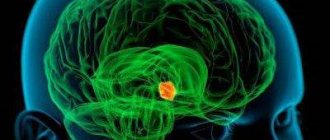
Glioblastoma is the most dangerous malignant tumor affecting the brain. This type of cancer is extremely life-threatening. Even if treated, the prognosis for glioblastoma remains disappointing. Life expectancy for glioblastoma is short. But the right therapy can improve the patient’s condition and give him some more precious time.
How long people live with glioblastoma depends on its shape and location, the general health of the patient, concomitant diseases and the quality of therapy provided.
What is glioblastoma
Brain cancer is practically a death sentence for most patients; life expectancy is greatly reduced. The most common location of tumors is the head. Glioblastoma is a malignant tumor of the brain that arises from astrocytes. During the pathological process, their uncontrolled division begins, which complicates the possibility of treatment. The prognosis for such patients is very disappointing. To a greater extent, there is a relapse, after which the patient dies.
The localization of glioblastoma of the brain is limited to the nervous system, most often in the frontal region and the left temporal lobe of the brain. Sometimes a tumor can be diagnosed in the area of the cerebellum and brain stem. Large cysts of the cerebral vascular plexuses often appear in tumor tissues. Even at the earliest stage of the disease, the impact on the centers responsible for mobility and speech can cause difficulty speaking, fainting and shifts in coordination of movements.
Non-standard approach to the treatment of glioblastoma
In addition to the above treatment method, for a disease such as brain cancer, scientists are testing the treatment of glioblastoma with unconventional methods and, according to the latest data, there are good results.
It was established that glioblastoma progresses on blood vessels and nerve endings; scientists created a special tube up to 6 mm long, on which they recreated the semblance of nerve endings and blood vessels, and a special gel was pumped into its core. Brain cancer mistakes artificial cells for real ones and begins to progress on the tube, and actually moves on its own towards its death.
During testing on rats, scientists found that more than 90% of cancer cells were localized precisely on this tube, which was previously implanted into the brain of a sick animal. No more than six months passed after the implantation operation.
Causes
The causes of glioblastoma have not been fully studied. There is a possibility that the development of pathology is influenced by the electromagnetic field emitted by mobile devices. The formation of glioblastoma can be caused by excessive alcohol consumption, addiction to drugs and nicotine.
Statistics show that, like other cancers, brain tumors are more common in people with a genetic predisposition. Often this can be inherited from close relatives. Also, a neoplasm develops in the brain of people who have acquired or congenital genetic defects.
There are other possible reasons for the development of glioblastoma:
- poor nutrition;
- environmental pollution;
- radioactive influence;
- chemical influences, etc.
More often, brain tumors occur in people:
- at the age of 40-60 years (men more often than women);
- with genetic pathologies;
- in contact with chemicals;
- with chronic viral infections.
Also, tumor growth can occur after TBI. All of the above reasons are not completely reliable, since there are patients in whom these factors were not found.
At-risk groups
- Men over 40. Statistics show that men from 40 to 60 years old suffer from this disease much more often than at any other age. In the second half of humanity, glioblastoma is much less common;
- Presence of astrocytomas. More than 10% of diagnosed fibrillary and pilocytic astrocytomas, which are not very malignant, subsequently degenerate into glioblastoma;
- Neurofibromatosis. Most often, glioblastoma occurs in patients who suffer from neurofibromatosis. The neoplasm occurs as a result of disorders at the genetic level;
- Ionizing radiation and exposure to polyvinyl chloride. Other chemicals also have a very negative effect on clial cells, which leads to malignant formation;
- Viral diseases;
- Hereditary predisposition;
- Penetration of infected cells into the cerebral cortex through the circulatory system.
Today it is difficult for specialists to indicate the main causes of this disease, but in any case, cause-and-effect relationships with the listed factors have been scientifically proven.
Kinds
Based on some characteristics, the tumor has several types:
- Giant cell glioblastoma is less dangerous. It has special reagents in the form of large atypical cells containing several nuclei.
- Polymorphic cell glioblastoma has large cells containing one nucleus. Tumor cells can be detected using cytological techniques.
- Glioblastoma multiforme is characterized by the presence of a large number of different cells and tissues. It usually occurs in the cerebral hemispheres, but sometimes the spinal cord system is affected.
- Isomorphic cell glioblastoma is a rare case when the neoplasm cells are almost identical, with minimal differences in the shape of the nuclei and their sizes. Most often round or oval in shape.
