Comprehensive rehabilitation is designed to help restore health after a traumatic brain injury, including:. But few people know that the third most common cause of death in Russia is traumatic brain injury. Most often they are received by victims of road accidents, but in some cases the cause of the tragedy is extreme sports or aggressive actions on the part of others. Serious brain damage often becomes a turning point in the fate of a person and his loved ones, even if doctors managed to save the patient’s life.
Signs of injury
Since a concussion occurs as a result of a traumatic situation, and its symptoms are pronounced, the disease can be recognized without much effort. Having received a blunt injury, as a rule, adults lose consciousness, after which they experience memory gaps and several other characteristic symptoms:
- clouding of consciousness;
- feeling of nausea;
- restless sleep;
- headache.
It is more difficult to determine the presence of a concussion in young children, since loss of consciousness does not occur in them, and other signs are not much different from other pathologies:
- restless sleep;
- tearfulness;
- regurgitation during feeding.
The situation is further complicated by the fact that the signs of more complex traumatic brain injuries (brain contusion) in children appear in exactly the same way.
Any injury, including concussion, leads to the development of catabolic reactions. This means that the need for proteins and amino acids increases significantly. If the necessary protein nutrition is missing, a person loses weight and his general condition worsens. In especially severe cases, protein structures in the body are affected.
Stages
During the course of the disease, it is customary to distinguish 3 basic stages (periods):
- The acute period, lasting from the moment of traumatic influence with the development of characteristic symptoms until the patient’s condition is stabilized, in adults, on average, from 1 to 2 weeks.
- Intermediate – the time from stabilization of impaired functions of the body in general and the brain in particular, to their compensation or normalization, its duration is usually 1-2 months.
- The long-term (residual) period in which the patient recovers or the emergence or progression of newly emerging neurological diseases caused by a previous injury (lasts 1.5–2.5 years, although in the case of progressive formation of characteristic symptoms, its duration may be unlimited).
In the acute period, the rate of metabolic processes (the so-called metabolic fire) in damaged tissues increases significantly, and autoimmune reactions are triggered in relation to neurons and companion cells. Intensification of metabolism quickly leads to the formation of energy deficiency and the development of secondary disorders of brain functions.
The intermediate period is characterized by the restoration of homeostasis either in a stable mode, which is a prerequisite for complete clinical recovery, or due to excessive stress, which creates the likelihood of the formation of new pathological conditions.
Long-term well-being is purely individual and is determined by the reserve capabilities of the central nervous system, the presence of pre-traumatic neurological pathology, immunological characteristics, the presence of concomitant diseases and other factors.
The main symptoms of a concussion are:
- a person loses consciousness for a certain period of time;
- there are injuries on the head, bleeding from the nose or ears;
- when the victim comes to his senses, he may complain of a feeling of nausea and dizziness;
- there is a disturbance in the functioning of the vestibular apparatus, deterioration of coordination, drowsiness;
- the person turns pale and sweats;
- the reaction to external stimuli becomes slower.
1st degree. Fainting lasts a short period of time, 2-5 minutes. There may be no loss of consciousness. After 15-20 minutes the patient feels better; mild nausea may occur. An unstable pulse and increased breathing may not be caused by internal damage, but by a stressful state.
2nd degree. Loss of consciousness can last from 10 to 20 minutes. The patient’s pupils are of different sizes; it is difficult for a person to concentrate his gaze on an object. A headache appears and convulsions may occur. The victim answers questions inappropriately, his speech is incoherent, and his time orientation is disturbed.
3rd degree. Fainting may take 30 minutes to an hour or more. A coma may develop. Short-term memory loss occurs when a person does not remember the period of time preceding the injury. The symptoms of the second stage include severe headache, tinnitus, bleeding from the ears and nose. Patients complain of increased sensitivity to light and noise.
The manifestation of symptoms depends on the age of the victim. Children under one year of age may not lose consciousness after an injury, but they experience a sharp pallor of the skin, increased heart rate, and drowsiness. Mature people most often lose consciousness even with a mild or moderate concussion.
What is harmful during a concussion?
In case of a concussion, the doctor prescribes bed rest and a diet consisting of easily digestible food. In this case, it is best to eat fresh foods, boiled or steamed. Also, do not overeat, so as not to further burden the body.
- For concussions, it is useful to take B vitamins, as they normalize the functioning of the nervous system. They are found in liver, pork, nuts, asparagus, potatoes, oysters, egg yolks, buckwheat, legumes (beans, peas), brewer's yeast, whole grain bread, milk and fish.
