Functions of transaction analysis
The main function of transactional analysis is to help a person solve all his problems that interfere with the normal functioning of the individual. The main functions of transactional analysis include:
- identifying unproductive stereotypes of one’s behavior;
- formation of new value systems and decision-making based on one’s own needs and capabilities;
- understanding and acceptance of oneself;
- understanding the peculiarities of your interaction with other people;
- expressing your feelings openly and without embarrassment;
- making attempts to trust yourself.
Transactional analysis can be practiced at home, at work, at school. In a word, in any place where a person is surrounded by people. This ease of use often becomes a source of criticism, because... Most psychotherapy specialists believe that qualitative personality changes are possible only under the supervision of a professional. However, people love transactional analysis precisely because of its simplicity.
Finished works on a similar topic
- Course work Transactional analysis in psychotherapy 400 rub.
- Abstract Transactional analysis in psychotherapy 230 rub.
- Test paper Transactional analysis in psychotherapy 230 rub.
Receive completed work or specialist advice on your educational project Find out the cost
Transactional analysis methods
Transactional analysis and its methods include the idea that every person from birth has early decisions that shape his position in life. There is a certain script created under the influence of a person’s environment - his family, teachers and peers. People making decisions in the moment are based on behaviors that were used in past years. However, often such behavior models are no longer relevant.
Methods of transactional analysis through the use of therapy make it possible to correct a person’s behavior, that is, to prepare a person to solve various situations in the present, without using habitual outdated attitudes. During therapy, life positions and lines of human behavior that prevent an adequate response to various situations are analyzed.
Of course, like any analysis, transactional analysis has several concepts. Some of them:
- Ego state
This concept is a system in which actions, thoughts and feelings are directly related to each other. The three states of “I” allow us to understand the structure of the human personality.
- Parent. This level reflects data received at an early age from loved ones. These can be various settings: norms of behavior, taboos, advice. In general, any attitudes divided into black and white, that is, good and evil. The I-parent state is easy to recognize: you can often notice that a person tries to imitate the actions or even words of his parents.
- Child. A level showing a person’s emotional state: his gullibility, simplicity, openness to something new. A person experiences pleasant feelings after communicating with an individual.
- Adult. At this stage, a person is able to adequately evaluate the actions and actions of people, find the right solutions for complex situations and problems. The individual is based on personal experience.
- Transactions (strokes)
Individuals located at any level of ego states can ask for help from each other and at the same time move from one level to another. This is a transaction.
- An additional transaction is an interaction between two individuals that does not cause any controversy and lasts a long time. These are ordinary relationships between people who know what to expect from each other.
- Cross transaction is rich in conflicts, since individuals are in an inadequate I-state.
- A hidden transaction implies the presence of 2 or more I-states. These are psychological games that are based on the need for recognition. For example, the true meaning of words seems to be hidden under the phrase itself, it is hidden from the eyes of strangers and can often be interpreted by different people in completely different ways.
- Life scenario
The life scenario is formed from childhood. First, the child thinks about what will happen next, based on his own principles. This is influenced by the child’s transactions with his environment.
A script, like any story, is divided into several parts: beginning, middle, end. The main plot part is written in the first years of a child’s life. Then verbal instructions received from parents come into play - they may relate to the life plan, certain areas of the children’s lives, as well as their gender. For example, “you’ll probably become famous,” “you’re a lousy pianist,” “what kind of girl are you?” In some cases, parental phrases can not only pull the child back and demotivate him, but also lead to depression and even suicide.
The script continues to be written until about 7 years of age, occasionally being supplemented. However, during adolescence, there is a high probability that an individual will reconsider his plans for life. It is much more difficult for adults to do this - they live for a long time with ideas in their heads, and even a slight deviation from the plan is a difficult task.
Life scenarios are the main tool for working with specialists. They show how and why a person is capable of creating problems for himself.
- Psychological position
There are 4 types of psychological position:
- I'm okay - you're okay;
- I'm not okay - you're not okay;
- I'm not okay - you're okay;
- I'm ok - you're not ok
Each of them characterizes a person’s life position. People can assert themselves at the expense of others, without deliberately torturing themselves by communicating with toxic people, just to maintain the usual scenario in communicating with the outside world and other people.
- Psychological games
A psychological game is a combination consisting of a hidden transaction. That is, all words and actions have a double bottom, which is easy to predict. The game has a hidden motivation; the goal is some emotional state that a person unconsciously tries to achieve. This happens due to the fact that children, who are attentive and inquisitive by nature, are accustomed to the attitudes that are established in their family. Often a child notices that the demonstration of some feelings leads to punishment, while others lead to encouragement. Therefore, the child tries to demonstrate only “good feelings” within the walls of the house. At a more mature age, he follows his habits.
Transactional analysis and its methods allow you to get rid of the above attitudes, because they often have a destructive impact and interfere with a person’s happy life.
