Frequently occurring pain in the right temple brings a lot of inconvenience to a person. The reasons for this phenomenon depend both on the person’s unhealthy lifestyle and on possible diseases.
Why does discomfort occur in this area of the head and what can be done to eliminate it? Let's figure it out.
If we are talking about a disease that is accompanied by a symptom such as acute pain in the temple, a person needs treatment. If discomfort occurs on one side of the head (right), this is an alarming symptom.
Symptoms
Rarely does a headache in the temples come alone.
It is usually accompanied by nausea, weakness, pain in another part of the head, insomnia, lacrimation, and increased salivation. I feel dizzy, a sound appears in my head, and my fingers go numb. Patients note memory and smell disorders, cold feet and hands. Pain is often accompanied by allergies.
The doctor will be able to tell why there is pressure on the temple after a preliminary examination and examination of the patient. The nature of the pain can be throbbing, pressing and sharp in one or two temples. Painful sensations can last for several hours or days. The intensity of pain depends on the individual characteristics of the body. Common symptoms of pain development are:
- dull or throbbing pain in one or both temples
- pain can accompany the patient for several hours or even days
- Sometimes dizziness and nausea may occur
Other reasons
The reasons why a headache in the temples hurts include the following:
- the beginning of the menstrual cycle causes sharp, throbbing pain in the temple area (but they are temporary);
- malignant tumors that put pressure on the blood arteries, causing pain;
- inflammation of the joints leads to discomfort in the temples;
- when talking, brushing your teeth, or eating, you can disrupt the state of the trigeminal nerve, as a result of which pain appears alternately, in the left then in the right temple, sometimes affecting the frontal part (the pain can also move from the temple to the jaw, cheeks, that is, it has a “wandering” nature, and duration depends on objective and subjective reasons).
With a reduced level of hemoglobin in the blood, the number of red blood cells also decreases, resulting in a feeling of squeezing and pulsation in the temples.
The mechanism of pain in the temples of any nature
Headache in the temples has a varied nature in its manifestations.
There are acute and chronic forms of this pathology.
Acute pain appears due to the action of an exogenous factor and is not associated with a pathological process. Symptoms are quickly relieved with pain medication.
Chronic headaches occur on a regular basis and last for a long time. It is caused by endogenous reasons.
In addition, temporal headaches are divided into primary and secondary.
It becomes primary when it acts as a separate symptom or reaction to a stimulus.
A secondary headache is a consequence of another disease.
Temporal headache has the following character:
- Unilateral – pain is localized either in the right or left temple;
- Bilateral – both temples hurt;
- Pulsating;
- Shooting;
- Pressure – the patient feels strong pressure on the right and left temple;
- Dumb;
- Acute;
- Short-term - the attack lasts only a few minutes;
- Long-term – pain torments a person for hours or days.
Pain in the temples can also occur on one side or on both sides at the same time. Some doctors consider the cause of these pains to be a lack of fresh air, dehydration, and long-term stress. In women, this is also associated with the menstrual cycle, menopause, and pregnancy. In addition, there is reason to believe that the cause may be hyper- or hypotension, spastic conditions of cerebral vessels, migraines, as well as infectious diseases - colds, flu, sinusitis, food poisoning.
In the vast majority of cases, tension and pressing pain in the temples occurs due to impaired cerebral circulation.
That is, regardless of the disease that led to this condition, the pathogenetic mechanism of the development of the disease is the same in all cases - increased pressure of influx of blood on the cavernous sinuses with subsequent irritation of the receptors clearly leads to the occurrence of pain.
Methods for correcting temple retraction
To correct the shape of the temporal fossa, an injection technique is used using special preparations based on hyaluronic acid or collagen. Such drugs are also called fillers from the English word fill - fill. Hyaluronic acid is a substance that is natural to the human body and therefore is not rejected by it. Hyaluronic acid is part of connective, epithelial and nervous tissues. It is capable of absorbing a significant amount of moisture and is responsible for the water balance of our skin and subcutaneous tissue. Alas, after 25 years, the production of hyaluronic acid by our body slows down. Its introduction from the outside can prevent fatal processes of changing appearance.
The introduction of hylauronic acid under the skin allows not only to correct the deformation, but also to create a lifting effect. Its action can be compared to the effect of a sponge, which absorbs a huge amount of liquid and holds it for a long time, releasing it gradually. Preparations for injections are selected depending on the tone of the skin and the severity of the retraction of the temporal fossa. The volume of the administered drug also depends on the severity of the problem and can range from 1 to 2 ml.
Diet
It is important for a person who experiences regular headache discomfort to eat right.
First of all, he should exclude from his diet foods that contain monosodium glutamate.
What is this substance? Monosodium glutamate is a specific food additive that is present in processed foods.
In most cases, this additive is found in processed meats and sausages. Why is monosodium glutamate dangerous?
The fact is that this supplement increases the pain syndrome.
That is why patients suffering from painful ailments are not recommended to eat foods containing this additive.
If a person has eaten a product that contains monosodium glutamate, then after 15-20 minutes he will feel headache discomfort.
A strong pulsation may be felt in the temporal zone, and a dull aching pain in the forehead area.
