Stress urinary incontinence is a very common urological problem. It is diagnosed mainly in the fair sex. Men get sick extremely rarely. The disease worsens a person’s quality of life, as he begins to experience not only physical, but also psychological discomfort.
Stress urinary incontinence is a pathological condition characterized by the involuntary release of urine. It occurs due to dysfunction of the urethral sphincter or weakness of the pelvic floor muscles. Because of this, some urine leaks out even with slight tension in the peritoneum. For example, during physical activity, coughing or sneezing. The problem first makes itself felt during reproductive age. After 70 years, almost every second woman suffers from this disease.
Medical statistics today are as follows: stress urinary incontinence is diagnosed in 40% of women from European countries. The problem is simultaneously urological, neurological and gynecological. Its development can be provoked by many unfavorable factors - from poor nutrition to difficult childbirth. Stress urinary incontinence is treated using conservative or surgical techniques. Also, sometimes therapy is supplemented with folk remedies that have a beneficial effect on the urinary and nervous systems. Specialists involved in solving the problem - urologist, gynecologist, neurologist.
Why does stress incontinence occur?
The disease is polyetiological. Previously, it was believed that involuntary urine production was associated only with physiological aging of the body. This is fundamentally wrong. The development of pathology is influenced by lifestyle, the presence of somatic diseases, and even childbirth.
The main causes of stress urinary incontinence:
- most often, uncontrolled leakage of urine is associated with weakened sphincter function (60% of cases) (in women, this condition can occur after gynecological surgery or difficult labor, the number of births does not matter in this case);
- hard physical labor;
- hormonal changes in the body associated with the onset of menopause;
- obesity;
- the presence of urological diseases – cystitis, urethritis;
- constipation;
- perineal injury;
- doing strength sports;
- chronic prostate diseases;
- undergoing radiation therapy.
The risk of developing pathology increases significantly if the patient has bronchial asthma or COPD. The reason is that these diseases are characterized by frequent episodes of increased intra-abdominal pressure. As a result of this, the ligamentous apparatus around the urethra is overstretched.
Traditional treatment tactics
Treatment of stress urinary incontinence is possible using both conservative and surgical methods.
Before deciding on the purpose and advisability of a particular treatment method, it is necessary to conduct a thorough diagnostic examination using ultrasound and urodynamic studies, as well as fibrocystoscopy.
Modern medicine in most cases prefers the use of conservative methods of therapy. These include the following treatment measures:
drug therapy;
- pelvic floor muscle training;
- physiotherapeutic procedures;
- wumbling.
Drug therapy involves the use of:
- Detrusitol (improves urodynamics);
- Spazmexa (relieves bladder spasms);
- Solifenacin (reduces smooth muscle tone);
- nootropics: Pantogam;
- metabolic drugs: Essentiale;
- antidepressants: Melipramine.
There is a technique whose main goal is to train the bladder. It includes the following steps:
- education;
- developing a urination plan;
- implementation of a plan.
The training consists of the patient stipulating and agreeing with the doctor on a plan according to which he will perform acts of urination, that is, the patient will need to urinate not when he feels the urge, but at the time prescribed by the doctor. In order to avoid unwanted urination, the patient needs to strongly squeeze the anal sphincter when the urge occurs.
The therapy process lasts for several months. Every 14 days you need to increase the interval by another 30 minutes. The main goal of the program is to maintain a time interval between acts of urination of up to 3.5 hours. The training is carried out along with the use of medications. These trainings are prescribed to all patients with this pathology. Modern medicine uses these exercises not only for therapeutic purposes, but also as a preventive measure.
In modern medicine, there are a number of physiotherapeutic procedures for the treatment of pathology. These include:
electrophoresis with anticholinergics;
- electrophoresis with the use of antispasmodic drugs;
- paraffin therapy;
- Ultrasound therapy;
- use of diadynamic and sinusoidal modulated currents;
- Ural Federal District;
- mud therapy;
- infrared laser therapy;
- electrosleep therapy.
If conservative therapy methods are ineffective or have not brought any results, surgical therapy is used. It involves the following procedures:
- colposuspension;
- sling operations (TVT, TVT-O, TVT SECUR system).
