First aid for traumatic brain injury is a necessity that can save a human life. Any injury to the head puts the person in danger; in this case, time is not in the victim’s favor. However, fifteen minutes may pass before the ambulance arrives, and when every minute counts, first aid for a traumatic brain injury becomes a “lifeline for a drowning person.”
TBI can damage soft tissues, the brain, and the bones of the skull. In addition, blood vessels and nerve endings are affected. According to medical statistics, various head injuries occupy first place. Unfortunately, the most common patients in the neurological department are children. Brain injury can lead to neurological impairment, disability and often death, making emergency care for traumatic brain injury one of the most important interventions.
Causes of TBI
Damage to the skull and brain can occur:
- due to falls from height;
- in production;
- at home;
- while playing sports;
- in fights;
- in a car accident.
During road accidents, the most severe and sometimes fatal injuries occur. Mild traumatic brain injuries occur due to falls from low heights and result in minimal or no consequences.
first aid for head injury, life safety consultation on the topic
FIRST AID
IN CASE OF HEAD INJURY
DAMAGE TO SOFT TISSUE OF THE HEAD
A bruise is a mechanical damage to soft tissues without violating their integrity. The main signs of bruises are pain, swelling, and discoloration of the skin. Since there are especially many vessels in the soft tissues of the head, swelling can be very large with bruises.
First aid consists of applying a pressure bandage and applying cold (ice packs, cold water bottles, snow wrapped in oilcloth, etc.).
REMEMBER! PATIENTS WITH HEAD CONTUSES NEED A MEDICAL EXAMINATION TO EXCLUDE SKULL FRACTURES AND CONCUSSION.
Wounds of soft tissues of the head. Their characteristic features are very high bleeding and detachment of soft tissues with the formation of flaps of skin (so-called scalped wounds).
First aid consists of applying a pressure bandage with a sterile bandage (or a clean, ironed cloth if possible).
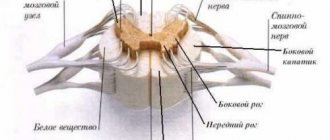
In case of arterial bleeding (blood flows out in a scarlet pulsating stream), a pressure bandage is ineffective. If the stream comes from a wound on the scalp, you can apply a tourniquet (medical rubber or improvised material), passing it horizontally across the forehead and over the ears (Fig.).
Rice. Application of a tourniquet when
stream bleeding from
scalp.
In case of large blood loss with pallor and dizziness, the patient should be placed horizontally on a stretcher (special or improvised) and transported to the hospital.
Particular attention should be paid to the moment when, when a flap of soft tissue is detached, it comes off completely. The torn flap should be thoroughly washed with boiled water (or better, of course, with a sterile solution of sodium chloride), wrapped in a clean (sterile) cloth and sent along with the victim (this flap will then be used by traumatologists to close the defect in the same victim).
CLOSED INJURIES OF THE SKULL AND BRAIN
For a person providing first aid for a closed fracture of the outer part of the skull, the so-called vault, in the absence of skin damage, it is sometimes very difficult to determine whether there is a bone fracture or just a severe bruise of soft tissues. This can only be done accurately enough by a doctor using an x-ray.
At the slightest suspicion of a fracture of the skull bones, assistance should be provided as with an obvious fracture - place the victim on a stretcher without a pillow, put cold on the head and transport him to the hospital.
Those victims who have a fracture of the skull vault combined with brain damage (concussion, contusion, contusion with compression) deserve special attention. They must be given assistance in full accordance with the severity of their condition, including artificial respiration.
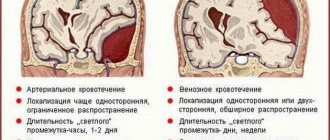
A basal skull fracture is a very severe injury to the central part of the skull. It occurs more often when falling from a height on the head or legs and, as a rule, is accompanied by damage or bruise to the brain. With a fracture of the base of the skull, soft tissue contusions are not detected. A characteristic sign of this is bleeding (or leakage of clear cerebrospinal fluid) from the nose and ears. Early symptoms of this fracture may include facial asymmetry (with compression and damage to the facial nerve), a sharp decrease in pulse (up to 35-30 beats per minute) due to increased intracranial pressure. After 18-24 hours, signs that are very typical for a fracture of the base of the skull appear: extensive, bruising on the eyelids of both eyes in the form of “spectacles” or behind both ears.
