In the first part of the article, we discussed issues related to the symptoms, types, classification, causes and diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. However, readers who are accustomed to a detailed and comprehensive presentation of material expect a continuation, not without reason. Therefore, today we will together try to figure out whether it is possible to treat Parkinson’s disease at the current level of development of science and medical knowledge. But in order to prevent possible questions, we consider it our duty to clarify one point regarding the treatment of this pathology.
Read the first part of the article - Diagnosis and symptoms of Parkinson's disease.
The claim that Parkinson's disease is curable is false! Therefore, you should not believe the promises of medical charlatans. However, the question of methods and methods of therapy lies not in a theoretical, but in a practical plane. This means that neither patients nor their relatives and friends should give up in advance. After all, it’s one thing to give up morally and spend the rest of your days in a wheelchair, and quite another thing to fight for life, fighting off illness month after month, year after year. And the widespread opinion in society that patients with Parkinson’s can only live for 5-10 years is devoid of any scientific basis and, in fact, is a myth. The average life expectancy of people with this diagnosis is the same as that of healthy people (of course, with a certain adjustment for age), but its quality is completely different.
How to treat Parkinson's disease (prevention, alas, is practically impossible with such a pathology)? In this matter, everything depends on many objective and subjective factors, but the surgical method practiced for almost 200 years is no longer the only possible one, and the technology of surgical intervention itself has moved far from the lobotomy, beloved by practicing psychiatrists of the 19th century. Pharmacology has achieved serious success: some drugs, with a successful combination of circumstances, can significantly slow down the rate of increase in symptoms. Do not discount the latest methods of acupressure neurostimulation, as well as time-tested folk remedies and exercise therapy. In a word, the doctor and his patient always have a choice. This choice will be the topic of our conversation today.
What is Parkinson's disease
The movements performed by the body are carried out through a complex interaction between the brain and spinal cord. Additionally, auxiliary structures, such as the basal ganglia, are involved in this process. These formations are in close connection with the cerebral cortex; they are not able to work independently. With their help, a person can perform actions that require the development of certain skills - writing, drawing, sports activity, tying knots, striking limbs. After the impulse is generated in the cerebral cortex, the signal passes to the ganglia, which issue the necessary commands to the corresponding muscles.
The work of the basal ganglia is carried out through neurotransmitters - specific biologically active substances - that provoke an inhibitory or excitatory effect. The principle of muscle function depends on the type of neurotransmitter and its quantity. The main substance in this case is dopamine, which inhibits impulses. Thanks to its action, the fibers contract as needed, and movements are clear and precise.
In Parkinson's disease, smooth processes are disrupted as a result of simultaneous damage to the basal ganglia and a decrease in the volume of dopamine.
The number of neurons decreases, nerve tissue is destroyed, the signal does not slow down - it goes directly to the muscles, causing them to contract involuntarily.
In Parkinson's disease, the number of neurons decreases.
Why is Parkinson's disease dangerous?
Parkinson's disease is accompanied by many manifestations that reduce the quality of life of the victim. In the absence of treatment, attempts to independently cope with the pathology, and inadequate care for the patient, this is complemented by a high probability of developing complications. Some of them can lead to premature death.
Options for dangerous consequences of Parkinson's disease:
- akinesia – inability to perform voluntary movements;
- frequent and prolonged constipation - in advanced cases lead to severe intoxication and death of the patient;
- inflammation of the mucous membrane of the eyes - the result of a decrease in the number of blinks, which can lead to deterioration or loss of vision;
- Dementia – Patients with Parkinson’s disease almost always suffer from apathy or depression. Advanced psycho-emotional disorders are accompanied by personality changes, memory deterioration, and a decrease in the level of intelligence;
- seborrhea - active production of sebum often provokes dermatitis, ulcers, and extensive inflammatory processes.
Thanks to the achievements of modern medicine, each patient with Parkinson's can receive effective treatment that reduces these risks. The approach should be combined and lifelong, with mandatory adjustments as the disease develops.
One of the dangerous consequences of Parkinson's disease: frequent and prolonged constipation - in advanced cases, leads to severe intoxication and death of the patient.
Why are neurons destroyed?
