrome of other etiologies;
- Thrombocytopenic purpura or another cause of decreased platelets in the general blood test, increased bleeding;
- Pregnancy at any stage;
- Childhood.
Pregnancy and childhood are contraindications due to the fact that studies have not been conducted on the appropriate groups of patients. In this case, fevarin can be prescribed if the expected benefit is greater than the possible harm.
special instructions
With depression, there is usually a high likelihood of attempting suicide, which may persist until sufficient remission is achieved.
Use with caution in patients with a history of seizures. If an epileptic seizure develops, treatment with fluvoxamine should be discontinued.
In patients with hepatic or renal insufficiency, fluvoxamine should be prescribed in low doses at the beginning of treatment under close medical supervision.
If symptoms due to increased liver enzyme activity occur, fluvoxamine should be discontinued.
In elderly patients, the dose of fluvoxamine should always be increased more slowly and with greater caution.
There are reports of the development of ecchymosis and purpura with the use of selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors. Given this, such drugs should be prescribed with caution, especially concomitantly with drugs that affect platelet function (for example, with atypical antipsychotics and phenothiazines, many tricyclic antidepressants, NSAIDs, including acetylsalicylic acid), as well as in patients with a history of bleeding.
During the treatment period, alcohol consumption is not allowed.
Due to the lack of clinical experience, fluvoxamine is not recommended for the treatment of depression in children.
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
In patients whose activities require concentration and high speed of psychomotor reactions, fluvoxamine should be used with caution until the individual response to treatment is finally determined.
Treatment with MAO inhibitors should be discontinued 2 weeks before starting fluvoxamine.
Fluvoxamine may slow down the elimination of drugs metabolized by liver microsomal enzymes.
Pharmacological properties of the drug Fluvoxamine Sandoz
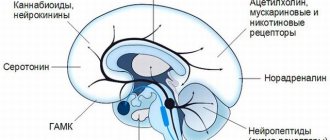
The mechanism of action of fluvoxamine is associated with selective inhibition of serotonin reuptake in brain neurons. The drug has virtually no effect on noradrenergic processes. Has little effect on α-, β-adrenergic, histaminergic, M-cholinergic, dopaminergic and serotonergic receptors. Fluvoxamine is completely absorbed after oral administration. The pharmacokinetics of the drug does not depend on food intake. The maximum concentration in blood plasma is achieved 3–8 hours after administration. Absolute bioavailability averages 53% due to the first-pass effect through the liver. Plasma protein binding is approximately 80%. Volume of distribution: 25 l/kg body weight. Fluvoxamine is extensively metabolized in the liver. The half-life of the drug from blood plasma is 13–15 hours after a single dose and 17–22 hours with a course of use of the drug. Equilibrium concentration in blood plasma is achieved after 10–14 days. The drug is metabolized mainly by oxidative demethylation with the formation of at least 9 metabolites, which are excreted by the kidneys. Two major metabolites exhibit negligible pharmacological activity. Fluvoxamine has linear pharmacokinetics after a single dose. The pharmacokinetics of fluvoxamine are similar in healthy adults, the elderly and patients with renal impairment. The metabolism of fluvoxamine is impaired in patients with liver disease. Steady-state plasma concentrations of fluvoxamine are twice as high in children (ages 6–11 years) than in adolescents (ages 12–17 years). Concentrations of the drug in blood plasma in adolescents are the same as in adults.
Reviews from patients who took the drug
Therapy with Fevarin has real positive results, in particular in patients with severe depression. Treatment takes a long time, and it is often possible to completely get rid of the problem only after 6-7 months.
The disadvantages of the drug include a wide list of adverse reactions that many patients complain about. A particularly striking side effect occurs when the dose is increased.
However, in most patients, the body adapts to the antidepressant within two weeks, after which side effects are rarely bothersome.
I trust Fevarin with the mental health of patients; in my practice, there have been no cases of ineffectiveness of the drug.
Treatment is long and expensive, which many patients complain about. However, in this case, it is necessary to focus on effective help, which is not always possible to achieve with the help of other, cheap antidepressants.
The opinion of psychiatrists is generally positive about Fevarin, but do not forget that in order to achieve a positive treatment result, it must be carried out under the strict guidance of a specialist.
