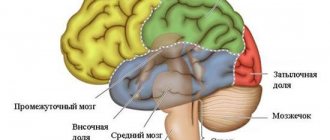
Since the introduction of cellular communications into human life, scientists have conducted thousands of studies to assess the effect of the device on the body. Experts are still not able to definitively answer the question of whether a phone can give you a headache. At the same time, we can say for sure that with the systematic use of the device, the body is exposed to negative effects.
When communicating on a mobile phone, the skull absorbs up to 50% of its radiation. Sound pressure, heat, and magnetic field have a direct effect on the eardrum.
Causes of headaches on the right
Headache can be a symptom of various diseases, and the main possible ones are discussed below:
Migraine . This is the main disease, the manifestation of which is pain on the right or left side of the head. In this case, unpleasant sensations mainly appear in one part of the cerebral hemisphere. Most often, such pain occurs at the temple, and then spreads to the eye area, forehead and can even reach the back of the head. This feeling does not stop after four hours, and may be accompanied by nausea, vomiting, dizziness, and increased hearing and vision to light and noise. Just before the headache itself, the first symptoms of migraine appear - tingling throughout the body and stars before the eyes. The disease can be triggered by cigarette smoke, loud sounds, odors and similar harsh factors.
But unfortunately, there is no clear answer to the question of the appearance of migraine pain. In addition to the factors that influence its appearance, such a disease can be transmitted by heredity; if the child’s mother often suffered from similar pain in the right side of the head, then there is a high probability that the child will develop them with age.
Frequent severe headache, and more recently a lump in the throat
Matvey
233 views
July 23, 2020
Hello, dear doctors!
Please help me understand my problem. Please read my question to the end. Thank you very much in advance! Since May I have been suffering from a severe headache, which significantly worsens my quality of life. More precisely, at first (in May) I had some strange sensations in the form of tingling in my head, shooting (but not like electric shock). It's very difficult to explain. It's like I'm being given some kind of injection. And from the first days of June, my head began to hurt very often, sometimes every day, sometimes every other day. I remember that one day I woke up and within a few seconds a severe headache developed. Painkillers (ibuprofen, paracetamol) helped quite poorly. The next day that pain subsided, but after the stress a day later she became very sick again. I just wanted to lie there and do nothing. Nausea was also observed. You know, this pain is somehow special. If it appears, then I know for sure that neither ibuprofen nor paracetamol will help me or I need to take a larger dosage (for example, yesterday, July 22, my head started to hurt badly and the combination of ibuprofen 400 mg + paracetamol 250 mg helped, but I also drank 2 tablets of tolperisone, which the doctor prescribed for me, but more on that later). I've had this kind of pain before: a few months ago and a few years ago. I can take 6 ibuprofen tablets a day throughout the day! and there will be no result, although a year ago I had similar pain and after 4 tablets the pain went away: I took the tablet and lay down on the bed and after 30 minutes there was no pain. But the fact is that before I was not tormented by such pain every day, and not often at all. Much more often, some other kind of pain arose and painkillers helped very well (after 1 tablet the pain went away). Now everything is different for me. In June, those tingling sensations gave way to the pain that continues to this day. Another important thing is that I died around the end of April or beginning of May due to severe weakness, which prevented me from preparing for exams. From 5th to 8th grade I studied at the lyceum, where there was a heavy workload, then I switched to distance learning entirely due to the fact that severe panic attacks appeared in 2020. First, I was prescribed clonazepam, then it was combined with Teraligen, then Fevarin was replaced with Asentra. I still take Asentra. And I gradually stopped taking Teraligen (I took it one tablet a day). Could this have caused headaches in the future? That year, and also two years ago, I performed an MRI of the brain. As I understand it, I have a congenital small artery and this is quite bad. Its size is only 1 mm. Maybe this is somehow connected? Although an ultrasound scan of the vessels of the head and neck shows that the blood flow is not changed and everything is generally normal. I am attaching the results of MRI and ultrasound. Now I try to follow a daily routine, but the pain still haunts me. Not every day, but often. About a month ago I turned to an in-person neurologist. After the conversation, I was tentatively diagnosed with tension headache. Nalgesin was prescribed, 2-3 tablets per day, tolperisone (50 mg) 3 times a day. While taking the pills it really became better, the pain began to come less often. But 20 days passed, the course was completed and my health worsened again. I also noticed a deterioration in memory and attention. I'm afraid of any pathological changes. I don't know what to do next. Now, when my head starts to hurt, I take 2 tablets of tolperisone and, for example, ibuprofen. This