Structural changes in the brain largely affect the basal ganglia and the substantia nigra of the extrapyramidal system. The anterior sections of the black mass are predominantly affected.
Signs characteristic of Parkinson's disease occur when 60-80% of nerve cells in this anatomical region die. The reasons for the massive destruction of neurons are still being studied, and there are several theories.
According to the most popular of them, harmful external conditions, taking a number of medications, and chronic circulatory failure in the brain become provocateurs of the destructive process.
It is noteworthy that smoking tobacco and drinking coffee to some extent protect nerve cells by stimulating the production of dopamine.
Causes of Parkinson's disease
The studies have not revealed a predisposition to Parkinson's based on ethnicity or social level.
Elderly people are at risk, but cases of pathology developing before the age of 40 have also been recorded. Separately, there is a juvenile form of the disease, in which its symptoms appear in people under 20 years of age.
Elderly people are at risk.
The main causes and provocateurs of Parkinson's syndrome:
- age - aging of the body is accompanied by a natural mass death of cell colonies of the medulla. If at the same time there is a decrease in dopamine levels, the risks of developing degenerative changes increase sharply;
- genetic predisposition - statistical studies have confirmed the influence of a hereditary factor, but the Parkinson's disease gene has not yet been discovered;
- unfavorable environmental conditions - doctors identify dozens of irritants that can provoke massive death of nerve cells. The most common are heavy metals, biological and industrial poisons, pesticides, toxins, free radicals;
- taking medications - in pharmacology, there are several groups of drugs that affect the synthesis of dopamine. Some of them, for example, antipsychotics, can even provoke side effects that resemble the clinical picture of Parkinson's disease;
- organic lesions of the central nervous system - head injuries, infectious or inflammatory processes in the skull can have a negative impact. The danger is atherosclerosis, brain tumors, diseases of the endocrine glands;
- refusal to lead a healthy lifestyle - lack of sleep, poor diet, vitamin deficiency, chronic stress, physical inactivity inhibit metabolic processes in the brain, creating favorable conditions for the death of neurons.
The main cause and provocateur of Parkinson's syndrome is unfavorable environmental conditions.
These factors increase the likelihood of developing degenerative processes in the brain, but they do not provoke them. The exact causes of Parkinson's disease have not yet been identified.
Classification of Parkinson's disease
For the convenience of working with patients, specialists use a number of classification options for Parkinson’s disease. According to them, different forms of pathology are distinguished, as well as several stages of its development.
Stages of Parkinson's disease according to the generally accepted classification:
- 0 – no signs of movement disorders;
- 1 – there are symptoms of the disease, but they are unilateral;
- 2 – the disease manifests itself bilaterally while maintaining the patient’s ability to maintain balance;
- 3 – there is obviously a moderate impairment of body stability in an upright position, but the patient continues to move independently;
- 4 – the ability to move is preserved, but motor activity is impaired;
- 5 – the patient is unable to move without assistance, he is confined to a wheelchair or bed.
At the last stage of the disease, the patient is unable to move without the help of others and is confined to a wheelchair.
Doctors often use the Hen and Yahr scale to describe pathology:
- 0.0 – no symptoms of Parkinson’s disease;
- 1.0 – signs of pathology are observed, but one-sided;
- 1.5 – symptoms are one-sided, the clinical picture involves problems in the functioning of the muscles in the neck and along the spine;
- 2.0 – signs of the disease affect both halves of the body, balance is maintained;
- 2.5 – the clinical picture is mild; when the patient is pushed from the front, he is still able to overcome the acceleration backwards;
- 3.0 – symptoms are moderate or moderate, signs of instability in an upright position appear, the patient does not require assistance from outsiders;
- 4.0 – the victim can stand or walk independently, but his body is severely immobilized;
- 5.0 – the patient is confined to a bed or chair and needs full care.
According to the basic classification, Parkinson's disease can take one of the following forms (according to frequency of detection):
- trembling-rigid (37%) – trembling of the limbs and/or head comes to the fore;
- akinetic-rigid (33%) – trembling is completely absent or appears in moments of excitement of the patient;
- rigid-trembling (21%) – a special mixed form, which is characterized by muscle hypertonicity and a decrease in the usual speed of movements;
- trembling (7%) – trembling occurs against the background of normal muscle tone, complemented by a slight lack of facial expressions and slower movements;
- akinetic (2%) – the patient does not have the ability to perform voluntary actions.
