Parkinson's disease is characterized by slowly progressive neurological and cognitive impairment. The problem of diagnosing the disease lies in the careless attitude of relatives and doctors to the first symptoms. Typical signs of damage to the nervous system are regarded as a manifestation of natural aging of the body. The disease can be suspected in the early stages using tests and questionnaires to assess the neurological and psychological status. Many of them are simple and do not require much effort or time, so close relatives can independently test for Parkinson's disease at home.
Memory tests
The simplest method for identifying memory impairment is the “5 words” test. The patient is given a sheet of paper on which 5 simple words from everyday vocabulary are written. After reading, the test taker must reproduce them. Then the patient is distracted by a conversation for 3-4 minutes and again asked to repeat the previously read words. If it is impossible to reproduce them immediately after reading, they speak of severe memory impairment, in other cases - of mild or moderate degree.
Another way to assess memory and memorization ability is a questionnaire test. The method is less informative because the testing does not exclude a subjective factor (a person may provide unreliable information). This test is suitable not only for the patient with Parkinson's disease, but also for his close relatives. Memory impairment is indicated when the answer is positive two or more times. The Parkinson's test consists of the following questions:
- Over the last month, have you forgotten to turn off the gas, iron or water?
- Have you lost things in the last month? If yes, how many times?
- Have you ever thought that a close relative looks completely different and you don’t recognize him?
- Do you have difficulty remembering a phone number or a date?
- Do you feel confused in a previously familiar area or area?
Another simple method for identifying the disease and concomitant mental disorders is the date recall test. The patient is asked to say when he or his immediate family was born. Long thinking, inability to answer a question, or ridiculous answers (for example, 03/45/1173) are an unfavorable sign.
Causes of Parkinson's disease
For a still unknown reason, Parkinson's disease affects men more often. But among coffee and cigarette lovers it is less common. Currently, research is still underway to determine the exact cause of the disease. But the factors that provoke it are already well known:
- aging;
- hereditary predisposition;
- impact of negative factors;
- long-term use of certain drugs;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- infectious diseases of the brain;
- some have chronic pathologies;
- stress and poor nutrition.
Disruption of the structure of the nerve fiber very often occurs due to age-related changes. It is not uncommon for tremor to appear in people who have relatives with this problem, especially for young patients. The toxic effects of poisons, heavy metals, and radiation can also lead to atrophy of brain tissue. The use of antidepressants and antipsychotics helps reduce the level of dopamine and the sensitivity of nerve synapses to it.
Treatment of Parkinson's disease in Moscow begins with identifying and eliminating the main cause of the development of the pathology. Ganglion structures are affected after encephalitis, meningitis, or injury as a result of injury. Psycho-emotional overload, constant lack of sleep, eating low-quality foods, and lack of necessary substances also contribute to disruption of the central nervous system.
Tests to assess attention and thinking
A quick way to identify disorders of thinking and intelligence are mathematical problems. The patient is asked to solve examples with simple arithmetic operations (addition, subtraction, multiplication). The second stage of testing is counting backwards with subtracting the number 7. The test taker must subtract 7 from a given number (usually 100 or 1000), then name the resulting difference. The arithmetic operation is performed at least three times.
Important! The inability to perform basic arithmetic operations is a sign of severe impairment of intelligence and thinking.
Another cognitive (thinking) test for Parkinson's can be done at home. To do this, the patient is told two words that are related in meaning (for example, cat and dog). The test taker must explain what the relationship is between these words. Not only is the absence of a solution considered incorrect, but also answers based on secondary features (for example, “a cat and a dog have a tail” or “an orange and a banana have a peel”).
An accessible method for identifying attention disorders is a digital test. During this procedure, the patient is told 5 numbers from the top ten at a rate of 1 number per second. The test taker must repeat the numbers in forward and reverse order. You can also use graphic cards to assess attention. 10 images are laid out in front of the patient and given 60 seconds to memorize. The test taker is then asked to turn away and one of the cards is removed. The patient must determine which image is missing.
Combined tests and questionnaires
In medicine, tests have been developed that allow one to identify several impaired mental functions at once. They consist of many tasks, each of which is responsible for memory, attention or thinking. The Mini-Cog test for Parkinson's disease has become widespread in clinical practice. At the beginning, the test taker is given 3 words that are not related to each other in meaning. The patient must then draw a clock face, place the numbers on it, and position the hands so that they show a specific time (for example, twenty minutes to four). After this, the test taker is asked to reproduce the words from the first task.
In clinical practice, another complex test is used - the Montreal Cognitive Function Assessment Questionnaire. It is used by psychiatrists to detect dementia due to Parkinson's disease. The test is considered difficult and requires 30-60 minutes to complete. It consists of several blocks and evaluates all higher brain functions of a person:
- abstract and spatial thinking;
- speed reaction;
- ability to remember and reproduce information;
- general level of intelligence;
- attention, its mobility and switchability;
- optical-spatial activity (the ability to determine the location, size, and distance of an object).
Important! The simplest and most informative method for identifying dementia in Parkinson's disease is the Mini-Cog test.
