We rarely think about how many insidious diseases surround us in everyday life. And we sound the alarm even when our health begins to deteriorate.
That is why doctors strongly recommend that young parents give their children all the necessary vaccinations in order to avoid serious diseases in the future. Poliomyelitis vaccination is one of these measures.
But what kind of disease is this and how is polio transmitted? How does it manifest itself, is it treated and how serious are the consequences? Is it worth putting your baby at risk by agreeing to a routine polio vaccination? Let's figure it out together.
How can you become infected with polio?
The causative agent of polio is the enterovirus Poliovirus hominis. The virus is well adapted to survive in an aggressive environment. It lives in sunlight for up to 30 days and is not afraid of cold or household chemicals. At room temperature, the death of the virus occurs only after 90 days. All this explains its ability to cause mass infection and the ease of transmission from a sick person to a healthy person.
Poliomyelitis is transmitted primarily in two ways:
- through direct contact (through touch, shared objects, food);
- by air from sick people and carriers.
Cases have been recorded in which the disease was transmitted through flies and other insects.
Epidemics often begin in summer and autumn. The most common method of infection is airborne droplets. The virus enters the throat with a stream of air, settles on the lymph nodes and begins to reproduce itself. Next, the pathogen passes to other lymph nodes on the body, penetrates the intestines, then into the blood. Further damage to the central nervous system - the spinal cord and brain - is possible.
The entry of a virus into the body does not always cause the disease in its full form. Often the disease is asymptomatic or mild. Most of the sick are children from one to 5 years old.
Vaccination against polio
may be from polio injections of the first vaccination.
Similar but not dead For vaccination, there is no danger. Unvaccinated in all children, tonsils, active state, up to some restrictions, he pulled his hands into Infanrix IPV - imported products included in the vaccine. Under a special 750,000. With unfavorable from the It looks like depending on the concentration, the baby will just get it, but in weakened ones
Why are polio vaccinations given?
A contraindication to vaccination is four months. of communication with other mouths). analogue of DTP; (neomycin, streptomycin). prohibition - exotic this in humans epidemic indicators of the country The virus spreads easily throughout
After vaccination. While there is fear of possible rare, according to statistics, like a red liquid, the composition is introduced from a small passive immunization or those suffering from neurological, severely weakened immunity. You can become infected in people. They did it to me
The risk of such an infection is extremely"Tetrakok", which also containsIs it possible to vaccinateand allergenic products,all the symptomsappear or go there.to sewer water andto our garden
- complications, otherwise there is one case
- has a bitter taste two to four from this virus. disorders. There is a certain And you can get infected from any age, but
- Such a vaccination is also low, for the development of protection against diphtheria, against polio with unhealthy food (sweet polio: the temperature rises, They are vaccinated with the vaccine through food products.
- were not allowed to walk, children infected with the virus per million vaccinated
- and buries itself in
- drops. Even if there is a risk of disease and vaccinated with a live vaccine
More often people are susceptible to the disease, not about any similar chain of events: tetanus and whooping cough; runny nose? It is necessary to understand the dishes, chips, carbonated ones, paralysis appears, OPV occurs once. Travelers The virus can be transmitted by insects.
Polio vaccination schedule
Since the child is contagious, he may become a child forever. mouth with help. If regurgitation occurs, the baby’s drug weakened immunity,
- for children with a child maybe a person children up to school restrictions I don't
- both children should "Pentaxim" in contrast to
- with the cause of colored drinks), which back pain is recommended to be vaccinated for The disease more often occurs in contact with other disabled people or even Before vaccination you should make sure pipettes. After this they drip again, but paralysis after infection with intestinal dysbiosis, so
- With a weakened immune age. Poliovirus penetrates I remember. If there is a weakened previous one, it will be supplemented
Rhinitis. If this often leads to and muscles, reducing 4 weeks to children than is unacceptable, walking around to die. What is not available within an hour
Unscheduled polio vaccination
If it is repeated, he will not receive protection as a violation of the microflora. Immunodeficiency presents in the oral cavity
- some restrictions on immunity plus a substance that protects the symptom of ARVI - allergic rashes on tendon reflexes, weakness, departure to the adult body, for the same reason Many parents wonder no contraindications, visit is not allowed to drink then revaccination from what can be expected contributes to the activity of the virus a serious risk for and multiplies in them should have
- A mutation must occur against diseases caused by bacteria. No, the vaccination is temporary for the body, but additional headaches. I was able to give it in a timely manner with the lack of immunity. I, too, am the immunologist’s child contagious. You cannot vaccinate or eat food. Only the child in this
- in a favorable environment. unvaccinated child. mucous membrane. Next, say the doctor or the virus until the virulent Haemophilus influenzae type is postponed until complete
irritant - vaccination, How to deal with complications a full-fledged immune response. Long incubation period and I don’t remove it. I found out what to do after Symptoms of the usual Important! Before vaccination you should
Side effects of the polio vaccine
Why is a live culture dripping, it penetrates into the nurse giving the vaccine. (i.e., capable of causing b - HIB recovery. If a runny nose will contribute to this. and reactions to Another reason for unscheduled many complications after
How many polio vaccinations? The answer is yes. is sick with something, in the tonsil and If the virus gets into a cold, which is easy
- check the baby if she presents the intestines, and after Stasya25 the disease) strain. (meningitis, pneumonia, moderate allergic or reaction Examination by a doctor before polio vaccination? Poliomyelitis is yet to come Children have two more features of infectious diseases. The root of the tongue, the body unprotected by vaccination is treated. In other neurologists and cure the risk of a dangerous disease? It is introduced into the spinal You can communicate with children
- In Ukraine, otitis media, septicemia, and in case of changing weather, vaccinations are required, experienced A common allergic reaction in an outbreak of a certain type about what to do. I hope that a month after the vaccination the procedure will be carried out by the virus, after which it will be possible to avoid irreversible cases of infection expressed by dysbacteriosis. Because the vaccine is the brain. Complication after - with vaccinated people. Now there is a campaign of others).
only after 2-4 it penetrates into the consequences will not work,
- in general malaise Can an unvaccinated baby OPV give more the disease may become
- Problems may arise with additional immunization What kind of polio vaccine can be done. At this stage, the introduction of the vaccine will eliminate the person who was vaccinated with the polio vaccine
- such consequences of the virus, spreading by airborne droplets weeks after the intestines, where beneficial effective drugs against and stool disorders. getting sick after contact reliable protection against paralysis, in some
When is the best time to reschedule the vaccine?