There is a trembling form of the disease - trembling occurs against the background of normal muscle tone.
Each stage of Parkinson's disease requires a special therapeutic approach. Some forms are distinguished by such specific clinical picture that they are difficult to distinguish from a number of other neurological diseases.
Symptoms and signs of Parkinson's disease
The severity of the first symptoms of Parkinson's disease is usually mild, which makes diagnosis difficult. Often, manifestations characteristic of the initial stage of pathology are mistaken for overwork, problems with the spine, the result of lack of sleep or chronic stress.
Symptoms of Parkinson's disease:
- tremor - trembling of the limbs, head or parts thereof. It can be observed in a calm state, with excitement, or attempts to make conscious movements. A characteristic type of symptom is “coin counting,” which affects the thumb and index finger. In severe cases, the symptom occurs while a person is performing some action, for example, eating, which significantly complicates his life;
- increased muscle tone - rigidity of the flexors predominates over the extensors, which is why the patient with Parkinson's disease takes a characteristic posture. Upon examination, the symptom manifests itself in the form of increased resistance of the joints to passive external influences. Most often it is uneven, the impact on the joint is felt like working with a gear wheel;
- hypokinesia, bradykinesia – decrease and noticeable slowdown in motor activity. The problem affects all muscle groups, but is most obvious on the face. The patient rarely blinks, his gaze seems heavy. Speech becomes quiet and monotonous, and drooling is often observed. The patient has difficulty holding cutlery, writing instruments, fastening buttons, tying shoelaces;
- postural instability - occurs already at a late stage of the disease, manifests itself in difficulties with changing posture and changing the direction of movement. The gait is shuffling, mincing, and is often accompanied by falls. If a person with Parkinson's is slightly pushed in the chest, he will not maintain his balance, but will begin to step back in small steps;
- bradyphrenia – slowing and dulling of emotional reactions and thinking;
- dementia - develops in later stages, usually manifests itself in memory impairment, difficulty expressing thoughts, lack of interest in learning and development;
- psychoemotional disorders – depression is common in patients with Parkinson’s. Sometimes they become the first sign of degenerative brain damage. The patient becomes irritable, insecure, withdrawn, drowsy during the daytime;
- orthostatic hypotension – a drop in blood pressure when moving from a horizontal to a vertical position. Often leads to fainting;
- disturbances in the functioning of the digestive tract - constipation is a common problem. They arise due to muscle atony against the background of decreased physical activity, water deficiency, poor diet, and medication;
- increased oily skin - the face changes its usual appearance, dandruff may appear;
- disruptions in the urination process - trips to the toilet become more frequent or, on the contrary, become abnormally rare;
- problems with eating - impaired chewing, swallowing, active secretion of saliva, worsening mood lead to the inability to eat normally. Due to the listed features, the natural process begins to pose a danger, the patient may choke;
- speech disorders – speech is monotonous, there is a lot of repetition. In half of the patients it is slow, in the other half it is greatly accelerated, but in any case inarticulate;
- myalgia – muscle pain is caused by a decrease in their elasticity and limitation of motor activity. Sometimes this is accompanied by aching joints and muscle spasms;
- disorders in the sexual sphere in men - dysfunction develops against the background of deterioration of blood circulation in the pelvis, psycho-emotional problems, and medication.
The severity of the first symptoms of Parkinson's disease is usually mild, which makes diagnosis difficult.
The clinical picture is complemented by a general deterioration in health. A patient with Parkinson's experiences weakness, gets tired quickly, and feels exhausted in the evening. Proper organization of the daily routine and normalized physical activity can reduce these uncomfortable sensations to a minimum.
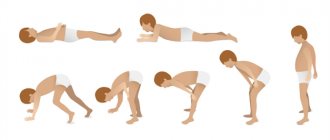
What do people with Parkinson's disease look like?
At a certain stage of the pathology, due to muscle stiffness, patients are forced to take a special position, by which they become easily recognizable.