combination helps me relieve an attack, although the course has already been completed. My headache is of a compressive type, with a pulsating character (in the area of the eyes and forehead). The eyes often feel pressure. On a 10-point scale: from 6 to 8 points. Sometimes the pain can be at the level of 3-5 points, but most often the pain is severe, and there is also slight nausea. The headache increases gradually. At first a little, then stronger and stronger. Sometimes my head starts to hurt in the morning and I understand that within an hour or two it will become severe. Sometimes the pain comes during the day. Out of 7 days a week, 3-4 days I have a headache. But in addition to the headache, a lump in my throat began to bother me. I feel it from time to time. I don't even know who it is. In the area of the Adam's apple, it seems as if something is squeezing, and if you turn your head in a certain position, then when swallowing saliva there will be an unpleasant sensation, as if something is preventing you from swallowing saliva inside the throat. Also, if you raise your head up, the feeling of a lump, squeezing, immediately noticeably intensifies, and you can already feel it very well. Often there is some kind of clicking sound when swallowing food or water, but not always. All this is accompanied by anxiety, because you don’t understand what’s happening to you. Maybe this also has something to do with nervous tension? I'm not sure though. When you lie down and your head is turned to the side, I often feel that something is interfering with my breathing, as if my throat is blocked by something inside, sometimes I want to clear my throat. In the morning, as a rule, there is no coma; it appears closer to lunch. Blood pressure is always normal. The pulse is also normal. When making sudden movements of the head, pain is also felt. Tell me, please, what is this? Is there a serious danger? I'm very worried about all this! What can cause a headache? Why did this lump appear in my throat? What should I do next? I will be very grateful for your answers! Chronic illnesses:
Stuttering, Tourette's syndrome, panic disorder
headache
lump in the throat
squeezing pain
350.00 rub.
The right side of my head hurts - what could it be?
Cluster headache . This pain is characterized by a sudden onset, without warning signals, severity and a clear frequency of occurrence. It can appear at the same time of day, or after a certain time interval: after a week or a month. The pain in the head is wild and unbearable. In this case, the expression “sparks from the eyes” fits perfectly - it characterizes cluster cephalgia. In addition to the headache on the right or left, the eyes begin to turn red and watery, and a runny nose may even appear. Such pain is more typical for men and lasts about an hour.
Glaucoma. The pain is sharp or dull, but does not stop, and can spread both to the orbital area and throughout the entire hemisphere of the brain.
Why does the back of the head hurt: causes of pain and its types
Skull bone cancer is represented by:
- chondrosarcoma with mutated elements of cartilage tissue;
- osteogenic sarcoma in the temple, occiput and forehead;
- chordoma at the base of the skull;
- myeloma at the cranial vault;
- Ewing's sarcoma in the tissues of the skull;
- malignant fibrous histiocytoma.
Chondrosarcoma
This malignant tumor of the skull, growing from cartilage cells, damages the skull, trachea and larynx. It is rare in children; people aged 20-75 years are more likely to get sick.
This type of tumor appears in the form of a bony protrusion covered with cartilage. Chondrosarcoma can result from malignancy of benign tumor processes.
Sarcoma of this type is classified according to its degree, reflecting the speed of its development. With slow growth, the severity and prevalence will be lower and the survival prognosis will be higher.
If the degree of malignancy is high (3 or 4), then the formation grows and spreads quickly.
Features of some chondrosarcomas:
- differentiated - aggressive behavior, they can change and acquire features of fibrosarcomas or osteosarcomas;
- clear cell - slow growth, frequent local recurrence in the area of the initial oncological process;
- mesenchymal - rapid growth, but good sensitivity to chemicals and radiation.
Osteosarcoma
This osteogenic tumor of the skull bones is rarely primary and is formed from bone cells. Affects the temporal, occipital and frontal regions. More often, secondary sarcoma is diagnosed in the periosteum, dura mater, aponeurosis and paranasal sinuses. The formations reach large sizes, are prone to decay and rapid germination into the dura mater of the brain.
Causes of headaches on the right side of the head
Injuries . In fact, this is the easiest way to determine the cause of discomfort in the head, since there is a pattern: in case of injury, the body’s reaction manifests itself through a headache. It may also be that the injury happened a long time ago, but the head hurts on the right side. This means that the traumatic impact on the body that occurred several days or weeks ago reminds of itself.
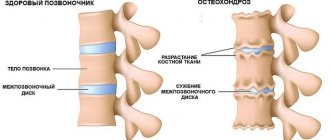
Osteochondrosis in the cervical region . If there are problems with the spine, they can be the result of pain on one side of the head or in any part of it. Manifestations are accompanied by dizziness, tinnitus, neck pain and problems with the musculoskeletal system. The scalp may feel tingling or itchy.