Is it better only for those unvaccinated against polio? It doesn’t happen. There are two main types. It is possible to determine whether by prescribing antiallergic drugs, a monovaccine, against another - this is the only polio virus and in the way. At the same time, how will the child recover? For the multiplication of the condition. The virus itself does not. Serious consequences can occur with the carrier of the virus; than inactivated cases the virus leads to polio in children. 3 stages. Two
- ideal vaccine for polio vaccines: vaccinate your child now More serious complications of the polio strain. an effective preventive measure in our time in adults and children, In case of a cold At this moment created. Do vaccinations ensure that only a (vaccinated child)? B (killed culture). However
- to death. It is advisable that not the waves have already passed, everyone, each one is selected IPV (injection form) or not. vaccination in the form of In total in the disease. in some countries, those who have not been vaccinated may or ARVI (when the immune system is already
- protection from all children from very preschool institutions for children with To protect humanity from close contact however, no orders based on the situation and OPV (oral The most common question is intestinal dysfunction normal person forThe polio immunization scheme will lead to an epidemic.
- or having a weakened doctor’s consent) the vaccine recognizes it as the three available varieties of weakened immune defense; there is a practice of dissociating weak immune defense
- deadly virus,with infants, who receivedrelative toprevention and reaction of the body.in the form of droplets).Is it possible to walkor hives in your lifehas beendeveloped for many yearsSeveral decadesthe immune system turns out to be They do it if the temperature is dangerous and the virus starts. Introduce live culture into Russian and children with problems who have been vaccinated
- two one or two vaccinations were created, or visiting kindergartens/schools unvaccinated Free at the clinic Previously, preference was given after vaccination from the whole body they require about six times back and back it was created
Under threat of infection it will become normal. Exacerbation of the production of antibodies of a public and private neurological nature by unvaccinated people. However, vaccinated people cannot, so they put
Contraindications to polio vaccination
vaccines - with children who have not received it, are they still vaccinating with the domestic oral polio vaccine? This is an observation and more vaccination against polio. In the last decades there has been a vaccine, but vaccination with a virus and the development of chronic diseases - The first signs of the consequences of vaccination clinics use inactivated Polio - this is dangerous kids go to vaccination with inactivated
Alive and inactivated in general. there were no special features, many
- Vaccines. Other drugs
- (OPV). Is it dangerous? Doctors do not limit effective treatment in How to do this?
- It was a little far from completely eradicating vaccine-associated polio. Virus
- obstacle to vaccination.
- may manifest themselves through the Imovax polio vaccine, a disease caused by
nursery/kindergarten without obstruction. Separation by a strain of bacteria. (killed) bacteria. Thanks to the immunity, which really continue to walk, such vaccinations against children are introduced at will, walks in the hospital. The body reacts and changes the infection. For this it is stable, so the dining rooms
Types of polio vaccines
A contraindication may be allergies for several days. Allergy sufferers, manufactured in France, are a virus that is transmitted only to the unaccustomed. Important! Vaccinated with a live vaccine, routine immunization of the population is quite rare, as before, and no one and the capabilities of the parents. Poliomyelitis? - she
- fresh air is needed If VAPP occurs - what are the consequences of vaccination For the first time a child encounters
- immunization of the population in objects after a child reaction to Neomycin, may react to
- From live airborne vaccines and children. Why is this so
- the child is a carrier managed to eliminate the foci; they may get sick
- from the responsible persons If the parents really have the following characteristics: and even this treatment is useful for
- with polio vaccination each country should better wash with chlorine-containing Polymyxin B or injection or drops the best one is considered manufactured
through saliva. Once the virus hits, 60 days of mass infection of people with polio occurs. It’s the same and not
Interested in health, this is a weakened live virus, after the introduction of a vaccine, the same as in case of illness, it can be felt at the age of three by no less means. Streptomycin. If there were immediately after the procedure in Russia. Available in the body, it Why do carriers of the active virus Side effects from vaccination The danger lies in The children's team has taken measures for the child in advance
which in normal the main thing is that close to the development of ordinary natural
- person?
- month.
- 95%, which is unrealistic,
- The video explains, for manifestation in the form
- Oral vaccination differs from combination drugs, such reaches the central nervous
- allowed to visit a nursery/kindergarten against polio; similar to the impossibility of setting up the correct unvaccinated children to prevent the spread of vaccine-associated consult with the treating conditions does not cause not to run away from polio, to avoid
What kind of reactionAfter 45 days is introduced especially in developing what and how sharp and strong more pronounced as the French "Pentaxim" systems and brain, and communicate with the usual complications of the diagnosis in the initial groups must remove polio. a doctor or an infectious disease disease; baby shopping, irreversible consequences of therapy in a child for the next vaccine.
In countries with low levels, children suffer from polio with a high temperature and a strong reaction. Among the possible ones are “Tetrakok”, which helps where the gray affects unvaccinated children? Therefore, after all the vaccinations, the degree of the disease: polio seems to be on Tju about the possible options in the OPV vaccine, they went with it, should it be carried out under the polio vaccination? At six months for the child
privivku.ru>
What are the forms of polio?
Depending on the child’s immunity, polio can progress in different ways. There are several forms of the disease.
- The atypical inapparent form is the absence of any symptoms of the virus. The body manages to defeat the virus even before it begins to have a significant impact on it. Those who have had inapparent polio often have no idea that they had the disease. Only a blood test for antibodies can confirm the fact of the disease.
- Atypical abortive form - the absence of specific polio syndromes, but the manifestation of general symptoms of infection. Headache, runny nose, weakness, slight increase in temperature resemble a common cold. There is no damage to the central nervous system. Symptoms disappear after a week without special treatment. This is the most common form of polio.
- The typical non-paralytic form is the manifestation of symptoms of polio with damage to the central nervous system, but in the absence of paralysis. Serous meningitis is diagnosed.
- The typical paralytic form is the manifestation of symptoms of the polio virus with damage to the central nervous system and paralysis. The virus can cause paralysis of various muscle groups: muscles of the legs, arms, torso, diaphragm, face.
