Poliomyelitis is an acute infectious disease that causes serious damage to the central nervous system. The disease causes the formation of damage to the lining of the brain (meningitis) or complete/partial paralysis of the patient.
The disease is especially often diagnosed in childhood - from 3 months to 5 years - which is why all children, without exception, undergo the vaccination procedure. In older children, the body's susceptibility to the virus is significantly reduced. And in case of infection, the disease passes easily, and the symptoms of the pathology are almost completely absent.
Testing for antibodies to polio at a stage prior to the development of paralysis excludes diseases such as influenza, ARVI, or intestinal infection. Serological blood testing allows you to identify antibodies to the polio antigen, determine their types and concentration.
Symptoms of the disease
Poliomyelitis belongs to a group of highly contagious (infectious) pathologies, the causative agent of which is the intestinal virus Poliovirus homini. The typical route of infection is the fecal-oral route. Transmission is possible through dirty hands and toys, poorly processed products. The first manifestations of the disease appear two weeks after the child comes into contact with the virus carrier.
Poliomyelitis typically has an acute onset, reminiscent of the flu:
- temperature rise to high levels;
- cough;
- runny nose;
- apathy and lethargy;
- deterioration or complete lack of appetite;
- tearfulness and irritability;
- stomach ache.
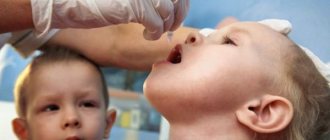
Timely vaccination against polio will help prevent infection
A few days after the onset of the disease, the child begins to feel better. But later - a week after the condition stabilized - the symptoms return. The clinical picture is complemented by paralysis of various muscle groups - legs and arms, face, intercostal muscles and diaphragm. Damage to the respiratory and vasomotor centers poses a particular danger to the child and his life.
Symptoms
Before moving on to a discussion of the diagnosis and principles of treatment of polio in children and adults, it is necessary to list the symptoms that indicate the development of such a specific disease.
The incubation period lasts 8-12 days. If the inapparent form develops, then the disease does not manifest itself clinically. It is detected only as a result of laboratory tests.
The visceral form of the disease is manifested by intoxication, fever, diarrhea, abdominal pain, and moderate catarrhal symptoms. The disease ends approximately 3-7 days after the symptoms make themselves felt. No residual neurological manifestations are observed.
The most severe disease is the paralytic form. Dyspepsia, tracheitis, pharyngitis, rhinitis, pain in the limbs and spine, 2-wave fever, convulsions, and confusion are observed. On days 3-6, the paralytic phase begins. By the end of the second week, the vital centers of the medulla oblongata are affected, and paralysis of the diaphragm and respiratory muscles is possible.
Analysis Methods
To conduct the study, venous blood is taken. It is best to visit the laboratory in the morning. It is necessary to try to reduce not only the physical, but also the emotional activity of the baby.
Blood testing is based on the acid-base titration technique, i.e., the neutralization reaction. When a result is obtained, when the titer of immune antibodies is less than 1:4, it is considered negative and confirms that the patient does not have polio.
The titer of class M antibodies is of diagnostic interest. If the study indicates that it exceeds more than 1:4, then the result is positive and indicates the presence of the Poliovirus homini virus in the human body.
Antibodies to polio appear in the blood already on the seventh day after the virus enters the baby’s body
Specific IgM immunoglobulins are formed in the baby’s blood within a week after infection. Their maximum is determined after 14 days and persists for the next 60 days. After recovery, the child develops specific antibodies of class G, thanks to which he develops stable lifelong immunity to polio.
Virological method
It is mandatory for diagnosing polio. It is very important to isolate the virus and identify it. The patient's feces are required as biomaterial. Liquor, blood, and nasopharyngeal swabs are taken a little less frequently.
The material is first filtered and then treated with an antibiotic. Then it is introduced into the culture of Hep-2 and RD cells (from human rhabdomyosarcoma). After approximately 5-7 days, the cytopathic effect of viruses (CPE) occurs, manifesting itself in the form of fine-grained cell destruction.
Virus identification is carried out in a neutralization reaction. This means that a virus combined with three types of polyvalent anti-polio serum is introduced into tissue cultures. This is the first stage. The next step is to maintain the virus with separate standard sera, which are monovalent. What is the result? If the serum and virus type are identical, then CPE is not observed.
Where can I get the analysis done?
Before vaccination, you need to make sure whether your child needs vaccination or not. That is why he may be prescribed a blood test to determine antibodies to polio. But in some cases, the research may be uninformative.