First aid. The victim is given a cold pack on his head and transported on a stretcher to the hospital. If the patient is unconscious, then, as is known, his tongue may become stuck and suffocation may occur. Therefore, for transportation you can choose one of the options:
1) lying horizontally on the stomach - then the tongue does not sink, and when vomiting, the masses from the stomach flow freely out and do not enter the respiratory tract. However, it is possible to transport a patient in this way only with sufficient control over him - after all, his face is turned downward;
2) lying horizontally on your back with fixation of the tongue with a puncture (stepping 2 cm from its tip with a safe pin, attach the tongue to a braid or strip of bandage tied around the neck) or a pressure bandage, pressing the tongue to the lower jaw.
When lying on your back, you must carefully monitor the patient and, if you have the urge to vomit, turn his head to the side so that the vomit does not enter the respiratory tract. It must be emphasized that patients with a fracture of the base of the skull, especially if it is accompanied by brain damage and blackouts, need to be very carefully transferred to a stretcher and gentle transportation. If there is no stretcher at hand, you need to build one from available materials (Fig.).
ATTENTION! THOSE CARRYING STRETCHERS SHOULD WALK AT WALKING WALK: THIS WILL PROVIDE GREATER PEACE FOR THE VICTIM.
BRAIN DAMAGE
They occur as a result of a fracture of the vault or base of the skull, and are also observed as an isolated injury during a fall or blow, when the bones of the head are not damaged.
Brain concussion. Its signs are: short-term loss of consciousness, dizziness, nausea, vomiting. Often the victim does not remember the events preceding the injury. Upon examination, the patient is weak, lies motionless and does not perceive his surroundings well.
First aid. Cold on the head and transportation on a stretcher in a prone position.
Brain contusion without compression. Due to the violation of the integrity of the blood vessels, the crushed brain matter is fed with blood: a “bruise zone” is created. With a mild injury, loss of consciousness lasts from several minutes to an hour, and with a moderate injury, up to 3-4 hours. The situation of the patient with a severe injury is especially alarming—consciousness is lost for many hours, and motor agitation develops.
First aid is the same as for a fracture of the base of the skull. Requires rapid transport to hospital.
Brain contusion with compression. Compression of the brain during trauma can occur due to the accumulation of blood in the cranial cavity (rupture of blood vessels), due to the introduction of bone fragments into the brain, or, finally, as a result of swelling of the brain substance. Victims with such compression are usually in serious condition from the moment of injury, but in some cases there is a so-called bright period when the patient is conscious for several hours, but then his condition sharply worsens; In both cases, a crisis can occur every minute, since increasing compression of the brain can lead to respiratory and cardiac arrest at any moment. Particularly reliable and ominous signs of a severe brain contusion with compression are the dilation of one pupil in the patient (this means that the brain is more compressed on this side) and the occurrence of convulsions.
First aid is organized in the same way as for fractures of the base of the skull. However, there are a few special notes to make:
Transporting such a victim to the hospital should be as fast and as gentle as possible.
At any time during transportation, the rescuer must be prepared to begin artificial respiration and chest compressions.
If convulsions occur that cover the entire body, you should insert the handle of a spoon wrapped in a scarf (or any cloth) between the patient’s teeth, otherwise he may bite his tongue.
REMINDER! AN UNCONSCIOUS VICTIM USUALLY HAS A STOPPED TONGUE! CHOKING MUST BE PREVENTED!
OPEN CRANIO-BRAIN INJURIES
The most severe are penetrating wounds of the skull, when a wounding weapon (bullet, knife or other object) violates not only the integrity of the skin and bones of the skull, but also destroys the substance of the brain: compression of the brain occurs due to its swelling, as well as due to the accumulation of blood.
First aid is the same as for closed skull injuries with compression. However, you need to additionally apply a sterile bandage (or ironed fabric) to the wound and make sure that the edges of the wound do not touch the stretcher. To do this, you can place a low roll of clothing under your head (the ends of the roll must be tied to make a ring).