- To fully absorb B vitamins, the body must have iron. Its sources are buckwheat, oatmeal, barley, wheat, legumes, spinach, liver, dogwood, poultry meat (pigeons, chicken).
- In addition, poultry meat also contains lecithin, which normalizes brain function. It is also found in eggs, liver and soy.
- During this period, it is useful to consume vegetable and cereal soups with fish or meat broth, borscht, rassolnik or beetroot soup, as they improve digestion.
- To maximize the enrichment of the body with vitamins and beneficial microelements, it is necessary to consume vegetables, fruits and herbs.
- During a concussion, the diet depends entirely on the medications taken. For example, if a patient is prescribed diuretics, you need to increase the amount of potassium-containing foods you consume. These can be dried apricots, dairy products, baked potatoes, different types of nuts, legumes, raisins, prunes, seaweed.
- It is useful to consume milk and dairy, as well as fermented milk products, also because they contain calcium, which improves immunity and has a positive effect on metabolic processes in the body.
- It is very important to eat fish regularly, as it contains Omega-3 polyunsaturated fatty acids.
- Eating foods with vitamin C helps the body fight stress and improves its overall condition. Sources of this vitamin are rose hips, black currants, sweet peppers, citrus fruits, honeysuckle, cabbage, viburnum, rowan, and spinach.
- Also, to normalize brain function and protect it from stress, you need magnesium, which is found in buckwheat, barley, oatmeal, millet, various types of nuts, seaweed, and legumes.
- You can add honey and dried fruits to your diet, as they contain glucose, which is necessary for the functioning of all cells of the body, including brain cells.
- To enrich the body with fats, it is better to use nuts and vegetable oil, such as olive.
A concussion is associated with enormous stress. Therefore, to support brain function, you need to include drinks from medicinal plants in your diet. They are prepared and consumed like regular teas. You can drink them after permission from a neurologist. Doctors recommend that patients take medicinal decoctions.
Soothing tea. It is prepared from lemon balm, fireweed, valerian root, birch leaves and St. John's wort. Per liter of medicine you need 3 tablespoons of the indicated components, which are selected in equal quantities. You need to consume it half a glass four times a day for 14 days.
For concussions, it is recommended to drink elecampane tea with myrtle. For 2 cups of boiling water, take a tablespoon of the mixture. You need to drink a glass of it twice a day.
For insomnia, it is recommended to include mint and cinnamon in your diet. A delicious soothing infusion is prepared from them. To get it, you should take a tablespoon of the indicated components and pour a liter of boiling water over them. Tea is infused in a thermos. Drink it half a glass up to 6 times a day.
To relieve the symptoms of a concussion, tea is prescribed from a collection of medicinal plants, which are taken in equal proportions: lemon balm, plantain leaves, nettle, mother grass, clover (flowers), mullein, rose hips, wild rosemary, currant branches.
To prepare the drink, brew 2 tablespoons of the mixture in a liter of boiling water using a water bath. Take it three tablespoons three times a day. If the general condition worsens, the portion of the drink increases.
In case of a brain injury, alcohol is primarily harmful. Neurologists advise excluding it for at least a year. No alcohol-containing drinks should be present in the diet, because they cause excessive stress on the brain.
During recovery from injury (at least six months), the following are strictly not recommended for use:
- Salty and spicy food. Eating these foods causes disruption of water and salt balance.
- Smoked foods, since they provoke stress on the brain affected by a concussion. Fried food has the same effect.
- During the period of treatment after a concussion, you should avoid foods based on margarine and mayonnaise.
- Dark chocolate with a high cocoa content should be avoided. Confectionery products are best consumed in reasonable quantities.
- If you have a concussion, it is important to give up strong tea and coffee. The caffeine contained in these drinks increases pain in the head and increases blood pressure.
Although a concussion is not accompanied by damage to the substance and structure of the organ, it leads to a disruption in the functioning of neurons, which affects the general condition of a person. As with any injury, in case of a concussion, a set of therapeutic measures is prescribed, including a certain nutritional system.
B vitamins benefit the body weakened by injury. They are found in the following foods: egg yolk, oysters, liver, legumes, buckwheat, pork, nuts, potatoes, fish, whole grain bread, milk.
In order for vitamins to be better absorbed, it is necessary to include iron-containing foods in your diet: chicken, legumes, spinach, barley, wheat, liver, oatmeal. Foods such as poultry, soy, liver and eggs also contain lecithin, which promotes normal brain function.