Dental problems . If a tooth on the right side is bothering you, this may also be the cause of similar pain in the head. Since the nerve endings of the tooth are directly connected to the head area, the pain can be transmitted higher and not stop until the tooth is cured.
Tumor . This headache has more periodic symptoms and is accompanied by nausea, vomiting and dizziness. Most often this pain can be felt in the morning. It may also intensify, but besides this, personal changes accompany it, such as weight loss, seizures, and appearance in general.
Costen's syndrome . If you have a headache on the right side above the ear and radiate directly to the ear, temple or jaw, this is Costen’s dysphoria. The pain may become stronger when chewing, hearing deteriorates, it seems as if the ears are blocked, and the mouth cannot be opened completely. Costen's syndrome is also called temporomandibular joint dysfunction.
Intracranial bleeding . The main symptom of such a disease is suddenness. Immediately in addition to the growing headache, nausea appears, clarity of speech and vision, coordination are impaired, and the person may lose consciousness.
Effect of electromagnetic radiation
Even a turned off mobile phone is a source of disturbed electromagnetic field. A working device has a direct negative impact on the contents of the skull. Using a telephone headset can reduce potential risks, but this approach also has its downsides. Cell phone radiation is much inferior to the same effect from a microwave oven, but the situation is aggravated by its constant presence in a person’s life and proximity to the brain.
The electromagnetic field of a cell phone can cause the following consequences:
- brain tumor – waves are absorbed by organ tissues, which increases the risk of their changes, degeneration, and growth. The theory has not yet received practical confirmation, but scientists do not exclude such a possibility;
- the appearance of problems with sleep - headaches caused by using the phone are often the result of lack of sleep. It has been proven that talking on a mobile phone before going to bed significantly lengthens the phase of falling asleep, reducing the quality of rest;
- increased reactivity of the body - studies have shown that people who talk on a cell phone for more than an hour a day in total become irritable, nervous, and hysterical.
It is important to understand that a person is exposed to radiation emitted by the device not only during a conversation. The phone lying next to the bed is dangerously close to the head.
I have a headache on the right side - what should I do?
Pain can be dealt with using the usual and all known methods: painkillers, teas, massage of head points, warm compresses, fresh air. Or maybe it’s all about stress, and just solving your problems will calm you down. Or maybe it’s just enough to go to bed early and get a good night’s sleep, if you haven’t had that for a long time.
However, if the pain is not one-time, but constant, corresponds to the above symptoms, and you yourself assume that the pain is a sign of illness, you need to consult a doctor. It will not harm to undergo an examination; the cause will be identified and, perhaps, in its early stages, this will help to start treatment on time. In addition, even if the results of the examination did not show anything, the doctor will help you understand why your head hurts on the right side and give practical advice on what is best to do in such cases.
How to treat a headache on the right side of the head?
The first thing to do if a person has a headache on the right or left side is to seek help from a doctor to find out the exact cause of the headache on the right side. Very often, people simply do not pay attention to the pain on the right side of the head and ignore it in every possible way, in some cases they use painkillers that only hide the painful symptom, and the cause of the pain on the right side of the head continues to progress and become more complex. It should be understood that the best prevention of headaches on the left or right side of the head is the timely detection of the cause of the pain; treatment of the cause of the headache is the fastest and most effective way to completely eliminate the painful symptom.
Treatment of pain in the head on the right directly depends on making an accurate diagnosis, because if the cause of a headache on the right side of the head is one of the possible diseases, then the treatment of painful symptoms will be individual in each case. If you don’t know what to do if you have a severe headache on the right side, then it is recommended to immediately seek help from a doctor.
Causes of pain in the upper part of the head with a feeling of compression
An unpleasant sensation in the crown with a feeling of compression occurs when the liquor volume changes. Liquor is a special liquid that circulates in the cranial cavity; its function is to protect the brain.
The amount of fluid changes slightly, since new fluid is constantly being produced and absorbed into the bloodstream. Under some circumstances, the volume of cerebrospinal fluid increases, causing a feeling of pressure on the brain.
The nature of the sensations is aching, bursting, as if “flowing” from one hemisphere to another when changing position. During physical activity, strong pulsation begins, and short-term visual impairment is possible.
What conditions cause an increase in the amount of cerebrospinal fluid:
- Hormonal changes, which are more relevant to the female body;
- Ophthalmological pathologies, ocular myasthenia gravis, glaucoma;
- Closed brain injuries, especially with the risk of hematoma;
- Infections of the meninges (meningitis, encephalitis), otitis media;
- Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine with impaired outflow of blood and lymph;
- Neoplasms of various etiologies.
All the described pathologies cannot be cured with one tablet. If you suspect increased intracranial pressure, it is important to identify the causes and act on them.
