How is MRI performed for multiple sclerosis?
One of the key examination methods for diagnosing multiple sclerosis is an MRI scan of the brain and spinal cord. It is not recommended to confirm the diagnosis during examination without scanning. Sclerotic changes are detected in the form of foci of damage to the myelin layer of nerve fibers. Thanks to this, it becomes possible to carry out dynamic monitoring and timely correction of drug therapy.
Foci of demyelination in the spinal cord in multiple sclerosis.
Diagnosis of the sclerotic process is relevant not only for making a diagnosis, but also for monitoring the nature of the development of the process, as well as for obtaining data on the effectiveness of the selected therapy - these parameters can be judged based on the assessment of control images over time.
There are several ways to perform MRI diagnostics for multiple sclerosis. Non-contrast diagnostics detect plaques by exposure to electromagnetic waves. Nerve cells react with molecular vibrations of hydrogen protons, which are recorded on computer media in the form of pathological structures against the background of healthy tissue. Unfortunately, non-contrast examination for damage to nerve fibers is not very informative. Basically, the presence of active lesions of multiple sclerosis is diagnosed using contrast-enhanced MRI . Contrast is administered at a rate of 0.1-0.2 mg/kg immediately before the diagnostic study. Diagnosis of multiple sclerosis requires obtaining images in three projections.
Contraindications
MRI is prohibited in the following situations:
- if the subject has implanted electronic mechanisms,
- implants and metal prostheses installed,
- non-removable metal structures,
- pregnancy at a period of less than 14 weeks for conventional magnetic resonance imaging and full gestation for magnetic resonance imaging with the introduction of contrast,
- mental pathology and neurological disorders,
- diseases of the blood system, cardiovascular system. Cannot be performed using a contrast agent
- allergic reactions to contrast agents.
Signs of multiple sclerosis on a tomogram
When assessing the results of the examination, one of the main aspects is the identification of clusters of affected fibers, designated as foci of darkening.
Thanks to the T1 and T2 modes of the magnetic resonance imaging scanner, it is possible to clearly monitor the localization of the process and the shape of the plaque due to areas of darkening.
Formations are classified according to location, shape, size, color intensity, and contrast accumulation. T1 displays signs in the form of areas of darkness, which indicates the presence of lesions in the processes of nerve cells.
MRI of the brain in multiple sclerosis
T2 functionally contrasts the object of examination, showing us plaques in the form of voluminous bright spots.
When assessing the morphology of a structural formation, attention is paid, first of all, to the size of the plaque. Microscopic lesions no larger than 5 millimeters in size usually have slightly intense staining. The presence of signs of a microscopic lesion indicates a recent onset of the pathology (3-5 years), and these morphological structures are difficult to recognize using other research methods.
The affected areas are prone not only to merging, but also to reversing the process. The images record small and large plaques, up to 2 cm in size. For a targeted assessment of the activity of the flow, it is recommended to use a contrast research method. The shape of the plaque is noteworthy: round, which diagnoses the acute phase of the disease; oval, characterizes the protracted course of the process.
A recurrent course is characterized by the appearance of a large lesion with blurred contours. Homogeneous staining indicates a recently begun process. Uneven “ring-shaped” staining indicates re-involvement of the affected area in the pathological process. There are such signs of sclerotic lesions as “semi-ring”, “crescent”.
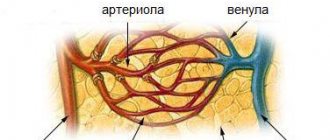
When assessing the location, it can be noted that usually the affected tissue is parallel to the venous vessels . The affected areas are located mainly in the white matter of the brain and spinal cord, this is due to a large accumulation of myelin. The typical location of plaques is the corpus callosum, tissues located near the ventricles of the brain, and the ventricles themselves. An important place in the interpretation of the examination results is occupied by the presence of such complications in brain images as tumors of the thalamus, inflammation of the veins and peripheral nerves.
We must not forget that immune cells can infect only the spinal cord in isolation, as evidenced by the diagnosis of local changes in one or more parts of the spine.
Brain MRI with contrast for multiple sclerosis
The cervical region suffers most often and is considered the most vulnerable area . On the tomogram, the plaques are located in a random order, are brightly colored, oval in shape, and accumulate contrast material well. If the plaque changes the shape of the segment, is large in size (2 segments or more), and spreads throughout the entire transverse section of the spine, then sclerotic pathology is likely to be excluded.
An exacerbation of the process is indicated by the accumulation of contrast in the area of damage to the brain matter. This can be interpreted as the penetration of contrast directly into the brain through the blood-brain barrier. In healthy people, the blood-brain barrier is impenetrable.
There are indirect signs of demyelination of nerve fibers. They consist in the expansion of the lateral ventricles, which indicates the accumulation of fluid in them. The next sign is the lining of the periventricular space, indicating a lack of nutrition to the medulla.