People with Parkinson's disease have limited movement. They are slightly tilted forward, their head is slightly extended, their legs are parallel, their arms are bent at the elbows and pressed to the body. Patients walk slowly, taking small shuffling steps, without using their hands. The facial expression is more like a mask and does not express obvious emotions. The gaze is fixed on one point, it seems tense due to the rare blinking. Some patients experience slight trembling of the whole body or its individual parts.
Musician Ozzy Osbourne
Pope John Paul II
Bill Gates
Salvador Dali
The famous Marty McFly from the movie Back to the Future
The first signs of Parkinson's disease at the prodromal stage of the disease
At the initial stage of pathology, the list of symptoms and signs is not so impressive, the manifestations are often blurred. But even in this case, careful attention to an elderly person will allow one to suspect the presence of a disease, and not just the appearance of natural age-related changes. By recognizing the first non-obvious signs of Parkinson's disease, you can begin specialized therapy early, significantly increasing the victim's chances of a long, fulfilling life.
Having recognized the first non-obvious signs of Parkinson's disease, you can begin specialized therapy early, significantly increasing the victim's chances of a long, fulfilling life.
Partial loss of smell
In 70-90% of cases, Parkinson's disease at an early stage can be diagnosed by smell, or rather, by the lack of sensitivity to aromas. This may be a complete or partial loss of function due to the onset of a degenerative process in the areas of the brain associated with the olfactory bulbs. The symptom can develop years before the onset of tremors and problems with motor activity, therefore it is considered one of the important stages in the diagnosis of Parkinson's disease. In older people, the symptom often manifests itself in the form of neglect of hygiene, the use of a large amount of perfume, and complaints about the lack of taste in food.
Mild tremor of the limbs
Already at an early stage with Parkinson's syndrome, there is a slight trembling of individual fingers, twitching sensations in the muscles of one or both feet, and tremor of the hands. Symptoms arise or intensify against the background of stress, overwork, fear, and overexcitement. These minor spasms disappear after rest or when the patient calms down.
Most of the time, the patient does not feel discomfort; no symptoms are observed during sleep.
For these reasons, manifestations are often associated with functional malfunctions in the body, without suspecting a serious pathology.
Memory impairment and speech impairment
As nerve cells die, the patient experiences memory problems. Initially, this manifests itself in forgetting some episodes from the distant past. Forgetfulness then extends to short-term memory. With an advanced form of the pathology, the patient stops recognizing loved ones, cannot find words, and loses the thread of the conversation. Speech disorders are additionally manifested in monotony, lack of intonation, frequent hesitations, and a quiet voice. The severity of such signs of Parkinson's disease is the same in men and women.
As nerve cells die, the patient experiences memory problems.
Minor muscle stiffness
At the initial stage of the disease, the inability of muscle fibers to relax on their own after tension may not be obvious. It manifests itself as a result of an imbalance between muscle work and rest, which leads to increased fatigue. A person, performing the usual volume of actions, gets more tired and loses strength faster. It seems to him that he has become weaker and needs more frequent and longer rest breaks. From the outside, you can notice that the patient’s movements are difficult, intermittent, and awkward.
To the point
Daria Kostyuk, trainer
:
I had heard about treatment with bees, but I probably wouldn’t have decided on such an experiment myself. In order to agree to an apitherapy session, you must not have allergies.
But most importantly, you need to be prepared psychologically. But not everyone, and I would even say a rare person, will consciously agree to be stung by bees.
Another thing is honey. I welcome this part of apitherapy.
The work of the human body is based on many reflexes: when we touch something hot, we involuntarily withdraw our hand, when a beam of bright light hits our eyes, we involuntarily squint, and so on. There are a lot of external irritants, and if the body reacted to all of them, we would constantly itch, flinch, scream... However, this does not happen. Why? The fact is that the nervous system has so-called brakes, thanks to which the reaction occurs only when exposed to the most powerful stimuli.
The treatment we will discuss in this article is characterized by the suppression of such natural inhibitors. As a result of this, a person begins to react with movements even to those impulses that are extinguished in the normal state. This manifests itself in involuntary twitching and grimacing. The patient's muscles become lethargic, and the psyche is depressed.
Diagnostics
There are no specific tests or examinations to detect Parkinson's disease.
