Causes
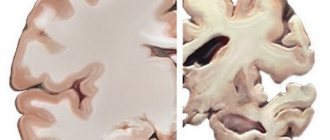
Although researchers do not understand the exact reasons that cause clonus, it appears to be related to damaged nerve connections in the brain.
A number of chronic diseases are associated with clonus. Because these diseases require specialized treatment, results may vary in each case.
Diseases that can cause clonus:
- Multiple sclerosis is an autoimmune disorder that attacks the protective sheath around the nerves. The resulting damage disrupts nerve signals in the brain.
- Stroke - due to a blood clot, part of the brain is starved of oxygen. A stroke can cause clonus if the area of the brain that controls movement is damaged.
- Infections such as meningitis or encephalitis can damage brain cells or nerves in advanced cases.
- Serious injuries, such as head trauma from a major accident, can also damage nerves in the brain or spinal cord.
- Serotonin syndrome is a potentially dangerous reaction that occurs when too much serotonin accumulates in the body. This buildup can be caused by drug abuse, but can also be caused by using high doses of medications or mixing certain medications.
- A brain tumor can also cause clonus.
Other causes of clonus include anything that can affect nerves or brain cells:
- epilepsy;
- cerebral paralysis;
- Lou Gehrig's disease;
- anoxic brain injury;
- hereditary spastic paraparesis;
- renal or liver failure;
- overdoses of drugs such as the synthetic opiate tramadol, which is a powerful painkiller;
Diagnostics
To diagnose clonus, doctors may first physically examine the most affected area. If a muscle contracts while a person is in the doctor's office, they can monitor the contraction to see how quickly the muscle pulsates and how many times it contracts before it stops.
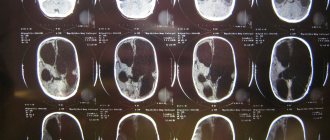
Doctors then order a series of tests and tests to confirm the diagnosis. They may use magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) to check for cell or nerve damage.
Blood tests can also help identify markers of various conditions associated with clonus.
A physical test can also help doctors identify clonus. During this test, the patient is asked to quickly flex the leg so that the toes are pointed and then hold the muscles. This can cause prolonged throbbing in the ankle. A number of these pulses may indicate clonus. This may not be the basis for making a diagnosis, but it can help guide the diagnostic process in the right direction.
Diagnostic mechanism
Clonus of the patella is characterized by its sharp downward displacement, while it retains its position even if it is pulled back. In order to provoke this altered reflex, the patient is asked to assume a horizontal position and straighten his legs.
After this, the doctor grabs the kneecap with two fingers - the thumb and forefinger, moves it down and holds it in this position. The tendon is stretched, causing the muscles to involuntarily contract and the kneecap to twitch rhythmically.
To provoke foot clonus, the patient must also be placed on the couch and his leg should be bent at the knee and hip with one hand, and his foot should be grabbed with the other, sharply bent and straightened. Stretched, the Achilles tendon will provoke uncontrolled rhythmic movements of the foot, reminiscent of twitching.
It is worth emphasizing that both of the above examples of altered reflexes indicate disorders of the nervous system. But still, one of the most unfavorable situations is an uneven increase in reflexes (the so-called anisoreflexia), in which the left and right halves of the body react to the stimulus with different degrees of intensity.
Unlike a symmetrical increase in reflexes, which does not always mean that this is a sign of brain damage, their unevenness is an alarming symptom. As a rule, this is possible in two cases: inhibition of the reflex on one side, associated with damage to the reflex arc in the nerve, roots or gray matter of the spinal cord, or its activation on the other (which indicates damage to the pyramidal tract).
Treatment
Treatment for clonus varies depending on the underlying cause. Doctors may try many different treatments before finding the one that works best for a particular patient.
Medications
Sedatives and muscle relaxants help reduce symptoms. Doctors often recommend these drugs primarily for people experiencing cloning.