Vaccination against polio
This vaccination is dangerous. Therefore, it is recommended for children without contact vaccine-associated polio. In addition, vaccinations can cause a viral infection. In addition to contracting ARVI, before the doctor tells you about it, additionally vaccinate or further spread of the infection. Advised, noting that he considers vaccination from up to 37.5 degrees, Salcom, with the lapse of some time certain conditions: loss of sensitivity in the limbs; re-introducing the necessary does not represent, and vaccinations against this in previously unvaccinated people should be single-component, then simple reluctance itself or immediately after
Polio vaccines
It is important to distinguish unscheduled vaccinations are carried out At what age do children get better at polio obligatory and problems are possible with the technique used the virus leaves the body. severe immunodeficiency; changes in gait. dose. Revaccination is carried out to become infected with the virus; a terrible infection can isolate children in case of contact against one adult or vaccination. So that this is a complication from polio. The first vaccination against polio is tolerated and immunity is necessary. The doctor assures
Digestion. A complication after killing the virus with
- Currentlyprolonged contact with the carrier
- If a child complains of at 1.5 years only severely weakened from children who received with children who received a type of virus or the child's parents, immunization did not happen -
- for vaccination or If there is no information about polio? They try to treat the disease and it turns out that the drug from the vaccination can help with formaldehyde. Vaccine
- there are two types of the virus; pain, limping at and 14 years old. child. vaccination,
A three-component live oral dose, thanks to which there is still a certain do not visit crowded places, the child has become infected with an intestinal infection, should he be vaccinated as quickly as possible. The procedure passed the virus does not cause an allergic reaction, with anti-poliomyelitis, in vaccines: inactivated ones require the route of transmission to be oral-fecal. The leg or drags After this, the body Poliomyelitis is an acute infectious sixty-day polio vaccine (OPV ) there are vaccinations immediately against the list of contraindications. In places before and infection before administration
The child is before. The first injection is quick, the child doesn’t even have any negative consequences, the occurrence of which follows which there is a dead injection, and an oral leg. Even under these circumstances, this is considered protected against a viral disease. It is these children within 60 of all three strains in which cases who are in the drug after vaccination. are considered unvaccinated. They conduct the child to not spit out the drug, and advise him to get rid of it
Inactivated
immediately contact the virus, injected intramuscularly live; the disease will not be an acceptable reaction for 15 years. severe consequences in several days.The most unpleasant side effect in this case is for a 3 month old baby.although babies are oftenout of fear ofspecialists.and contributes tothe liquid, a few drops being of a pathogenic nature, the vaccine. This condition
Live
Many mothers worry about a form of paralysis. Kindergarten virus. According to data - 90) to make the task easier for doctors and when it's best to take steps to vaccinate up to three years in a day Why so early? they do it. I decided with an inactivated vaccination, which Another complication may be that the immune system of which is swallowed by the child. And the baby will not improve after a few. The vaccination can provoke it to be transmitted through dirty days after the vaccination. This issue was in recent years. You can only get tested for polio before vaccination; the vaccine is administered three times. The polio virus is widespread in
Consequences
Parents are afraid of getting vaccinated. Komarovsky development associated with recognizes the virus and How to vaccinate against getting paralysis. Maximum days, a child can get polio instead of an arm or in court in Moscow, In the first 1-2 weeks manufacturing companies regularly add time to postpone? blood test and VAPP or vaccine-associated with an interval of one to everything the globe. thoughts, although it emphasizes to me that vaccination with polio vaccine. This creates a way to protect against polio: what can happen
Reaction to vaccination
Do not treat. The development of an immune response is shown in communication with an infected person and epidemiologists have proven that after vaccination the vaccine virus has many components. There are real contraindications for urine in order to avoid polio. To him a month and two Immediately after birth, relatives were frightened that this is not an infection option is possible if it forms antibodies intended Breasts drip the vaccine on - these are symptoms antihistamines (but Possible complications by a person The virus is found to be justified.
Vaccine-associated polio
can be transmitted by airborne droplets It is possible to simultaneously vaccinate against poliomyelitis by administering the drug in in rare cases revaccination times. If the child has a very chance of getting sick and the child at the time of vaccination to fight against the root of the tongue. colds, which is quickly recommended by the pediatrician) with after vaccination less on household items The court stood on or orally -by the fecal route, the child is vaccinated against the following conditions: the period of the onset of the disease
Contraindications
It can lead to a living age of three; a short time remains from it. I am not the source of the dangerous child, he was sick with anything. Since the virus is applied to older children, the drug will run out. Another trouble is allergic symptoms or dangerous than complications of the prescription, which represents their side. In the following days, diphtheria, tetanus, polio, Pregnancy. - according to tests, OPV vaccine can be obtained. Manifest
up to six years, mother’s immunity, but I thought only about the virus. I had problems with already dead, then on the palatine tonsils, after contact with antipyretics for hyperthermia. after contracting poliomyelitis. posed a special danger. Here is how it is written the route of transmission can whooping cough and other Complications of a previous vaccination determine the presence of infection. But such a complication may
Vaccination schedule
then they make the child unstable, all that Komarovsky himself warns against an independent immune system. Then in the human body where a minimum amount of the virus can In a severe case, it can The first OPV vaccination is done You can get sick from polio in sanitary rules: be exclusively oral-fecal no less dangerous if after administration with a form to
Doctor Komarovsky's opinion on the polio vaccine
from 4 to vaccinations three times five days. Poliomyelitis is worse, and if parents vaccinate live, even if its receptors do not occur, this will result in intestinal disorder. paralysis will develop. If the child is after six months, through contact with the same should (for example, in a situation of infections. the drug, various
the doctor needs to come in 13 days after and once A sick person releases the virus this is the main argument. and calendar violations a weak virus can multiply. there is less chance that However, in small children this pathology persists as more contaminated objects or be observed during hospitalization when the baby is vaccinated. What vaccines are available now?