DAMAGE
MAXILLOFACIAL AREA
A facial bruise is characterized by swelling and tenderness at the site of injury, which requires the application of cold and a pressure bandage. It is very important to distinguish a facial bruise from a jaw fracture.
Fracture of the lower jaw occurs most often. It should be remembered that it differs from a bruise in that with a fracture the patient cannot speak, chew or swallow. The mouth is usually half-open and saliva flows abundantly from it - up to 1.2-1.5 liters per day. In addition, the victim's tongue (even though he is conscious) may become stuck (danger of suffocation!). It is not uncommon to find malocclusion and tooth fractures.
A fracture of the upper jaw does not occur as often as the lower jaw. It often occurs as an additional injury following a fracture of the base of the skull. Characteristics of such a fracture are considered to be severe pain when palpating the injury site and a sudden change in the face (disfigurement) due to rapidly increasing hemorrhage in the tissue.
First aid. First of all, you need to prevent suffocation from falling tongue. The tongue must be pulled forward and fixed. After this, remove blood and vomit from the oropharynx with a finger wrapped in some kind of cloth.
With jaw fractures there is very strong jet (arterial) bleeding. As a rule, it cannot be stopped with a pressure bandage. Therefore, the rescuer needs to know the points on the face, by pressing which you can press down the arterial vessels and stop the flow of blood. There are two such points: one slightly in front of the tragus of the auricle (the artery at this point must be pressed against the zygomatic bone, the second - on the lower jaw slightly in front of the anterior edge of the masticatory muscle. If, by pressing hard with your finger on these points, it is not possible to stop the bleeding, you will have to doctor or until delivery to the hospital, press the carotid artery on this side (Fig.). Such patients must be transported in a prone position so that blood does not enter the windpipe. If the bleeding is severe and the patient is dizzy, “flies” fly in front of eyes, and he suddenly turns pale, you need to slightly raise the foot end of the stretcher to increase blood flow to the head and avoid shock.
NOSE DAMAGE.
The nose is often subject to injury, and there may be fractures of the nasal bones, which are always accompanied by bleeding.
REMEMBER! BLEEDING FROM THE NOSE MAY BE A SIGN OF A FRACTURE OF THE BASE OF THE SKULL. This is usually accompanied by loss of consciousness. You can’t put such a sick person in prison!
On the contrary, in case of fractures of the nasal bones, the victim should not be laid horizontally, as blood may enter the respiratory tract. After sitting the patient down, you need to put cold on his nose and slightly tilt his head forward to reduce the pressure in the blood vessels. Usually the bleeding stops after 3-5 minutes. If this does not happen, only a medical professional can stop the bleeding by performing anterior or posterior nasal packing. In any case, if a fracture of the nasal bones is suspected, the victim should be taken to an emergency room or hospital.
EYE DAMAGE
Eye injuries occur very often. They account for about 30% of all human injuries. Eye damage has dangerous consequences and often leads to disability.
Foreign bodies (specks) quite often get behind the eyelids and, in contact with the surface of the eyeball (cornea), cause severe pain and lacrimation. When you blink, the tear washes away the speck and the pain goes away. However, this does not always happen.
REMEMBER! IF A FOREIGN BODY ENTERS, DO NOT RUB YOUR EYE, as the speck can penetrate into the eyeball and cause inflammation!
If there is no foreign body on the lower eyelid, you need to look behind the lower eyelid first. You need to pull the eyelid down with your finger, inspect it and, having found a speck, carefully remove it with a wet cotton wool wound on a match, or the tip of a handkerchief.
If there is no foreign body on the lower eyelid, you need to pull the upper eyelid by the eyelashes and pull it back and forth. If the pain stops, it means the speck has come out; if it doesn’t stop, you need to turn out the upper eyelid. To do this, take the upper eyelid with the index finger and thumb of your right hand and pull it slightly anteriorly and downward. At the same time, the fingers of the left hand should be placed on the patient’s head so that the thumb fits comfortably under the eyebrow on the upper eyelid. Then you need to sharply pull the eyelid forward and upward with your right hand, as if wrapping it around the thumb of your left hand. At this moment, with the finger of your left hand, on which the front part of the eyelid is “wrapped”, you need to move the back part of it downwards - the eyelid should turn out! Immediately you need to press the eyelashes of the inverted eyelid to the eyebrow with the thumb of your left hand and hold the eyelid. The speck from the upper eyelid is removed with a wet cotton swab in the same way as from the lower eyelid.