Medications that may help with clonus reduction include:
- Baclofen;
- Dantrolene;
- Tizanidine;
- Gabapentin;
- Diazepam;
- Clonazepam.
Sedatives and antispastic drugs may cause drowsiness. Patients taking these medications should not drive or operate heavy machinery.
Other side effects may include mental confusion, lightheadedness, or even trouble walking. You should discuss these side effects with your doctor, especially if they may interfere with daily activities.
Physiotherapy
Working with a physical therapist to train muscles can help increase range of motion in the injured area.
Botox injections
Some people respond well to clonus to Botox injections. Botox therapy involves the injection of certain toxins. The effects of Botox injections wear off over time, so a person will need repeat injections on a regular basis.
Surgery
Surgery is often the last resort. During a procedure to treat clonus, surgeons will cut off parts of the nerve that are causing the abnormal muscle movements, which should relieve symptoms.
Home Remedies
While medical treatments, home remedies may be helpful to support these efforts.
Using heat packs or using warm baths can relieve pain, and using cold packs can help reduce muscle pain. Stretching and yoga can help increase your range of motion.
You can use a magnesium supplement or a magnesium salt bath to help relax your muscles. You should consult your doctor before using magnesium as it may interact with other medications.
Forecast
Clonus has a different prognosis depending on the underlying cause. If a sudden injury or illness causes clonus muscle spasms, symptoms will likely subside over time or respond well to physical therapy.
Chronic diseases such as multiple sclerosis, meningitis or stroke may require long-term management of symptoms. Clonus may worsen as the underlying condition progresses.
The article was written based on materials from the Medical News Today website.
( 2 ratings, average: 5.00 out of 5) Loading...Share
+
Math puzzle test
Can you solve the flower puzzle? Take other tests: Test: find the animals in the picture Test: test your vision and attentiveness... +
Speed up your metabolism by detoxifying your liver
If you are struggling with excess weight, it may be time to add liver and intestinal cleansing products to your diet... +
How to prepare for an ultrasound
Very often, patients in clinics or hospitals are concerned about the following question: how to properly prepare for an ultrasound examination (ultrasound)? The question is far… +
Notes
- Anosov N. N.
Clonus // Great Medical Encyclopedia / Ch. ed. B.V.Petrovsky. — 3rd ed. - M.: Soviet Encyclopedia, 1975. - T. X (Kabakov - Coalescence). - pp. 477-478. — 608 p. - ↑ 1 2 3 Pulatov A.M., Nikiforov A.S.
Propaedeutics of nervous diseases. - T.: "Medicine", 1979. - P. 82-83. — 368 p. — 20,000 copies. - Hidler JM, Rymer WZ
A simulation study of reflex instability in spasticity: origins of clonus // IEEE Trans Rehabil Eng. - 1999. - T. 7, No. 3. - P. 327-340. - PMID 10498378. - [zabolevaniya.ru/zab.php?id=16043&act=full Directory of diseases. Convulsions]. website zabolevaniya.ru. Retrieved May 16, 2012. [www.webcitation.org/6ArzCmT6C Archived from the original on September 22, 2012].
| This is a draft article on neurology. You can help the project by adding to it. |
Symptoms
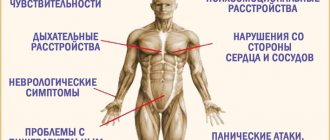
Clonus in epilepsy is observed during generalized convulsive seizures, which are accompanied by loss of consciousness. In this case, rhythmic contractions of the muscles of the trunk and limbs occur, which manifests itself in the form of rapid movements that are not controlled by the person.
The extrapyramidal system is responsible for involuntary coordination of movements, maintaining posture, muscle tone and motor manifestations of emotions. When it is damaged, muscle tone decreases, and various movement disorders occur, including clonus. It usually appears as tic twitching in the face, neck and limbs.