If the child is less than six months old and receives breast milk, then protective antibodies are transferred to him from the mother. During the period of life from six months to a year, all the protective antibodies he receives are retained in the baby’s blood.
Blood tests can be carried out both in a public clinic and in a private medical center
A pediatrician will help you decide when to vaccinate against polio and, if necessary, prescribe a blood test.
Where can I get tested? You can donate blood for testing either in the treatment room of a district clinic, or you can go to a private medical laboratory or center. In particular, an antibody test can be taken at the Invitro laboratory at the time of direct application.
Laboratory diagnostics
To fully reveal the ongoing process, specialized medical centers conduct comprehensive laboratory diagnostics for polio, including the following research methods:
- virological study;
- retrospective diagnosis (serological study);
- biological method for differentiation of viruses;
- express diagnostics;
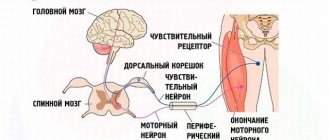
- Electroneuromyography – determines the level and severity of damage to motor neurons.
Sources
- https://NashiNervy.ru/infektsionnye-zabolevaniya/analiz-krovi-na-nalichie-antitel-k-poliomielitu.html
- https://onevrologii.ru/infektsionnye-zabolevaniya/analiz-na-antitela-k-poliomielitu
- https://live-academy.ru/analiz-krovi-na-poliomielit-v-invitro/
- https://telemedicina.ru/disease/diagnostika/analiz-poliomielit
[collapse]
How to prepare your child for testing
The need for a test is determined by the attending doctor or local pediatrician. A similar need arises if the child’s medical record does not contain information about certain vaccinations or it has been lost. A referral to the treatment room is issued by a pediatrician.
Preparing to donate blood is quite simple:
- collection of biological material is performed on an empty stomach;
- The procedure is best carried out in the morning - from 7 to 11.
Today, vaccination is the only possible way to prevent polio infection in children of all ages.
Poliomyelitis is one of the most severe viral diseases. Complications of the disease provoke dangerous damage to the nervous system and even death. The main principle of combating the disease is to vaccinate the population. However, this is not entirely successfully implemented in the countries of Asia and Africa, where polio is characterized by an epidemiological threshold. In recent years, cases of a dangerous virus have been recorded in areas adjacent to the borders of the Russian Federation.
Antibodies in medicine include proteins of a certain effect produced by lymphocytes when antigens enter the human body. This is how the immune system fights pathogenic microorganisms. These also include antigens of non-infectious origin. Various allergens, transplanted tissues and organs are pathological in nature.
It also happens that antibodies are produced, the reasons have not yet been precisely established, against the tissues and organs of one’s own body. They are called autoantibodies. This process may affect:
- phospholipids;
- hormones;
- DNA fragments;
- thyroid enzymes.
The study of autoimmune diseases has allowed scientists and doctors to come to the conclusion that the best panacea for such problems is vaccination. If a person has immunity to dangerous viruses, then the likelihood of infection is practically reduced to zero. Infection can be prevented using the following methods:
- vaccination;
- revaccination.
It is important to know! Sustained immunity can only be developed in people who have had the disease or been vaccinated with a live vaccine. The polio virus is no exception.
In order to identify the body's resistance to polio infection, it is necessary to conduct a serological blood test. This approach is currently the most effective method for determining infection risks.
Forms of the disease
When discussing the diagnosis of polio in children and adults, it is necessary to make a reservation that the notorious differentiation is always carried out on the basis of symptoms. And each form of the disease is individual. The following list can be distinguished:
- Meningeal form. Manifestations: severe pain, tense roots of the spinal nerves and nerve trunks, their pain on palpation.
- Spinal shape. Manifestations: gentle, non-paretic gait, preservation of muscle tone, discomfort in the joints during passive movements, increased deep reflexes, inflammatory changes in the blood. This disease is often confused with polyradiculoneuritis, diphtheria polyneuropathy, and Werdnig-Hoffmann spinal amyotrophy.
- Poliomyelitis form. The pathological process is diagnosed in the cervical segments. Manifestations: paralysis of the muscles of the shoulder girdle and neck, flaccid paresis, lymphocytic pleocytosis (minor, 40-60 cells), increased protein levels (approximately 0.66-1.0 g/l). When studying the material being studied in the laboratory diagnosis of polio, doctors take into account the epidemiological history. This could be drinking raw milk, being bitten by a tick, etc.