Stages of MRI
No special preparation is needed for the procedure. It is necessary to wear loose clothing without metal accessories, remove all unnecessary items, and use earplugs. To obtain the most accurate results possible for diagnosing the disease, you must first administer a contrast agent.
This is a completely harmless procedure, but occasionally it becomes a factor in the development of allergies. Before contrast is administered, you should stop eating and drinking for several hours.
The magnetic resonance imaging procedure includes:
Patient preparation and instruction . There are often situations when you have to do a test to check whether there is a personal intolerance to the contrast agent.
Carrying out the procedure itself . First, a contrast agent is administered, after which the patient is placed on a retractable couch, secured with special belts and driven into the tomograph opening.
The result is ready-made images that reflect problem areas in different planes and angles. The information ends up on the computer. The procedure lasts from half an hour to fifty minutes.
Completion of the procedure. The couch extends out of the tomograph tube. The straps are unfastened from the patient's body. After an hour or two, the specialist processes the received images, records them on electronic media and sends them to print to conduct further examination.
Features of diagnosing sclerosis using MRI?
In most patients with clinical signs of multiple sclerosis, the diagnosis is confirmed by MRI scans of the brain and spinal cord. But the results may be false negative. Due to age-related changes in brain structures, multiple sclerosis is visualized as a false-positive by MRI.
There are multiple contrast agents available to help you perform a safer and more accurate scan. Determination of the presence of white matter pathologies can without a doubt be interpreted as immune damage to nervous tissue. The severity of the disease cannot be judged using MRI diagnostics. MRI of the spinal cord is indicated in the presence of spinal clinical symptoms. In the absence of signs of spinal lesions, tomography is desirable, but there are no direct indications for its implementation.
The quality of the resulting images largely depends on the power of the magnetic field source in the magnetic resonance imaging scanner. For multiple sclerosis that is not confirmed by MRI diagnostics, repeat tomography is recommended 3 months after the exacerbation. If the result again turns out to be negative, then the diagnosis is not removed, but an appearance for scanning is scheduled again after 3 months
Parkinson's disease (PD)
Despite the incurability of PD, in medical centers patients are prescribed drug and non-drug therapy. With timely diagnosis, the death of brain cells can be stopped. For this, patients are prescribed an MRI scan.
It allows you to identify minor damage in the cerebral cortex, which in the future can cause shaking paralysis. Next, we will consider all situations in which a specialist prescribes a targeted MRI examination.
1.1. Neurodegeneration of the brain
PD belongs to a group of neurodegenerative processes that develop in brain cells. Some of these disorders lead to complete personality degradation and cannot be treated with modern medicine.
In each individual case, the problem manifests itself with distinctive symptoms, but the result of neurodegenerative disorders is the same - mental retardation and death from somatic diseases. It is a mistake to believe that neurodegeneration of the brain is a problem specific to older people. Signs of the disorder can appear at any age.
Patient Interview
Identified signs of a pathological process should be a signal to go to the doctor. Initially, you will have to make an appointment with a therapist at the hospital at your place of residence. If the specialist has good reasons, he will refer you to a neurologist who will conduct an initial examination.
The doctor will ask about the symptoms that appear, so before going to see him, it is advisable to remember all the signs that you had. This must be done so that the specialist can assess the development of the pathological process. An important detail is the time of onset of symptoms and the reasons why they worsen.
During the conversation, you will need to clarify whether this is your first visit to a neurologist and at the same time the doctor will ask about the following points:
- The presence of other pathologies or any health problems;
- List of previous diseases;
- Medicines used;
- The presence of similar pathological processes in the family;
- Abuse of bad habits.
All these points are important for the doctor, since based on them, he will be able to assess the presence of multiple sclerosis. That is why it is extremely important to provide him with all the necessary information and not hide any details from the specialist.
Examination by a neurologist
After receiving the necessary data, the specialist will need to verify what he has heard and for this he will need to examine the patient. The essence of the procedure is to identify neurological abnormalities in order to find out the severity of the functional disorder of the nervous system.
During the examination, the neurologist will need to evaluate the following functions:
- Functionality of cranial nerve pathways;
- Muscle tissue tone;
- Motor functions;
- Degree of sensitivity;
- Expressiveness of reflexes.
However, they can also be characteristic of many other pathological processes, for example, compression of the spinal canal due to osteochondrosis or hernia, etc. That is why you will have to undergo tests and undergo instrumental diagnostic methods in order to accurately identify or refute MS.
Who to contact
At the first signs of the disease, you must visit a neurologist or neurologist at the clinic.
At the first appointment, the doctor diagnoses:
- evaluates the functional functioning of cranial nerve endings;
- determines muscle tone affecting the motor system;
- assesses sensitivity and reflexivity.
After the initial examination, the specialist will prescribe a number of mandatory tests. For the final diagnosis of multiple sclerosis, patients are usually sent to a hospital, where additional diagnostics and immediate treatment are carried out.