Sling interventions are classified as minimally invasive, but at the same time they are the most effective and safe methods of treating uncontrolled loss of urine.
A sling is a small strip made from synthetic and harmless material. During the operation, the sling is placed under the urethra and supports it. This creates protection to keep urine in the bladder. The duration of the surgical intervention does not exceed 30 minutes. The patient can be discharged the next day. Full recovery takes one month.
Clinical picture
The main sign of the presence of this disease is involuntary leakage of urine from the bladder. At the same time, there is no urge to empty it. Urine leaks out during physical exertion.
Degrees:
- Easy. Urine leaks only when you cough, sneeze or exercise. If these factors are absent, then no leakage is observed. Urine is also released only when the bladder itself is sufficiently full.
- Average. Urine leakage occurs due to a sudden rise from a place. It can also occur when walking or running quickly.
- Heavy. Urine is released involuntarily even in a state of complete rest.
If these symptoms occur, you should consult a doctor for consultation, diagnosis and treatment.
Urinary incontinence
3203 30 January
IMPORTANT!
The information in this section cannot be used for self-diagnosis and self-treatment.
In case of pain or other exacerbation of the disease, diagnostic tests should be prescribed only by the attending physician. To make a diagnosis and properly prescribe treatment, you should contact your doctor. One of the delicate problems that worsens the quality of life and causes psychological and physical discomfort is incontinence, or urinary incontinence.
Incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine. Incontinence is a symptom of many pathological processes, and it is important to understand in time what changes have occurred in the body and begin treatment.
The problem of urinary incontinence is more common among older people and preschool children, but about a quarter of women of reproductive age suffer from some form of urinary incontinence.
Urinary retention and urination are controlled by special structures (micturition centers) located in the brain and spinal cord. When the muscles of the bladder neck, urethra and pelvic floor contract, urine accumulates, and when they relax and the bladder (detrusor) muscle contracts simultaneously, urine is excreted. A person normally feels the urge to urinate when 200-300 ml of urine collects in the bladder.
Types of urinary incontinence
There are several classifications of this urological problem.
False
Urinary incontinence occurs due to congenital or acquired defects of the urethra or bladder.
True
Urinary incontinence occurs without the above defects of the urinary system.
The international classification identifies the following types of urinary incontinence:
- Stress
incontinence, or
stress
, is the involuntary loss of urine when coughing, exercising, or sneezing. Caused by increased intra-abdominal pressure and insufficiency of the urethral sphincter apparatus. - Imperative (urgent)
incontinence is the involuntary release of urine with an unbearable (imperative) urge to urinate. Often a symptom of an overactive bladder.
- Situational
urinary incontinence is the involuntary loss of urine during various situations, for example, during sexual intercourse or laughter. - Enuresis
is bedwetting during sleep.
Causes of urinary incontinence
The causes of involuntary urination in people of different age groups may be different.
When considering the problem of urinary incontinence in children, it is important to consider the age of the child.
Only towards the end of the first year of life does the urinary retention reflex develop. From the age of one and a half years, a child is able to learn to control urination, and until the age of 4-4.5 years, isolated episodes of involuntary urination at night are the norm.
There are several hypotheses for urinary incontinence in children.
- Delayed maturation of the nervous system is the most popular theory for the occurrence of involuntary urination. Immaturity of the nervous system leads to impaired regulation of urination. The development of such a condition is possible after suffering hypoxic and traumatic brain damage during pregnancy and childbirth.
- Disruption of the rhythm of antidiuretic hormone secretion by the hypothalamus leads to the release of large amounts of urine at night and, as a consequence, to night urination.
- Hereditary factors. If parents suffered from enuresis in childhood, then the likelihood of this disorder occurring in children increases.
- Social and psychological factors.
In the first years of a child’s life, stressful situations can result in involuntary urination. Therefore, during treatment, it is important not to make the child’s problem public, even within the family circle, and any punishment for “wrongdoing” must be avoided.
Among the causes of involuntary urination in young and middle-aged women are obstetric and gynecological pathologies.