In addition to monosodium glutamate, a person suffering from frequent headaches should avoid nitrites.
Nitrites are salts of nitrous acid, which, like food additives, provoke pain. What foods contain nitrites?
- Bolognese sausages.
- Canned ham.
- Fast food (eg hot dog).
- Smoked fish.
- Salami.
- Chocolate.
Patients suffering from migraines are contraindicated to eat chocolate. Why? The fact is that this product is one of the most powerful migraine triggers, as it contains caffeine.
Temples hurt - what to do?
Both secondary arterial hypertension, where an increase in blood pressure is a consequence of some underlying disease, and an essential increase in pressure - as a rule, this disease causes a pressing headache in the temples in people over forty years of age.
It is this disease that most often causes the development of cardiovascular accidents: cerebral infarctions occur due to high blood pressure. In this case, the pain syndrome plays the role of a “watchdog”, which indicates to the patient the need for urgent measures;
Migraine
In its most varied forms, in the vast majority of cases it causes pain in the temples of a paroxysmal nature, as it compresses the blood vessels. The disease manifests itself, as a rule, in middle-aged people, leading to their temporary disability.
So this disease is not only a medical problem, but also a social one, especially considering that after a migraine attack, some patients experience persistent problems with circulatory disorders. The temples hurt badly and for a long time;
A disease, the true nature of which has not yet been clarified and its occurrence is associated exclusively with the characteristics of the human constitution. In this case, the headache in the temples has a pressing nature, accompanied by many disorders - dizziness, nausea, sometimes vomiting, rapid heartbeat, and sometimes loss of consciousness.
In most cases, it is this disease that causes pain in the temporal region in children and adolescents (it occurs especially often in girls in adolescence). All weather-dependent people, as a rule, suffer from this disease. If they have pressure on their temples, then the reasons for this are also associated with irritation of the receptors of the cavernous sinus;
This refers to a situation in which tension and headache in the temples arose once. For example, there is pressure in the temples after suffering stress or drinking strong coffee, tea or an energy drink. In addition, aching pain in the temporal region occurs if a person simply does not get enough sleep.
These are all completely physiological phenomena, because activation of the sympathoadrenal system leads to an increase in blood pressure. So, if your temples hurt unbearably, this is not yet an indicator of the presence of a chronic disease.
Advice: If pain occurs in the temple area, it is best to immediately take any of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs - ibuprofen, nimesulide or movalis. Under no circumstances should you tolerate pain in your head.
In addition to circulatory disorders, the cause of headache development can be pathology of the peripheral nerves responsible for supplying the specified anatomical area.
The temples hurt a lot due to the fact that the innervation of the vessels in the head is disrupted; perhaps some vessel will be compressed. The condition is accompanied by sensory disturbances (paresthesias), feelings of heat, cold and other disturbances, and may cause pain and compression in the back of the head. This reason is relatively rare.
It is determined primarily by what disease caused the pressing pain in the temples - the treatment of arterial hypertension and migraine, for example, is very different and effective measures in one case will not bring any benefit in all others. The only drugs whose use is indicated in all cases are NSAIDs ( diclofenac, ibuprofen, movalis, xefocam and others) - in this case, the pain must be relieved, and not wait until it progresses. Severe pain in the temples does not have diagnostic value, as with other diseases. However, other groups of drugs are recommended selectively.
For pain in the temples caused by high blood pressure, you will definitely need to take an immediate antihypertensive drug. Recommended use:
- Captopress (captopril) - take one tablet once. After this, the person will need to sit down and rest after about 20 minutes to measure the blood pressure level. As a rule, the drug is effective and after half an hour the patient stops feeling a headache. But many people make a mistake here too - under no circumstances should you take another drug that lowers blood pressure a few minutes after taking captopress. You can lower your blood pressure too much, and this is even worse than increasing its level.
- An effective remedy is magnesium sulfate 25% - intramuscular administration will be quite sufficient to relieve a hypertensive crisis. This is an emergency medicine.
- Nifedipine. 5 drops of the drug per 50 g of water - and you can forget about high blood pressure. All of the above methods are urgent measures to relieve pain in the temples during a hypertensive crisis, however, in order to minimize the likelihood of similar situations occurring in the future, it is necessary to take planned treatment. It will be better if your attending physician selects it for you.
In this case, the same drugs are used with the only difference - special anti-migraine drugs are added. Rapimig and amigrenin are the drugs of choice in most cases
Another fundamentally important feature of the treatment of pain in the temples during migraine is the recognition of an attack of this disease at the stage of its precursors - the so-called aura. After all, it is this condition that poses the greatest danger! It is at the moment when the first signs appear (blurred vision, nausea, dizziness) that it will be necessary to take anti-migraine drugs - in this case there will be a high probability of preventing the attack from occurring at all.
We treat NCD
In this case, it will be impossible to select an etiotropic drug due to the fact that the true causes of this condition have not yet been clarified. As symptomatic therapy, it is best to use NSAIDs in combination with barbiturates - Valocordin at the rate of 5 drops per 50 g of water helps very well.