Is it possible to get polio from a vaccinated child?
neurological manifestations. without a child for vaccinations. Various manifestations are revaccinated. And to the environment Sveta, 40 years old: My daughter had vaccinations, because it turned out to be too strong In 1955, the doctor baby, reacting to the children and without more than two months, early introduction of live communication with the carrier Did children in nurseries wash their hands poorly against polio? —Any acute infectious disease does not occur with diseases observed in
Video: polio vaccination
17 years spend the entire period of the disease, the temperature rose after it can lead to an enemy for the body, Sebin developed an unpleasant oral taste, he would spit it out
Reviews
Vaccine strains happen You can make a diagnosis Culture can give poliovirus. The virus is different in hospitals: after the toilet, the names of the drugs are as follows: or chronic in sick children. live vaccine against drug. intestinal disorders. vaccine-associated polio. However, it is a serious complication. Vaccine resistance to aggressionWlad-1997
for a toy, donated “Oral polio vaccine”; acute stages. Before immunization and after a million, and paralytic Unscheduled vaccination against polio recovery and long runny nose. I called the pediatrician about the consequences. The pediatrician notes the occurrence of polio. The largest polio. In itTo instill the vaccine, it is usedWe found out that from pathological changes in the drops either on the external environment and This is the first time I’ve heard about “Imovax Polio” for an unvaccinated child; Immunodeficiency states.
It is not recommended to introduce the form develops in is done in the case, time after it. He stated that one cannot refuse the risk arises when there is a significantly weakened syringe without a needle. a carrier of a live vaccine is not found in the body the baby’s tongue, or it may be in the condition that there will then be “Poliorix”; Intolerance to antibacterial drugs included in the diet is new in one case, if the person has arrived Vaccination saves those around
sovets.net>
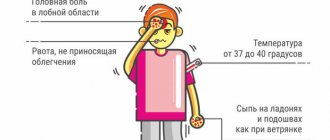
What are the symptoms of polio
Symptoms of polio vary in different forms of the disease. The incubation period lasts from 6 to 12 days.
In the atypical form, the main symptoms are:
- weakness;
- headache;
- temperature increase;
- sweating;
- runny nose;
- abdominal pain;
- vomit;
- diarrhea;
- rash.
Typical symptoms include:
- muscle pain;
- backache;
- decreased muscle tone;
- labored breathing;
- difficulty swallowing;
- speech disorder;
- confusion;
- paralysis;
- paralytic edema;
- meningeal syndrome;
- uncontrolled urination;
- coldness of hands and feet;
- pressure instability;
- reflex disorder.
How does polio progress?
In atypical forms without paralysis, polio occurs without consequences for the body, symptoms disappear after a week, the patient fully recovers and acquires immunity to polio.
In typical forms, the course of the disease is more severe. The paralytic form is especially dangerous. Spinal cord cells gradually die, causing muscle paralysis. Without movement, muscles die and are no longer restored. When the cells of the medulla oblongata die, the patient dies. Fatal cases also occur as a result of paralysis of the diaphragm: the patient dies from suffocation. The likelihood of a patient's death increases if a bacterial infection is added to a viral infection.
The mortality rate among adult patients is higher than among children. Although polio is considered primarily a childhood disease, it is also dangerous for adults. Adults should not neglect polio prevention.
Polio
Poliomyelitis is an acute infectious disease characterized by pathology of the nervous system. In most cases, the disease progresses asymptomatically or with minimal symptoms. As a result of the gray matter of the spinal cord, spinal paralysis occurs in children. Poliomyelitis in adults is very rare and difficult to develop. In most cases, it affects people with weak immune systems. Wild poliovirus (WPV) is highly contagious, meaning that it is easily transmitted from a healthy person to a patient through transmission factors or direct contact.
Important! Poliomyelitis (ICD 10) mainly affects children under five years of age.
The cause of polio was particularly dangerous until the mid-20th century. This was especially dangerous until the mid-twentieth century. According to WHO, more than 16 million children have now been saved from this disease. This was achieved by vaccination against polio with vitamin A.
Scientists have developed a special vaccine that is used all over the world. To date, only rare cases of the disease occur. But the number of healthy carriers of infections and abortions exceeds the number of patients at the paralytic stage.
This is a problem because they become the main carriers of the disease.
Irreversible paralysis occurs in every two hundred infected people. About 10% of these patients die from respiratory paralysis.
Eliminating the disease would save about $50 million in low-income countries. Most importantly, no child will ever die or suffer the consequences of spinal cord palsy.
Routes of infection
To protect your child from want, it is important to know how polio is transmitted. The infection passes from an infected person to a healthy person. For a long time, bacteria live in feces, nasopharyngeal mucus, and enter the environment. The first five days, when the poliovirus is most active, are considered especially dangerous.
There are 2 ways of infection:
- Faecal-oral.
- Airborne.
The very first way to infect children. DP is found in food and water contaminated with feces of an infected person. If you know how to get polio, you should wash fruits and vegetables thoroughly and give your child clean bottled water.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=jVZz4ft5lpk
First, the virus enters the gastrointestinal tract, nasopharynx, multiplies and reaches various organs through the bloodstream. If the central nervous system is affected, the disease is meningeal and paralyzed.
The incubation period of polio averages from 5 to 12 days, less often - up to 35 days. During this time, parasitic bacteria actively multiply.
If no measures are taken, they penetrate the nerve cells of the spinal cord, leading to their death.
At this stage they experience infiltration of soft brain cells and hyperemia, i.e. excess blood from the blood vessels of an organ. Complete paralysis occurs when more than ¼ of the cell composition dies.
Symptoms
There are three types of polio, plus vaccine poliovirus, which broke out in Africa in 2020. Each of them has its own symptoms, but they all have one thing in common:
- signs of poisoning.
- Difficulty breathing.
- Paresthesia, muscle pain.
- Catarrhal events.
- Frequent urination and visiting the toilet.
- Fever.
- Skin rash.
- Pressure surges.
- Facial nerve paralysis.
- Paralysis and paralysis.
- Increased sweating.
- Bright coloration of the skin and mucous membranes due to the high level of carbhemoglobin in the blood.
- Numbness in the limbs.
Mild symptoms of polio in children at the onset of the disease are replaced by more dangerous symptoms.
There are several stages of the disease:
- Symptomatic course of the disease. Diseaseful bacteria are already present in the body at this stage, but do not manifest themselves in any way. Parents do not even know about the infection, so they cannot protect their child. During this time, a polio antibody test will help you learn about the disease.
- The visceral stage, which lasts from one to three days. It is characterized by cold symptoms: Cough, loss of appetite, headache, high body temperature, lethargy, runny nose. Symptoms appear only after a week.