All microelements important for the body are found in vegetables and fruits.
Calcium, which improves metabolic processes and strengthens the immune system, is found in dairy products.
Fish provides the body with Omega-3 fatty acids, so it should also be included in a regular diet.
To restore the body's strength after stress, foods with vitamin C are required. Citrus fruits, spinach, viburnum, black currants, and cabbage contain it.
Magnesium improves brain functioning and protects it from stress. To obtain it, it is important to eat oatmeal, legumes, seaweed, nuts, millet, and buckwheat.
For smooth functioning of cells, the body needs glucose, which is present in fruits and dried fruits.
Important fats for humans are found in nuts and olive oil, so doctors strongly recommend consuming these products if you have a concussion.
Doctors are unanimous in their opinion and advise excluding the following foods from the diet during a concussion:
- fatty foods, which not only impair blood circulation in the brain, but also lead to gaining extra pounds;
- various spices and seasonings: they are irritants to the nervous system;
- confectionery and various sweets;
- spicy and salty foods;
- alcohol (strictly prohibited in case of injury): it not only destroys neurons, but also has a negative effect on cerebral circulation and the central nervous system;
- strong coffee and tea: they contribute to increased blood pressure.
All of the above products can cause serious harm in case of a concussion. During this period, it is necessary to be especially vigilant about what and in what quantity enters the body.
Proper nutrition is an integral part of injury recovery. It is important to remember that only comprehensive treatment and compliance with all recommendations leads to a quick and complete recovery of the patient. Not only medications and diet are important, but also a good mood, a positive attitude, fresh air and, of course, rest.
A severe concussion requires drug therapy in a hospital, where the patient is under full medical supervision. Only this method guarantees recovery and the absence of any complications.
When a concussion occurs, the clinical picture is similar to signs of severe intoxication. If a person takes the risk of drinking alcohol during treatment, he has a high risk of resuming all these symptoms. The patient may experience hallucinations, irritability, and hysteria. It is not uncommon for simple beer drunk during an injury to cause mental disorders, including delirium tremens, which can occur even when taking a small dose of alcohol.
When the brain begins to recover after a concussion, a small amount of alcohol leads to hypertension, headaches, and sudden changes in mood. Symptoms of injury intensify, the signs become more pronounced, and it often happens that the brain begins to swell. Due to swelling of the brain, the patient may lose consciousness or fall into a coma. Alcohol often causes a stroke during concussion treatment.
Foods you should avoid eating
Experts agreed that it is necessary to exclude some foods from the daily menu in case of a concussion of varying severity. The list of main dishes that you should avoid if you have a concussion includes:
- foods high in fat, which impairs blood flow;
- various seasonings and spices are contraindicated for concussion: they irritate the central nervous system;
- sweets, buns and various confectionery dishes;
- when the “gray matter” is shaken, it is not recommended to eat salty, spicy food;
- alcoholic drinks: they not only contribute to the destruction of neurons, but also have a negative effect on the blood circulation of the brain and nervous system;
- coffee cocktails, strong tea drinks: increase blood pressure.
All of these products can significantly worsen the patient's condition during the recovery period after an injury.
A proper diet for mild concussions is an integral part of a comprehensive recovery. It should be realized that adequate therapy and compliance with all the doctor’s advice leads to the recovery of the victim. It is important not only drug treatment, but also good nutrition, a positive attitude, rest and walks in the fresh air.
Moderate TBI requires treatment in a hospital setting, where the patient is constantly under the supervision of doctors. Only this approach guarantees complete recovery of the body.
Foods to avoid if you have a concussion
With a concussion, the clinical picture is similar to the symptoms of severe alcohol intoxication. If the victim abuses alcohol-containing cocktails during therapy, there is a risk that signs of the pathological syndrome will recur. The patient may experience hysterical attacks, hallucinations, and irritability.
When the “gray matter” begins to recover after the blow, the “recreational” cocktails cause attacks of headaches, hypertension, and sudden mood swings. Symptoms of a concussion intensify, and swelling of the brain is sometimes observed. As a result, the patient may lose consciousness or fall into a coma. Drinking alcohol during therapy often provokes a stroke.
Negative effects of alcohol on the brain
Drinking alcohol for any head injuries is unacceptable, since brain injury is incompatible with such drinks.