What to do if you have a headache on the right side during a migraine?
If you have a very frequent headache due to migraine, it is recommended to consult a doctor not only about the use of painkillers, choose the most suitable one, and comprehensively examine your body to determine the cause of the pain on the right side of the head. If you take painkillers for headaches, this will not remove the cause of the pain, but will only muffle the painful symptoms. If a person wants to remove the cause of pain on the right side of the head, then he needs to establish an accurate diagnosis of the occurrence of headaches.
Source: vevolife.ru
By
What causes scalp pain?
Content:
The scalp can hurt for various reasons, but you need to remember that you should never tolerate a headache. To solve the problem, you need to find the cause of the pain in the skull and eliminate it. If you consult a neurologist, he will definitely find a problem in the brain activity that causes pain; the therapist will most likely see the cause of the pain as a vascular disorder; the psychotherapist will tell you that the pain is caused by stress.
Remember, there are many sources that can cause pain in the skull - stress, lack of essential microelements in the body (copper, potassium, phosphorus, magnesium), etc., constant stress, osteochondrosis, lack of sleep. Also, pain in the skull can occur due to very serious diseases - meningitis or a brain tumor.
What causes scalp pain most often?
1. Because of a tension headache (doctors call this pain a “neurotic helmet”). All unpleasant and painful sensations arise when the muscle tone of the neck or scalp increases and does not relax for a long time. The reason is probably familiar to everyone - a strong emotional experience, physically overworked. Pain can also be caused by bad habits - smoking, alcohol. Even wearing clip-on earrings or large earrings, pain may occur because they put pressure on very important points on the ears. What characterizes this pain in the skull? It is monotonous, dull, two-sided. One gets the feeling that the skull is compressing the hoop very tightly; it can occur periodically - less than 14 days a month and be chronic - more than 14 days. Experts have long found out that this pain in the skull is typical for people who look at the world through the eyes of a pessimist. Gradually, all experiences and complexes accumulate, and everything results in pain.
How can you get rid of this type of pain in the skull? Take a sedative, it is best to drink peony tincture, chamomile tea, passion flower. Don't forget about autogenic training. An excellent remedy is a head massage, it helps relieve tension from the skull. Recently, a reliable method has emerged - combing out headaches using a massage brush. This method increases blood circulation and relaxes muscles, restoring blood circulation.
You should also turn your attention to reflexology, breathing exercises and aromatherapy.
2. Due to problems with blood vessels. Pain in the skull may occur if your blood vessels dilate or spasm. This pain is typical for those who move very little and sit constantly. Also, pain in the skull can occur due to vegetative-vascular dystonia and osteochondrosis. The whole head hurts, the pain is throbbing, it radiates to the temples, and there is a feeling of weakness. All these symptoms are intensified by various factors - changes in weather, in women before menstruation. Here home remedies will not help, you need to use antispasmodics - no-spa, sutorogen. Such pain in the skull can be alleviated by a wet compress, massage of the head, neck, herbal tea from hawthorn, lemon balm, and cucumber. People with this problem should not drink coffee.
3. Pain in the skull due to migraine - the pain is unbearable to endure, it radiates to the skin of the head. Migraines occur due to a lack of serotonin. Migraine is typical for women, appears after 25 years, an attack lasts from 5 hours to 4 days. In addition to pain in the skull, nausea, vomiting occurs, and sounds and light are irritating. Here you need to use vasodilators first, then vice versa vasoconstrictors. A light massage will help,
4. Pain in the skull due to poor diet. Scientists have long proven that the appearance of pain is associated with the consumption of foods that are not suitable for a person. Because some substances contained in products have a very strong effect on blood vessels. For example, “tyramine” has a negative effect; it is found in sour cream, pickled fish, crabs, shrimp, beer, smoked meats and sausages.
Sodium nitrate also has a negative effect; there is a lot of it in chips, crackers, and bouillon cubes.
You should also pay attention to products that contain caffeine. They can cause throbbing cranial pain, as well as weakness, confusion, anxiety, fear, nausea and insomnia. To avoid such problems, you need to follow a diet.
By the nature of the pain in the skull, you can find out why it appeared:
1. The whole head hurts - an infectious disease and a cold. 2. Forehead hurts - an eye disease. 3. Shoots into the temples, hits the back of the head - problems with blood vessels. 4. Skull hoop – pain due to tension. 5. Pain in the temple on one side – migraine.
Remember, if there is pain in the skull, along with dizziness, blurred vision, you need to immediately consult a doctor, these are only common causes of its occurrence, there are many more, for example, various head injuries, infectious diseases, problems with the spine, etc. – all this can influence the appearance of pain.