It is important not only to notice strange behavior in yourself in time, but also to contact a qualified specialist. Psychological Training Center Orange Sun
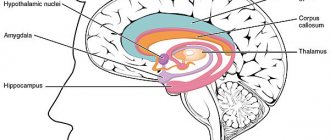
Three ego states according to Eric Berne
American psychologist Eric Berne believes that there are three probable ego states that determine our entire lives - our behavior, characteristics of interpersonal communication, thoughts, words, actions, desires, and so on. These ego states are:
- I-Parent – behavior and instructions acquired from the outside, primarily under the influence of parents. Outwardly, this manifests itself in critical and overly caring behavior towards others. Internally, they take on the form of old parental admonitions. A parent is caring, he can help and console if something happens to the child. However, it is also critical. At the right time, he will criticize, give orders, and may even threaten;
- I am an Adult – acceptance and awareness of reality. In this state, a person is adapted to life, organized, enterprising and rational. His actions always correspond to his capabilities. The Adult is an intermediary between the Child and the Parent. After analyzing the situation, he determines what behavior is acceptable and what is better to refuse;
- I-Child is a state in which a person restrains within himself any desire that, like a child, arises naturally. A person is sensitive to experiences and reactions towards him. In this state his creative abilities awaken. The child is spontaneous, impulsive, self-centered, knows how to quickly adapt to a changing environment due to his helplessness and timidity, and can be compliant and can also rebel if he doesn’t like something.
Too lazy to read?
Ask a question to the experts and get an answer within 15 minutes!
Ask a Question
From time to time, a person can be possessed by two of the three permissible states, and the transition from one to the other is quite abrupt. So, for example, when a person wakes up in the morning, he wants to stay in bed and sleep a little more, but still gets up and goes to work. Thus, the Child-I and the Parent-I struggle within him.
Note 1
It is difficult to say which condition is the most important. Harmony between these states is important, which helps a person remain adequate and correctly distribute his resources and time.
Script theory
Another cornerstone of transactional analysis is scenario theory.
. This theory was first developed by Eric Berne and improved by Claude Steiner.
Scenario
- this is “a life plan drawn up in childhood.” The scenario is chosen by the child based on those proposed by parents or society. The choice of scenario is influenced by both external factors and the will of the child. Byrne cites the case of two brothers who were told by their mother, “You’re both going to end up in a mental hospital.” Subsequently, one of the brothers became a chronic mental patient, and the second became a psychiatrist. According to script theory, each of us already in childhood knows the important moments for the script. For example, the number of future children.
Counter-scenario
- a certain sequence of actions leading to “getting rid” of the scenario. The counter-script is laid in another ego state. For example, for the scenario “You must suffer,” the counter-scenario could be “Your life will improve if you get married successfully.” In this case, Eric Berne drew an analogy of the counter-scenario with “lifting the curse of the evil witch” (from the fairy tale “Sleeping Beauty”).
Anti-script
- “the opposite scenario” can be formed when it is impossible to act according to the scenario. A person who acts directly opposite to his script is nevertheless still subject to its influence. The script continues to guide the person, but what the script should have done well, the person does poorly, and vice versa. For example, a young man who was meant to be close to a single mother in his old age, and therefore take care of himself and have minimal contact with girls, begins to change girlfriends every week, use drugs and engage in extreme sports. In this example, human behavior is still dependent on parental attitudes and therefore predictable.
Thus, the anti-script determines a person’s life style, while the script determines his destiny.
It is argued that a parent considers a child an adult only when the child begins to fully fulfill the parental script.
Script theory is explained in detail by Berne in his book What Do You Say After You Say Hello? (“What do you say after you say “Hello”?”). In the Russian-speaking space, this book is better known under the title “People Who Play Games,” since in most cases it was published under this title.
Transactions
Transactions are verbal and nonverbal interactions between people, as well as the exchange of influences between the ego states of two people. They consist of a stimulus and a response. For example, stimulus: “What are you doing here?”, reaction: “Well, they let you leave work early.”
Transactions can be as follows:
- complementary (or parallel) - transactions in which a stimulus emanating from one person is directly transmitted to another and complemented by his reaction. For example, the stimulus “Where is the library?” is supplemented by the reaction (answer to the question) “On Spring Street.” During this type of transaction, no conflicts arise and interactions between people can continue for a long time;
- intersecting (or cross) – with this type of transaction, quarrels and conflicts are possible. So, for example, a husband asks: “Where are my sneakers?”, to which his wife answers: “I’m always to blame for everything!” Thus, the husband sends the stimulus of his Adult to his wife's Adult, but her response flows from her inner Child. Such transactions begin with caustic remarks, mutual reproaches, and can continue throughout family life, until both people consciously decide to include Adults;
- Covert is the most complex type of transaction because it activates more than one ego state per person, since the message is disguised as a socially acceptable stimulus, but a response is expected from the covert message effect. Most problems that arise during family life can be resolved if they are identified and corrected in time.
Literature
Books
- Bern, E.
Transactional analysis in psychotherapy / trans. from English A. Gruzberg. - M.: Eksmo, 2009. - 416 p. — (Psychological bestseller). — ISBN 978-5-699-31579-6. - Bern, E.
Games that people play. People who play games / trans. from English A. Gruzberg. - M.: Eksmo, 2014. - 576 p. (Psychology of communication). — ISBN 978-5-699-27303-4, ISBN 978-5-699-18299-2. - Stewart, Ian;
Joines, Vann . Modern transactional analysis. - St. Petersburg: Social and Psychological Center, 1996. - 332 p. — ISBN 5-89121-002-9.
Articles
- Letova, I.
Modern transactional analysis.
How to determine what condition you are in
It is enough to observe the behavior a little. Each ego state has its own characteristic features:
- The “child” often says the following phrases: “I want,” “This makes me very angry,” “I don’t care about this.” Emotions are shown on his face. This could be a look somewhere at your feet, trembling lips, an expression of delight.
- “Parents” constantly prohibit something, point it out, and remind them of their sense of duty. They shake their heads, look menacing, and cross their arms over their chest.
And finally, “adults”. They look for benefits in everything, offer to calculate the benefits, discuss the appropriateness of this or that action or decision. They are constantly thinking about something.