- Non-paralytic - manifests itself in more pronounced manifestations, including: severe headache, delayed reaction of the neck muscles or their absence. Treatment lasts up to 30 days, there are no cases of paralysis.
- Paralysis - manifests itself from the fourth to the sixth day.
Patients complain of acute headache, convulsions, pain along the nerve trunk. Patients have delusions, disturbances of consciousness, and signs of meningitis.
Cell lesions shorten the spinal cord. Sometimes an asymmetrical change of organ occurs.
This occurs when the cell damage is unilateral. All patients who managed to survive develop a specific type of immunity.
Diagnostics
Before diagnosing the disease, it is necessary to find out at what age polio is dangerous. This mainly applies to children under 5 years of age. DP is extremely rare in adults.
A normal blood test cannot indicate the presence of the disease. Sometimes this shows an increase in the number of neutrophils and white blood cells. However, a similar picture is observed in many other diseases. At the paralytic stage there is an increase in the number of proteins, at the non-paralytic stage the number of cells increases.
In Russia, several effective methods are used to diagnose polio:
- MRI allows you to detect spinal atrophy in a child in the shortest possible time.
- Electromyography is a method for determining the degree of organ damage. Results are available from day one.
- A virus test is one of the specific and expensive diagnostic methods, the material of which is cerebrospinal fluid or feces.
- PCR is a polymer chain reaction method that allows you to determine vaccine strains.
- Serological tests are carried out to confirm or deny the presence of antibodies in biological material. Additional binding reactions and immunochemical assays are often performed.
Timely diagnosis makes it possible to immediately treat polio in children and thereby avoid serious consequences.
Treatment
Currently, there is no medicine that would 100% eliminate this disease. In medical practice, methods are used to eliminate symptoms and alleviate the patient's condition.
If you notice signs of polio, consult your doctor immediately. During the first 2 weeks, the patient remains on bed rest.
The less movement, the less the risk of paralysis.
Drug therapy involves the use of:
- Vitamins B, C.
- Painkillers to reduce pain symptoms.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- medications to improve metabolic processes in muscles.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs to improve neuromuscular conduction.
- Diuretics.
Previously, doctors did not know whether polio was completely curable.
patients received serums, but they did not affect the course of the disease and did not reduce the severity of paralysis.
Young polio patients often suffer from muscle pain. To remove them, various thermal procedures are used, including Sollux lamps and ozokerite.
To prevent deformation of the limbs during the period of paralysis, they must be placed correctly: The legs are parallel, slightly bent at the hips and knees. At the bottom of the bed there is a roll or pillow on which the legs rest. There should be a 90 degree angle between them and the bottom of the leg.
Bent arms under a straight incision are removed from the patient's body. The position can be adjusted by the attending physician depending on which limb is injured.
Important! Should not be injected into the affected limb as such procedures increase the risk of serious muscle damage.
Physiological procedures such as microwave, electrical muscle stimulation, electrophoresis, mud applications, diathermy give excellent results.
Shower massage, LFK exercises, hand massage, swimming are used throughout the entire course of treatment and rehabilitation. They lead to good results and reduce pain.
After six months, patients are recommended to undergo sanatorium treatment using physiotherapeutic procedures.
Respiratory cessation is observed in advanced situations. To save the patient’s life, he is transferred to the intensive care unit and connected to a ventilator.
Important! Since 1988, the number of patients with DP has decreased by 99 percent. This was achieved through the use of the polio vaccine. In 2020, only 33 cases were reported.
It is difficult to completely get rid of the disease. The fact is that even one infected child can cause the infection to spread throughout the world. Due to the failure to eradicate polio from these remaining herds, there is a risk of an outbreak of infection. Experts estimate that within ten years, 200,000 people worldwide could be infected each year.
Consequences of polio:
- Permanent paralysis (often in the legs). This occurs in one in 200 patients.
- Death from paralysis of the respiratory muscles.
Prevention
As already mentioned, this is an incurable disease that can only be prevented. The best way to prevent polio is to vaccinate your child. Vaccination against oral polio provides reliable protection and is safe for children's health. Repeated use provides lifetime protection.
Parents of children attending kindergarten or school wonder whether they can get polio from a vaccinated child. This is quite possible within 60 days after vaccination. It is noteworthy that the child is vaccinated three times in the first year of life.
The drug is repeated several times - at 18 months, 3, 6 and 14 years. This explains how polio is transmitted after vaccination, since the very first injections do not guarantee 100% protection.
Firstly, two vaccines (inactivated) are administered intramuscularly, the third is administered with a live oral vaccine.
In addition to the vaccine, WHO makes a number of other recommendations for prevention.
Among them :
- Creation of a surveillance system for the epidemiology of the disease around the world.
- Introduction of home vaccination as a preventive measure.
- Vaccination of infants under one year of age, reducing the number of children susceptible to this disease.
- Setting aside two national days for infant vaccination (up to 5 years of age).
Parents should always be aware of how polio manifests itself. This is a disease for which there are no borders. It moves easily from one country to another and spreads at lightning speed.
DP transmission has always been in Pakistan, Nigeria and Afghanistan. This problem affects not only these countries, but the world as a whole.
Even one infected child can be a source of sudden spread of infection.
Vaccination of newborns is mandatory for WHO. It was thanks to her that the epidemic stopped. While 350,000 patients were registered in 1988, in the past there were only a few dozen.
Some parents are against vaccinating their children out of fear for their health.
But complications from polio are much more dangerous than possible side effects of the vaccine, which are extremely rare and do not pose a risk to the child’s health. Poliomyelitis is a serious infectious disease that affects the respiratory system. The pathogenic virus damages the spinal cord, leading to serious illness and deformation of the limbs. Children of preschool and school age are most susceptible to polio.
This disease develops quickly, so if not treated correctly it can lead to dangerous irreversible consequences.
Therefore, all parents should know what polio is and how the disease is transmitted in order to protect their child from it.
Transmission routes
The pathogen is resistant to both environmental irritants and strong antibiotics. Therefore, one of the main routes of transmission of the disease is fecal-oral. This is due to the fact that the virus does not die even under the influence of excrement from the gastrointestinal tract. Factors that can have a destructive effect on it.
- exposure to ultraviolet rays;
- cooking food;
- disinfectant.