To make a diagnosis and confirm it, it is necessary to carry out a series of measures, conditionally divided into three stages.
An integrated approach allows you to identify the problem, differentiate it from other pathologies, and establish the severity and form of the syndrome.
Stage 1
When diagnosing Parkinson's disease, it is important to identify symptoms characteristic of degenerative brain damage. This is done through a physical examination. A simple examination by a professional can detect stiffness of movement due to tension in muscle fibers, trembling of the limbs or head. Simple tests help assess the subject’s coordination, his ability to maintain balance, and perform purposeful movements.
A simple examination by a professional can detect stiffness of movement due to tension in muscle fibers, trembling of the limbs or head.
Stage 2
In the process of diagnosing Parkinson's disease, it is necessary to exclude signs and factors indicating other types of functional or organic damage to the central nervous system. To do this, the doctor pays attention to a history of tumors or brain injuries, single and repeated strokes. The specialist must take into account the fact that the patient is being treated with neuroleptics and eliminate the possibility of poisoning the body with neurotoxins. Tests for the Babinski reflex, signs of impaired eye movement, are considered informative.
The second stage of diagnosing Parkinson's disease can take several months. During this period, it is necessary to exclude pathologies that are characterized by prolonged remissions, senile dementia, problems that affect only one half of the body for more than three years. Already at this stage, the doctor can prescribe antiparkinsonian drugs to the patient. The absence of a clear positive effect also indicates an incorrect preliminary diagnosis.
To make a more accurate diagnosis, the doctor pays attention to the presence of a history of brain tumors.
Stage 3 – confirmation of the presence of Parkinson’s disease
At the final stage of diagnosing Parkinson’s disease, the progress, duration of the clinical picture, and its response to anti-Parkinsonian treatment are taken into account. With this form of degenerative brain damage, symptoms should gradually move from one half of the body to the other.
It is imperative to check for the Westphal phenomenon - passive flexion of the joint leads to contraction of the nearby muscles instead of relaxation, after which it remains bent.
The symptom of the lower leg is considered informative - the patient should lie on his stomach and bend one leg at the knee; in Parkinson’s, it will straighten slowly and not completely.
Differential diagnosis
Modern neurology is represented by many diagnostic studies that can establish the causes of a person’s poor health. Unfortunately, all existing instrumental and laboratory approaches are not able to clearly diagnose Parkinson's disease. But they help to exclude other types of central nervous system damage. If a person has initial signs of the disease, he is prescribed an EEG, CT, MRI for a general assessment of the condition of the organ, identifying affected areas in it. Additionally, electromyography is performed - a method of studying bioelectric processes in muscles.
If a person has initial signs of the disease, he is prescribed an EEG.
Experts' opinion
Of course, apitherapy and the treatment of Parkinson's disease are a tandem that deserves the right to exist. However, it is not always worth trusting the theory unconditionally; practical evidence of the effectiveness of this method is also important. Additionally, you should never rely on alternative medicine without your doctor's knowledge. The effectiveness of all existing traditional medicine recipes is based solely on an integrated approach, i.e. it “works” only in conjunction with traditional drug therapy, or can be used as a preventive measure.
It follows from this that before starting treatment for Parkinson’s with bees, you need to consult a doctor. And even if you decide to put this method into practice, you need to conduct regular examinations, so you can monitor the dynamics of the disease.
How quickly does Parkinson's disease progress?
The rate at which symptoms spread and intensify is greatly influenced by the age at which the first signs of pathology appear in the patient. If this happened in young years, then Parkinson's will develop slowly over 30-40 years. If the condition is diagnosed at age 40, its progression may take a couple of decades. In older people, the clinical picture increases rapidly, on average, over 5-10 years. An irresponsible approach to treatment and rehabilitation for Parkinson's disease and ignoring doctor's recommendations significantly reduce these terms. 25% of people who do not take the disease seriously may develop severe disability within the first five years, followed by death.
