What is this
A CT scanner looks like an X-ray machine, but it differs from it in the quality of its photography. A standard x-ray takes a static image, and a CT scan of the brain allows you to view the organ from different angles. The equipment is able to distinguish even those tissues that are similar to each other, and therefore the doctor can obtain more information than with a conventional x-ray.
Head CT is performed for children aged three years and older and for adults. It is extremely important to remain still during the procedure and not move while the test is being performed. This is why infants are not allowed to undergo brain CT scans. In extreme cases, a light anesthesia may be given so that the child falls asleep and does not move during the procedure.
Computed tomography of the head allows you to scan the organ in detail using x-rays. The rays will penetrate the tissue, and with their help it will be possible to see a clear pattern on the film. The doctor will be able to evaluate the image itself, the rate of penetration of radiation, and the body’s reaction to this intervention. These data will allow us to identify the presence of the disease, as well as see the dynamics of its development.
Some people worry that a CT scan of the brain will harm the body. The procedure itself is safe and the human body will not be damaged. The radiation dose is minimal, so there will be no noticeable harm from it. At the same time, the benefit is high, because the doctor will be able to fully analyze the condition of the head.
Each person can decide for himself whether to undergo a CT scan of the brain or not . Doctors cannot force anyone to undergo this examination. Parents or guardians will decide for children and incapacitated patients.
Indications
The brain examination procedure is a serious type of research. You should not produce it unnecessarily. Indications for a CT scan of the brain may include:
- frequent headaches;
- regular cramps;
- frequent feeling of weakness and dizziness for unknown reasons.
Also, a CT scan is sometimes necessary before surgery. CT scan is prescribed to patients if there is a suspicion of a tumor, or for various head injuries that could affect the integrity of the cranium and the condition of the brain.
It is important to remember that if a tumor is detected after therapy, it is worth doing MRI examinations to evaluate the results, since after therapy it is necessary to be examined dynamically, and computed tomography is not suitable for this.
Brain tomography may be prescribed for encephalitis or meningitis, since these infectious diseases can cause the development of pathological processes in the brain. Another important indication is the ban on MRI examinations. Thanks to computed tomography, it is possible to detect hemorrhages in the brain or developing pathologies in the early stages.
Computed tomography of the brain has its contraindications despite the fact that it is relatively safe. The main contraindications are the patient's age under 12 years, since children are more susceptible to radiation. It is prohibited for pregnant women to undergo examination in any trimester, people with degree of obesity, whose weight exceeds 120 kg due to the fact that the tomograph has a weight category limit.
There are relative contraindications, for example, the lactation period, as well as allergies to iodine-containing drugs or insufficient kidney function.
If it is necessary to conduct an examination with contrast, it is also important to take into account breastfeeding, allergies and the presence of diseases such as diabetes.
You should not perform tomography if you have kidney or liver failure. This may worsen the pathology. In this case, other methods of studying the brain are selected.
It is forbidden to carry out such an examination on people who suffer from serious mental disorders, but in this case it all depends on the purpose of the study. Only a doctor can decide whether a CT scan is necessary. In the case of people who have deviations in their mental state, it is possible to administer a drug that allows the patient to be put to sleep for a while.
A CT scan of the brain is performed if there is a suspicion of dysfunction of the organ and its surrounding vessels. The purpose of the study is to find foci of pathological processes, assess the degree and nature of damage after injuries, confirm or refute the presence of benign and malignant formations.
Using CT, the effectiveness and appropriateness of treatment is monitored after confirmation of the diagnosis, and dynamics are observed. If it is necessary to observe the general condition of the tissues, a CT scan is performed without contrast, and in case of vascular diseases and disorders of their patency, contrast is administered.
The attending physician may prescribe tests. Indications for the use of computed tomography are:
- headaches, after excluding other causes;
- circulatory disorders;
- suffered a stroke;
- suspected swelling and hemorrhage;
- condition after head injuries;
- suspicion of the formation of abscesses and cystic growths;
- infectious diseases;
- oncopathology;
- abnormal proliferation of blood vessels;
- pathological changes in blood flow;
- suspicion of hydrocephalus;
- neurological symptoms.