- Diphtheria form. Manifestations: symmetry of lesions, slow increase in paresis over several weeks, detection of disturbances in bioelectrical activity during electroneuromyography. Diagnosed 1.5-2 months after diphtheria.
- Polyradiculoneuritis. Manifestations: slow development and further increase in symmetrical paresis, sensitivity disorder of the radicular and polyneuritic types, increased amount of protein in the cerebrospinal fluid.
- Pontine form. Manifestations: decreased taste sensitivity for salty and sweet, lacrimation on the affected side, pain in the trigeminal points felt upon palpation, disturbances in facial sensitivity and spontaneous pain.
- Bulbar form. Manifestations: convulsive syndrome and deep disturbances of consciousness. It is important to differentiate it from stem encephalitis.
Within the framework of the topic concerning the differential and microbiological diagnosis of poliomyelitis, it must be noted that lesions of the nervous system, which are clinically no different from the disease in question, are often caused by enteroviruses of the Coxsackie-ECHO group. In such cases, the entire range of serological and virological diagnostic methods and the previously mentioned PCR method are used.
Where is the analysis done?
The correct approach to vaccination is to determine whether or not the patient should be vaccinated. It is for this purpose that it is important to do a blood test for antibodies to polio. The analysis is important and is an informative source for any doctor. However, such information may not be reliable in the following cases:
- When the child is under 6 months old and is breastfed. At this age, the baby is protected by antibodies from the mother’s body that come with breast milk.
- From 6 months to a year. The protective functions of the mother's immunity are still preserved. The baby is also vaccinated against a number of other infections.
A competent and intelligent doctor will help you understand the question of when it is better to get vaccinated and when you need to get tested for antibodies to polio. A similar service is provided by both private centers and government centers. However, in some of them, patients are redirected to other institutions.
There is not a very wide demand for this procedure, it is costly and unjustified to create the necessary clinical conditions. An antibody test can be taken at the Invitro laboratory at any time. Qualified specialists will explain all the intricacies of preparing for the analysis and conduct it in accordance with sanitary and epidemiological standards.
Taking the vaccine
In the vast majority of hospitals in the CIS countries, the oral vaccine is distributed. The vaccination is done simply: the drug described above is instilled into the oral cavity.
This is done after the child turns 3 months old. Next, you will need to do two more vaccinations. The interval between them is 1.5 months. It turns out that the baby will need to be taken to the doctor when he is 4 and 6, respectively. Revaccination is carried out at 18 and 20 months, and then only at 14 years.
You need to be warned that after the introduction of weakened viruses into the body, so-called vaccine-associated polio can develop. The probability is very small, but it exists. Most often, the disease develops in infants after their first vaccination. What is the reason? Usually – reduced immunity or spontaneous mutation of the virus in the child’s body.
And, by the way, since after vaccination the baby becomes a potential carrier of the virus, not vaccinated people, but also those whose immunity is suppressed, can become infected from it.
Sources used:
- https://onevrologii.ru/infektsionnye-zabolevaniya/analiz-na-antitela-k-poliomielitu
- https://fb.ru/article/447397/diagnostika-poliomelita-osnovnyie-metodyi-analizyi-chem-opasen-poliomelit
How to take the test correctly
The need for a blood test for polio is determined by the attending physician or local physician, or by a pediatrician in the case of children. This measure is necessary first of all then. When the medical record does not contain any information about vaccinations. A referral is issued by an infectious disease specialist at the clinic at the place of registration for free services. If desired, any patient can take the test, but then the test will be carried out for a fee. The price range for polio testing ranges from one to three thousand rubles.
You should only come to the laboratory on an empty stomach and preferably in the morning. Typically the hours are from 7 to 11 am. Blood sampling from a vein is necessary. The enzyme immunoassay method allows us to determine the quantity and quality of antibodies to polio in the body. Blood plasma and serum are used as the determining material. It is possible to confirm that the patient has immunity to a dangerous infection with a minimum value of 12 U/ml and above.
Diagnostics
Having considered the causes, symptoms and types of polio, you need to pay attention to this topic. This serious, rare disease is usually suspected by a pediatric neurologist or pediatrician. The basis for assumptions is anamnesis, diagnostically significant symptoms and epidemiological data.
There are certain difficulties. Not all doctors immediately prescribe a test for polio, since this particular disease is not always suspected. Serous meningitis, acute intestinal infection, ARVI, and influenza are often mistakenly diagnosed.