Vladimir, 46 years old, Krasnodar: Work takes a lot of energy and nerves, which is why my sleep was greatly disturbed, I walked around irritated during the day and couldn’t concentrate. The psychiatrist prescribed an appointment with Fevarin, which gave me peace of mind during the day and sound sleep at night. The pills are expensive, but the drug is worth it.
The drug is very heavy. I took it to treat depression, the therapy lasted for several months. As a result, I developed a dependence on the drug and began to feel worse when the dose was reduced.
I decided to stop taking the antidepressant. After that, my depression returned, only in an even more severe form.
It must be remembered that in order to avoid negative reactions of the body when stopping an antidepressant, you should not abruptly interrupt its use! The dosage should be reduced gradually until the drug is completely discontinued.
Antidepressant Fluvoxamine: indications, instructions, reviews
Hello! I wanted to find out if I can take the drug Fluvoxamine, can you advise me? I recently took Fluoxetine to no avail. I’ll tell you in more detail….. I have been tormented by a sleepy state for many years. I really want this condition to go away, it really interferes with my life. I struggled with it for so many years, but no one, not even one doctor, could help me. When I entered the technical school, I wanted to hear all this information. to get so that in the future I could work in this profession, but my condition, the attack did not allow me to listen to lectures, I could not fight, I just took it and switched off for a few minutes, initially it was 5-10 minutes, then more and more, and so on in each class. I got a job, everything got worse, I felt like I was not myself, my body was sitting and my brain was sleeping, I came home and immediately switched off for 1 hour or more. I waited for so many years, I thought it would go away with age, but nothing changes. For many years I have been tormented by a sleepy state, weakness, fatigue, and increased sweating in the armpit area is interfering with my life. It all started around 2010. 15-16 years old. Around 7th grade 8, my vision began to deteriorate sharply and I was sitting in the front desk, and then I realized. that in some subjects I really wanted to sleep and I used to lie down for a couple of minutes, everything got worse and now I enter the technical school after 9th grade in the 1st year, it seems that when I entered in the summer everything was fine and after one competition, maybe from a lot of experience everything became worse. I sat in class and couldn’t control myself, I passed out for 10 minutes, although I really wanted to listen to the lectures, but it was unbearable to cope with it. In the 2nd year, I suddenly developed increased sweating, the girls emphasized this, saying that you were wet in circles, and after that everything went wrong, I stopped communicating with my friends, in general, when I was 18, I sat at home. At the age of 19 I got a job. The work was very responsible, I studied for a long time and wanted to stay there, but my actions tormented me and did not allow me to work calmly and open up to show myself from the side that I would like. Sitting at work, even on the phone next to the computer, I would sometimes turn on music, watch something, but it didn’t help, I feel like an attack suddenly makes me fall asleep, it’s hard to navigate, I get hot, I can’t control my actions, my head goes numb, as if it’s not mine, everything is pinched, it’s difficult to communicate with people perceive information. Even early in the morning I did exercises, nothing helps at work, so I worked for 5 years with joints and every day I lived with the hope that everything would pass, but it got worse. I left this job, they asked me to leave, I liked my job so much, but I couldn’t do it anymore. I came home, ate and immediately filled the house with work, nothing changed. I moved to the city of Kazan, changed jobs, got a job in a construction company, but everything remained there. I also couldn’t sit, I’m starting to say stupid, it’s just that this attack started every half an hour, even earlier during lunch, as soon as I eat I pass out, lunch will not let me go through this state, I’m sitting I’m working, typing, and it’s as if someone suddenly hit me in the head, I just fall, then it lets go, and so on every time. I get on the transport and immediately fall asleep, as if I haven’t been robbed yet, it’s already dangerous. I’m sitting somewhere, for example, at a doctor’s appointment, there’s a long line, I can fall asleep there, and I also sleep every trip if I’m on the bus. I left and was laid off from this job, I don’t know what to do, no one can help me, I can’t even understand that it’s like some kind of curse with me, I live with the hope that this will pass. I contacted a neurologist several times and they made diagnoses. In 2010, he was diagnosed with hypothalamic syndrome and intracranial hypertension. In 2011, after an MRI, I was diagnosed with hypothalamic narcolepsy syndrome. In 2014, the diagnosis was: Autonomic dysfunction syndrome with cranialgia of tension.; Syndrome of autonomic dysfunction with cranialgia of tension.; Astheno-neurotic state. In 2020, VSD with cranialgia.