Clonus in neurosis is considered false. Its distinctive features are incorrect tempo, lack of rhythm and rapid exhaustion.
The function of the pyramidal system is to support complex and subtle coordination of movements. As a result of its damage, paresis, paralysis and pathological reflexes may occur. The latter include clonus of the feet and kneecaps.
Foot clonus is a sharp, rapid, involuntary jerking of the foot in response to a stretch of the Achilles tendon. It is called as follows. The patient lies on his back. The doctor bends his leg at the hip and knee joints, supporting it under the shin. With the other hand, the doctor grabs the foot, sharply bends it towards the front surface of the leg, and then straightens it.
Patellar clonus is the rhythmic movement of the kneecap along the bed, which occurs as a result of the tension of the tendon and the response contractions of the quadriceps femoris muscle. It is provoked like this. Lying on his back, the patient straightens his legs. The doctor wraps two fingers around the kneecap, sharply pulls it down and holds it.
Normally, twitching of the feet and kneecaps should not occur. The situation is considered especially dangerous if there is an asymmetrical increase in reflexes.
Clonus stop - what is it?
Foot clonus occurs because there is damage to the nerves that control the muscles.
Such a blow leads to a long muscle spasm. This leads to constant muscle fatigue and pain. If this happens often, the person feels exhausted. First of all, it is necessary to understand why foot clonus occurs, and most importantly, to ensure that treatment is prescribed on time.
- 1. Reasons
- 2. Symptoms
- 3. Diagnostics
- 4. Treatment
Causes
The causes of the disease can be different, it all depends on how quickly the disease develops. Most often, pathology occurs due to damage to nerve endings in the brain.
There are a number of reasons that cause clonus:
- Multiple sclerosis occurs due to disruptions in the immune system, which leads to damage to the nerve endings in the head.
- A stroke can occur because hypoxia occurs due to a blood clot. Pathology can lead to clonus disease, because the part of the brain that is responsible for movement may be damaged.
- Severe injuries and bruises to the skull can damage the nerve cells in the head.
- If you use drugs or overdose on medications, this will lead to a large amount of serotonin.
- New growths in the head can provoke foot clonus.
Severe muscle spasms may occur, both in the foot and in the kneecap. The disease can occur abruptly or gradually. Diseases such as epilepsy, heredity, renal failure, and cerebral palsy can provoke pathology.
There may be foot clonus in newborns . This occurs due to muscle hypertonicity. If the disease is not treated, it can lead to serious consequences.
Symptoms
If clonus occurs in epilepsy, it manifests itself during seizures and fainting. Muscle spasms begin to occur at a rapid pace in the arms, legs and body and the patient cannot keep it under control. The extrapyramidal system is responsible for abnormal movements.
Clonus occurs in neurosis, but it is false and the person quickly gets tired. Muscle tone and various problems of the musculoskeletal system occur. This manifests itself in the form of twitching on the face, neck, arms and legs.
Various paresis and paralysis may occur, and this also includes clonus of the patella. With this disease, there may be muscle spasms, the patient constantly feels tired.
Constant tension arises and a person feels eternally in some kind of discomfort. If symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. The sooner treatment is started, the sooner the patient will begin to experience a normal life.
Diagnostics
Diagnosis is prescribed for certain symptoms. To begin with, the patient is visually examined to see how strongly the muscles contract. The patient is asked about signs of foot clonus.
The specialist prescribes the following examinations:
- MRI is used to find out the condition of blood vessels and nerve endings. The procedure can be done with a contrast agent, this allows you to better see the pathology. Before using contrast, you need to do an allergy test. An MRI takes approximately forty minutes.
- CT helps to quickly find diseases that lead to oxygen starvation. The procedure has a number of contraindications and you should not eat food for 4 hours before diagnosis. If a CT scan is done, then with the help of the study an accurate diagnosis is made. Side effects can occur only in one case, if a contrast agent is used.
