There are various types of tumors in the central nervous system. Their source is various fabrics. It is known that the main tissue of the nervous system is neurons. Their bodies form the cerebral cortex, or substantia serine, and also lie in the middle of the spinal cord. Their processes – dendrites and axons – form pathways, or white matter.
But, in addition to nerve cells, there are helper cells that perform a connecting and trophic function. They are called glial tissue, or neuroglia, and they make up about half the mass of the entire nervous system. There can be up to 40-50 neuroglial cells per neuron. For example, oligodendrocytes are representatives of oligodendroglia, and astrocytes, which have star-shaped processes, are astroglia.
Astrocytes form the supporting skeleton of the neural network, regulate their nutrition, maintain glycogen reserves, and protect neurons. In general, these are “nanny” cells .
But sometimes it happens that it is from these cells that malignant tumors arise, such as brain astrocytoma. Since there are so many astrocytes, astrocytoma is the most common among all brain tumors.
ICD-10 does not provide separate histological labeling for tumors. Localization options exist . Therefore, the general code C71 is provided for any tumor, and in the case of the presence of any tumor, for example, the cerebral hemispheres or cerebellum, including astrocytoma, the ICD -10 code is set accordingly
Causes
Scientists still cannot figure out why brain cancer occurs. Only factors that contribute to pathological transformations are known. This:
- influence of chemicals (mercury, arsenic, lead);
- smoking and excessive alcohol consumption;
- oncology in the family;
- weakened immunity (especially for people with HIV infection);
- traumatic brain injuries;
- genetic diseases. In particular, tuberous sclerosis (Bourneville disease) is almost always the cause of giant cell astrocytoma. Studies of genes that become tumor suppressors have revealed that in 40% of cases of astrocytomas there were mutations of the p53 gene, and in 70% of cases of glioblastomas there were mutations of the MMAC and EGFR genes. Identifying these lesions will prevent the disease from malignant forms of AGM;
- radiation. Long-term exposure to radiation associated with work conditions, environmental pollution, or even used to treat other diseases can lead to the formation of brain astrocytoma.
Of course, if a person, for example, has been exposed to radiation, this does not mean that he will necessarily develop a tumor. But, a combination of several of these factors (work in harmful conditions, bad habits, bad heredity) can become a catalyst for the onset of mutations in brain cells.
Forms of the disease
Depending on the cellular composition, astrocytomas are divided into several types:
| Anaplastic astrocytoma. | A malignant tumor (III degree of malignancy), characterized by the absence of clear boundaries and rapid infiltrative growth. It most often affects men over 30 years of age. |
| Piloid astrocytoma | The tumor is benign and has distinct and clear boundaries. It is formed mainly in the area of the brain stem or cerebellum. Children are at risk. The prognosis for treatment of this form of tumor is always favorable, since it responds well to treatment and without complications. But late seeking help increases the likelihood of its degeneration into malignancy in 70% of cases. |
| Glioblastoma | The malignant and most dangerous type of astrocytomas (IV degree of malignancy). It has no boundaries, quickly grows into surrounding tissues and gives metastases. Typically observed in men between 40 and 70 years of age. |
| Fibrillar form | This is a benign type of neoplasm, but the possibility of its transformation into a malignant form increases. The tumor has no definition and grows much faster than pilocytic astrocytoma. Therapy, including surgery, does not give a 100% good result. Most often, this form is detected in young people under 30 years of age. |
Well-differentiated (benign) astrocytomas account for 10% of the total number of brain tumors, 60% are anaplastic astrocytomas and gliomas.
Classification
For ease of classification, all brain tumors are divided into types depending on the type of cells from which the cancerous formation originated. In addition, the classification takes into account the localization of the lesion in the brain and the stage of malignancy:
- Grade 1 – pilocytic astrocytomas (including cerebellum), giant cell subependymal astrocytomas.
- Grade 2: fibrillar, gemistocytic and protoplasmic astrocytoma, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma.
- Grade 3: anaplastic astrocytoma, oligoastrocytoma.
- Grade 4: glioblastoma multiforme.