Alcohol intake causes increased destruction of brain cells and blood vessels, and also leads to the following possible complications:
- intellectual abilities decrease;
- dementia develops;
- concentration and coordination of movements are impaired;
- chronic migraine occurs;
- I often feel dizzy.
A person who drinks alcohol harms all his internal organs, but intoxication harms the brain to the greatest extent. In people who drink, even without any head injury, alcohol poisons change the structure of nerve cells and lead to disruption of abstract thinking and logic. During an injury, the brain becomes more susceptible to the influence of alcohol. The changes that regular beer would bring about in a healthy person in a year, take about a month in a person with TBI.
Alcohol sticks together red blood cells, and along with them small blood vessels. Due to the formation of blood clots, the blood vessels rupture and stop supplying the brain cells. During a concussion, drinking alcohol is strictly prohibited, since during this period the rate of cell death accelerates several times.
Brain injury causes disruption of the central nervous system. The patient suffers from headaches, nausea, vomiting, and sleep dysfunction. Intense catabolic reactions occur in the affected brain, accompanied by a high need for proteins and glucose.
Since during a concussion, the brain requires a significant amount of energy and building material for cells, with poor nutrition, protein deficiency can develop in the body, manifested in weight loss and increased severity of clinical symptoms of damage to the nervous system.
Therefore, nutrition during relief from symptoms of traumatic brain injury should include easily digestible protein and carbohydrate foods.
Trauma happens:
- mild (symptoms last about 20 minutes, then relief occurs);
- moderate (signs are prolonged, but do not reach the point of loss of consciousness);
- severe (loss of consciousness, memory gaps and other severe signs of concussion).
If you suspect a concussion, it is important to immediately contact a traumatologist or neurologist and follow all the doctor’s instructions.
Classification
Depending on the severity of the damage to health and what the clinical symptoms are, there are 3 degrees of this condition:
- Easy. If a mild concussion occurs, the victim’s consciousness is not impaired, but he may experience dizziness, disorientation, headache, and nausea for 20 minutes. after suffering a trauma. A mild concussion can lead to a slight increase in temperature - up to 38 degrees. Further, general health improves, unpleasant symptoms disappear.
- Average. The person remains conscious, but he exhibits characteristic signs of this condition - nausea, disorientation, headache, dizziness. These signs do not disappear for more than 20 minutes. Brief memory loss may also occur. In most cases, this is retrograde amnesia, where the victim does not remember several minutes before the injury occurred.
- Heavy. There is a loss of consciousness for a short time. This state can last for minutes or hours. The person does not remember what happened - he develops retrograde amnesia. After an injury, unpleasant symptoms may remain with the victim for one or several weeks. During this period, dizziness, headaches, nausea, disorientation, fatigue, poor sleep and appetite are noted.
Traditional methods of treatment
The goal of therapeutic therapy is primarily aimed at stabilizing cerebral circulation, as well as improving the general well-being of the patient.
In the first case, drugs are prescribed to improve the tone and nutrition of cerebral vessels, as well as diuretics. The selection of drugs directly depends on the severity of the injury and the presence of complications.
Stabilization of the condition is based on the elimination of symptoms such as dizziness, anxiety, headaches, insomnia, etc. In this case, sedatives, painkillers, and sometimes sleeping pills are used.
Folk remedies have proven themselves well as auxiliary in the treatment of injury. But they should be taken only after consultation with a specialist: otherwise, you can get the opposite result.
In practice, soothing infusions from herbs such as Ivan tea, lemon balm, valerian root and other herbs are successfully used. They have a sedative effect.
What to eat if you have a concussion
It is beneficial for the patient to eat easily digestible food, fresh or steamed. You can't eat too much because it overloads the nervous system. It is useful to eat the following dishes:
- Foods rich in thiamine or riboflavin. They improve a person’s condition and normalize the functionality of the brain. They are found in nuts, pork, legumes, asparagus, shellfish, eggs, buckwheat, fish and dairy products.
- B vitamins are absorbed even better if the body does not have enough iron. Sources of this microelement are buckwheat and oatmeal, wheat flour products, some vegetables, liver, and game meat.
- It is beneficial for patients to eat foods containing lecithin. It is present in egg yolk, soy, liver.
- Broths, pickles, and beet soups help improve digestion.
- To saturate the body with vitamins and microelements, you need to eat enough greens, vegetables and fruits.
- If the patient is taking diuretics, the menu should include food enriched with potassium. These are dried apricots, dairy products, nuts, raisins, and kelp.