We recommend reading Hemangioma on the face in children and adults - diagnosis, treatment, prognosis
How malignant a tumor is is determined by the maturity of the cells.
Glioblastoma multiforme
This type is considered the most dangerous and malignant. Glioblastoma multiforme in the brain contains not only randomly located cells of different sizes, but also areas of proliferation of brain blood vessels. With a more detailed study, foci of necrotic damage can be detected. This type is the most severe, grade 4, and is practically incurable.
Classification
In accordance with the characteristics of the pathology, experts distinguish three forms of glioblastoma of the brain. This allows you to establish a more accurate diagnosis and determine the correct course of therapy.
Multiform
In the medical literature it is called multifocal. A feature of this form is that neoplasia cells acquire increased plasticity.
As the tumor increases, the lumen of the blood vessels decreases, which leads to the spread of tissue necrosis and hemorrhages.
Glioblastoma multiforme also contains many small vessels inside.
Gliosarcoma
When carrying out instrumental and laboratory diagnostic methods, the presence of elements of sarcoma is established.
Specific symptoms arise at the second stage, as a result of which identifying the disease at the first stage of development is difficult.
Giant cell
This form got its name due to the fact that the tumor contains large multinucleated cells.
Degrees
The malignancy of the tumor is determined by histological analysis of the affected tissue.
Glioblastoma is divided into four stages of the disease:
- Stage 1 occurs without any signs of malignancy. Gradually, the neoplasm affects healthy cells, but is still subject to treatment.
- At stage 2, atypical signs appear, but tumor growth does not accelerate. With timely diagnosis, the progression of the disease to the next stage can be prevented.
- Stage 3 is characterized by emerging necrosis. The tumor grows together with the brain tissue and develops very quickly. Even if the surgery is successful, there is no guarantee of a complete recovery. There is a high probability of relapse.
- Glioblastoma grade 4 is characterized by rapid growth and severe progression. No pills can help you recover. The tumor can no longer even be surgically removed, as this can aggravate an already difficult situation, and survival rate is minimal.
If the first suspicion of glioblastoma of the brain arises, it is necessary to undergo examination in the hospital as soon as possible.
Diagnostics
During the initial stage, the tumor is not large in size, so it is very difficult to determine. Glioblastoma may not manifest itself in any way until its size begins to put pressure on the structure of the brain, disrupting its normal functioning. Sometimes glioblastoma is detected during a routine examination that has nothing to do with head diseases.
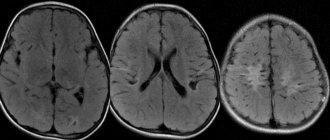
When diagnosing glioblastoma, MRI and CT are the most effective. These results are extremely important, since magnetic resonance imaging allows us to determine the size, location and boundaries of the tumor. Tomotherapy can also be performed. Using a biopsy of tumor particles, the doctor can obtain an accurate clinical picture. But if the tumor is located in a hard-to-reach area, it is not always possible to perform a biopsy.
We recommend reading: Subserous uterine fibroids - symptoms, signs and treatment
With qualified treatment, glioblastoma detected in the early stages can still be treated and the patient has a chance to survive. Treatment is prescribed by the doctor based on diagnostic studies and test results. The oncologist may prescribe medications or surgery. The course of therapy for each patient is selected individually, based on his age, general health, type of tumor and stage of its development. Its size and location also play an important role.
Symptoms
Symptoms of glioblastoma primarily depend on the location and can manifest in different ways. Symptoms are classified according to their nature: focal and cerebral. General cerebral signs of the disease are also divided into vestibular and hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome.
In the latter case, cancer has the following symptoms:
- nausea and vascular constriction;
- drowsiness;
- fatigue;
- loss of appetite;
- excruciating headache.
Gradually, a patient with glioblastoma's blood pressure decreases. The pain becomes stronger, a person feels it during physical activity, sudden movements, coughing and sneezing. Antispasmodics in this case do not help get rid of pain symptoms. As the tumor progresses, it destroys brain tissue, veins and blood vessels.
When the tumor affects the posterior cranial fossa, the pons or the cerebellar peduncles, the patient’s vestibular apparatus deteriorates. This syndrome is characterized by impaired coordination and frequent dizziness. The patient experiences many disorders, including:
- deterioration of speech and vision;
- short-term memory loss;
- difficulties in performing difficult tasks;
- clouding of mind;
- degradation of mental abilities;
- tactile and auditory hallucinations.