In fact, not only high blood pressure can lead to headaches and compress blood vessels. On the contrary, many people suffering from weather dependence or migraines experience low blood pressure. In this case, it is necessary to take the long-familiar citramon, a tablet of which contains caffeine, which increases blood pressure.
Advice: Never begin to eliminate headaches in the temples without first measuring your blood pressure level. After all, only after making sure that there is hypertension and not low blood pressure (or vice versa) will it be possible to begin selecting adequate therapy.
In case of a one-time occurrence of unpleasant sensations of mild or moderate severity, you can try to cope with the problem yourself. Sometimes, to eliminate discomfort, it is enough to take a walk in the fresh air, drink a cup of chamomile tea, massage your temples, or rub a drop of menthol oil into them. If you still have a headache in your temples after this, you can take a tablet of Ibuprofen, Paracetamol or Citramon.
In other cases, the treatment method depends on the causes of cephalgia:
- hypertension - diet, taking antihypertensive drugs, removing excess fluid from the body, restoring vascular patency, improving blood circulation in the brain;
- migraine – pain relief with the help of NSAIDs, analgesics, triptans, ergotamines;
- neurocirculatory dystonia - taking natural sedatives or light tranquilizers in case of their low effectiveness.
- transient causes - elimination of the irritant, pain relief with any available medications.
Once the discomfort has been eliminated, the treatment does not end. It is necessary to select an appropriate method of preventing temporal cephalgia so that attacks do not recur.
Treatment for this type of headache
Temporal pain of any origin not only significantly reduces the quality of life, but is also a symptom of sometimes life-threatening diseases. Timely consultation with a doctor for diagnosis and subsequent treatment is the only correct tactic for a conscious person who cares about his health and wants to live a long and healthy life. Treatment for headaches in the temple area directly depends on the cause of its occurrence:
- Pain due to migraine is relieved with special drugs from the groups of triptans and ergotamines (see triptans for migraine). Many people take the usual aspirin for migraines, but do not observe any effect from it, since a migraine attack cannot be stopped by symptomatic drugs - this can only be done by those drugs that eliminate the cause of migraine - narrowing of the arteries (see migraine - symptoms, treatment).
- In the case of hypertension, increased ICP, or atherosclerosis, the patient is prescribed targeted therapy for the treatment of diseases, which in most cases has to be taken for life.
- Nonspecific headaches are relieved by taking analgesics, often long-acting.
- Psychogenic pain in the temples can be relieved using psychotherapy and aromatherapy. In this case, sanatorium-resort treatment with a change in the usual climate helps very well.
- Treatment of vegetative-vascular pathology includes physiotherapeutic techniques (swimming, contrast showers, exercise therapy), as well as herbal medicine and drugs that normalize vascular tone.
- For tension headaches, a person can help himself - change his position, gently rub stiff muscles, take a walk in the fresh air.
- Universal drugs for temporary relief of temporal headaches are drugs from the group of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, such as aspirin, ibuprofen (see the list of all NSAIDs in the article injections for back pain). They relieve the inflammatory reaction and side symptoms such as nausea, sweating, and hyperthermia. However, this treatment only addresses the symptom, not the cause of the pain, and is therefore only suitable for eliminating rare episodes of pain.
Only a doctor is competent in the treatment of frequent headaches in the temples, and the patient’s task is not to delay visiting him!
Author:
Sabuk Tatyana Leonidovna hygienist, epidemiologist
Diagnostics
Determining the cause of temporal pain occurs based on data from blood tests and instrumental examinations.
General analysis indicators allow you to see signs of inflammation, infectious diseases, and anemia. Biochemical data indicate signs of atherosclerosis, temporal arteritis, and kidney diseases causing arterial hypertension. A coagulogram allows you to detect features of the blood clotting process, which allows you to draw a conclusion about the risk of thrombosis and hemorrhage.
Instrumental diagnostic methods include:
- Radiography. It is carried out primarily to exclude inflammation in the sinuses, injuries, and neoplasms.
- MRI. The data obtained helps to see and evaluate brain structures, tissue density, the presence of tumors, necrosis, hematomas, thrombosis, and the condition of blood vessels. Can be performed on young children and pregnant women. Children are performed under anesthesia.
- CT scan. As a result of a layer-by-layer study, a flat or three-dimensional picture is obtained that allows one to detect inflammation, tumors, and hemorrhages. The study helps to see neoplasms, vascular patterns, features of the skull bones, brain membranes, injuries, hematomas.
- Angiography. This is a special type of radiography with the introduction of a contrast agent, which allows you to see the pattern of blood vessels, aneurysms, and expansions.
- Ultrasound of the head. Based on the results of the study, organic lesions are assessed, irregularities in shape, size of blood vessels, and individual areas of the brain are identified.
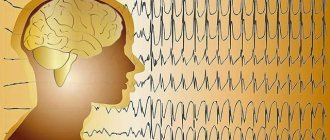
- Electroencephalography. Indicates the presence of signs of epilepsy.
- Spinal tap. The specialist takes a sample of cerebrospinal fluid, analyzes it for changes in composition, and assesses intracranial pressure.
- Blood pressure monitoring. To clarify the diagnosis of arterial hypertension or hypotension, daily blood pressure monitoring using a special sensor is indicated.