- There should be fish on the menu every day. It contains polyunsaturated essential acids.
- Eating foods with ascorbic acid strengthens the body and helps it fight stress. This vitamin is found in large quantities in rose hips, currants, sweet peppers, lemons and oranges, apples, spinach, and vegetables.
- Magnesium is found in kelp, legumes, and nuts. This substance is necessary for the smooth functioning of the nervous system.
Useful products for bruises
When diagnosing a “gray matter” injury, the patient is prescribed rest, bed rest and nutrition for a mild concussion, including carbohydrate and protein foods. The treatment menu for TBI is reminiscent of the famous Atkins diet.
All meals included in the diet should include:
- Boiled.
- Fresh.
- Steamed products.
- Vegetables, meat, fish, baked in the oven.
Healthy foods necessary in the diet
During the treatment of a bruise, it is recommended to take B vitamins, which have a beneficial effect on the nervous system. These beneficial substances are found in foods such as:
- asparagus, liver;
- seafood;
- for concussions, eat eggs and legumes;
- nuts, buckwheat;
- lean fish, dairy products.
We suggest you familiarize yourself with what will happen to the body if you drink 3 bottles of beer every day for a month
To quickly absorb an element of group B, you should supplement your diet with food containing iron: spinach, legumes, various cereals, meat.
It is recommended to eat chicken and turkey every day - their fillet contains lecithin, which has a beneficial effect on the brain center. This substance is also present in pork liver and soy. It is better to supplement the diet with low-fat vegetable soups, beetroot soups, solyanka, borscht - anything that speeds up the digestion process.
The body needs to be given maximum support; it requires a lot of minerals and nutrients contained in fruits and fresh vegetables.
What's the forecast?
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=Y9PjC7tpDvk
If the patient follows the doctor’s recommendations and instructions, then everything ends in a complete recovery. Residual symptoms such as dizziness, fatigue, and insomnia may persist for several months. Then they gradually decrease until they disappear completely.
If there are concomitant pathologies and medical recommendations are not followed, as well as with severe injuries, there may be complications in the form of VSD and even epileptic seizures, especially if alcohol habits are present.
First aid
If a concussion does occur, you must adhere to the following algorithm of actions. What to do if you have a concussion.
The first action is to call a medical ambulance. First aid for a concussion is to lay the patient down, with the head on an elevation, and do not allow the victim to fall asleep, eat or drink. It is strictly forbidden to suddenly move or transport the patient; you should also not give medications without prior examination by a medical professional.
It is better to unbutton the clothes on the patient’s body so that nothing restricts breathing, do not create a crowd, in order to ensure normal access of oxygen to the victim. Ensure normal patency of the upper respiratory tract. If the patient is unconscious, to ensure breathing, you should turn your head to the side and stick out your tongue.
If for some reason it is not possible to call medical help and it is necessary to transport the patient yourself, transportation is allowed in a supine position in the back seat. In order to bring the victim to consciousness, you can use a piece of cotton wool moistened with a few drops of ammonia.
In this case, first aid for a concussion will not have a positive result. This situation requires prompt provision of assistance by medical workers. In a medical institution, the necessary examination is carried out; if the diagnosis is confirmed, only neurosurgical intervention can help the patient.
After examining the victim, first aid should be provided for a concussion. If there are wounds or abrasions on the patient’s head, they need to be treated, carefully washed from dirt with an antiseptic (septomirin, miramistin), and the edges lubricated with iodine.
After calling a doctor, place the injured person, if spinal injuries are excluded, on the right side. The left arm and leg can be bent at an angle of 90 degrees. You need to raise your head a little. The victim should not sleep for at least an hour until doctors arrive if he is conscious. The patient is not recommended to eat, but can drink a limited amount of water.
If the patient is unconscious, with first aid his head is thrown back and his face is turned to the ground. With this position of the body, air freely enters the lungs, the tongue does not sink, and mucus and blood do not enter the respiratory tract. In case of vomiting, the liquid will come out without entering the internal organs.
A cooling compress is placed on the affected area of the head. Special “snowflakes” or frozen food products are used. The best option is to use a package of sour cream from the refrigerator, wrapped in a handkerchief, for first aid.
If it is not possible to wait for doctors to arrive on site, the victim must be taken to the hospital on his own. To do this, the person is placed on a hard horizontal surface. It is advisable to avoid unnecessary shaking during transportation.
