Posthypoxic encephalopathy is a condition that is characterized by changes in the structure of brain tissue and impaired brain function due to oxygen deprivation. The progression of degenerative changes in the brain matter correlates with a delay in the mental and physical development of children. The consequences of damage to central nervous system tissues during the perinatal period are the main cause of the development of neurological disorders in patients of early childhood. One of the complications is cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy). The prevalence of PEP (perinatal encephalopathy) of hypoxic origin is about 5% of cases among the total number of newborns.
Types of posthypoxic encephalopathy
Depending on the reason why hypoxia occurred, the following types of pathological process are distinguished:
- The level of oxygen in the circulating blood drops as a result of a violation of primary diffusion, i.e., the passage of air from the pulmonary alveoli into the blood. Such a disorder can be observed due to disruptions in breathing and/or heart function.
- With hemorrhagic anemia, when there is not enough hemoglobin in the blood to transport oxygen within the body, a hypoxic state occurs.
- Insufficient oxygen supply to the fetus during childbirth can lead to the development of encephalopathy in the newborn.
- Oxygen starvation of tissues due to ischemia.
- Shock states in the later stages, terminal (pre-agony, agony) and comatose states, as well as clinical death can lead to the development of post-hypoxic encephalopathy.
- Poisoning with endo- and exotoxins.
Hypertension can lead to the death of neurons in the brain. Hypertensive encephalopathy is a serious disease that can be fatal.
Long-term alcohol consumption causes damage to brain cells. Read about what alcoholic encephalopathy is and the dangerous consequences of the disease here.
Pathologies that are not treated in childhood can also manifest in adults. Perinatal encephalopathy can lead to coronary heart disease and also increase the risk of stroke. Read more about the disease in this topic.
Diagnostics
The level of consciousness of adult patients who have suffered hypoxia of toxic origin is assessed using the Glasgow scale, and the severity of intellectual impairment is assessed using the MMSE scale. The condition and functionality of the nervous system is determined using neurological tests and instrumental diagnostic methods. Laboratory tests show elevated serum concentrations of malondialdehyde and lactic acid. To diagnose perinatal hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy, instrumental methods are used:
- Ultrasound, neurosonography.
- Echoencephalography, electroencephalography.
- MRI, CT.
- Rheoencephalography.
- Cerebral angiography.
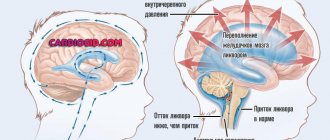
During instrumental diagnostics, intraventricular hemorrhages, damage to brain tissue of ischemic origin, predominantly of periventricular localization, and cerebral edema are detected. A blood test shows a decrease in hemoglobin levels - anemia of varying severity.
Stages of the disease
The initial stage of the pathology is practically asymptomatic and is not diagnosed. The general genesis of the disease is typical for both infants and adults:
- Compensatory stage - alternative oxidation processes in brain cells are inactivated and succinate oxidation without the participation of oxygen is activated, but such compensation is not enough for a long time, and the next stage begins.
- Decompensation is hypoxic suppression of the functioning of nerve receptors. The body's compensatory systems wear out and, due to oxygen starvation, the first noticeable symptoms of the disease begin to appear.
- Terminal stage - death of brain cells occurs, which can cause death.
Description of the disease
PE is a pathology that is not inflammatory or infectious in nature, but entails a degenerative disorder of brain tissue. Such lesions are caused by a lack of oxygen and are diffuse in nature. Due to hypoxia, neurons (nerve cells) undergo hypoxic shock and eventually die.
This disease carries with it a variety of disorders of the central nervous system, since it all depends on which area of the brain is affected. These include:
- Motor dysfunction
- Disorder of the functions of internal organs
- Sensation and perception disorder
- Functional disorders of higher nervous activity
It is important to know: oxygen starvation can be a consequence of a number of reasons: stroke, suffocation, etc.
We will find out exactly how PE is subdivided below in the article.
Causes
The cause may be a complication of childbirth, with untimely passage of the placenta, which interferes with normal breathing of the fetus, or with the umbilical cord wrapped around the baby’s neck.