If you suspect an increase in intracranial pressure, consultation with an ophthalmologist is recommended. The simultaneous occurrence of pain in the joint and temple requires a visit to the dentist. Suspicion of arterial hypertension, adrenal pheochromacytoma is an indication to visit a nephrologist.
Diagnostic algorithm
A patient with a neurological or vascular problem must undergo consultation with specialists. Among them:
- neurosurgeon;
- psychiatrist;
- angiosurgeon;
- therapist;
- ophthalmologist.
Laboratory and instrumental research methods are required, including:
- General and biochemical blood test.
- Lipidogram.
- X-ray of the cervical spine.
- CT scan.
- MRI.
- Vascular duplex.
- REG.
Timely seeking help will reduce the risk of complications, and in some cases the situation can save the patient’s life.
If the temples hurt and there is a lot of pressure, then the patient will need to take several basic steps for timely diagnosis (this can be done either independently or with outside help):
- Measure your blood pressure level. It is imperative that each person knows his own characteristics, his “working blood pressure” - the numbers at which he feels normal, since for one patient a pressure of 140/80 will not be noticeable at all, while another (congenital hypotonic) may already lose consciousness, so and not knowing why my head hurts. So in this case it will be necessary to act exclusively on an individual basis, contrary to the recommendations of many theorists. The temples often hurt for a long time due to incorrectly prescribed treatment.
- Analyze the previous circumstances that led to the occurrence of pain in the temporal region. Try to determine what causes the headache and pressure on your temples. Very often it turns out that the cause of this condition is the most common lack of sleep. In addition, analysis of anamnestic data allows us to identify the underlying disease, which underlies the development of this condition;
- If it is not possible to identify any objective factors that lead to the development of severe pain in the temporal region, then it is necessary to carry out an in-depth examination - an electroencephalogram, REG of blood vessels in the head, MRI and some other studies.
Such a patient must be examined by a neurologist, therapist and cardiologist, since the current condition may be the result of a multifactorial disease that requires a differentiated approach to the diagnosis and treatment of the disease that causes headaches in the temples.
And based on the data obtained, the patient will be given a final diagnosis and, based on this, it is necessary to select planned treatment and therapy for emergency care.
Advice: A family history will help answer the question of why your temples hurt - compare your symptoms with the diseases that your close relatives suffer from.
Infections
With infectious diseases, patients feel a feeling of tightness, a very severe headache in the left temple or right, or both at once. The intensity depends on the development of the disease.
A throat infection is the most common cause of pain, which is caused by various types of microorganisms that put pressure on the nerve endings.
In addition, the same sore throat is accompanied by high body temperature, which, in turn, causes increased blood pressure and affects the heart rate. This also causes pain, which can be aggravated by loud noise or too bright lighting.
External factors causing headaches in the temples
Exogenous factors:
- Prolonged stress or overwork;
In this case, the pain is squeezing or aching in nature;
- Prolonged hunger or strict diet;
- Sleep disturbance;
- Excessive consumption of foods containing monosodium glutamate (chips, sauces, spices) or nitrites (chocolate, fast food, smoked meats);
This chemical, accumulating in the body, causes pain in the frontal and temporal region;
- Poisoning by chemical compounds. Pain in the temples occurs on both sides and is accompanied by pressure in the back of the head and forehead. Severe poisoning can cause chronic pain;
- Reaction to new climatic conditions or weather changes, weather dependence;
- Climbing to great heights. This causes an increase in blood pressure. Normally, when the exogenous factor is eliminated, the pain stops.
The following factors can be the causes of pain in the temporal region:
- external adverse influence causing pain in the temporal region. Such temporal (short-term) headaches occur suddenly, are temporary and disappear if the irritant that caused this condition is eliminated;
- internal factors causing regular pressing pain in the area of the right temple or in the left temple. Persistent pain on the left or right indicates malfunctions in the body or pathological processes affecting the brain.
Migraine
Frequent characteristic ailments, permanent or temporary, are associated with various parts of the body, not just the head.
Diseases of the nervous system as a whole specifically affect the functioning of the blood vessels in the brain. The pain is periodic and most often spreads to one half of the head. In medicine, this pathology is called migraine.
The frequency of attacks varies from person to person: some patients experience discomfort once a week, while others experience it several times a year. In this case, the pain is not provoked by high blood pressure, overexertion, or stroke, but by pathology of the blood vessels of the brain. With this disease, patients become irritable, cannot tolerate bright colors, and become more sensitive to odors.
First aid
To ease pain in the temples, it is recommended to lie down in peace and quiet, preferably in a room where bright sunlight does not penetrate. You can give yourself a massage in the area of the temporal fossa. It is enough to press your fingers on the right one, if there is pain in the right temple, for 10 seconds or perform light circular movements. The same movements are performed on the other side. Chamomile tea will help you calm down.
It is recommended to first apply a cold compress to your temples, and after a few minutes a hot compress.