The test for Parkinson's disease consists of drawing a broken line, a three-dimensional object (cube, parallelepiped), or a clock dial with a given time. The questionnaire also contains arithmetic operations, reproduction of named words, naming numbers in reverse order, and simple logical tasks.
Treatment methods for Parkinson's disease
Treatment of Parkinson's disease in Moscow and other cities should begin with its first manifestations. It is best to involve experienced specialists in this problem who will help you choose the best methods of assistance and rehabilitation.
The lack of therapy or the wrong approach to it significantly shortens the life of a patient suffering from Parkinson's disease. After ten years, and sometimes earlier, he becomes disabled or dies, and after 15 years from the onset of the disease, the mortality rate is already 80%. And even with a sluggish form, without taking medications and using modern techniques, strong everyday disadaptation quite soon occurs, a person’s ability to work and socialization decreases. The quality of life suffers greatly, and the patient himself becomes a heavy burden for family and friends.
Treatment for Parkinson's disease includes:
- taking medications;
- physiotherapy;
- psychological assistance;
- therapeutic exercises;
- special diet.
To correct dopamine, drugs are used that help:
- increase dopamine levels;
- stimulate dopamine receptors;
- inhibit the reuptake of this substance;
- reduce its destruction.
The following medications are used for this:
- Levodopa drugs.
They are among the most effective medications for the treatment of Parkinson's disease, which are used in both early and late stages of the disease. They are recommended in case of disorders associated with functional adaptation, and to a lesser extent these drugs affect tremor. The dose is selected individually; the patient needs to monitor the condition during therapy, since levodopa drugs have multiple side effects.
- Dopamine agonists.
They allow direct stimulation of dopamine receptors and are also recommended for use at any stage. Treatment of Parkinson's disease with their help is carried out in combination with levodopa drugs. Recent studies indicate that the use of dopamine agonists early in the disease helps reduce the likelihood of dikinesia or significantly delay its onset.
- Anticholinergic drugs.
They help reduce the manifestation of tremor and do not have a special effect on the phenomenon of bradykinesia. They are preferable to start treatment of Parkinson's disease in young patients and middle-aged people with a predominance of limb tremors and the absence of cognitive impairment.
- COMT inhibitors.
These medications can increase the concentration of levodopa drugs in the blood plasma. This allows you to achieve the desired effect of therapy using lower dosages of the main drug. Recommended for treatment at any stage of the disease.
- Antidepressants.
This group of drugs helps with depression and decreased social activity of a person. Best used in conjunction with the work of a psychotherapist.
If the disease is at an early stage, the person may not be prescribed medications. His normal activity is maintained with the help of physical therapy, massage, and physiotherapeutic procedures. Psychological assistance is provided to the patient and his environment with the help of experienced specialists.
24/7 CONSULTATION BY PHONE: +7
Tests to detect neurological disorders
Parkinson's disease is characterized not only by memory loss or cognitive-thinking dysfunction, but also by damage to the extrapyramidal system of the brain. It is responsible for movement, muscle tone and maintaining posture. Early signs of Parkinson's disease can be detected through simple neurological testing.
Neurological testing for Parkinson's disease
| Test | Norm | Parkinson's disease |
| Walking on level ground | Rhythmic steps at a speed of 80-100 per minute (for older people - at a pace that is comfortable for them), friendly hand movements while walking. When walking, the body is positioned vertically. | When walking, the center of gravity is shifted and the torso is tilted forward. The movement is carried out in small shuffling steps, the arms are chained to the body and immobilized. |
| Facial expression test with forehead frowning | 3-4 longitudinal folds on the forehead are clearly visible. | There are no facial wrinkles. |
| Graphics test | Individual handwriting, formed since childhood. | Distortion of handwriting due to trembling: slow and choppy writing of letters, small print (micrography). |
| Muscle tone test | Bending of the arm (the limb is bent not by the patient himself, but by another person) at the elbow joint occurs smoothly and without difficulty, then the limb acquires a physiological and comfortable position. | Bending the patient's arm requires effort and occurs intermittently, while the limb remains in a given position. |
Neurological disorders in parkinsonism appear earlier than cognitive-mental ones. Often the first symptom of the disease is tremor - shaking of the hands or nodding (like “yes-yes” or “no-no”) movements of the head. Tremors in Parkinson's can be distinguished from other neurological diseases in a simple way. Asking the patient to perform an action (for example, handing a glass or leafing through a book) will reduce the trembling. Weakening of tremor during movement is characteristic only of Parkinson's disease.
Question 4. How to diagnose the disease?
- It is enough to visit an experienced neurologist.
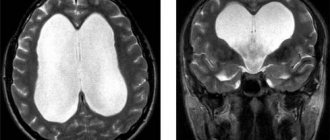
- The diagnosis is confirmed by magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and computed tomography (CT).
- Special instrumental studies are required.
Answer: 3. To confirm the diagnosis, transcranial sonography is performed, which makes it possible to detect the hyperechogenicity of the substantia nigra in the brain and calculate its area. The study is prescribed only after consultation with a qualified neurologist in several medical institutions in Belarus.
Standard CT or MRI of the brain is not informative and is used to exclude other diseases.