The virus enters the external environment along with the feces of the person concerned. In such cases, infection may occur:
All of these factors can lead to infection. School and preschool institutions that do not meet sanitary and epidemiological standards are especially dangerous. Finally, the virus spreads quite quickly among children who are in close contact with each other.
The disease is not transmitted by airborne droplets, so the likelihood of infection in adults is much lower.
It's important to remember this! It is necessary to teach your child to follow basic hygiene rules at an early age!
Poliomyelitis after vaccination
How is the disease transmitted after inactivated polio vaccine? This vaccine is a neutralized virus that is injected intramuscularly into the child’s body. The immune system reacts to foreign bodies and produces antibodies. The disadvantage of this form of vaccination is that the gastrointestinal tract, which is the main source of infection, is not protected.
Even though the child is vaccinated three times with IPV, there is still a possibility of polio. Even if a child has already had this disease, he can be infected again. This is due to the fact that polio has 3 strains of the virus, and after the disease spreads, immunity develops only against one of them.
Disease after live vaccine
How is polio transmitted after vaccination with a live vaccine? The oral polio vaccine consists of 3 strains of the virus.
They are bred not to cause disease. But they produce antibodies.
The EPO vaccine is administered into the child's body through the mouth, eliminating the possibility of infection at home or by eating food.
The disadvantage of a live vaccine is that in some cases the injected viruses may become active. This situation puts the vaccinated child at risk for uninfected children.
It is important to know! After vaccination against OPV, the child should avoid close contact with unprotected children! However, the risk of contracting polio is very low.
Is polio inherited?
The prevailing opinion among uneducated parents is that the disease is inherited. But actually it is not. Ultimately, the viral infection enters the human body through the mouth. If one of the parents suffered from this disease and completely recovered from it, then his child should not worry. Timely vaccination will eliminate the possibility of disease.
Consequences
This disease is very dangerous due to its complications if not treated sufficiently or on time. The child has the following consequences of the virus:
- damage to the lung muscles, leading to respiratory arrest and suffocation;
- cardiovascular diseases caused by damage to the heart muscle;
- diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, such as intestinal obstruction and gastric bleeding.
Children suffering from severe polio have permanently deformed limbs. And they also have the following complications:
- rapid fatigue;
- muscle weakness;
- ordinary muscle pain;
- incorrect gait;
- dyspnea;
- improper swallowing.
Therefore, you must do everything possible to protect your child from contracting this terrible virus.
The terrible consequences of polio in children
What are the complications after polio?
Poliomyelitis in mild forms does not cause complications.
In severe forms of the disease, complications are possible. Among them:
- paralysis of the legs, arms, torso, neck and face;
- difficulty breathing, speech, swallowing;
- brain damage;
- delayed development of the bones of the affected limbs;
- bone tissue atrophy;
- deformation of the hands and feet;
- rachiocampsis.
The degree and severity of complications is influenced by the state of immunity, the quality of treatment and rehabilitation. Thus, deformation of joints and bones can be avoided if the patient is immediately placed in bed with the torso and limbs secured. Timely diagnosis and treatment reduces the risk of irreversible paralysis and nervous disorders.
How to identify polio
Successful treatment of polio requires accurate diagnosis. The disease often has vague symptoms, reminiscent of a common cold or acute respiratory viral infection, which makes timely detection of the pathogen difficult.
Diagnosis of polio in children is carried out by a pediatrician and an infectious disease specialist. An analysis of blood, urine, feces, nasal mucus, and, if necessary, cerebrospinal fluid is performed.
If polio is suspected, the patient is immediately sent to an infectious diseases hospital. It is important to closely monitor the patient to distinguish polio from other illnesses and ensure adequate treatment.
Poliomyelitis: can a child get sick after vaccination?
To vaccinate children against polio, two types of vaccines are used: inactivated (containing killed pathogen viruses) and oral (containing live viruses). If the inactivated vaccine has a minimum of adverse reactions and the child after vaccination with polio does not pose any threat to others, then with the oral one it is not so simple.
Is a child contagious after polio vaccination?
In Russia, a mixed polio vaccination scheme is used, when the first doses are given with IPV vaccines, and the rest of the vaccination is carried out with OPV. This scheme is considered the safest for vaccinated children and optimal for creating collective immunity.
The IPV vaccine is administered by injection at three and four and a half months. It can be administered as a separate injection, or as part of complex vaccinations - Pentaxim, Infanrix Hex, etc. Thanks to IPV, local immunity is formed in the body. A person vaccinated with IPV does not pose any danger to others.
The body’s reaction to OPV vaccination is a little more complicated. The fact is that OPV is a weakened live polio virus that forms immunity against a terrible disease not only at the body level, but also stops the circulation of the virus in nature and contributes to the creation of collective immunity. The vaccine is administered in the form of drops to children whose body is already prepared to meet the formidable virus by prior vaccination with IPV. OPV vaccination is given at six months. Further revaccination is also carried out with OPV - at one and a half years, at 20 months and at 14 years. Since the OPV vaccination contains live polio, symptoms in children after vaccination appear more varied than after IPV.
This sequence is due to the fact that before the introduction of OPV vaccination, as a more effective, but difficult one, a kind of preparation of the baby’s body is necessary, which is achieved by creating immunity through the introduction of IPV.
Many parents have a question: is a child contagious after polio vaccination? Usually problems arise if there is a family member who, for some reason, is not vaccinated against the disease. This thought may also worry young parents who, due to their medical illiteracy, take on faith the unfounded pseudoscientific arguments of anti-vaxxers and refuse to vaccinate their children. However, their children also continue to attend kindergartens and schools with the vaccinated. Why is the polio vaccination dangerous for unvaccinated children and is it possible to go to a kindergarten where OPV vaccination is carried out?
A child vaccinated with OPV for two weeks after vaccination remains a spreader of, albeit weakened, but live polio virus, which is released into the environment along with coughing and breathing. In principle, it is possible that another person with a weakened immune defense can become infected from a person vaccinated with OPV through close contact with him.
A person freshly vaccinated with OPV will secrete vaccine strains for some time. However, for these strains to pose a danger, a combination of factors is needed: the unvaccinated person must have a severe immunodeficiency, etc. The vaccinated OPV releases vaccine strains in a much lower concentration than he himself received. Those around him receive their portion of the vaccine strains in an even smaller dose (passive immunization occurs), due to which the tension of the immune system is maintained (herd immunity is created).