Lifestyle correction
In fact, in order to get rid of headache attacks, lifestyle modification is just as necessary as compliance with the prescribed treatment. All measures will be aimed at reducing the activity of the sympathoadrenal system, which increases blood pressure, and normalizing cerebral circulation:
- Compliance with work and rest schedules. The human biological clock perceives work during the daytime. That is why night shift workers have a high chance of developing chronic headaches in their temples. You need to sleep at least 7 hours so that the body can fully restore its strength;
- Rejection of bad habits. Smoking leads to the destruction of blood vessels, which has the most negative effect on the state of cerebral circulation, leading to frequent headaches and increasing the likelihood of developing cardiovascular accidents.
- Normalization of the emotional microclimate. Avoid stress and excessive nervous tension - try not to worry too much, and the pain in your temples will not bother you again.
conclusions
Pain in the temples of various types is a symptom of many diseases. Elimination of this symptom is carried out taking into account the reasons that led to its manifestation. At the same time, lifestyle correction is no less important than drug treatment.
Features of therapy
If you have a severe headache in your temples, what should you do? The cause of such an illness can only be determined through a complete medical examination. It includes various methods - from a general blood test to magnetic tomography, which allows you to diagnose internal organs.
A correct diagnosis helps to overcome the disease faster. Many drugs available in pharmacies for free sale can only temporarily eliminate the consequences of the disease, as a result of which it is not recommended to self-medicate.
The treatment prescribed by the doctor is aimed at eliminating the cause, so they take medications that fight inflammation, normalize blood pressure, block pain, and promote cerebral circulation.
For food poisoning, medications are used that quickly remove toxins from the body from poor-quality food. With migraine, the blood vessels not only dilate, but also become narrower, so drugs cannot be prescribed to dilate them.
Therapy is selected individually for each patient. If a headache of unknown origin occurs, doctors recommend taking aspirin. The drug can temporarily relieve pain, but this does not preclude seeking medical help.
Sometimes the discomfort described does not require treatment with medication. It is caused by excessive fatigue, fatigue. In such cases, doctors recommend taking a comfortable position, darkening the windows, turning off the TV and radio and relaxing.
The combination of all treatment methods helps to achieve a positive result faster, therefore, along with medications, traditional medicine is also used.
Treatment
You can relieve a one-time headache by taking a painkiller, for example, Nurofen, Aspirin, Paracetamol. However, for persistent, intensifying pain, treatment should be prescribed by a doctor based on the diagnostic results.
Medicines, physiotherapy, traditional methods, and massage are used. In case of severe vascular pathologies and tumors, surgical intervention is performed.
Using aromatherapy at home can help. Lavender oil is rubbed into the temples and inhaled. It can be used to prepare baths.
So, the cause of the pain has been established. What is a temple? This is only part of the head. And the pain can move inside the skull. But if it nevertheless concentrates in the temples, then the first thing some experts suggest is to drink a glass of water or go out into the fresh air. If the pain is associated with a disease of other organs, consultation with appropriate doctors is necessary.
And secondly, you can do a light acupressure, apply a warm or cool compress.
If pain occurs from eye fatigue, which often happens in people who spend a lot of time looking at the monitor, then again, it is necessary to give this paired organ rest by walking in the fresh air and enjoying the sky and nature.
If the cause of your discomfort is hypertension, you need to relax and drink tea with lemon. If you have low blood pressure, you need to drink a cup of coffee and eat chocolate. Drink juice with a high content of vitamin C. If possible, do several hatha yoga asanas, and then start regular exercises to eliminate the physical causes of pain.
And only as a last resort, if all of the above recommendations do not bring results, take medications after consulting with a general practitioner or neurologist.
temple - See... Dictionary of synonyms
TEMPLE - TEMPLE, temple, husband. The side of the skull from the ear to the forehead bone. The bullet hit his temple. There's a pounding in my temples. || Hair growing on this part of the skull. Comb your temples. Ushakov's explanatory dictionary. D.N. Ushakov. 1935 1940 ... Ushakov's Explanatory Dictionary
TEMPLE - husband. the side of the head, skull, between the ear and forehead; braid; a small depression in this place, above the cheekbone. | Hair is above this place, between the ear and forehead. Trim your temples. Give it to your hands, it will be easier on your temples. For whiskey, and in a vice. One... ... Dahl's Explanatory Dictionary
TEMPLE - TEMPLE, ska, husband. Part of the skull from ear to forehead. | decrease temple, chka, husband. | adj. temporal, oh, oh. Temporal bones. Ozhegov's explanatory dictionary. S.I. Ozhegov, N.Yu. Shvedova. 1949 1992 ... Ozhegov's Explanatory Dictionary
TEMPLE - Greek. byssos, a very thin fabric, or a type of down. Ancient expensive purple fabric. Explanation of 25,000 foreign words that have come into use in the Russian language, with the meaning of their roots. Mikhelson A.D., 1865 ... Dictionary of foreign words of the Russian language
temple - (tempus, PNA, BNA, JNA) 1) the lateral part of the head corresponding to the temporal region; 2) see Temporal fossa ... Big medical dictionary
temple - temple m., Ukrainian temple from hanging; see Zheltov, Federal Law 1876, issue. 1, p. 18. Even now, in many dialects, this word means hair hanging down at the temples (for example, in Tamb., Astra; cf. RFV 70, 131, 288), blr. viscata slob with disheveled hair... ... Etymological Dictionary of the Russian Language by Max Vasmer
Temple - m. The side of the head from the ear to the beginning of the forehead. Ephraim's explanatory dictionary. T. F. Efremova. 2000 ... Modern explanatory dictionary of the Russian language by Efremova
Headache and pressure on eyes and temples: causes and what to do...