If a person is injured and is unconscious or shows signs of disorientation, an ambulance should be called immediately.
- The unconscious victim must be laid on his right side, with his legs and elbows bent and the surface hard. The head should be tilted back and turned towards the ground to ensure good air flow and to prevent choking when vomiting. You should not turn the patient over again and try to determine how badly he was injured. It's better to wait for the doctors.
- If a person is bleeding, it should be stopped with a bandage.
- The conscious victim should be placed in a horizontal position and his head should be raised slightly. It is necessary to monitor his condition, since a period of imaginary well-being may be replaced by a sharp manifestation of serious symptoms.
- It is important to see a specialist, even if the injury seems minor.
Nutrition is the key to recovery
If a concussion is detected, especially a moderate or severe one, the doctor prescribes treatment, which includes a number of procedures, the main one being complete rest and lack of stress for the patient. At the same time, he explains to the patient what to eat during a concussion in order to reduce its consequences and achieve a full recovery.
Nutrition for a concussion follows the principles of the “Kremlin diet” and includes the consumption of predominantly protein foods and complex carbohydrates. To restore nerve cells, you need a large amount of amino acids and biologically active substances, which commercial organizations offer to use as supplements, but they can be obtained from regular food.
First, let's highlight dangerous foods and substances that should be completely excluded from the diet:
- alcohol in any doses. It increases the load on the heart and blood vessels, negatively affecting the functioning of the central nervous system. The alcohol ban for the victim must last for a year;
- strong coffee and tea. They excite the nervous system, which only worsens the patient’s condition and contributes to the appearance of headaches. The period of abstinence is about six months;
- fatty foods. A large amount of animal fats not only worsens the condition of blood vessels, forming atherosclerotic plaques, but also helps to gain excess weight, which can easily come under conditions of reduced physical activity;
- confectionery flour products and sweets affect the body similarly to fatty foods;
- spices and seasonings have a stimulating effect on the nervous system, inhibiting the recovery process after a concussion. This also applies to various pickles and smoked meats.
The basis of nutrition should be light food, for the digestion of which the body does not require extra energy. It is recommended to eat it fresh, boiled, baked or steamed. Welcome:
- soups;
- porridge;
- dairy products;
- vegetables and fruits;
- eggs;
- Fish and seafood;
- whole wheat bread.
The first item on the menu can be seaweed - rich in vitamins, minerals and very easily digestible. But it is recommended to eat it in small portions.
The diet for severe TBI must include a large amount of B vitamins, especially B1. They help restore the structure of neurons and connections between them. Sufficient amounts of vitamin B can be obtained from:
- asparagus;
- seafood;
- nuts;
- fish;
- legumes;
- eggs;
- liver;
- milk;
- buckwheat and other cereals.
For better absorption of B vitamins, the diet should contain foods with high levels of iron: spinach, meat, pomegranates, legumes and various cereals. Most meat products contain lecithin, a substance that has a healing effect on the brain. It is found in large quantities in poultry meat, pork liver and soybeans.
In addition, you need to eat foods with high levels of potassium:
- dried fruits: raisins, dried apricots, prunes;
- any types of nuts;
- baked potato;
- legumes;
- dairy products.
The latter, in addition to potassium, contain a large amount of calcium, which is useful not only for the head, but also for strengthening the immune system in general and improving metabolism. Normal metabolism helps to quickly restore brain function and get rid of the consequences of concussion.
Vitamin C must be present in the diet after TBI. It helps reduce the effects of stress from injury and improve the supply of nutrients to the brain. This vitamin is found in large quantities in plant foods:
- bell pepper;
- cranberries;
- spinach;
- cabbage;
- rosehip;
- black currant and others.
It is enough to wash them in clean water and eat them fresh; with strong cooking, vitamin C is usually destroyed. Magnesium, which is found in high concentrations in cereals and milk products, also helps reduce stress.
To supply the brain with sufficient energy, nutrition for a brain injury should include glucose. However, it should be obtained not from sweets and flour confectionery products, but from natural sources. First of all, it is honey and dried fruits. There is a lot of glucose in figs, grapes, dates. A small amount of these healthy fruits per day will meet the body's needs.
You can make the sweet according to a well-known dietary recipe yourself: take equal proportions of dried apricots, raisins, prunes, and walnuts. Wash them and grind them in a meat grinder or blender, mix with honey. In a closed jar, this dessert can be stored in the refrigerator for several months. You can eat several spoons of treats per day, which will provide a sufficient amount of glucose, vitamins and microelements, but will not lead to serious consequences in the form of excess weight.