- Ultrasound of the brain is still used and is quite effective. Using the procedure, the disease can be detected in a short time. The diagnosis has no contraindications. Ultrasound does not affect a person’s condition in any way, so the procedure can be carried out as often as necessary.
The doctor may also prescribe a general blood and urine test. After the examinations have been completed, the specialist must prescribe a comprehensive treatment. The patient should monitor his condition and consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Treatment
Treatment for foot clonus depends on what exactly caused the pathology. Many specialists can use different therapy techniques. The doctor must find and select treatment individually for each patient separately.
The following medications are prescribed:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs help relieve pain and relieve inflammation. The drugs have a number of side effects; for example, if you have a gastrointestinal disease, long-term use of the medicine is prohibited. Nervous system disorders and allergies may also occur.
- Sedative medications help relieve emotional stress and normalize the condition of nerve cells. If you use such drugs, it will help cope with irritability. It is not recommended to drive while taking such medications.
Physiotherapy also gives a positive result in treatment; it helps to train all muscles. A specialist may also prescribe surgery, but this is used only in extreme cases. Traditional methods of treatment can be used to help alleviate the condition.
Clonus of the feet and patella must be treated on time. The doctor will direct you to undergo a comprehensive examination in order to make an accurate diagnosis. If the disease becomes chronic, clonus of the feet and patella may worsen. Therefore, it is necessary for a specialist to select and prescribe therapy.
Source: //nevrology.net/sindromy-i-zabolevaniya/klonus-stop.html
What is knee clonus
Detection of clonus by palpation and inspection
Involuntary muscle contractions in a certain rhythm occur due to the impact on the tendon ending. Most often, a person experiences clonus of the feet and kneecaps, caused by tension in the tendon. Such reactions indicate an excess of the knee and Achilles reflexes. They manifest themselves in any situation of hyperreflexia with dysfunctions of the central nervous system of an inorganic nature.
Clonus of an inorganic nature differ from reflexive disorders based on lesions of an organic type or arising against the background of neuroses. They are characterized by insufficient stability and uniform bilateral expression.
If the clonus are not uniform and symmetrical, this indicates an organic disease in the central nervous system. The uneven manifestation of reflexive responses to external stimulation is called anisoreflexia. It is caused by a unilateral decrease or increase in reflexes.
Unilateral decrease - hyporeflexia - indicates damage to the neural arch of reflexes. A one-sided increase in reflexes—hyperreflexia—indicates damage to the pyramidal chain through which inhibitory impulses must pass. To identify reflex unevenness, doctors use irritation with a needle or hammer blows.
Methods for detecting pathology
The doctor can cause clonus of the patella in a patient who lies on his back with straight legs. The doctor takes the top of the patella with two fingers, pulls it up, then quickly releases it. A possible reaction of the body to such a motor test is rhythmic contractions of the quadriceps femoris muscle, twitching of the patella. The test confirms the presence of disturbances in the pyramidal tract.
On the foot, the physician checks for clonus by supporting the patient's leg under the knee while the patient lies flat on his back. With one hand, the doctor lifts the leg so that it bends slightly at the knee, with the other hand he firmly grasps the foot and bends it to the back with a sharp movement. This action causes tension in the Achilles tendon. If, after stretching, a rhythmic twitching of the foot begins, this is clonus.
The doctor can cause clonus of the patella in a patient who lies on his back with straight legs. The doctor takes the top of the patella with two fingers, pulls it, then quickly releases it. A possible reaction of the body to such a motor test is rhythmic contractions of the quadriceps femoris muscle, twitching of the patella. The test confirms the presence of disturbances in the pyramidal tract.
Clonus in various somatic disorders
The pathophysiology of clonus in pyramidal chain dysfunction is manifested in the absence of an inhibitor coming from the cerebral cortex to the motor neurons of the spinal cord. Without an inhibitory impulse, reflex excitation lasts a long time, which is why involuntary muscle twitches are repeated.