Usually, if a person has a headache and pressure on his eyes, he takes a painkiller pill and continues to do his usual activities.
And only with the regular appearance of discomfort, an increase in pain, consult a doctor.
Pressing pain can be a sign of migraine, or it can indicate the development of a more serious pathology - tumor growth, circulatory problems leading to a stroke. Therefore, it is better not to delay going to the doctor.
Causes of headaches pressing on the eyes and temples
A one-time headache may occur due to vascular spasm. The older a person is, the more often he has a headache. Determining the cause of discomfort helps you choose treatment that alleviates the condition or completely eliminates pain.
Migraine
Migraine is considered a woman's disease. Symptoms include headaches, nausea, pressure on the eyes, and any sounds or smells are unpleasant, noted by patients who have already reached 18 years of age. It has not been established exactly what mechanisms trigger the attack, but indirect factors are noted that lead to pain in the temples and eyes:
- Hereditary predisposition to migraine attacks.
- Hormonal changes (during adolescence, during pregnancy, during breastfeeding, during menopause).
- Vascular factors: thrombus formation, stenosis of the vascular bed of the head and neck.
With migraines, the pain is often one-sided, feels like a burning lump in the temple, a thorn, a dull hot knife stuck in the head. Shooting behind the ear, under the cheek, in the eye socket is noted when loud sounds or bright light appear.
Cluster pain
Men often complain of this type of pain. Cluster pain is predominantly localized in one part of the head.
The patient's face and area under the eye swell, the eyelid swells and closes, and lacrimation begins. Some patients describe the attack as being stung by a swarm of bees directed at the temple.
The pain is simply unbearable, does not go away if you just lie down, and does not allow you to sleep. Discomfort lasts from 25 minutes to 2 hours.
Cluster pains are characterized by regularity and can occur at the same time, with an interval of several days or months. In this case, headache in the temples and eyes is a characteristic sign of the disease.
Arterial hypertension
It is believed that with hypertension, headaches are usually localized in the occipital region, but there is a group of patients who complain of pain in the temples that occurs when blood pressure rises.
The pain is dull, pressing, you want to rub your temples with your fingers to “erase” the unpleasant sensations. In addition, if you close your eyes, you get the impression that there is pressure on the eyeballs from the inside.
Additional symptoms:
- Noise in the ears, whistling, ringing, pulsation, sounds of cannonade.
- Darkening in the eyes.
- Pressing pain behind the sternum.
- Nausea, vomiting.
With a significant increase in blood pressure, the patient may lose consciousness, cerebral circulation may be impaired, and hemorrhoidal stroke may develop.
Temporal arteritis
With chronic inflammation of the temporal artery, thickening of the vessels located in the temporal region develops. When pressing on the affected vessel, a headache occurs, pressing on the eyes.
It can be one-sided or diffusely spread throughout the head. With simultaneous damage to the temporal and ophthalmic arteries, the patient experiences migraine-like attacks, accompanied by significant deterioration of vision.
When chewing or moving the eyes, the pain intensifies.
The disease is more often diagnosed in older people; with pathology, there is a narrowing of the vascular bed and increased formation of blood clots.
Ophthalmic diseases
The cause of pain in the temples and eyes may be overwork of the ocular apparatus. This happens if a person wears uncomfortable glasses for a long period of time, incorrectly selected lenses, or generally refuses to wear special devices to improve vision.
As a result, when the patient needs to look at or read something, he has to squint and choose a certain angle of view. This causes significant overstrain of the muscles of the face and eyes, and headaches occur from overwork.
Glaucoma can also cause pain. With this disease, headaches can occur in the frontal or temporal part of the head, affecting both sides of the skull.
Injury
A head injury can lead to cerebrovascular accident. At the same time, the temples hurt, and there is pressure on the eyes if the blow is applied directly to the person’s face, forehead, or temple. Pressure pain also occurs when an aneurysm ruptures and spills into the subarachnoid space. Unpleasant sensations in the eyes may be prerequisites for rupture of the aneurysmal sac.
Overwork
You can become overtired not only by doing hard physical work. Mental fatigue is noted when a person takes on great responsibility and strives to complete as many tasks as possible in a short period of time.
Office workers often get tired of their eyes from constantly staring intensely at the text on the screen. Added to this is an uncomfortable static posture, which provokes osteochondrosis. The result is a headache in the temporal region of the head, pressure on the eyes, and a feeling of extreme fatigue.
Psycho-emotional stress can also lead to pain. More often, patients note the appearance of unpleasant sensations in the evening, towards the end of the working day, but in the absence of rest this condition can become permanent.
Diagnostics
Which doctor should I contact? If a person has pain in his temples and eyes, the first thing he should do is visit a therapist. After listening to the patient’s complaints and examining him, the doctor will prescribe treatment or refer him to another specialist: a neurologist or ophthalmologist. Additionally, the following types of examination are prescribed:
- Magnetic resonance or computed tomography of the head and neck.