Laboratory tests, which will be discussed in detail below, can help accurately determine the disease. Now we need to discuss other methods.
It is important to differentiate the virus, and therefore a polymerase chain reaction is performed. A lumbar puncture is also often prescribed. During this procedure, cerebrospinal fluid flows out under high pressure. The study reveals its colorlessness, transparency, as well as increased glucose and protein content. After electromyography, it is possible to confirm the lesion at the level of the anterior horns of the spinal cord.
When talking about methods for diagnosing polio, it should also be noted that the disease must be promptly differentiated from botulism, myelitis, Guillain-Barré syndrome, serous meningitis, tick-borne encephalitis and polio-like diseases.
Poliomyelitis and vaccination
According to statistics from the World Health Organization, almost 10 million people who have had polio suffer from paralysis to one degree or another. In the last decade, significant progress has been made in stopping the spread of the virus. Polio case data from health ministries around the world has dropped tenfold. The population's immunity is strengthened thanks to mass vaccination against a dangerous infection.
The recommended age for vaccination is from 3 months to 3 years. In Russia, according to the immunization plan, almost 99 percent of children were vaccinated against polio. The figure is unique, especially considering the fact that the overall world statistics in a combined percentage reached only 74. The country has created a system for registering paralysis as a result of polio.
Planned explanatory and preventive work is carried out on all social categories of the population. Particular emphasis here is placed on educating young parents about the importance of protecting children's immunity. Many of them, exposed to the erroneously common belief that vaccinations are harmful to infants, simply deny them immune protection. Fortunately, cases of such carelessness are rare and most parents agree to vaccination.
Polio
Poliomyelitis
– infections caused by viruses of the Enterovirus genus are widespread throughout the world. Infection with poliovirus causes illness, often leading to paralysis and even death. Three types of poliovirus are actually pathogenic for humans:
Type 1 (Brunhilde) – often with severe symptoms;
Type 2 (Lansing) – with milder symptoms;
Type 3 (Leon) – rare, but with severe symptoms;
Polioviruses
enter the human body mainly through the fecal-oral route through handshakes, contaminated objects, water or food, as well as through airborne droplets through the respiratory tract. Having fixed itself on the cells of the pharynx and intestines, the virus begins to multiply and occupy the lymph nodes of the small intestine, from where it safely enters the blood. In the next phase of viremia, poliovirus colonizes almost the entire body and, in particular, the central nervous system (CNS).
More than 90% of infected patients do not experience any subjective symptoms. In other cases, there may be complaints of headache, sore throat, diarrhea, nausea and vomiting, and increased body temperature. Classic paralysis with pain in the muscles and nerves of the spinal cord is very rarely observed. The recovery period can last up to two years, but the resulting damage often cannot be eliminated. There is no specific treatment for polio. Only symptomatic therapy and, if possible, exercise are indicated.
The disease begins acutely - the symptoms of polio are similar to the flu:
- temperature increase up to 40 °C;
- cough;
- headache;
- runny nose;
- lethargy;
- decreased appetite;
- vomit;
- muscle pain.
After a few days, the child’s well-being improves; after 5-7 days, the pathological process resumes - this time it is manifested by paralysis of various muscles: limbs, face, diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
The greatest danger is damage to the vasomotor and respiratory centers - this leads to difficulty breathing and threatens the baby’s life. If a sick child has the following main signs, the doctor recommends an immunological test:
- skin hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity);
- hypotension;
- decreased reflexes.
- signs of nervous system dysfunction;
To conduct research in our laboratory, we use the enzyme immunoassay method. Diagnosticum made in Germany, “IBL”. This laboratory test allows you to detect IgG antibodies to two types of Poliovirus simultaneously (in total):
- Type 1 (Brunhilde)
- Type 3 (Leon).
Reference values:
- 8-12 U/ml - indeterminate. (If clinical symptoms persist, it is recommended to retest the blood serum sample after 10-14 days).
- > 12 U/ml - positive (i.e., indicates infection with Poliovirus homini).
The response of a serological test can be either a consequence of a previous illness or immunity due to vaccination. After an infection, the child develops specific class G antibodies, which provide lifelong immunity.
The result of the analysis should be considered only by the attending physician in conjunction with the clinical picture, the patient’s medical history and indicators of other laboratory tests.
You can perform an analysis for the qualitative and quantitative determination of IgG antibodies to the polio virus in the GEMOSKRIN laboratory. Detailed information by phone: 8495-953-27-57.