CT scans are also performed to monitor the dynamics after surgery. If the patient has contraindications to the MRI procedure, computed tomography successfully replaces it.
Like any medical procedure, computed tomography has a number of contraindications. When carrying out diagnostics, the body is exposed, although minimally, to radiation, and due to the risk of developing pathologies in a child, CT scans are not recommended for pregnant women. Contraindications to tomography can be categorical and relative, when the information content of the study outweighs the risks.
During lactation, CT diagnosis is permissible only if contrast is used; feeding must be avoided for several days, since the substance passes into the milk and can harm the baby.
Computed tomography with contrast is contraindicated in people with cardiac renal failure. Sick kidneys may not be able to cope with the timely removal of the substance and cause intoxication of the body. But the contrast with iodine can also cause a complex allergic reaction, so it is important to clarify this information before introducing it. Relative contraindications are endocrine diseases and myeloma.
The computed tomography machine does not allow examination of people with large weight. For technical reasons, the diagnostic chamber is not able to accommodate a person weighing more than 120–130 kg, but these are not contraindications, but rather limitations.
Existing CT readings:
- Chronic fatigue, apathy, irritability, emotional instability, sleep disturbance, decreased concentration, memory impairment and slowed thinking.
- Recurrent and chronic headaches. Loss of consciousness, nausea, vomiting. Headaches that are not relieved by painkillers. Acute headache, similar to a blow to the head, is a direct indication for CT scanning for stroke.
- A complex of autonomic disorders: constipation, diarrhea, feeling of lack of air, palpitations, sweating, dizziness, tremors in the limbs, cold hands and fingers.
- Traumatic brain injuries: contusion, bone fracture, brain damage, concussion, penetrating trauma
- New onset seizures, persistent changes in mental status, history of tumors or seizures.
- Chronic alcoholism, drug addiction.
- Neurological focal symptoms with loss of neurological functions, for example, loss of visual fields, sudden absence of speech, different pupil sizes.
CT examination is indicated not only in the presence of symptoms, but also as a routine diagnosis and preventive measure for a specific population, for example, people working with radiation. A CT examination is also prescribed to monitor the dynamics and effectiveness of treatment, for example, chemotherapy.
Computed tomography is also used when it is necessary to monitor the progress of a therapeutic or diagnostic operation. For example, a brain biopsy (intravital tissue collection) is performed under computed tomography visualization: it is necessary to control and look for the passage of the puncture needle through the brain.
Computed tomography uses x-rays and is therefore associated with minor harm to the body. Therefore, there are absolute contraindications to CT (when the study cannot be done under any circumstances):
- Pregnancy.
- Excessive body weight of the patient, due to which he does not fit into the scanning device.
Contrast is used for greater detail. It helps highlight the blood vessels of the brain. However, a contrast agent is a pharmacological drug, the use of which has contraindications:
- Kidney and liver failure.
- History of allergies.
- Exacerbation or decompensation of diabetes mellitus.
- Decompensation of heart failure.
- Pregnancy.
- Unsatisfactory condition of the subject (poor health).
- Thyroid diseases
The possibility of performing a CT scan with metal crowns is decided by the diagnostician. The presence of foreign bodies of such a structure is fraught with danger: during the examination, the crowns can heat up, which can lead to burns or simply unpleasant sensations. Therefore, always tell your doctor if you have metal crowns.
Universal indications for examination are:
- oncology search: detection of tumors of internal organs, bones, soft tissues;
- determining the stage of the oncological process, searching for metastases, obtaining information about the structure and spread of the tumor before surgical removal or starting radiation therapy;
- injuries and their consequences: bleeding, hematoma, rupture of a hollow organ, damage to internal organs, fractures and cracks of bones, etc.;
- the presence of changes in X-rays, ultrasound and other examination methods that cannot be interpreted due to lack of data;
- monitoring the effectiveness of treatment after radiation or chemotherapy;
- examination of the body area, organ, blood vessels before the upcoming operation;
- monitoring the condition of tissues after surgery.