Pilocytic astrocytomas
Pilocytic astrocytoma is a benign tumor in the international classification of glioblastomas. The tumor, as a rule, is small, grows slowly in size, does not affect neighboring tissues due to the presence of a capsule, and rarely provokes the development of symptoms of neurological deficit. Microscopic examination of the tissues of the formation can reveal normal astrocytes without signs of cellular degeneration, united into one node.
Pilocytic astrocytomas are the least aggressive of all types of astrocytomas.
Neoplasms of the piloid type are diagnosed mainly in children and young people under 20 years of age.
Common locations of the lesion are the brainstem, cerebellum, and the optic nerve region. Due to its location, a growing tumor provokes the development of characteristic symptoms:
- Expanding headache in the occipital region due to impaired outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Hydrocephalus in children.
- Jumps in blood pressure, attacks of tachycardia.
- Movement coordination disorder.
- Paresis and paralysis of the limbs, increasing as the formation grows and occurring sporadically.
- Dizziness, imbalance due to damage to the cerebellum.
In children, these types of astrocytomas are mainly localized in the cerebellum.
Piloid astrocytoma, detected in the early stages of development, suggests a complete cure for the disease, provided that the tumor is removed in a timely manner. The prognosis is usually favorable.
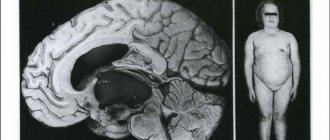
Subependymal giant cell astrocytoma
This type of tumor belongs to benign gliomas. In most cases, the development of education is associated with tuberous sclerosis, a genetic disease characterized by the occurrence of many benign tumors.
Subependymal astrocytoma is located in the retina or along the borders of the lateral ventricles of the brain
Microscopic examination of tissue reveals many astrocytes originating from the subependymal zone of the brain and having large sizes. The tumor is localized mainly in the area of the lateral ventricles of the brain, completely blocking their lumen as it grows. Due to deformation of the ventricles, the disease manifests itself as characteristic pressing headaches in the occipital region due to the development of intracranial hypertension.
The prognosis is favorable if the disease is detected early. Lack of treatment leads to an increase in tumor size and its transition to malignancy.
Fibrillary astrocytomas
Fibrillary astrocytoma of the brain is much more common than other types of gliomas. This tumor is a relatively safe type due to grade 2 malignancy and the possibility of surgical treatment. Histologically, it consists of astrocytes of the fibrillar type, which are enclosed in one large formation of the same structure with the absence of necrotic foci and areas of vascular deformation. When examining a formation under a microscope, its cellular elements are almost no different from healthy ones - they have no signs of abnormal division.
Fluid-filled cysts often form inside a fibrillary astrocytoma - this occurs due to a discrepancy between the mass of tumor nodes and the volume of blood supply to the tumor.
Fibrillary astrocytoma consists primarily of fibrillary tumor astrocytes
Symptoms depend on the location of the tumor. When the formation is located in the thickness of the white matter of the brain, the occurrence of convulsive seizures is characteristic - this is why the disease often begins with causeless epileptic seizures in people who have not previously had brain diseases. As the tumor grows, the symptoms increase - paresis, paralysis, and impaired coordination of movements occur.
The prognosis for early detection of a tumor is favorable, but many factors must be taken into account:
- Size and localization of formation.
- General condition of the patient's body.
- Structural changes in brain tissue.
- Timeliness and completeness of treatment.
The main treatment method for fibrillary astrocytomas is removal - this is possible due to the presence of a clear border; in some cases, chemotherapy and radiation therapy are additionally performed. If the disease progresses, the prognosis is less optimistic.
Gemistocytic astrocytoma
It is characterized by the presence in the thickness of fibrillary astrocytoma of a large number of special cells - gemistocytes, which differ in their intracellular structure.
Protoplasmic diffuse astrocytoma
It is considered a rare type of tumor that consists of astrocytes with thin processes. A characteristic feature of protoplasmic astrocytoma is the presence of multiple microcysts.
Protoplasmic astrocytoma is a rare type of tumor
Pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma
This type of tumor is considered a rare type of disease. Mostly young people are affected. The formation is localized mainly in the cortex and white matter of the brain, often involving the pia mater in the process. Large cysts often form within the tumor. Despite severe cell degeneration, pleomorphic xanthoastrocytoma is relatively benign.