Thus, during pregnancy, up to 85% of women experience involuntary loss of small amounts of urine during the day. Damage to the pelvic floor muscles during natural childbirth, previous surgeries on the pelvic organs and the development of complications can also lead to incontinence. Risk factors for the development of urinary incontinence may include diabetes mellitus, obesity, cognitive impairment, oral estrogen intake, prostatectomy and other pelvic surgery.
Temporary disruption of urination can be caused by inflammatory diseases of the urinary system: cystitis (inflammation of the bladder), urethritis (inflammation of the urethra).
Involuntary loss of urine in older people has several causes:
- age-related changes (decreased contractility of the bladder walls, changes in urethral pressure, weakening of brain functions);
- increased volume of residual urine (for example, with prostate adenoma);
- urinary tract infections (often occur when personal hygiene rules are violated in bedridden patients);
- use of medications (diuretics, sedatives, anticholinergic drugs).
What diseases cause urinary incontinence?
When diagnosing incontinence, it is important to take into account the patient’s age, since each age category has its own characteristics.
In children, it is important to separate daytime and nighttime urinary incontinence. If involuntary urination occurs during the daytime, the cause may be:
- overactive bladder;
- hypoactive (lazy) bladder;
- situational urinary incontinence (a rare form of incontinence).
If loss of urine occurs only at night, then it is either nocturnal polyuria or idiopathic enuresis.
Causes of urinary incontinence in adults:
- stress;
- genitourinary fistula (after radiation therapy, during purulent processes, after injury);
- inflammatory diseases of the genitourinary system;
- prolapse or prolapse (loss) of the pelvic organs;
- tumors of the brain or spinal cord;
- spina bifida;
- neurological disorders after stroke;
- benign prostatic hyperplasia and prostate cancer;
- Iron-deficiency anemia.
Which doctors should I contact if I have urinary incontinence?
To diagnose the cause of urinary incontinence, consultation with a wide range of specialists is necessary. An adult patient should see a doctor, and a child and teenager should be taken to a doctor. The doctor conducts a survey and general examination of the patient, after which he refers to specialists for a gynecological or urological examination.
Depending on the accompanying symptoms, the patient may be examined by doctors such as:
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- ;
- oncologist;
- psychiatrist.
Diagnosis and examination of urinary incontinence
During the examination, it is possible to use both laboratory tests and instrumental examinations.
Laboratory research.
- General urine analysis.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis of the disease begins with an initial examination and interview with the patient. Next, the doctor usually recommends starting to keep a special urination diary, in which you must indicate:
- bedtime and wake-up time;
- amount of liquid consumed per day;
- number of urinations per day;
- amount (in milliliters) of urine excreted at one time;
- frequency of changing pads or diapers;
- frequency of incontinence episodes, it is necessary to note what the person was doing at that moment.
Diagnostic measures for illness
Patient's story about disturbing symptoms
When compiling a patient’s medical history, the time when signs began to appear and the presence of similar manifestations in close relatives are taken into account. Additionally, it is determined whether the patient had nocturnal enuresis in childhood. In addition, the person is asked to fill out a specially created questionnaire to find out the causes of stress illness, which includes questions on the type and frequency of performing heavy exercises, being in a tense state, and lifting heavy objects.
Urinary Diary
To make a more accurate diagnosis, the doctor gives the patient a diary in which he describes the acts of urination. The person records the time when urination occurs. It describes how much fluid the patient consumed per day, in what quantities, what activities the patient was engaged in, and when the involuntary release of fluid occurred. A person should note approximately how much urine came out during this period, and whether there was an unbearable desire to urinate before. Thus, the patient describes everything that happened to him during the day.
Conducting a PAD test
It is not always possible to accurately determine from patient descriptions how much fluid was released during urination. Uncontrolled urination in women is tested using the PAD test. For this purpose, urological pads are used, which are weighed before testing and after use. The test can last from 20 minutes to 2 hours a day. If the study is designed for a short period of time, then before it drink half a liter of still water.
Vaginal examination
The woman's genitals are examined to exclude the presence of concomitant diseases. During examination of patients, doctors often detect drying of the vaginal mucosa, the appearance of large fistulas, and uterine prolapse. These abnormalities, identified together with stress urinary incontinence, can lead to complications. During the examination, the woman must be forced to cough in order to monitor the discharge from the urethra.