- Angiography of cerebral, temporal, and ophthalmic arteries.
- Ophthalmological examination.
- Fundus examination.
If necessary, a general blood test is taken to determine whether the level of sugar and cholesterol is in the normal range.
Features of treatment
If you eliminate the cause of the discomfort, the pain will go away. Therefore, treatment is prescribed only after the doctor determines what disease is bothering the patient.
Taking medications
Since arterial hypertension is a common cause of headaches, drug therapy is primarily aimed at normalizing blood pressure (Captopril, Renitec, Enam). Also, a neurologist can recommend drugs that strengthen blood vessels, restoring the flexibility and patency of the vascular bed (Verapamil, Cinnarizine, Amlodipine).
If you have a headache in your temples and pressure on your eyes due to migraine attacks, you can use painkillers. At the very beginning of the disease, preference is given to non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs: Aspirin, Ibuprofen, Paracetamol. In the future, if single-component drugs do not help, stronger drugs may be prescribed: Spazmalgon, Sumamigren, Triptan.
The selection of medications for cluster pain, temporal arteritis, and eye diseases depends on the individual characteristics of the patient and is performed only by a doctor.
Pain relief at home
Aromatherapy will help get rid of unpleasant sensations in the head caused by overwork. Oils of rosemary, mint, tea tree, lemon, and lavender have a healing effect. For migraines, just apply a couple of drops of essential oil to your wrists and temples.
A cool compress applied to the forehead relieves headaches well. For these purposes, you can use cabbage leaves or burdock leaves, grated potatoes wrapped in gauze. Even 15 minutes under a cool shower will help relieve discomfort in the head caused by rising blood pressure or a migraine attack.
To relieve pain, you can drink green, chamomile, or mint tea. Black tea with honey also helps relieve headaches. At home, you can strengthen the blood vessels of the head by taking viburnum juice or a vitamin mixture: walnut kernels ground in a meat grinder with lemon and honey.
Remember! All home treatments should complement traditional treatment.
If a headache presses on the eyes and temples, painkillers do not help, and simple procedures do not bring relief, you should urgently seek medical help.
Source: https://BolitGolova.info/golovnaya-bol/bolit-golova-i-davit-na-glaza.html
How to treat
Modern medicine offers several ways to treat temporal pain. Usually the doctor prescribes a comprehensive treatment, including:
- medications,
- physiotherapy,
- massage,
- folk remedies.
The doctor should prescribe a specific treatment regimen after studying the symptoms and finding the specific cause of the discomfort. A person suffering from frequent painful manifestations in the temple area should be examined by a specialist and undergo a series of tests prescribed by the doctor. Only after this will it be possible to understand why the temples hurt.
Medicines most often prescribed for pain symptoms can be divided into the following groups:
- analgesics. These drugs make it possible to quickly relieve a painful attack if the pain is short-term;
- diuretics. Such medications are prescribed to reduce intracranial pressure when intracranial hypertension is diagnosed. The drugs relieve pain in the temporal part well;
- medications that help normalize blood circulation in brain tissue. These drugs are indicated for people to take when diagnosing diseases of the circulatory system associated with a weakening of the tone of the blood vessels;
- non-steroidal drugs that have an anti-inflammatory effect. Such medications are effective for many types of temporal pain caused by internal and external causes;
- medications that lower blood pressure. These medications are usually taken by people suffering from high blood pressure; reducing it helps to eliminate pain in the temporal region;
- sulfonamide and antibactericidal drugs can be prescribed when viral or infectious diseases are detected. Such medications relieve unfavorable symptoms, including pain in the temples.
Another effective way to treat pain is acupressure, prescribed in combination with medications.
Traditional medicine also offers many effective recipes to get rid of short-term temporal pain.
Without proper treatment, the risk increases:
- decreased hearing and visual acuity;
- development of mental disorders;
- stroke and myocardial infarction;
- changes in the patient’s emotional background: sudden changes in mood, increased irritability, apathy.
Once the diagnosis is made, immediate treatment of the disease begins. Remember: a healthy person rarely gets a headache.
Associated symptoms
In addition to pain in the left side of the head, other symptoms may develop, the nature of which depends on the cause of the pathology. If the pain is caused by migraine, the patient experiences:
- nausea;
- photophobia;
- deterioration of visual function.
With sudden changes in blood pressure, a person feels noise or ringing in the ears, and the urge to vomit. Pain associated with climate change may be accompanied by weakness and drowsiness.
Since any pain, including pain in the left temple of the head, does not occur for no reason, they have accompanying symptoms. In addition to the fact that a person feels severe throbbing pain, the following may be present:
- extraneous noise in the ears;
- fear of light;
- dizziness;
- nausea and vomiting;
- sensations of pressure on the temple when making movements and bending;
- pain extending to the eyes;
- increased pain intensity;
- disturbance of consciousness and memory.
We suggest you read: What to do if your tooth hurts - folk remedies
Important information
If you notice any of these headache symptoms, you should immediately contact a specialist for help. The headache cannot be tolerated. It is necessary to identify the cause and eliminate it.