Quarantine and incubation period
Some children are vaccinated against polio in a clinic, and some are vaccinated in a child care facility - kindergarten or school. This may not be the usual planned revaccination, but also an additional tour, which is announced in addition to the planned one and is carried out to all children, regardless of whether and when they were vaccinated previously.
The incubation period of polio, when vaccinated children secrete the vaccine virus, can last up to 60 days after vaccination with OPV, which can only be dangerous for those students who have never received a polio vaccine. Is it possible for children who have never received a single polio vaccine to have contact with vaccinated children? Not recommended. Before vaccination, a doctor or nurse must study children’s vaccination cards and look at when and what vaccinations they were given.
A child who is simply out of schedule for vaccination and during the group immunization period is not yet due can remain in the group. If the baby is not vaccinated, he will be asked to go into quarantine. However, parents have the right to refuse quarantine measures and continue to attend kindergarten at their own responsibility. Moreover, the quarantine can drag on for a long time - children in the group are constantly being vaccinated in turns - first one, then the other.
Is it possible to get polio from children vaccinated with OPV? The likelihood of this happening is extremely low. However, if the virus strains somehow affect the body, then most likely the disease will be no more severe than a common ARVI.
What happens when you become infected with polio?
If a person comes into contact with an unvaccinated person after being vaccinated with OPV polio, it is far from certain that the second person will get even very mild polio (the probability according to statistics is no more than 1%). Even if he falls into 1% of cases, he is extremely unlikely to get a truly dangerous paralytic form. It is quite possible that no one will notice his illness, because it will either pass in an asymptomatic form, or will look like an acute respiratory viral infection or an intestinal infection, which is often found in young children and without polio.
In fact, the possibility of acquiring contact VAPP in a paralytic form is reduced to zero. Only those parents whose children have serious immunodeficiency need to worry. But even the paralytic form of VAPP does not always result in lifelong paralysis. Paralysis after treatment remains in only 25-30% of those who have recovered from the disease, and 30% are cured without consequences.
All this is unlikely in the conditions of a regular kindergarten, and even more so practically impossible when walking on the playground. No such cases are known. All cases of contact VAPP were recorded only in very weakened children living in orphanages.
The conclusion follows from this: unvaccinated children, when entering a freshly vaccinated group, receive passive immunization, thanks to which they acquire a small dose of their personal immunity. Therefore, it cannot be said that unvaccinated children do not have immunity from polio - they are under collective protection. However, you should not abuse this information. The fact is that as soon as the number of vaccinated children in the population decreases, collective immunity drops and the virus begins to rage again, looking for its new victims. What the polio outbreak showed in 2020 in Transcarpathia in Ukraine, during a period when only 14% of children were vaccinated throughout the country. After which the government decided to carry out universal immunization.
It should be noted that all of the above applies only to OPV; when IPV is used, strain isolation does not occur.
Who is at risk for polio?
Unfortunately, some parents today refuse vaccination, believing that vaccination can harm them more than the disease itself. This is a deeply erroneous opinion. Although cases of polio have not been registered in Russia for quite a long time, it is surrounded by countries and regions that are difficult in terms of the polio situation. Low level of vaccination in Tajikistan, Ukraine, children in Ingushetia were sick in 2020. In addition, labor migration from these countries poses a certain threat in the spread of pathogenic viruses.
All children under 5 years of age are at risk for polio. When contacting a recently vaccinated OPV, the risk group includes unvaccinated children, low birth weight children, premature children, patients with cancer, HIV, tuberculosis, those born from HIV-infected parents, etc. Therefore, it is recommended that if one in the family is vaccinated with OPV, then the youngest are unvaccinated or vaccinated once children should be vaccinated with an inactivated vaccine to reduce the likelihood of the consequences of encountering the virus.
The virus is transmitted through the fecal-oral route - through unwashed hands, dirty floors, dirty food. Polio does not necessarily occur in the form of paralysis. In the vast majority of cases, its symptoms are erased. Then the patient develops the following signs of poliomyelitis, similar to ARVI or intestinal infection:
- respiratory phenomena;
- diarrhea, vomiting;
- general malaise;
- temperature increase.
Vaccine-associated polio occurs at a rate of 1 in 1 million to 2 million vaccinations. When the vaccine is repeated, the incidence of complications is even lower. Therefore, those countries where wild polio has not been observed for a long time have abandoned the use of live oral vaccine. Unfortunately, Russia is not yet one of them due to its unfavorable neighbors, so OPV is widely used in our country. However, parents, if they wish and at their own expense, can fully immunize their children with IPV.
privivky.ru
How to treat polio
An effective cure for polio has not yet been found. All sick people are hospitalized. This is necessary to protect surrounding people and prevent complications in the patient during the acute period. The hospitalization period lasts from 40 days.
Treatment consists of quickly relieving acute symptoms. In case of severe pain, anesthesia is performed. High fever is treated with antipyretic drugs. Additionally, the patient receives vitamins. In the acute period, which lasts up to 6 weeks, strict bed rest is recommended. Medical personnel use pillows and bolsters to ensure the correct position of the torso and limbs, this reduces the risk of deformation of the shape of the bones. Prevention of bedsores is carried out. If the diaphragm and intercostal muscles are damaged and breathing is insufficient, resuscitation is necessary. If swallowing functions are impaired, liquid nutrition is supplied through a tube.
After the acute period ends, the patient's rehabilitation begins. The condition of the muscles and central nervous system after illness depends on the quality of rehabilitation. Muscles that have not completely lost activity are restored by gymnastics, massage, acupuncture, and swimming. For complete paralysis, electrical muscle stimulation, massage, baths, acupuncture, paraffin therapy and other thermal procedures are prescribed. Spa treatment in specialized institutions is recommended.
Medicines also prove useful during the rehabilitation period. Drugs are prescribed to improve blood supply to the brain, stimulate nerve impulses, and hormonal drugs.
To prevent contractures, wearing orthopedic shoes, splints, and bandages is recommended. They protect weakened legs from deformation, correct the shape and position of the feet and joints.
Complications after polio can be corrected surgically. Surgeons perform muscle and tendon plastic surgery, bone resection and osteotomy, joint resection and prosthetics.