Among fats, preference should be given to vegetable oils. Nuts also contain enough lipids. Healthy fats, together with vitamin E, restore brain activity, but do not form unwanted deposits on the walls of blood vessels.
It is especially important that the concussion diet be strictly followed in the first weeks after injury. At the same time, it is important to create a balanced menu, which will contain a sufficient amount of all the nutrients needed by the body, without the predominance of any specific foods.
There is no specially designed diet for concussion. However, proper nutrition is a good helper for a quick recovery and restoration of the body’s strength. Vegetables and fruits, steamed or boiled foods are beneficial. It is necessary to refrain from salty foods, fried and fatty foods, strong coffee, chocolate, and tea.
If you are injured, you need to rest more and eat easily digestible food. This includes fresh, boiled or steamed foods. Since movement is limited during this period, overeating should be avoided: this way the body will not be overloaded.
Dangerous products
- Drinking alcohol during a concussion is strongly discouraged by doctors. It increases the load on blood vessels, having a negative effect on the central nervous system. You need to forget about alcoholic drinks for a year after the injury.
- Strong tea and coffee are contraindications. These drinks are famous for their stimulating effect on the nervous system. Along with increased blood pressure, they can increase headaches.
- Fatty foods impair blood circulation and contribute to weight gain. It is also advisable to exclude confectionery and sweets in large quantities.
- Spices and seasonings of various types are irritants to the nervous system. Their use is also not recommended.
In the first months after an injury, you need to be especially vigilant when choosing foods for your table. The diet recommended by your doctor will help you recover faster. It should be noted that nutrition should also be balanced; its insufficiency or excessive consumption of food negatively affects the brain. Therefore, try to plan your diet correctly.
Symptoms and types of concussion
The cause of traumatic brain injury can be blows to the head, sudden movements and unsuccessful falls, leading to internal hematoma. It is quite easy to determine that these actions had consequences in adults. To do this, you need to pay attention to the following symptoms:
- the appearance of nausea and vomiting;
- speech disorders;
- sleep disturbance;
- constant headache and dizziness;
- loss of a sense of space and confusion of thoughts in a person;
- partial or complete memory loss;
- increased sensitivity to sound and light, ringing in the ears and pain when moving the eyes;
- split image, with the patient’s pupils often having different sizes;
- pressure drops appear;
- change in behavior, lethargy, impaired concentration, hand tremors.
It is more difficult to detect a concussion in a small child, since babies do not lose consciousness, and other symptoms are similar to other diseases:
- sleep disturbance;
- anxiety, tearfulness;
- Frequent regurgitation during feeding.
Depending on the severity of the injury, concussion is divided into:
- mild – symptoms last no more than half an hour;
- medium – the symptoms are quite long-lasting, but there is no loss of consciousness;
- severe - there are vivid symptoms, accompanied by complete loss of consciousness.
In adults, recognizing a concussion is usually not difficult, because... after receiving a blunt head injury, they most often lose consciousness, and after it returns, they experience memory loss (amnesia), as well as:
- nausea and vomiting,
- headache,
- confusion,
- sleep disturbance and so on.
It is more difficult to identify a concussion in children under one and a half years old, because... when injured, they never lose consciousness, and the rest of the symptoms are very similar to a number of other pathologies:
- frequent regurgitation when feeding,
- tearfulness,
- sleep disturbance and so on.
The problem of diagnosing a concussion in children is further complicated by the fact that the listed symptoms are also characteristic of a brain contusion - a more severe head injury, dangerous not only to the health, but also to the life of the child.
Types of injury
A concussion can be:
- mild: the main symptoms last 15-20 minutes;
- moderate: symptoms are quite long, but complete loss of consciousness is not observed;
- severe: there is a complete loss of consciousness, amnesia and other pronounced symptoms of a concussion.
At the slightest suspicion of this injury, especially in children, you must immediately contact a neurologist and traumatologist, and then strictly follow their instructions and prescriptions.
Traumatic brain injuries: danger, consequences, treatment
For any head injury, even a minor one, you should consult a doctor. And pay attention to subtle symptoms that may indicate a concussion. A concussion is a form of closed head injury. Most often, this is an easily reversible disorder of brain function, which occurs due to a bruise, blow, or sudden movement of the head. Despite the fact that this injury is called an easily reversible disorder, it can cause serious problems for a person. Therefore, in case of any head injury, it is necessary to provide proper first aid and consult a doctor in time. Mild concussions are often ignored.