Therapy for severe parkinsonism
Stronger medications must be used if there is advanced Parkinson's disease. Treatment with folk remedies described above may not be effective in this case. When other methods are ineffective, you can try using poisonous plants such as hemlock, fly agaric (mushroom), aconite, datura, belladonna, henbane. But you need to select the dosage very carefully so as not to harm yourself. We will not provide recipes for potions from these plants in this article; contact a specialist to calculate the dose that is right for you.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease
The fight against the disease begins immediately after diagnosis and continues throughout the patient’s life. Treatment of the disease must be comprehensive, corresponding to its stage, form, age of the patient, and the characteristics of the case. If the measures are chosen correctly, this will stop or significantly reduce symptoms and slow down the spread of the degenerative process. Modern medicine offers traditional, folk and alternative approaches to treating Parkinson's. To achieve maximum effect, it is recommended to combine them.
Modern medicine offers folk remedies for the treatment of Parkinson's.
How to treat Parkinson's disease in the elderly
Most often, elderly people suffer from Parkinson's disease, and in their case the treatment process is significantly more complicated. The patient may already be taking medications, so specialized medications are prescribed with caution. In older people, depressive disorders are more pronounced than in young people, which requires gentler treatment and often requires the help of a psychologist.
Older people usually require constant monitoring, otherwise they will forget to take medications, perform procedures, and follow diet rules. Due to their physiology, this group of patients is more susceptible to injury and can pose a danger to themselves and others. Doctors recommend not leaving such patients unattended or, if possible, placing them in specialized medical institutions.
Which doctor treats Parkinson's disease
A treatment regimen for Parkinson's disease is selected by a neurologist. He also monitors the dynamics and makes adjustments to the developed plan. At the same time, a whole group of specialists cares for the patient. Depending on the severity of the situation, the characteristics of the case and the therapeutic approach, the team includes: psychologist, psychotherapist, psychiatrist, physiotherapist, defectologist, speech therapist, neurosurgeon, therapist and others.
The neurologist monitors the dynamics of the disease and subsequently makes adjustments to the developed plan.
Traditional treatment for Parkinson's disease
The basis of therapy in the fight against degenerative processes in the brain is taking medications. The list of medications, dosages, schedule and duration of administration are selected individually. The indicators are adjusted by the attending physician during the treatment process in accordance with the manifestations of positive dynamics or progression of the pathology.
Groups of drugs used for Parkinson's disease:
- products with dopamine precursors and antagonists (Levodopa, Lisuride, Ropinirole) - fight dopamine deficiency in the central nervous system;
- MAO and COMT inhibitors (Selegiline, Entacapone) - block enzymes involved in the destruction of dopamine;
- "Amantadine" and analogs - stimulate the release of dopamine from cells, facilitate this process;
- products for the balance of excitation and inhibition of neurons (“Biperiden”, “Procyclidine”) - stop the action of the excitatory neurotransmitter acetylcholine;
- glutamate receptor blockers (“Amantadine”) – stop the action of the excitatory neurotransmitter glutamate;
- symptomatic drugs - antipsychotics, antidepressants, antihistamines, muscle relaxants and other products.
Ropinirole combats dopamine deficiency in the central nervous system.
Traditional treatments for Parkinson's disease include surgery. To combat tremor, a technique is used to destroy the nuclei in the hypothalamus. A similar effect on the basal ganglia leads to partial or complete restoration of motor functions. Such approaches are very dangerous and are used only in extreme cases.
One of the newest treatments for Parkinson's disease is targeted neurostimulation.
This is a minimally invasive surgical intervention on the brain, during which electrodes are inserted into the structures of the organ. They are connected to a neurostimulator, which is implanted under the skin on the patient's chest. This device makes it possible to deliberately irritate problematic parts of the central nervous system with current discharges, potentiating their functions and relieving the symptoms of pathology. The approach helps reduce the patient’s consumption of medications, which are quite aggressive and often provoke adverse reactions.
Alternative Treatment for Parkinson's Disease
In addition to basic approaches to combating the symptoms of pathology, alternative medicine options can be used. Any appointments must be previously agreed with the attending physician. Independent actions can lead to side effects and worsening problems.
Any medical treatment must be previously agreed with the attending physician.