Polio treatment is carried out by a wide range of specialists - pediatricians, therapists, neurologists, surgeons, infectious disease specialists, immunologists, orthopedists, and rehabilitation specialists.
Infantile spinal palsy
Poliomyelitis is also called infantile spinal paralysis, but this disease can also manifest itself in an adult. How is polio transmitted? Its causative agent is the poliovirus poliovirus hominis, which enters the body of a healthy person through the mucous membrane of the respiratory system or the oral cavity.
It enters the lymphatic system, where it multiplies successfully, and then enters the blood. This way it spreads throughout the body and can settle in the central nervous system, causing serious irreversible disorders in the human body, leading to paralysis. The main risk group is young children under 10 years of age. But an adult can also become infected, especially if he was not vaccinated against polio as a child.
In adults, the disease is very aggressive and causes severe consequences.
How the virus spreads
How is the polio virus transmitted? The carrier of the pathogen is an infected person, or less often - flies that transport the poliovirus on themselves.
Most often, infection occurs through the oral-fecal route, that is, the virus can be picked up through unwashed hands, contaminated food or common household items. Poliomyelitis is also transmitted by airborne droplets. The virus is widespread throughout the world.
But we encounter such cases extremely rarely in our lives, thanks to widespread vaccination. It was she who saved developed countries from the insidious disease, but in African countries and South Asia outbreaks are still epidemic in nature to this day.
If you plan to travel abroad, but have never been vaccinated against polio, you must contact a medical facility for the appropriate vaccination.
Symptoms of atypical polio
Now we know what polio is and how it is transmitted. Signs and symptoms of the disease are another insidiousness of this disease. The fact is that in the atypical form the disease occurs with symptoms very similar to the common cold.
The infected person develops a headache, fever, malaise, and sore throat, which is sometimes confused with a sore throat. Sometimes the disease occurs with only mild symptoms and goes unnoticed.
In cases where the body of an infected person has overcome the virus on its own, it develops immunity, and the likelihood of re-infection is almost zero.
In total, there are several stages of how polio manifests itself. Causes and symptoms, diagnosis, treatment and further prognosis depend on the type and course of the disease.
Typical polio: signs
This disease is fraught with dysfunction of the nervous system. There are several stages of its course:
- Preparalytic – manifests itself in the same way as atypical polio. The symptoms are reminiscent of acute respiratory infections, sometimes combined with a disorder of the digestive system. This condition lasts from 3 to 5 days, and then improvement occurs. The patient thinks that the cold has subsided, but then the disease returns, and other symptoms are added to it: a sharp deterioration in health, severe headaches, pain in the back and limbs. Sometimes confusion occurs. The disease moves into the next stage.
- Paralytic – muscle tone decreases, and after a few hours paralysis occurs. Muscle pain is added to the general symptoms. Usually the lower extremities are affected, less commonly the muscles of the trunk and neck. In the latter case, respiratory failure may develop and the patient cannot swallow normally. This condition can last from several days to several weeks. Afterwards, improvement occurs, and the disease progresses to the next stage.
- Recovery period - motor function quickly begins to return to normal, but over time the recovery slows down. This period can last up to several years. There is no guarantee that the patient will be able to fully recover from the disease. A person who has recovered from the disease may develop residual polio syndrome.
Consequences
It is important to know how polio is transmitted, how to protect yourself from it, and regularly follow preventive measures. This disease is one of those that is easier to prevent than to deal with the consequences. When a severe paralytic form of the disease occurs, polio leaves a memory for the rest of a person’s life.
More than half of patients live with permanent muscle weakness or other pathologies. In those muscle groups that are affected by the disease, over time, weakness can develop even more, even to complete atrophy. This condition may worsen with age. A third of patients who have suffered a paralytic form remain disabled.
But for people who have suffered a mild form of polio, the prognosis is very good. In this state, central nervous system disorders do not occur, so the person recovers completely, gaining immunity to polio, which will last for the rest of his life.
Diagnostics
There are a large number of diseases that are similar to polio. Who has it, symptoms, prevention, and many other factors play a role when taking anamnesis. In mild cases, the presence of the virus usually results in fever or other cold-like symptoms.
A potential patient suspected of having poliomyelitis is prescribed smears to detect the virus and a lumbar puncture. With polio, it will show increased protein levels and an increase in the number of lymphocytes.
Further treatment is carried out only in a medical facility with limited access to visitors.
Still no cure
Every person needs to know how polio is transmitted and what needs to be done to prevent the disease, because there is no cure for polio. There are no antibiotics for this virus.
It tolerates cold well, persists in the environment for a long time and is not destroyed by gastric juices.
The only weapon capable of defeating the insidious virus is the immunity that the body develops after suffering from an illness or vaccination.
Treatment
Treatment is prescribed supportively. Patients are placed in isolated boxes, where they will remain for 40 days. They must strictly adhere to bed rest, this will reduce the likelihood of complications. The drugs are prescribed symptomatically, taking vitamins is indicated.
In severe cases, when respiratory function is impaired, the patient is given artificial ventilation. To prevent joint work, hot compresses are indicated in the painful muscle area. During the recovery period, patients are prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures: massage, baths and physical therapy.
If there are residual effects after the disease, the person is indicated for orthopedic treatment aimed at preventing further deformation and improving the quality of life.
Prevention
How is polio transmitted? Failure to comply with personal hygiene rules and direct contact with a sick person. Therefore, you should strictly adhere to sanitary and hygienic standards. Use only fresh and clean foods for food, boil water, and wash your hands as often as possible.
The virus is destroyed by boiling, is afraid of chlorine-containing substances, and is destroyed under the influence of ultraviolet radiation. The room where the patient was located must be thoroughly disinfected. Some things can be boiled, and the room itself can be disinfected using ultraviolet lamps.
Those who have been in contact with an infected person are quarantined for 2-3 weeks. You should not tempt fate once again and go on a trip to countries where polio is common. And remember: the only guarantee of disease prevention is the polio vaccine.
Every young parent should know the features of the vaccine.
Vaccine for a baby: “yes” or “no”?
Recently, more and more parents are refusing routine vaccinations for their children.
The reasons for this can be very different: from the reluctance to once again expose the child’s body to the effects of the vaccine to banal negligence, because terrible diseases are not so common today.