Wounds to the eyelids (especially through them) can lead to facial disfigurement, especially if the wound is directed perpendicularly or at an angle to the edge of the eyelid. It is very important not to contaminate the wound, as the infection can spread to the entire orbit and further into the cranial cavity. Therefore, if the eyelids are wounded, the skin around the circumference (carefully!) should be lubricated with a 1% alcohol solution of brilliant green (“brilliant green”). Do not wash the wound of the eyelid, tear off or cut off hanging fragments.
If the eyelid is completely torn off, you should not throw it away, but you should wrap it in a clean (preferably sterile) cloth and take it with you to the doctor. If you have a first aid kit at hand, the patient should be given 0.5-1 g of sulfadimethoxine or an antibiotic tablet orally. A bandage is applied to the eye (Fig.) and the victim is sent to the hospital (and, if available, directly to the eye
trauma center).
If an injury or bruise to the eyeball occurs, the patient should be taken to a specialist as soon as possible, since the victim is at risk of blindness in this eye. Therefore, if, after bruising the eye or being injured by a sharp object, vision has sharply decreased, the eye has turned red, pain has appeared, the shape of the pupil has changed, and even more so if a wound to the eyeball is visible, it is necessary to drip a 30% solution of sodium sulfacyl (albucid) into the eye, and if it is not available, drink cold, freshly brewed tea, apply a sterile bandage to the eye without pressure, and quickly transport the victim to an ophthalmologist.
A chemical burn to the eye can lead to blindness, especially if the substance has alkaline properties. If a liquid chemical, such as glue, alcohol, or household chemicals gets into your eye, you MUST FIRST RINSE YOUR EYE WITH WATER. To do this, a lump of clean cotton wool should be immersed in water and, without squeezing, rub it many times from the temple to the nose along the palpebral fissure. This will wash away the chemical. One note: you need to apply the cotton wool, barely touching the eyelids; the patient should not squeeze the eyelids tightly.
It is important to emphasize that if solid chemicals (for example, lime, potassium permanganate, etc.) get into the eye, before rinsing the eye with water, it is necessary to remove all solid particles from the surface of the eyeball and from the inner surface of the eyelids (otherwise they form highly concentrated solution of a chemical substance). After washing the eye, the victim should be immediately referred to a doctor who specializes in eye diseases.
Types of TBI
Traumatic brain injuries can be closed, open or penetrating:
- Closed TBIs include concussion, brain contusion and compression, while there may be minor skin damage on the outside;
- with open injuries, damage to the aponeurosis occurs;
- penetrating injuries, such as a skull fracture, lead to disruption of the integrity of the meninges.
Any injuries are divided into three degrees of severity, depending on how much time the person spent in an unconscious state. In this case, a skull fracture can be linear, comminuted, or multiple according to the location of the fracture line, the number of bone fragments and the fractures themselves. PMP should be provided equally quickly, regardless of what type of damage there is.
Providing first aid to children
Hyperactivity in children often causes skull injuries. If a child injures his head, it is important to immediately call an ambulance for an examination.
Before the ambulance team arrives, the baby must be placed on a hard and flat surface and ensure his immobility. To exclude the possibility of suffocation during loss of consciousness, the child should be turned on his side.
Even if he has no visible injuries after hitting his head, to exclude the possibility of developing serious consequences, he should be submitted to a doctor for a detailed examination and diagnosis.
Clinical picture
The symptoms of each specific type of injury depend on the severity. Each type of injury differs from each other in clinical signs.
Brain concussion
During a concussion, symptoms appear that occur with diffuse brain damage. However, during the CT scan the doctor does not observe any morphological changes.