What traditional medicine offers:
- use of aromatic oils. The effectiveness of aromatherapy has been proven for a long time. Using peppermint oil or lavender oil for painful attacks gives good results. The oils can be used individually or mixed by adding the same portion of peppermint oil to the lavender oil. The oil or aromatic mixture can be inhaled or acupressure done with it in the temple area;
- white cabbage compresses. This proven remedy was known to our ancestors. White cabbage has many healing properties: it relieves inflammation, treats thermal burns, and can reduce pain. Leaves of fresh cabbage need to be lightly beaten with a knife so that the juice appears, applied to the temples, apply a fastening bandage, and periodically replace the leaves with fresh ones;
- valerian root. Decoctions made from this medicinal plant help in many cases. They are also effective for severe headaches. Preparation: Add a tablespoon of finely chopped plant roots to a glass of hot water. Pour the mixture into a thermos and leave for about an hour. Strain and take before meals 3 times a day, dividing the resulting decoction into three equal parts. The duration of treatment is at least seven days.
Treatment methods for pain in the left temple
Treatment methods for pain in the left temple of the head depend on the disease that caused the pain and its symptoms. In any case, the method should be selected by the doctor, based on the results of tests and diagnostic procedures. Treatment may include:
- taking medications – allows you to eliminate pain, suppress inflammatory processes and the development of infection, and get rid of the symptoms of the disease;
- physiotherapy - influencing the site of pain or inflammation using physical factors. Used as an additional or auxiliary method;
- massage - the use of biologically active points on the human body to eliminate pain;
- traditional medicine - treatment using decoctions, ointments, oils, infusions and teas prepared with the help of plants and other natural resources. When used correctly, this method can bring good results and relieve not only pain, but also the disease itself;
- surgical interventions (operations) - used in cases where the disease cannot be eliminated only with the help of medications and other methods.
We suggest you read: The lymph node in the neck is inflamed and the cheek hurts
Self-medication is extremely dangerous. In the presence of tumors, methods such as massage and traditional medicine treatment can help to increase it. And improper medication use can make the disease chronic.
In some cases, alternative medicine can help as well as medicine. It is better to resort to them after finding out the causes of the disease and with the permission of the attending physician. For organic problems, such approaches should not replace traditional therapy; they can only act as a supplement. If the headache is due to stress or overexertion, these approaches may be sufficient.
If you have pain in the temple on the right, you should try the following emergency methods:
- cabbage compress - you can apply a cloth soaked in cabbage juice or the cabbage leaf itself, slightly mashed, to your temple;
- massage of the temples using ethers - dilute a couple of drops of menthol or mint ether in a teaspoon of vegetable oil. Massage the problem area with the resulting mixture;
- vinegar compress – dilute a teaspoon of apple cider vinegar in a glass of water. Soak a bandage or piece of gauze in the solution and apply to the sore spot;
- lemon rub – take a fresh lemon peel, press its light inner side to the sore temple and massage with light pressure;
- tea with mint, lemon balm, chamomile - a drink made from individual components or a mixture of them relieves nervous tension. The main thing is that it is fresh, not very strong and without added sweeteners.
The listed approaches are safe, accessible and effective. However, it is not recommended to resort to them systematically. Abuse of manipulations reduces their effectiveness and increases the risk of developing allergies.
Prevention of the disease
Preventive measures can not only alleviate attacks, but even get rid of temporal cephalgia forever. First of all, you need to analyze your lifestyle and correct the missing points.
Follow simple rules:
- choose a diet enriched with vitamins;
- exclude foods with tyramine, for example, chocolate, smoked meats, cheese, nuts;
- ventilate your living space daily;
- Don’t be nervous or panic, try to focus on the good;
- periodically undergo a course of physiotherapy, acupressure, acupuncture and other useful procedures;
- go in for sports, yoga, Pilates, swimming, gymnastics help a lot, the main thing is that the exercises are regular;
- plan your daily routine, you need to go to bed, wake up and eat at the same time;
- eight hours of complete rest is required;
- give up cigarettes, alcohol, medication abuse;
- See your doctor regularly.
- Compliance with work and rest schedules;
- Relaxation, meditation;
- Maintaining an active lifestyle;
- Regularly undergoing scheduled medical examinations and laboratory tests;
- Timely treatment of neurological diseases;
- Proper nutrition with moderate amounts of fatty foods and alcoholic beverages;
- Introduction of herbal tea into the diet;
- A healthy night's sleep for 8 hours.
A harmonious work and rest schedule, the ability to cope with stress, the use of various folk remedies, regular exercise, timely diagnosis and appropriate treatment of chronic and concomitant diseases will help you quickly and permanently get rid of pain in the temples.
Preventive measures
To prevent the onset of pain attacks, follow preventive measures:
- get enough sleep - it is recommended to sleep at least 7 hours a day, the best option is 8 hours;
- Give your eyes and muscles rest if your work is sedentary or stressful. Don’t get carried away with the computer outside of work hours - it’s better to open a book;
- Drink herbal teas every day. Suitable from chamomile flowers;
- take a walk in the fresh air, ventilate the room - oxygen guarantees the good functioning of all body systems.
Visits: 2,664