If the mother suffers from hypoxia during childbirth, for example, her heart and breathing stopped, then the fetus will inevitably suffer if it is not removed from the mother’s body in time.
The development of hypoxia can be facilitated by severe blood loss, which entails a state of shock and subsequent terminal conditions. In this case, a sharp decrease in oxygen supply occurs, first due to blood loss and vascular spasm, then due to inhibition of the respiratory center, which is the most dangerous. That is why victims of severe injuries are prescribed oxygen therapy as first aid.
It is worth noting that terminal conditions can be caused not only by blood loss, but also by other severe injuries and illnesses.
Encephalopathy may occur due to a genetic predisposition. In such cases, you need to closely monitor your health and undergo examinations at the slightest disturbance.
With prolonged hypoxia with prolonged development of damage to the central nervous system, mental disorders are sometimes diagnosed, such as: delirium (“delirium tremens”), loss of memory and orientation, substitution of real events for fictional ones, dementia.
Possible consequences and prognosis
The prognosis is most favorable for mild disease. In this case, therapy includes saturating the blood with oxygen and stimulating normal cerebral circulation. As a rule, anxiety symptoms disappear successfully in the first weeks of a baby’s life. No negative consequences or neurological disorders are observed.
In all other cases, there is a risk of developing the following consequences:
- child development disorder;
- brain dysfunction;
- disruption of the functioning of some internal organs;
- local neurological disorders;
- hydrocephalus;
- autonomic dysfunction;
- epilepsy.
Impaired brain function may subsequently manifest itself as an inability to concentrate for long periods of time and weakened memory. There is a high probability that such a child will study poorly due to restlessness.
Developmental disorders may manifest as speech therapy impairments and growth retardation. In this case, the baby is indicated for treatment in special medical institutions.
Disruption of the functioning of certain internal organs requires careful monitoring of symptoms and timely treatment in case of exacerbations. You can get rid of this problem only if you pay attention to the alarming symptoms in a timely manner.
Hydrocephalus due to encephalopathy requires timely treatment, including surgery. This disease can also cause a number of neurological disorders.
With severe encephalopathy, the risk of further development of epilepsy is high. This is due to disruption of the functioning of certain areas of the brain and the death of neurons, as a result of which patients experience an increase in the excitability of certain areas of the brain and, as a result, convulsive seizures. However, timely treatment of acquired epilepsy often allows one to successfully get rid of convulsive seizures.
Symptoms
Pathology can be diagnosed at the time of development only of such forms as:
- acute
- subacute
- chronic.
The fulminant form of the disease can cause death within a minimum time - up to 2 minutes. The rapidity of hypoxia does not allow obvious clinical symptoms to be identified in such a short time.
The acute form is manifested by the insufficiency of all body systems at once, and first of all the parts of the central nervous system, respiratory and cardiovascular are affected, a drop in blood pressure occurs, the strength and then the heart rate decreases, and breathing weakens. If hypoxia is not eliminated at this stage, then organ failure worsens and progresses to coma.
Hypoxia in a child during childbirth
Subacute and chronic forms are distinguished by hypoxic syndrome. It is represented primarily by symptoms from the central nervous system (dizziness, convulsions, drowsiness, headache), since the brain is more sensitive to a lack of oxygen, due to which foci of necrosis, hemorrhage and other types of cell death rapidly appear in its tissues. Due to these disorders, against the background of oxygen deficiency, at the initial stage of hypoxia, euphoria, an excited state, and increased motor activity develop. One's own condition is not assessed critically.
This further leads to depression of the cerebral cortex and is manifested by symptoms such as:
- hypersomnia;
- decreased activity tone;
- headache, dizziness, vomiting;
- tinnitus, passivity and lethargy;
- disorder of consciousness;
- uncontrolled emptying of urine and feces;
- impaired motor coordination;
- convulsive conditions.
Convulsive attacks develop gradually. They start with the facial muscles, then move to the arms, legs, and then to the stomach. Seizures are triggered by external factors, such as light, noise, fear, etc.