– one of the dangerous viral diseases, the fight against which is being successfully carried out throughout the globe. The only effective means of preventing the disease is immunization of the population through vaccinations. In most countries of the world, children receive a full course of vaccinations and revaccinations against the virus by the time they graduate from school. The most disadvantaged regions in this sense are still Africa and some Asian countries.
In Russia and the CIS countries, things are going well with vaccinations, but sometimes there are exceptions - refusal of vaccination and the arrival of emigrants from pandemic countries, trips to unfavorable areas, etc. In some cases, it is advisable to take a blood test for antibodies to polio.
Causes
This disease is caused by antigenic types of poliovirus, which belong to the genus of enteroviruses. There are three of them in total. But the greatest danger is caused by the first type of virus – it accounts for 85% of cases. It is very tenacious and can survive up to 6 months in feces and up to 100 days in water.
It even tolerates freezing and drying, and is not affected by antibiotics or digestive juices. The virus can die only as a result of the following effects:
- Heating and subsequent boiling.
- Treatment with disinfectants.
- Ultraviolet irradiation.
The source of the virus can be not only an infected person. It can be spread by an asymptomatic carrier. He himself may not have polio. However, it will spread through its nasopharyngeal mucus and feces. The virus is transmitted by fecal-oral, airborne and contact routes.
Once in the body, it is introduced into cells, as a result of which the synthesis of protein and nucleic acids is disrupted. The result is destructive and dystrophic changes. Complete death of the neuron is possible. The consequence of the destruction of 1/3-1/4 nerve cells is the development of complete paralysis and paresis.
How to test for antibodies to polio
Antibodies, or immunoglobulins, are special protein molecules produced by plasma cells. An antibody test helps make a diagnosis, check the level of immunity after vaccination, and detect diseases with an asymptomatic course (or in the incubation period).
A referral for analysis (hemotest) is issued by an infectious disease doctor at the clinic at your place of residence.
You can donate blood in another place (a clinic not related to your place of residence, a private medical center) for a fee.
Blood for analysis that detects the presence of antibodies is taken from a vein. Blood serum and plasma are examined for analysis.
Serological method
It is also used to diagnose polio. It helps determine whether the antibody titer is increasing in the blood of recovered patients.
To do this, a neutralization reaction is used in tissue culture with paired sera that were obtained during the acute stage of the disease, as well as at the time of convalescence.
An enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA) is performed, as well as a complement fixation reaction (CFR). In case of a positive result, it is possible to determine a 4-fold increase in the antibody titer in the 2nd serum when compared with the 1st.
What is ELISA analysis? An actively developing field of chemical enzymology. This is a method with a unique specificity of the immunochemical reaction. Simply put, antibodies bind only to specific antigens. ELISA has been widely introduced into various medical fields, since the reagents used are stable, registration methods are simple, and the cost is quite low.
In what cases is a study prescribed?
Sometimes doctors encounter patients whose medical records do not contain information about vaccinations for some reason. Someone may fall behind the vaccination schedule and miss important stages of immunization. In such cases, it is necessary to find out whether a person’s blood contains antibodies to pathogens of dangerous diseases. This determines whether the patient needs additional vaccinations and when it is appropriate to vaccinate.
Parents are often worried that their child may become infected in a child care facility (kindergarten, nursery, school) from other children vaccinated against polio with a live vaccine. They want to find out whether their child has immunity against this disease and, accordingly, how high the risk of infection is. In recent years, there has been a growing trend among some "advanced" parents to avoid vaccinating their children. For some reason, this category of parents is convinced that vaccinations are harmful, not always correctly comparing possible complications with the risk of contracting a dangerous disease. However, in the future they put not only their children in danger, but also the children with whom their children communicate.
The danger of polio, meanwhile, has not been disputed by anyone for a long time. This disease kills about 5% of those affected and makes 25-30% disabled for life.
An antibody test may be prescribed for diagnostic purposes when a disease is suspected. If the disease has already been detected and the patient is prescribed treatment, an immunoglobulin test helps control this process.
Briefly about the disease
Before discussing the principles of diagnosing polio, it is necessary to study the specifics of this disease. This is an enteroviral infection caused by polioviruses. They affect the motor neurons of the anterior horns of the spinal cord. This impact leads to serious paralytic complications with subsequent disability of the patient.
As a rule, the disease affects children under 4 years of age. They account for 60-80% of cases.