Forecasts are made individually, taking into account many factors. With timely treatment, a cure is possible, but the risk of relapse remains.
Anaplastic astrocytoma
This malignant tumor is characterized by invasive growth with localization of the process in the cerebral hemispheres and cerebellum. It is widely believed that anaplastic astrocytoma is a consequence of malignancy of a previously benign diffuse astrocytoma. There are signs of diffuse growth involving surrounding tissues with severe cellular degeneration. Clinically, malignant anaplastic astrocytoma manifests itself with signs of intracranial hypertension with a rapid increase in neurological symptoms. The prognosis in this case is unfavorable - even with full treatment, life expectancy rarely exceeds 3 years. This is due to the rapid transition of astrocytoma to glioblastoma, which has an extreme degree of malignancy.
Oligoastrocytoma
Oligoastrocytomas are mixed type tumors containing several types of cells. These formations have a third degree of malignancy; they are characterized by rapid growth of the formation with a rapid increase in neurological symptoms. Foci of necrosis and vascular transformations are often observed in the thickness of the tumor. Most often men over 45 years of age are affected. The prognosis depends on many factors, but on average life expectancy is no more than 5 years.
Brain glioma – what is it? This term is used to refer to any tumor of this organ. Brain glioma, regardless of its type, poses a danger to human life. Next, we will learn about one of the forms of tumors in this part of the body.
Symptoms of astrocytoma
All symptoms associated with the development of tumors in the brain are divided into two large groups: general and local. Common symptoms associated with increased intracranial pressure:
- constant headache;
- convulsive syndrome;
- nausea, vomiting in the morning;
- general cognitive impairment (decreased memory, attention, intellectual functions).
Local symptoms are associated with the direct effect of the tumor on brain tissue. Their manifestations depend on the location of the astrocytoma:
- disturbances of speech and its perception;
- problems with sensitivity and movement in the limbs;
- deterioration of vision, smell;
- mood disorders.
Diagnostics
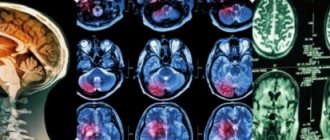
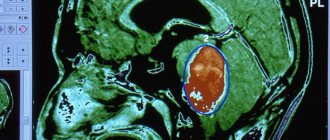
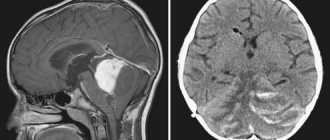
The main way to diagnose a tumor in the brain is to perform a computed tomography (CT) scan or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI). MRI is also used during the operation: this helps to monitor the process of node removal.
Sometimes brain astrocytoma is diagnosed using an additional method - magnetic resonance spectroscopy (MRS). This makes it possible to conduct a biochemical analysis of tumor tissue and identify the state of the tumor.
Recurrence of brain tumors is determined using positron emission tomography (PET).
Diagnostic measures
Today, several methods are used to identify the disease and recognize the stage of the pathology. These include, in particular:
1. Tomography. This type of research is divided into several subtypes. They can be used to diagnose astrocytoma. Tomography happens:
- Magnetic resonance. This study is considered one of the most accurate today. Thanks to this method, a specialist can determine the degree of malignancy - tumor areas will be highlighted in the image.
- Computer. This study creates a layer-by-layer image of all brain structures. Using computed tomography, the structure and location of the tumor are revealed.
- Positron emission. Before the procedure, a small dose of radioactive glucose is injected into the patient's vein. It will be an indicator with which you can easily identify the location of the tumor. Glucose will accumulate in areas of high and low grade tumors. At the same time, the latter will absorb less sugar. Positron emission tomography is also used to evaluate the effectiveness of the treatment used.
2. Biopsy. This method involves taking a fragment of the affected material and examining it. It is a biopsy that allows us to establish a final accurate diagnosis.
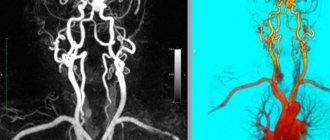
3. Angiography. This procedure involves the introduction of a special dye, which is used to identify the vessels feeding the tumor tissue. This method allows you to plan surgical intervention.
4. Neurological examination. As a rule, this method is auxiliary. A neurological examination consists of assessing brain function and the correctness of reflexes.