Collection of urinary analysis
If the patient has inflammation in the urinary system, then small amounts of urine may be released. A urine test is performed to determine a person’s level of white blood cells, red blood cells, and the presence of harmful microorganisms. To obtain more accurate data, material is collected in the morning. Before collecting the test, it is recommended to wash your genitals and urinate in a sterile container. Women will additionally need to cover their vagina with a clean cloth while urinating.
Treatment
All options for combating stress urinary incontinence are divided into 2 large groups - conservative and surgical. The first group includes physiotherapy, medications, as well as special exercises that help strengthen the pelvic floor muscles. Separately, there are also folk remedies that can be supplemented with the main therapy. It is strictly not recommended to use them as the only means of combating pathology.
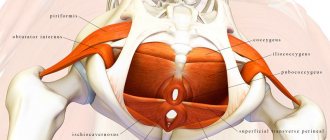
Exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles
Patients are advised to perform Kegel exercises daily. They will help restore tone to the periurethral and perivaginal muscles. Repeat the workout three times a day. The simplest exercise is to sit down and imagine the process of emptying the bladder. Then you need to tense the same muscles that, if necessary, stop this process. Repeat several times. It is necessary to alternate slow compression and relaxation with frequent contractions.
Kegel exercises to strengthen the pelvic floor muscles
Drug treatment
Treatment with medications for stress urinary incontinence is not always effective. It all depends on the stage of incontinence and the root cause of its development. To improve the patient's condition, the following groups of drugs are used:
- Nootropics. The treatment plan is included if the patient has also been diagnosed with neurological disorders. Prescribed: “Cortexin”, “Pantogam” and others;
- Adrenergic agonists (most often prescribed "Gutron"). Increases the tone of the urethra and sphincter. Use with extreme caution, as they provoke an increase in blood pressure;
- Anticholinergic. Included in the treatment plan when diagnosing bladder hypotension. Drugs – “Detrusitol”, “Ubretide”;
- Antidepressants (Duloxetine). The main goal is to prevent psychological factors that may cause spontaneous urine discharge.
The drugs are usually prescribed in tablet form. When it is necessary to act on the problem locally, medicinal ointments, creams and suppositories can be used.
If the cause of stress urinary incontinence is gynecological pathologies, estrogens and combined oral contraceptives can be added to the treatment plan.
Physiotherapy
Most often, to improve the contractility of the pelvic muscles, patients are prescribed electrical stimulation. The essence of the procedure is that the muscle fibers are exposed to low-intensity current. Other procedures may also be prescribed:
- electrophoresis;
- magnetic therapy;
- electrosleep;
- Darsonvalization.
A better result can be achieved if exercises, physical procedures, and medications are used to treat the disease. The treatment plan is written strictly individually for each patient.
Surgical methods
Surgery for stress urinary incontinence can help completely get rid of this unpleasant pathology. The type of intervention is selected by the doctor based on the degree of development of the disease and the anatomical features of the structure of the urinary system.
What is the disease?
According to statistics, stress urinary incontinence is very common throughout the world. Thus, in European countries, about 40% of all women suffer from urinary incontinence, significantly worsening their quality of life. This pathology relates to several areas of medicine. This is not only a urological problem, but also a gynecological and neurological one.
Important! It should be remembered that urinary incontinence is not an independent disease, but a symptom of various pathologies, the treatment tactics of which can be completely different.
Stress urinary incontinence is a pathology in which loss of urine occurs as a result of stress on the anterior abdominal wall and increased pressure inside the abdominal cavity. This increase in pressure causes urinary incontinence when coughing, laughing, lifting heavy objects, running and sneezing. The same effect can occur as a result of sexual intercourse. An increase in pressure immediately affects the bladder, causing urine to flow out from a couple of drops to a stream of urine.
Mechanism of stress urinary incontinence
There are several types of urinary incontinence, each of which has its own characteristics:
- Stress urinary incontinence occurs involuntarily when a person sneezes, coughs, laughs, or performs certain physical activity. This is the result of an increase in intra-abdominal pressure. A characteristic feature of this pathology can be considered that there is no urge to urinate. This type of incontinence is recorded in half of all cases of treatment with this pathology.