The main signs of injury are as follows:
- the person faints for a short period (the time of unconsciousness depends on the severity of the injury);
- presence of headache, nausea and vomiting;
- the skin throughout the body becomes pale, and an unhealthy blush appears on the face;
- heart rhythm disturbance occurs;
- There is a violation of coordination of movements and orientation in space.
With a more severe degree of damage, visual impairment, temporary strabismus and nystagmus may occur.
Brain contusion
During a bruise, brain tissue is injured. This occurs when the brain hits the skull during a sudden movement of the head or a fall on the buttocks. Symptoms depend on which lobe of the brain the contusion occurred in, how much brain tissue has been destroyed, and what degree of brain dislocation there is.
Recovery forecast
How successful rehabilitation will be is directly influenced by various factors - the degree of damage, the quality of care provided, the speed of initiation of treatment. Also, the speed of rehabilitation is determined by the age category of the victim - the younger the person, the faster he will recover. The chances of a full recovery even after severe injuries are also increased.
The rehabilitation prognosis is approximately as follows:
- With a mild degree, in most situations the prognosis is favorable. A return to a full life is noted in almost all cases. The danger lies in systematic injuries due to the profession (for example, among boxers). In this case, there is a risk that dementia or encephalopathy will develop over time.
- If the patient is diagnosed with a moderate degree of damage, then it will take about six months to recover.
- In severe cases, death occurs in half of the victims. The second half of patients lose their ability to work. Mental and neurological disorders become a constant companion of life.
Providing first aid
Providing first aid for a traumatic brain injury should be carried out immediately at the scene of the incident, because every wasted minute can cost a person’s life. When traumatic brain injuries occur, first aid should always begin with calling a medical team. The ambulance dispatcher should quickly but clearly describe the situation so that he can send a car equipped with special resuscitation equipment to the scene of the injury.
While waiting for doctors, the person providing first aid performs the following actions:
- Assess the condition of the victim;
- Checks consciousness and tries to bring the victim to his senses;
- Determines the nature of the injury (closed, open);
- Looks for bleeding and liquorrhea;
- Checks heartbeat, pulse and breathing, if necessary, carries out resuscitation measures;
- In case of an open type of injury, cover the wound with a sterile bandage; if this is prevented by protruding bone fragments, then the bandage is placed along the edges of the wound;
- If there is liquorrhea, cover the ears and nose with gauze or bandage tampons;
- If the victim is unconscious, checks the patency of the airways, and removes foreign bodies from there, if any, removes the sunken tongue, places the patient on his right side;
- When the victim is in a conscious state, places him on a hard surface, fixing his neck with rollers on both sides;
- If there are no skin lesions, apply cold to the injury.
Activities before the arrival of doctors
The patency of the upper respiratory tract is maintained by carefully turning the head to the side to avoid inhalation (aspiration) of vomit. In the absence of consciousness, the tongue may sink in - you need to place your palm on the victim’s cheek (the thumb will be on the cheekbone), with the pad of your index finger press on the corner of the lower jaw, which will move forward.
Emergency cardiopulmonary resuscitation is performed only in cases of significant absence of breathing and pulse. The victim should lie on his back, on a hard surface. The approximate ratio is 2 artificial breaths per 10 (for children), 15 (for adults) chest compressions. The condition is checked every 2-3 cycles.
A set of measures aimed at restoring the vitality of the body is called cardiopulmonary resuscitation.
Open TBI is accompanied by bleeding. To stop (reduce) it at the first aid stage, applying a pressure bandage or manually pressing a clean cloth will be sufficient. In an emergency situation, with massive bleeding from a large vessel, it is allowed to press it into the wound with your fingers.
To fix the head and cervical segments, at the stage of pre-hospital emergency care, it is enough to apply an improvised cushion to prevent accidental movements.
Diagnosis and treatment of TBI
After primary care, the victim is taken to the neurological department of the nearest hospital, where an anamnesis of the injury is collected, an X-ray examination, computed tomography, magnetic resonance imaging, lumbar puncture, as well as general tests - blood, urine, blood group and Rh factor - are performed. For minor injuries, some types of examination may not be performed.
If the patient's condition is critical, he is immediately admitted to the intensive care unit for emergency treatment. In case of a concussion, the patient is prescribed bed rest with the use of drugs to restore brain functionality.