The last epidemic occurred in the middle of the last century. In the late 80s, WHO adopted a resolution whose goal was to eliminate this disease throughout the world.
Today, in countries where preventive vaccination against polio is carried out, the disease occurs in the form of sporadic isolated cases. These are India, Afghanistan, Syria, Nigeria, Pakistan. Our country, as well as North America and Western European countries, are free from polio.
Types of polio diagnostics
Several methods are used to make accurate diagnoses in medicine. As for polio, its causative agent is a virus that can be modified into various types (strains). To identify it, several types of tests are carried out: laboratory and differential diagnostics, a general antibody test or a serological blood test.
Laboratory diagnostics
Laboratory tests are carried out to detect not only the virus and antibodies, but also the strain of the polio pathogen. This is done at an early stage of the disease. Depending on the type of analysis, stool, blood, nasopharyngeal wash or cerebrospinal fluid are taken for research.
Differential diagnosis
The differential method allows you to distinguish different forms of polio from diseases with similar symptoms. For example, the meningeal form of poliomyelitis is differentiated from serous meningitis of another etiology: tuberculosis, enterovirus, mumps. To diagnose the spinal form, you should make sure that you are not talking about an osteoarticular pathology not related to poliomyelitis. The same applies to other manifestations of pathology.
Differential diagnosis is carried out on the basis of laboratory, radiological, electromyographic and other studies.
Antibody test
Immunoglobulins are detected in the blood, cerebrospinal fluid, and other fluids in the human body at the slightest contact with the virus. Antibodies to polio appear in a person’s blood immediately after infection, even before signs of the disease appear. The body begins to fight during the incubation period, before tangible symptoms appear. The role of antibodies is to prevent pathogens from entering the central nervous system. In this way, the body’s protection from irreversible consequences associated with impaired brain function is activated.
Complications and prognosis
It is impossible not to talk about why polio is dangerous. This disease often leads to disability. If the paralyzed limbs begin to move, they remain deformed - they shorten and the muscles atrophy.
The pathological process can affect the respiratory system, and this is fraught with respiratory disorders, due to which a person can even die (suffocate).
Mild forms of the disease usually pass without a trace. And due to targeted long-term vaccine prevention, only abortive and inapparent forms of infection predominate in the structure. They are being treated successfully. Paralytic forms only affect people who have not been vaccinated against polio. And this is mandatory prevention.
If suddenly there is a suspicion that a child has become infected with polio, he is immediately isolated, and the premises where he was located are disinfected. Persons with whom he had contact are placed under observation and are also immunized with OPV out of turn.
How to prepare your child for testing
2-3 days before the test, it is advisable to eliminate physical and emotional stress. It is also recommended not to carry out physical therapy procedures the day before blood sampling.
A small child needs to be prepared mentally, given that taking a blood test from a vein is not the most pleasant procedure. If blood from a vein is donated for the first time, the baby may experience fear. Parents should try to adjust the child accordingly. Maybe even include some game moment, maybe persuade you to be patient if a needle pricks - there can be many options. But, in any case, the child’s panic will only prevent the nurse from performing manipulations.
Immunity to polio
A person who has had polio remains immune. However, it will only fight one strain of the virus. If you come into contact with another strain, you can get sick again.
Lasting immunity to this insidious disease is developed by using vaccines made from three types of virus. At the same time, stronger immunity appears when vaccinated with a live vaccine. However, the live vaccine is not suitable for everyone. It is strictly not recommended to vaccinate children under the age of one and a half years with it. In Russia, there are cases where infants, after an incorrect vaccination, began to develop symptoms of epilepsy and other complications.
Experts have not yet reached a consensus on whether to vaccinate all children according to the same schedule or to vaccinate selectively. This means: first take a blood test for antibodies to polio and only if they are absent (or insufficient) vaccinate. It turned out that some people can develop immunity to diseases naturally, without vaccinations. In this case, the person himself does not get sick. It turns out that the main thing in disease prevention is strengthening the immune system in any way. Discussions concern only the role of vaccines for each specific organism and individual reactions.
Treatment
A little attention should be paid to clinical recommendations. Poliomyelitis of manifest forms is always treated inpatiently. The patient is prescribed isolation, rest, a high-calorie diet and bed rest.
It is very important to give the limbs the correct physiological position. Chest massage and bedsore prevention are necessary. If the patient has dysphagia, then nutrition is provided through a nasogastric tube. If spontaneous breathing is impaired, artificial ventilation is indicated.