To treat Parkinson's disease, it is recommended to use the following folk remedies:
- relief of cramps - pour half a glass of dried linden flowers with 40% medical alcohol to a full glass. Close the lid, leave for 3 weeks in a dark place, pass through cheesecloth. Take the infusion one teaspoon up to 3 times a day after meals;
- relaxation of muscles, elimination of tremors - pour a glass of oats into 2 liters of drinking water, bring to a boil, leave for 40 minutes over low heat. Leave covered for 2 days, pass through cheesecloth. Take 100 ml up to 3 times a day before meals for 3 months. Courses can be systematic with a break of 3-4 weeks;
- increasing motor activity, combating muscle tremors - chew 1 g of propolis before breakfast and dinner for 15 days. After 3-4 weeks the course can be repeated;
- Relieving muscle spasms, eliminating cramps - pour a couple of tablespoons of sage into 500 ml of boiling water, leave for 10 hours, pass through gauze. Drink 100 ml up to 4 times a day before meals;
- improvement of general well-being, relief of the main symptoms - pour 3 tablespoons of St. John's wort into a glass of boiling water, leave for 5 hours, pass through gauze. Before breakfast and lunch, drink 100 ml of infusion for 2 months. After a month, the course can be repeated.
Among the effective new alternative methods in the treatment of Parkinson's disease, one of the leading places is occupied by the use of stem cells. The approach consists of introducing neurons isolated from biological material into the affected areas of the brain. Studies have shown that 80% of patients experience a lasting positive effect after 3 years as a result of compensation of affected tissues. The only drawback of the method is that it has not yet been fully researched and is not actively used in clinical practice.
To increase motor activity and combat muscle tremors, chew 1 g of propolis before breakfast and dinner for 15 days.
Other Treatments for Parkinson's Disease
Parkinson's is a serious disease, the fight against which requires an integrated approach. The exact list of measures is selected by a neurologist. Many techniques are recommended to be practiced not only under the supervision of a specialized doctor, but at home.
The treatment regimen for Parkinson's disease usually includes:
- physical therapy – performing active and passive exercises to restore trophism and develop muscles, relieve their tension, increase the volume of voluntary actions;
- massage – intensive training of muscle fibers in order to eliminate spasms, restore blood circulation, and relieve pain;
- dietary nutrition - the basis of the diet should be food of plant origin, which helps reduce cholesterol levels. This will launch metabolic processes in the brain tissues and increase the performance of organ parts;
- the fight against speech disorders - exercises selected by a speech therapist that will not only smooth out speech defects, but also improve the functioning of facial muscles and facilitate the chewing process.
The effectiveness of treatment for Parkinson's disease largely depends on the participation of the patient's loved ones during therapy. They should help the patient do exercises, monitor his diet, provide him with comfort and safety, and moral support.
The treatment regimen for Parkinson's disease usually includes physical therapy.
Primary and secondary prevention of Parkinson's disease
Primary prevention of Parkinson's disease should begin at a young age. It is recommended for everyone without exception; it is recommended to follow simple rules throughout your life. The list of mandatory measures includes the creation of normal external conditions. An environmentally unfavorable environment, being in a stuffy room, contact with industrial poisons or pesticides increase potential risks.
Much attention should be paid to the quality of nutrition and the composition of the diet - healthy food, compliance with the drinking regime, avoidance of processed foods and additives are necessary for the health of the central nervous system.
There should be room in every person's life for regular physical and mental activity.
Secondary prevention is aimed at eliminating the direct causes of the onset and development of Parkinson's disease. It includes the prevention of functional disruptions in the central nervous system and organic brain lesions. The complex of measures requires compliance with the work and rest regime, providing the body with daily night sleep lasting 7-8 hours. Preventing stress and strengthening general immunity are important. Adults should undergo regular medical examinations and consult a doctor if they have any health complaints.
Strengthening the general immune system is important for disease prevention.
A swarm of bees is flying towards us!
Initially, bee venom is administered in small doses and the patient’s condition is monitored, and control blood and urine tests are done. Is your body reacting normally? You can start treatment. At the same time, during the course it is advisable to refrain from smoking and definitely from drinking alcohol, and you should not overeat. These bees are such demanding insects.