Psychoorganic syndrome
This complex of symptoms manifests itself in varying degrees, but occurs with the following manifestations:
• Memory and ability of intellectual thinking are impaired; • There is an affective disorder; • Cerebroasthenic changes appear;
The patient suffers from a decrease in the perception of reality, loses the desire to acquire new skills, and previously acquired knowledge is lost. The ability to think becomes primitive, one-sided, speech is impaired, and vocabulary is significantly reduced. In a conversation, a person is unable to specify the topic and easily jumps from one thought to another. Forgets what was discussed earlier, cannot answer the question asked. Memory suffers the most, it becomes short-term, the memory function is lost, amnesia, paramnesia, and confabulation develop.
Affective disorder has the following manifestations: mood is depressed, a tendency to depression and inappropriate mood appears. The person suddenly becomes aggressive, irritable, touchy, whiny. You may suddenly feel euphoric and optimistic.
Treatment of posthypoxic disease
The methodology of therapeutic interventions is aimed at:
- Combating impaired blood circulation: restoring the volume of circulating blood, treating hypotension, avoiding vascular pinching.
- Treatment of neurological disorders: monitoring the functioning of restored areas of the brain.
- Treatment of symptoms that have developed against the background of cerebral hypoxia: disruption of the heart and other vital organs.
- Normalization of hypoergosis and blood chemical parameters.
To bring blood counts back to normal, antihypoxants are prescribed.
These include:
- Neotone;
- Mexico;
- Actovegin;
- combination drug Cytoflavin.
Also indicated for use are nootropic drugs to stimulate metabolism and antioxidants.
In addition to medications, you need to eat more foods rich in vitamin E, C, and fiber. Grapes, nuts, kiwi, and red berries have these properties. It is not recommended to drink drinks containing alcohol.
In pregnant women, existing diseases may worsen or pathologies to which there is a predisposition may arise. Encephalopathy in pregnant women occurs against the background of changes in the body of the expectant mother.
We will talk about the symptoms and treatment of dysmetabolic encephalopathy in this article.
You need to try to get more rest, often walk in the fresh air, and avoid nervous tension. Such measures significantly improve the condition of nerve cells, which is very important for recovery. Moderate physical activity also has a positive effect on health.
Treatment of the disease
After the diagnosis is made, they proceed directly to its treatment. Both drug and non-drug treatment are used. Severe disease is treated in hospital. Therapy for such a pathology takes a long time; in this situation, complex treatment and great patience are necessary.
Treatment for this pathology in children depends on age. Typically, several courses are required each year.
Drug treatment includes the use of the following drugs:
- Antihypoxants
- When epileptic seizures occur, anticonvulsant medications are used
- Diuretics
- Medicines are used to improve metabolism in brain tissue and their blood supply
- Vitamin complexes
Therapy in adults is similar to that described above. In addition, patients need to give up bad habits and eat right. In addition, it is necessary to avoid stressful situations.
Non-drug methods include massage, physiotherapy, various exercises, herbal and aromatherapy.
Often, the prognosis with a competent approach is rather favorable, especially for childhood PE. With each passing year of the baby, the signs of pathology will gradually disappear. Ultimately, the disease completely recedes, and the child continues to live a full life. This is especially true if the pathology was identified at an early stage of development, but this does not always happen. In some situations, the consequences of pathology remain for life.
In adults, the following consequences of the disease may be observed:
- Depression
- Dizziness
- Fast fatiguability
- Sleep disorder
- Memory disorder
- Decreased mental performance
- Speech impairment, etc.
In addition, this disease in children can lead to serious complications:
- Epileptic seizures
- cerebral palsy
- Hydrocephalus of the brain
- Mental retardation
But such consequences arise only if therapy was not carried out at all or PE was detected untimely.
It should also be noted that medicine does not stand still; many scientists are interested in this disease and, most likely, new methods of treating PE will be presented in the near future.
PE is a serious disease, but with the right and timely approach, the prognosis is very favorable. It is necessary to lead a healthy and active lifestyle, take rest breaks and avoid stressful situations. If you notice symptoms of the disease, consult a specialist; this is the only way you can avoid serious consequences.
Noticed a mistake? Select it and press Ctrl+Enter to let us know.