- With urgency incontinence, urine leaks involuntarily. A strong urge is felt, which is called “imperative” or “imperative”. Patients simply cannot make it to the toilet in time. The number of patients with this pathology is 22%.
- Mixed incontinence is characterized by involuntary and uncontrollable loss of urine, which is accompanied by a sharp urge and tension. This also includes the occurrence of urinary incontinence when coughing and sneezing. This pathology accounts for about 30% of all cases. It combines signs of stress and urge incontinence. Patients note that there is a strong urge to urinate, after which urine leaks.
- Overflow incontinence is a rather rare form of the disease, which occurs in most cases in men with problems with the prostate gland. This pathology is characterized by impaired urine outflow, which leads to overfilling and overstretching of the bladder.
- For children, the form of incontinence is enuresis. In 95% of cases, this disease occurs in childhood. 4% of patients are teenagers and only 1% of patients are adults. In 75% of cases, symptoms of the disease appear during night sleep. The cause of enuresis is still not exactly clear. There are theories that claim that the disease occurs against the background of a traumatic situation, as a result of autonomic disorders, or has a hereditary factor.
Traditional methods of treatment
It is permissible to use folk remedies to treat any disease only after consultation with your doctor. This therapy should not be the only treatment option. It serves as an addition to the main plan.
For more information about the treatment of stress urinary incontinence, watch the video:
Herbal folk remedies help improve the patient’s general condition and reduce the severity of symptoms. From plants you can use:
- nettle;
- chicory;
- marshmallow root;
- yarrow;
- centaury root;
- rose hip;
- sage;
- St. John's wort;
- Bay leaf;
- plantain.
St. John's wort decoction
To prepare, you will need to take 50 g of St. John's wort and pour it with a liter of boiling water. Leave the mixture for 4 hours. There are no restrictions on the use of this product.
Decoction of bay leaves
Add 3-4 bay leaves to 250 ml of water and boil over medium heat for 15 minutes. Then cool the finished broth. Take 100 ml three times a day.
Collection with nettles
Mix 100 g of marshmallow root and nettle. Add 70 g of yarrow. Take 2 tablespoons of the resulting dry mixture and pour into a thermos. Add a liter of boiling water. Leave for 8 hours so that the herb releases all its beneficial substances. Use 4-5 times a day in small portions.
Diagnosis and treatment
In addition to collecting general symptoms and diary indicators, which the patient should keep before visiting a doctor, other diagnostics will be needed. In particular, a physical examination is carried out, where the abdominal organs are examined by palpation for the possible presence of a hernia, ascites, etc. The rectum, vagina, and external genitalia are examined. Neurological diagnostics are used to study the functionality and general sensitivity of the legs.
Blood and urine samples are taken for analysis to identify or exclude diabetes mellitus, the presence of infections in the body, and kidney disease. As a diagnosis, a test called the cough method is performed, in which the patient is asked to drink a liquid and cough after a short period of time. Ultrasound and cystometry are also performed.
Conservative therapy is recommended for all women who went to the hospital at an early stage of the disease. In addition to the use of medications, it consists of changing lifestyle, giving up bad habits (drinking alcohol, smoking, overeating). Overweight people will need to start eating right, eliminating all unhealthy foods, coffee and strong tea from their diet.
Treatment of stress urinary incontinence in women is carried out by training the muscles of the pelvic organs. In particular, Kegel exercises are used, which are recommended for all older women, especially pregnant women and those who have given birth. The simplest exercise is to sit on the floor or a chair (you can squat) and try to relax the muscles in this position, as when urinating, and then immediately tense. The number of repetitions can be unlimited.
While performing the exercises, you can alternate the force of squeezing and unclenching the muscles, pushing, simulating the birth process. This must be done at least 3 times during the day. Since they are performed absolutely simply and unnoticed by others, they can be performed at home, in the office or while traveling on public transport. During urination, you should try to hold the stream of urine, then relax the muscles and empty the bladder.