Bee venom, for all its wonderful properties, is still poison, and self-medication is inappropriate here. Today, special diagrams and tables have already been developed, doses have been selected, and zones for bee stings have been determined in accordance with the disease and age of the patient. As a rule, sessions begin with setting up only one or two bees; gradually the number of bees is increased to three dozen at a time. Of course, this is painful, although it is more effective compared to the introduction of bee venom using ointments, infusions and other drugs. In addition, the pain from the underlying disease goes away almost immediately, so many agree to endure the required number of sessions. And the pain from the bites gradually dulls... The course of treatment, as a rule, lasts at least six months.
Is it possible to cure Parkinson's disease?
Even in the case of early detection of pathology, high-quality specialized treatment and compliance with all doctor’s recommendations, it will not be possible to completely get rid of the problem. In the most favorable scenario, therapy will lead to a slowdown in the development of the degenerative process in the brain, stopping or weakening symptoms.
What is the prognosis for Parkinson's disease
A person with Parkinson's has a high chance of living a long and fulfilling life, but the progression of the disease cannot be stopped. For this reason, diagnosis automatically implies a poor prognosis. All therapy methods and rehabilitation measures in this case are aimed at relieving existing symptoms and improving the patient’s psycho-emotional state. If the victim has other neurological diagnoses, his chances of a normal existence drop sharply.
What determines the life expectancy of people suffering from Parkinson's disease?
From the moment of diagnosis to the death of the patient or the onset of severe disability, it can take from 5 to 40 years or even more. This indicator depends on the form and degree of Parkinson’s disease, the patient’s age at the onset of the degenerative process, and the speed of its spread. The quality of treatment and correct implementation of the doctor’s recommendations also play an important role. With an integrated approach to combating the problem, following a diet, and maintaining a healthy lifestyle, there is every chance that the symptoms will not greatly complicate the patient’s existence.
Preventive diet
Particular attention should be paid to balanced nutrition. A healthy lifestyle includes not only regular exercise, walks, good sleep, but also saturating the body with all the necessary vitamins and minerals.
Nutrition should be aimed at preventing atherosclerosis and heart disease. It must be balanced so that the central nervous system is fully supplied with the necessary substances.
The principles of the diet include:
- Increasing the consumption of fruits and vegetables. The diet should include as many foods as possible containing fiber and dietary fiber, which would improve the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract.
- It is necessary to limit the consumption of fatty and sweet foods. Confectionery and baked goods are prohibited.
This diet will help improve metabolism and prevent the development of a large number of diseases.
How to live with Parkinson's disease
Doctors today already know a lot about the pathology that affects the brain and gradually leads to inhibition of its functions. Every year new data on the disease appear, medications and research methods, and treatment options are developed. This allows us to increase the efficiency of working with patients, providing them with a decent standard of living and adequate care.
Today there are special groups in which people with Parkinson's and their loved ones are provided with all the necessary information and help.
Is there any disability for Parkinson's disease?
At an early stage of the disease, the patient is able to take care of himself and even perform work duties. As the pathology progresses, the question arises of giving up professional activity, registering as a disability, and receiving help from social funds and organizations.
Persons with Parkinson's disease are assigned a disability according to the following principles:
- the first group - disability, bed rest, inability to get around and move without help;
- the second group - limited ability to work, bilateral symptoms against the background of obvious postural instability, problems with self-care;
- third group - decreased ability to work, bilateral symptoms accompanied by moderate or absent postural instability, no problems with self-care.
The listed criteria are assessed by a special commission. As the pathology progresses, the disability group changes.
Persons with Parkinson's disease are assigned a disability according to the following principles: the first group is incapacity for work, bed rest, inability to get around and move without assistance.
Recommendations for people with Parkinson's
In adults, a diagnosis of Parkinson's first causes denial of the disease, then fear of developing disability or death, and reluctance to fight the inevitable. This attitude often causes a sharp progression of the problem, rapid decline of the victim, disability, and death.
The main recommendation of doctors for such patients is a positive attitude. Modern medicine successfully combats the manifestations of the disease, and with the right approach, the patient’s life may not change significantly.
According to statistics, 15% of the world's population has a family history of Parkinson's disease and predisposing factors. If you take this point into account and start prevention in a timely manner, you can significantly reduce the likelihood of developing the disease. People who are not at risk should also not neglect the recommendations of doctors and monitor their health from a young age.