Sample menu
During treatment for a concussion, you should eat in small portions several times a day (about 5-6 times). In addition to the main meals, it is advisable to include a second breakfast, an afternoon snack and a second dinner in the daily routine. A sample menu for the day might look like this:
- breakfast: porridge with milk, fruit, weak tea;
- second breakfast: yogurt;
- lunch: vegetable or meat soup, omelet;
- afternoon snack: a handful of nuts or an apple;
- dinner: vegetable salad, rosehip broth, stewed meat with vegetables;
- second dinner: a glass of kefir or a banana.
At home, many patients are lazy to follow a diet and quickly switch to their usual food. However, with such nutrition it is impossible to get good results in the near future. The introduction of “forbidden” foods into the diet should occur gradually after the doctor’s permission.
It is especially difficult to organize proper nutrition for older people and small children, since it is difficult for them to follow a diet. It makes no sense for babies who receive nutrients from their mother's milk to change their diet, but their mothers do. A woman should reconsider her diet, removing harmful foods from it and replacing them with healthy ones as much as possible.
There is no specific diet that describes the list of products that should be included in the menu for a concussion. But there are a number of recommendations that, if followed, will allow for a faster recovery and significantly reduce the consequences of the injury.
Diagnostics and examination
Often people do not understand exactly which doctor to contact if they have a concussion. It is important to note the following: you should contact your doctor immediately. That is, after an injury, it is important to call emergency care, whose specialists will assess the patient’s condition and determine who to take the child to in case of a concussion or where to hospitalize the adult. Such signs should be addressed to neurological specialists.
How to diagnose a concussion? The doctor conducts a survey and examination, paying attention to the characteristic signs of the condition:
- The victim experiences pain when he moves his eyes to the sides; he cannot move them to the most extreme position.
- Immediately after the injury - in the first hours - there is a slight narrowing or dilatation of the pupils. However, they react normally to light.
- There is a slight asymmetry of reflexes - skin and tendon. On the right and on the left they are different. But since this sign is very variable, upon repeated examination the picture may change.
- In the extreme position, slight return movements of the pupil are observed.
- Unsteadiness is noted when a person takes the Romberg position (eyes closed, legs together, arms in front of you).
- Your doctor may notice mild neck tension that goes away within the first three days.
In the process of establishing a diagnosis, a specialist can use the following methods:
- examination, questioning of the patient;
- radiography of the skull bones;
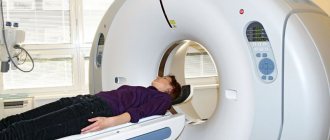
- CT scan;
- MRI;
- electroencephalography;
- neurosonography (children under 2 years old).
Only a doctor can give an accurate answer on what to do in case of a concussion after a thorough examination of the patient, a detailed interview and a diagnostic examination. Even if minor deviations from the norm are recorded in a person’s condition after a head injury, a medical examination is mandatory, this will help to avoid complications.
The doctor conducts a survey using the Glasgow scale. The patient is tested and a score is assigned according to his condition. If the specialist counts 13-15 points, the patient is diagnosed with a concussion.
Additional research:
- EEG – to determine the biological activity of certain parts of the brain.
- To determine whether intracranial pressure has increased, an examination of the fundus is performed.
- Ultrasound of cerebral vessels, carotid artery, and blood vessels of the neck.
- X-ray of the head, cervical spine.
- CT scan.
- MRI of the brain.
Since some symptoms of a concussion may appear in a patient 12-15 hours after a head injury, the patient should be in the hospital for the first 24 hours after the incident. If it worsens, treatment may take several days.
Diagnosis of a concussion is difficult due to the paucity of objective data, the lack of specific signs and is based mainly on the patient’s complaints.
One of the main diagnostic criteria for the disease is regression of symptoms within 3–7 days.
In order to differentiate a possible brain contusion, the following instrumental studies are carried out:
- radiography of the skull bones (no fractures);
- electroencephalography (diffuse cerebral changes in bioelectrical activity);
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging (no changes in the density of gray and white matter of the brain and the structure of the cerebrospinal fluid containing intracranial spaces).
Carrying out a lumbar puncture in cases of suspected brain injury is contraindicated due to lack of information and a threat to the patient’s health due to possible dislocation of the brain stem; the only indication for it is the suspicion of the development of post-traumatic meningitis.