You can get a referral from your doctor for an abdominal examination in the following cases:
- determining the cause of obstructive jaundice;
- identification and control of the dynamics of development of aortic aneurysm;
- identification of damage to the abdominal organs, hematomas, free fluid, foreign bodies that may appear after abdominal trauma;
- determination of the condition of the lymph nodes in cases of lymphogranulomatosis, lymphosarcoma and some other diseases of the hematopoietic system.
Preparation for the procedure
If a person needs to undergo a CT scan of the head, he does not have to worry about negative feelings from the examination. There will be no pain, and no special preparation is even required. You just need to take into account certain recommendations so that the procedure does not cause difficulties.
First of all, for a CT scan of the brain vessels with contrast, you must obtain a referral from your attending physician. You should take with you a medical history and a verdict from previous doctors. If you have previously had a CT scan of the brain, you should have the results with you. If there are any other documents related to the examination, then they should also be brought.
Preparing for a CT scan of the brain requires that a person remove jewelry, all metal objects, existing dentures and hearing aids.
It is also worth wearing comfortable clothes so that it does not cause discomfort during the procedure. Otherwise, a head CT scan does not require any other preparatory manipulations.
How the research is carried out
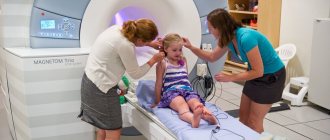
During a CT scan of the brain, the person will need to lie on their back in a comfortable position. The patient will be placed in the tomographic tunnel using a sliding table. The doctor will leave the room because he will need to observe what is happening from the next room. If you need to communicate with a patient, a special microphone is used for this.
When performing a CT scan of the head, a special ring will rotate around the table, on which many sensors are located. When the equipment is working, a person will not feel anything. He will only hear instrument noises and slight crackling sounds.
In cases where a person cannot lie still, his head is secured with special straps. They will not allow you to make any movements that distort the result of a head CT scan. This option is most often used for children.
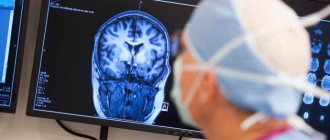
A CT scan of the brain displays the results on a screen for a physician to see. After the study, there will be pictures of the desired organ in different projections. Deciphering a CT scan of the brain is possible only by a specialist, because an ordinary person will not understand the photographs. That is why, before consulting with a specialist, it will not be possible to find out about the presence of pathology.
A CT scan of the brain with contrast is often performed. This substance is based on low dosage iodine. The solution is needed in order to see the structure of the head in more detail, because the contrast can change color.
Often, an examination is performed when it is necessary to find out details about tumors and obtain objective data about them. A CT scan of the brain with contrast is often performed when the patient has cysts or vascular pathologies.
What can you see
A CT scan of the brain helps to obtain various information about the condition of the organ. That is why this examination is carried out if any head pathology is suspected.
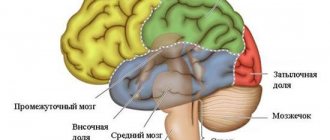
It can be used to assess the fine structure of an organ, the level of metabolism, and the quality of blood circulation. CT scan of the brain and neck vessels helps to understand the condition of the veins and large arteries, as well as analyze the performance of areas of the head.
The procedure has many advantages when compared with x-rays. If a CT scan of the brain is done with contrast, then more accurate data can be obtained. It will be possible to detect blood clots, hematomas, tumors, the presence of meningitis and other pathologies. That is why CT scan of the brain is indispensable in many situations where there is suspicion of illness.
In what areas of medicine is brain CT used?
CT of brain tissue and skull bones is successfully used in:
- neurology to identify hemorrhagic strokes, damage to brain tissue and skull bones, inflammatory diseases, abnormalities in the development of head structures, and to establish the causes of increased intracranial pressure;
- oncology for the diagnosis of tumor processes;
- maxillofacial surgery – to prepare the patient for operations, assess the condition of the temporomandibular joint;
- dentistry – to assess the condition of the jaw before dental implantation;
- other areas of medicine.
Contraindications
You need to understand that a CT scan of the head, although it does not pose a particular health hazard, is still harmful. Therefore, it is impossible to undergo research often. It is indicated in rare situations when it is important to know exactly the condition of the organ. For example, a CT scan of the brain is necessary when there is a risk of edema. In such a situation, doctors cannot hesitate and make do with safer diagnostic methods.