Unfortunately, no specific treatment has been developed. Vaccines, the features of which were discussed above, prevent the development of the disease, preventing it from developing (the development of immunity). But they don't cure polio. Therefore, pathogenetic and symptomatic therapy is carried out.
Prescribed intake of ascorbic acid, B vitamins, dehydrating and analgesic drugs, respiratory analeptics, neostigmine, etc.
During the recovery period, time is devoted to rehabilitation measures. Namely:
- Physiotherapy.
- UHF.
- Treatment in sanatoriums.
- Orthopedic massage.
- General therapeutic baths.
- Paraffin treatment.
Treatment and prevention of children is always carried out with the direct participation of a pediatric orthopedist. If a risk of developing contractures is detected, splints, plaster casts, orthopedic splints, and special shoes are prescribed.
There is always the possibility of residual effects. Their treatment usually includes tendon-muscular plasty, tenomyotomy, arthrorrhiza, tenodesis, resection and further osteotomy of bones, surgical correction of scoliosis, etc.
Blood test for polio
Poliomyelitis
is an acute, highly contagious infection that causes spinal paralysis.
Its causative agent, Poliovirus homini
, belongs to the family of intestinal viruses, most often children under five years of age are susceptible to the disease. Infection occurs through the fecal-oral route (through dirty hands, toys, poorly processed food) from a sick child or an asymptomatic virus carrier. The first clinical manifestations can be noticed in the baby two weeks after infection.
The disease begins acutely - symptoms of polio
Similar to the flu:
- temperature rise to 39.5 °C;
- cough;
- runny nose;
- lethargy;
- decreased appetite;
- tearfulness;
- pain in the abdomen.
After a few days, the child’s well-being improves, but 5-7 days pass and the pathological process resumes - this time it is manifested by paralysis of various muscles: limbs, face, diaphragm and intercostal muscles.
The greatest danger is damage to the vasomotor and respiratory centers - this leads to difficulty breathing and threatens the baby’s life. Diagnosis of polio
at the pre-paralysis stage presents difficulties: most often the diagnosis of influenza, intestinal infection, or acute respiratory viral infection is mistakenly made.
Timely clinical differentiation of diseases is based on serological diagnosis
the Poliovirus homini
antigen in the child’s circulating blood , determination of their type and concentration.
When is a test ordered?
The main indication for the study is differential diagnosis of polio in a child.
.
Practicing specialists - pediatricians, infectious disease specialists, neurologists recommend immunological analysis
if a young patient has:
- signs of nervous system dysfunction;
- skin hyperesthesia (increased sensitivity);
- hypotension;
- decreased reflexes.
Analysis methodology
Biological material - blood from a vein
, the selection is carried out at the medical center in the morning. On the eve of the analysis, it is recommended to reduce the child’s physical and emotional activity; blood is drawn on an empty stomach.
To conduct the study, the method of enzyme immunoassay is used.
Diagnosticum made in Germany, “IBL”.
Analysis transcript
The result of the analysis should be considered only by the attending physician in conjunction with the clinical picture, the patient’s medical history and indicators of other laboratory tests.
This laboratory test detects IgG antibodies
to three types of Poliovirus simultaneously (in total):
- Type 1 (Brunhilde);
- Type 2 (Lansing);
- Type 3 (Leon).
The best tests for polio - rating, addresses and telephone numbers
100 reviews • Aeroportovskaya 1-ya, 5 • • weekdays from 08:00 to 20:00; Sat from 09:00 to 19:00
Good doctors who treat and are not rude (unlike Medsi), convenient location. Highly recommend.
4 reviews • st. Korolenko, 2 building 1, 107014 • 8 (499) 673-07-07
All the necessary doctors are available! I go to a nutritionist - I am fundamentally different from nutritionists, both in approach and in the outcome. I recommend!
Krasnoarmeyskaya, 23a • • weekdays from 08:00 to 20:00; Sat from 09:00 to 19:00
The Literary Fund Children's Clinic is a multidisciplinary medical institution that provides a full range of medical services for children and adolescents in…
Academician Chelomeya, 10B • • weekdays from 08:00 to 21:00; weekends from 09:00 to 21:00
The advantage of our Medical Center is a well-organized combination of medical work and instrumental diagnostics using modern…
2 reviews • Moscow region, Krasnogorsk, Pavshinsky Boulevard, 5 • • Mon–Sat from 08:00 to 20:00
Aviamotornaya, 4k3 • • daily from 09:00 to 21:00
Multidisciplinary medical center. Examination of adults and children from birth. 10 minutes walk from the metro. The clinic uses expert equipment…
Davydkovskaya, 6 • • weekdays from 08:00 to 19:00; Sat from 09:00 to 12:00
The main goal of our medical center is to make you healthy and confident! We have assembled a team of the best specialists who work...