Treatment of brain astrocytoma
Depending on the degree of differentiation of brain astrocytoma, its treatment is carried out by one or more of the following methods: surgical, chemotherapy, radiosurgery, radiation.
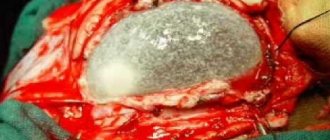
Stereotactic radiosurgical removal is possible only for small tumor sizes (up to 3 cm) and is performed under tomographic control using a stereotactic frame placed on the patient’s head. For cerebral astrocytoma, this method can be used only in rare cases of a benign course and limited tumor growth. The extent of surgical intervention performed by craniotomy depends on the nature of the growth of the astrocytoma. Often, due to diffuse growth of the tumor into the surrounding brain tissue, radical surgical treatment is impossible. In such cases, palliative surgery may be performed to reduce the size of the tumor or shunt surgery to reduce hydrocephalus.
Radiation therapy for cerebral astrocytoma is carried out through repeated (10 to 30 sessions) external irradiation of the affected area. Chemotherapy is carried out with cytostatics using oral drugs and intravenous administration. It is preferred in cases where brain astrocytoma is observed in children. Recently, active development has been underway to create new chemotherapeutic drugs that can selectively act on tumor cells without having a damaging effect on healthy ones.
Radiation therapy
With this type of exposure, cells that participate in the life support of the neoplasm are affected. At the same time, healthy tissues remain undamaged. Radiation therapy is carried out in courses. This allows you to significantly improve the quality of therapeutic effects. Treatment in this case can be carried out in two ways:
- Internal influence. In this case, special radioactive substances are injected into the damaged tissue.
- External influence. In this case, the radiation source is located outside the human body.
Forecast
Prediction of the disease is made by the doctor based on the following points:
- patient's age;
- degree of malignancy;
- location of the tumor;
- how rapid is the transition from one stage of the disease to another and whether it took place;
- number of relapses.
Based on the overall picture, the specialist makes an approximate prognosis for cerebral astrocytoma. In the first stage of the disease, the patient’s life expectancy will be no more than 10 years.
With the subsequent transition from a benign tumor to a malignant one, the life time will decrease. In the second stage, it can be reduced to 7-5 years, in the third - up to 3-4 years, and in the last stage, the patient can live more than a year if the clinical picture is positive.
Stages of pathology
There are four main stages of the disease and, accordingly, 4 forms of tumor:
- Pilocytic astrocytoma of the brain. The prognosis of this pathology is most favorable, since this neoplasm is considered benign. However, if you do not contact a specialist in a timely manner, the likelihood of this form becoming malignant increases to 70%.
- Fibrillary astrocytoma. This type of tumor is also considered benign. However, at this second stage of the disease, the risk of the neoplasm becoming malignant is even higher.
- Anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain. This is the third stage of the pathology. Anaplastic astrocytoma grows very quickly. Healthy cells are affected by the tumor quite actively. Anaplastic astrocytoma quite often leads to the fourth stage.
- Glioblastoma. This is the last stage of the disease. At this stage, the patient suffers from quite severe headaches. Specialists prescribe very strong painkillers.
It should be noted that at the first stage, tumor cells are practically no different from healthy ones. The same cannot be said when a patient has an anaplastic astrocytoma of the brain. The prognosis for the last two stages is very disappointing. The tissues of the organ can hardly be called normally functioning. There are other types of tumors. These include, in particular, diffuse and piloid astrocytoma of the brain.
Prevention
Taking into account how many causes cause the appearance of astrocytoma, as well as how many people have sought medical help in recent years, it is necessary to pay attention to measures to prevent this disease.
Such preventive methods include:
- Strengthening immune defense.
- Elimination of stressful situations.
- Accommodation in environmentally safe areas.
- Proper nutrition. It is important to exclude smoked and fried foods, fatty foods, and canned food. Add more steamed dishes, fruits, and vegetables to your diet.
- Rejection of bad habits.
- Preventing head injuries.
- Regular medical examinations.
If a brain astrocytoma is detected, do not despair and give up. It is important to remain optimistic, believe in a good result, and have a positive attitude. Only with such a positive attitude and faith can you defeat oncology.