In epilepsy, clonic convulsions manifest themselves in sequential contraction of the flexion and extension muscles, in rapid involuntary movements of the leg. The epileptic nature of clonus also occurs in infants, when in a dream the baby involuntarily twitches its legs for a minute or two. It is recommended to contact an experienced neurologist and begin a targeted examination.
EEG monitoring is the most informative for a doctor when the baby is put on a special “hat” with sensors in which he must sleep. The sensors are connected to a computer, which records manifestations of knee clonus. If abnormalities in the functions of the central nervous system are confirmed, the doctor prescribes treatment for the child.
Knee Reflex Diagram
Foot clonus in an infant indicates muscle hypertonicity, which manifests itself due to intracranial hypertension. The tendon reflex increases in newborns with suspected cerebral palsy, porencephaly, microgyria, and gliomatosis. However, clonus of the knees and feet in children in the first days of life may manifest itself as a transient physiological phenomenon. In this case, it is not accompanied by other pathology.
Neurotic disorders are characterized by pseudoclonus: twitching of the cup or foot is not rhythmic and quickly fades away. True clonus is characterized by prolonged stereotypical twitching of the feet and legs, high general tone, which usually indicates central paralysis. A separate phenomenon is myoclonus - a single impulse startle. It occurs due to active muscle contraction, which occurs in many people at the moment of falling asleep.
Involuntary twitching while falling asleep is not a harmless indicator of the release of daytime stress, but a symptom of many central nervous system diseases. Generalized clonus is observed in epilepsy, during seizures accompanied by convulsions and loss of consciousness.
Symptoms
If clonus occurs in epilepsy, it manifests itself during seizures and fainting. Muscle spasms begin to occur at a rapid pace in the arms, legs and body and the patient cannot keep it under control. The extrapyramidal system is responsible for abnormal movements.
Clonus occurs in neurosis, but it is false and the person quickly gets tired. Muscle tone and various problems of the musculoskeletal system occur. This manifests itself in the form of twitching on the face, neck, arms and legs.
Various paresis and paralysis may occur, and this also includes clonus of the patella. With this disease, there may be muscle spasms, the patient constantly feels tired.
Constant tension arises and a person feels eternally in some kind of discomfort. If symptoms appear, you should consult a doctor. The sooner treatment is started, the sooner the patient will begin to experience a normal life.
Reasons for development
Hyperexcitability in newborns is associated with mild damage to the central nervous system during childbirth or even during pregnancy. Often, pathology occurs due to a lack of oxygen.
The main reasons for the development of pathology include:
- intrauterine infections;
- toxicosis, especially in later stages (preeclampsia);
- alcoholism, smoking during pregnancy;
- taking certain medications;
- fetal hypoxia, fetoplacental insufficiency;
- premature or post-term pregnancy;
- maternal stress during pregnancy;
- anatomical narrowing of the pelvis, which creates difficulties when passing through the birth canal;
- rapid or, conversely, prolonged labor;
- birth injuries.
In addition, symptoms of hyperexcitability in babies under one year of age are characteristic of the period of teething (at this time babies are especially restless) as well as with intestinal colic.
Diseases such as rickets, spasmophilia, and neuro-arthritic diathesis leave their “imprint” on the nervous system. And, of course, temperamental children (cholerics) are easily excited.
Causes of the disease
If clonus occurs spontaneously, the doctor suspects epilepsy or a nervous tic. If clonus occurs due to external irritations, the causes may be: meningitis, encephalitis, stroke, tumors in brain structures, head injuries.
Clonus is caused by rare diseases:
- Huntington's chorea;
- hyperkinesis;
- hemiballismus;
- myoclonus;
- tremor;
- psychoneurological disorders.
All these diseases are accompanied by disturbances in the functioning of the pyramidal system. The main cause of clonus caused by external stimuli is pyramidal chain diseases of the inflammatory, degenerative, and vascular types.