Moscow region, Balashikha, Zarechnaya street, 29 • 8 (905) 578-44-77 • weekdays from 08:00 to 21:00; weekends from 09:00 to 21:00
Odintsovo, st. Severnaya 5, building 4 • • weekdays from 07:30 to 20:00; weekends from 08:00 to 17:00
New medical clinic. Doctors with unique work experience. The most friendly and professional approach to patients. Now the walkthrough...
2 reviews • Shcherbinka, Sportivnaya street, 23 • • daily from 09:00 to 21:00
I visited the dentist Dmitry Sergeevich Utolin. At the first appointment in November there was nerve removal and tooth restoration, which went absolutely well...
Privolnaya, 70k1 • • Mon–Sat from 08:00 to 21:00; Sun from 08:00 to 20:00
The modern diagnostics clinic, located on Privolnaya Street, is a highly equipped private clinic. As the name suggests, the main…
Balashikha, Green, 32 • • daily from 08:00 to 20:00
The Galimed family clinic was opened in 2012. in Balashikha. Today the clinic accepts the following…
Zoological street, 12k2 • • Mon–Sat from 09:00 to 21:00; Sun from 09:00 to 19:00
At the HBP-clinic pharmacy you can purchase essential medicines and medical products (antipyretics,…
Moscow region, Kotelniki, Sosnovaya st., 2, building 4 • 8 (495) 788-00-01 • daily from 07:00 to 20:00
Filevsky Boulevard, 40 • • daily from 09:00 to 20:00
alfa.clinic | ALPHA CLINIC Russian-German medical clinic
st. Nagatinskaya embankment, 10 bldg. 3 • • daily from 07:00 to 21:00
The Health Clinic provides a wide range of medical services. gynecology, urology, dentistry, neurology, ultrasound, reproduction, video colposcopy.…
2 reviews • Ostrovityanova street, 25k1 • • daily from 07:30 to 20:30
If necessary, I turn to this medical center for help. I am confident in the quality of the specialists’ work, so I don’t go to other places. To me…
Marshala Chuikova, 12 • • weekdays from 07:30 to 19:00; weekends from 08:00 to 16:00
The company has been on the market since 2004 and has been providing full cycle laboratory diagnostic services for more than 14 years. The network has more than 250...
Zoological street, 12k2 • • Mon–Sat from 09:00 to 21:00; Sun from 09:00 to 19:00
We treat the causes of the disease, not the symptoms, combining European technologies and Eastern clinical practice. In our clinic you can take any…
Moscow region, Lyubertsy, Komsomolsky prospect, 11B • 8 (495) 505-60-56 • daily from 09:00 to 21:00
Lukinskaya, 14k1 • • weekdays from 08:00 to 20:00; Sat from 09:00 to 20:00; Sun from 09:00 to 18:00
Network of medical centers
Vnukovskoye settlement, Anna Akhmatova street, 2 • 8 (495) 287-60-00 • weekdays from 08:00 to 20:00; Sat from 09:00 to 20:00; Sun from 09:00 to 18:00
Moscow region, Mytishchi, Borisovka street, 22 • 8 (499) 350-22-82 • Mon–Sat from 09:00 to 21:00; Sun from 09:00 to 19:00
Borovskoe highway, 30 • • weekdays from 08:00 to 20:00; Sat from 09:00 to 20:00; Sun from 09:00 to 18:00
Network of medical centers
Borovskoe highway, 56 • • weekdays from 08:00 to 20:00; Sat from 09:00 to 20:00; Sun from 09:00 to 18:00
Sculptor Mukhina, 14 • • weekdays from 08:00 to 20:00; Sat from 09:00 to 20:00; Sun from 09:00 to 18:00
Network of medical centers
Krasnogorsk, Pavshinskaya floodplain, Krasnogorsky Boulevard, 7 • 8 (495) 144-03-03 • weekdays from 07:00 to 21:00; weekends from 09:00 to 21:00
At our medical center you will find excellent service and qualified doctors. Check out our price list, the prices will pleasantly surprise you.
Request to establishments - order a service, specify the price