In 2010, I took an MRI and the conclusion was: the MRI picture of the brain was within normal limits. In 2014, I took tests for T3, T4, TSH; T3 St. result - 2.80, units. change pg/ml, reference values -2.56 -5.01; when taking OK: 2.55-4.46; T4 free result -12.17, unit. pmol/l, comment below, reference values - 12.61-20.97; TSH sensitive (thyroid-stimulating hormone) result -2.3200, unit. µIU/ml; In 2020, I also made an MRI conclusion: MRI data of single residual lesions in the white matter of the cerebral hemispheres; no data were obtained for the volumetric process, hydrocephalus, anomaly of the CVS, also a Rheoencephalographic study (4-channel REG) was taken, conclusions on it: The volume of pulse blood supply is increased in the CB and in the VBB. The elasticity of large-caliber arterial vessels is moderately reduced in the CB and in the VBB. The tone of the arterial vessels is unstable with a tendency to hypotension of the arterial vessels of the caliber in the CB and in the VBB. Venous outflow is significantly hampered in the VBB. On 04/05/2018, an X-ray of the articulation of the occipital bone and the first cervical vertebra (craniovertebral junction) was taken. Protocol: EED 0.08 m3v. Indirect signs of intracranial hypertension. The apex of the odontoid process is located at the level of McGregory's line. Degenerative-dystrophic changes in the Cruvelier joint. The statics of the cervical spine has changed—straightening of physiological lordosis. The anterior upper corners of the bodies C3, C4, C5, C6 are beveled. The height of the vertebral bodies and intervertebral discs is preserved. Conclusion: signs of ICH, initial signs of osteochondrosis. changes in SHOP statics. Also underwent Rheoencephalography Dystonia of the hypertensive type. Venous outflow is obstructed on the right and electroencephalography was performed. Conclusion 6 No focus of pathological slow and epiactive activity is detected in this recording. General cerebral disturbances of bioelectrical activity are moderate in the form of disorganization of the basic rhythm of a regulatory nature. at a low amplitude level with signs of severe dysfunction of the diencephalic midline structures of the brain. Echoencephalography - signs of intracranial hypertension and hydrocephalus: absent. Initially I took Cavinton, nootropil. tincture of ginseng, grandaxin, escitalopram, glycine, elektroukok, valerian, motherwort, piracetam, amitriptyline, this drug generally makes you feel lethargic, take half a tablet, take even more sleep, Mexidol, Noopept. I took piracetam for 10 days in 2020, Cavinton injection B6. Cytoflavin drip, Cyanocobalamin intramuscularly, sodium chloride intravenously, I took a lot of medications, but everything was useless.
I also have such a fear from my increased sweating, I behave very self-consciously even at work when someone comes close, I start to feel uncomfortable, doubt myself, I’m especially embarrassed when men approach me, it bothers me so much, I tried all the deodorants, I tried nothing helped on dry dry There was still hope, I thought it would save, it was also useless. I began to experience excessive sweating in 2012, in my 2nd year, I was about 18-19 years old and I still can’t come to terms with it, I’m very embarrassed, I can’t go out into the crowd, I get lost, embarrassed.
Disinterested opinion
Reviews from people who have taken Fluvoxamine are mixed.
The drug was prescribed for a course of 14 days, but after the first 4 days I began to notice specific problems associated with the genitourinary system. I had to refuse further treatment, despite good results for the underlying disease.
Michael
The action was positive, joy and a desire to do something appeared, but I really wanted to sleep.
Anastasia
The drug is performing well, I just started taking it, literally 2 days have passed. Anxiety disappeared, dark thoughts became less intrusive. So far I'm happy.
Peter
As a doctor, I want to warn you that the drug cannot be used for self-treatment. The attending physician prescribes an exact dosage that is compatible with the existing disease.
Stepan
Chemical properties
serotonin reuptake inhibitors . The antidepressant is synthesized in the form of a white or white with various shades of odorless crystalline powder. The product is highly soluble in chloroform and ethylene , poorly soluble in water, and practically insoluble in ethers . The substance has lipophilic properties. Molecular weight of the compound = 318.3 grams per mole.
The pharmacological activity of the drug is similar to Fluoxetine , however, the effect of taking Fluvoxamine develops faster.
The medicine is usually released in the form of tablets, dosage of 100 or 50 mg.