If a person feels weakness or any unpleasant symptoms after undergoing the procedure, they should immediately report this to a specialist . He will decide whether such a reaction can be considered normal. Naturally, a CT scan of the brain should not be done unless clearly necessary. If a person is not bothered by unpleasant symptoms, then he should not undergo radiation for the sake of curiosity.
It is worth noting that CT of the head has a small number of contraindications. For this reason, it is common and often prescribed by doctors. A CT scan of the brain cannot be performed only in a number of situations, and there are reasons for this.
Contraindications: Children under 3 years of age. Sometimes, even older children cannot undergo the procedure if they cannot lie still. Pregnancy period. The presence in the body of foreign objects made of metal or metal-plastic. Body weight is more than 130 kg.
In the case when it is necessary to do a CT scan of the vessels of the brain and neck with contrast, the list of contraindications becomes wider. This is not allowed for those who are allergic to the component, have a severe stage of diabetes, or have kidney or liver failure.
Also, CT scan of the brain is contraindicated for people with mental disorders and claustrophobia. In other situations, this examination is prescribed, and it takes place without any complications.
A head CT scan is indispensable in diagnosing many ailments, because it provides a wide range of information about the condition of the organ. In a free clinic, the test can be done free of charge if you have a referral from a doctor. Without it, a CT scan of the brain will cost 4,000 rubles and more. When there are suspicions of pathology, you should not refuse the procedure, as it allows you to identify them in the early stages.
What does a brain CT scan diagnose?
The procedure for undergoing tomography and the results of the study in adults and children are systematized in the table:
| CT scan of the brain | In adults | In children |
| Which doctor refers you for examination? | neurologist, neurosurgeon, vascular surgeon, oncologist, endocrinologist, ophthalmologist, otolaryngologist | pediatrician, neurosurgeon, vascular surgeon, oncologist |
| Indications for the procedure | severe injuries, pain and dizziness, before and after operations, neoplasms, endocrine disruptions | severe injuries, before and after operations, neoplasms |
| Contraindications | pregnancy; lactation; weight more than 120 kg; renal or liver failure; diabetes mellitus in severe forms; allergic reactions to the drug | renal or liver failure; diabetes mellitus in severe forms; allergic reactions to the drug |
| What they check | brain size; thickness of blood vessels; blood flow speed; blood clots and hemorrhages; foreign bodies; liquid; nerve fibers; darkening of tissues, presence of light spots | brain size; the presence of blood clots and hemorrhages; foreign bodies; liquid; darkening of tissues, presence of light spots |
| Contrast agent | iodine | iodine |
| Preparing for diagnosis | blood tests for urea and creatine levels; do not eat for about 4 hours; remove metal jewelry; bring the results of previous studies and a doctor’s opinion | blood tests for urea and creatine levels; do not eat for about 4 hours; remove metal jewelry; bring the results of previous studies and a doctor’s opinion |
| Time spending | administration of contrast – about 15-20 minutes; CT – 5-10 minutes; hand delivery of results – 60-90 minutes | administration of contrast – about 15-20 minutes; CT – 5-10 minutes; hand delivery of results – 60-90 minutes |
| Tomography results | pictures; electronic records; written expert opinion | pictures; electronic records; written expert opinion |
| Pathologies | hemorrhage and stroke (ischemic and hemorrhagic); fracture of the base of the skull; bleeding; circulatory disorders in the brain; trauma and hematoma; tumor and cyst; abscess; encephalitis; aneurysm; developmental anomaly; presence of foreign bodies | fracture of the base of the skull; trauma and hematoma; tumor; abscess; developmental anomaly; presence of foreign bodies |
| Price | 2-8 thousand rubles. | 2-8 thousand rubles. |
The quality of the X-ray machine directly affects the accuracy of the results. Different types of devices give different results. The novelty of the technology determines the degree of harm caused to the body and the likelihood of detecting the disease at the initial stage.
A high-quality tomogram is obtained:
- if professional doctors;
- The patient does not move during the procedure, which allows for a clear image.