It is recommended to refrain from watching TV, reading books, working on a computer, and doing any activities that excite the brain.
For severe injuries, surgical treatment is used. Doctors can pump out excess cerebrospinal fluid, suture damaged tissue, and coagulate blood vessels.
The duration of the rehabilitation period for traumatic brain injury depends on its type and severity. Sometimes a person gets away with only quickly passing headaches and recovers in a week; in severe cases, the patient can expect lifelong recovery and disability.
Directions of rehabilitation
Just a few years ago, no specific treatment was provided for victims whose danger had passed. The person was discharged and returned to his family, but the danger of becoming disabled due to severe injury is great. Five years ago, special rehabilitation centers gradually began to open for such patients, to which they are sent for the upcoming restoration of the functioning of the entire body.
It is very important to listen to the recommendations of specialists and not to refuse further rehabilitation in specialized institutions, both medical and sanatorium-resort types.
The key goal of a number of specialists is:
- complete restoration of self-care abilities. This includes both the ability to move around the house independently and the ability to ride as a driver. In this case, this is the task of the occupational therapist;
- a speech therapist helps get rid of articulation disorders and restores normal diction;
- The kinesiotherapist works to eliminate disturbances in motor activity and restore gait;
- a physiotherapist helps cope with constant headaches and dizziness;
- the psychotherapist works on adaptation to new conditions and correction of behavioral reactions;
- a traumatologist, neurologist and rehabilitation specialist coordinate the treatment regimen in each specific case, making adjustments to it if necessary.
Only a specialist after appropriate examinations can talk about the patient’s complete recovery. It is not recommended to change the treatment regimen on your own or abandon the proposed methods of therapy.
A long rehabilitation period is required. Depending on how complex the damage was, recovery lasts from several months to several years. Sometimes the rehabilitation period lasts a lifetime.
The consequences of injury are eliminated by therapeutic methods, these include medication, physiotherapy and exercise therapy. There are cases when a person loses his sense of smell after suffering a trauma. Some patients, especially those with spinal cord injury, may experience arm paralysis. Rehabilitation for such pathologies takes place with special attention.
5/5 (6 votes)
Share with friends or Save for yourself!
The need to provide first aid and go to the clinic in case of emergency
Any intervention in the functions of the brain of the head, even first medical aid, can significantly affect the further course of symptoms, their duration and expected negative manifestations, which, with the right and careful approach, can be prevented or, in extreme cases, minimized.
If the victim is conscious, he must be convinced to go to the hospital and, after offering help, be escorted directly to the doctor's office.
The fact is that when an injury occurs, the pathological processes have not yet gained strength. In addition, the victim himself, being in an excited state of shock, may not feel any pain or malaise at first and will decide that he can cope with such minor problems on his own.
The patient must also be informed as much as possible and fully aware of the trouble that has happened to him, aware of the fact that a careless attitude and untimely reaction can cost him too much.
>
Treatment of traumatic brain injury
The treatment process for CMP and the rehabilitation period primarily depend on the severity and characteristic features of the injury. Initially, it is necessary to ensure that the respiratory system has sufficient patency, and if damage is detected, take appropriate measures.
It is imperative to stabilize hemodynamics and, if necessary, use methods of anti-shock therapy and ventilation. General therapy should be aimed at strictly observing the norms of water-salt balance in the body, normalizing blood pressure, maintaining acceptable body temperature and coordination of movements.
As for the main methods, they consist of antibacterial and drug therapy and include the possibility of surgical intervention.
After doctors manage to bring the patient to consciousness, their task becomes to conduct activating therapy. An important point for doctors and medical staff is to maintain normal intracranial pressure and sufficiently ensure the supply of oxygen to the brain in order to avoid the process of hypoxia, as this entails damage to the brain at the cellular level. If bleeding has completely stopped or is absent, then generally accepted conservative methods of treatment and prevention are used.
The rehabilitation period, which occurs at different times for each patient, involves maintaining a certain rhythm of life after an injury. A person should not be overtired, go to bed on time and take short walks in the fresh air as often as possible, since the brain needs oxygen.