The patient can smell the faintest odors, hear unexplained sounds and feel touch. Due to severe headaches, a hemorrhagic stroke is possible. Because it is caused by bleeding in the brain, the consequence of a hemorrhagic stroke is often death.
During the last stage of brain tumor development, the following symptoms occur:
- headache;
- loss of sensation in the limbs;
- paralysis;
- epileptic seizures.
These symptoms appear due to the uncontrolled growth of the tumor. This is a very serious condition for the patient, requiring immediate hospitalization. If the patient can no longer be treated through surgical removal or drug therapy, oncologists have no choice but to send him home, where he may die suddenly. Once the diagnosis has been made, treatment begins immediately.
Treatment
Treatment of glioblastoma of the brain is possible using the following methods:
- Surgery is the most radical way to cure cancer. For the operation to be effective, the patient is injected with a product that allows the borders of the tumor to be colored. Surgery does not provide a 100% guarantee that the disease will be completely cured, since complete elimination of the tumor is very rare, and if the cancer cells are not completely removed, the remaining ones will grow again and affect the brain cells. In this case, it is impossible to say exactly how many days they live after surgery, since brain swelling is possible after removal of the tumor.
- Radiation therapy for glioblastoma - used on all tissues along with chemotherapy. Ionizing radiation destroys cancer cells within a month. The main goal is to completely suppress the growth of neoplasm.
- Radiological treatment is a type of radiation therapy aimed at the lesion.
- Traditional medicine is treatment with folk remedies, which can provide an additional effect to the main drug treatment in the early stages.
We recommend reading: Prognosis for rectal adenocarcinoma and its treatment
The course of treatment for this tumor is usually combined, but in the case of stage 4 glioblastoma of the brain, treatment will most likely be unsuccessful.
If signs of a tumor are detected in a timely manner, you should immediately go to the hospital; treatment at home with unconventional methods can only worsen the situation.
Chemotherapy
Treatment of glioblastoma with medications that contain temozolomide is usually carried out after neurosurgical operations as a prevention of tumor recurrence. Most often prescribed together with radiation therapy. The course of chemotherapy treatment for glioblastoma of the brain consists of 42 days.
With further progression, treatment with the drug is stopped.
Neurosurgery
Treatment of glioblastoma involves complete surgical removal of the tumor. A person with this diagnosis can live longer only if the primary tumor is removed. After all, the effect of further procedures will be noticeable only in case of successful neurosurgical treatment. Therefore, the first stage of treatment for the disease is to remove the tumor.
Previously, there were more difficulties with the operation. Even experienced neurosurgeons were unable to remove the tumor due to the fact that it grows into the brain tissue and entangles vital centers of the brain. Therefore, tumor particles remained, and the operation was stopped without obtaining the desired result.
Today, surgery is performed using aminolevulinic acid, which illuminates areas of the brain affected by malignant cells. This allows doctors to see the boundaries between healthy and diseased tissue. This technique makes it possible to successfully remove even previously inoperable tumors.
Consequences and prognosis
The survival prognosis for glioblastoma, even in treated patients, is poor. Only 10% of patients with this diagnosis can live for about 2 years. Even after the elimination of the tumor, relapse after complete removal of the tumor is very likely. If a patient has grade 4 glioblastoma of the brain, life expectancy remains minimal. Even after a successful operation, the patient will not live even five years.
In order not to die from a brain tumor, you should immediately go to the hospital at the first signs of this disease and undergo a thorough examination. To understand how people die with glioblastoma, it is enough to imagine that people live out their last days in agony, often completely paralyzed with impaired mental activity.
Combination therapy
After the glioblastoma is removed, other types of treatment are prescribed. Radiation therapy for glioblastoma is usually prescribed over a course of 6 weeks. The patient undergoes the procedure 5 times a week. For the entire treatment, he receives a radiation dose of 60 gray. This is the maximum allowable amount, which allows you to destroy malignant cells without serious complications for the patient’s body.
In addition to radiation, the drug Temodal, designed specifically to eliminate tumors, is also prescribed. It is administered to the patient every day. The medicine is prescribed 4 weeks after radiation therapy. Take the drug for five days and take a break for 23 days. To achieve the desired effect, at least six courses may be needed.