What should you do if the doctor reports on an ultrasound that your child has enlarged ventricles of the brain? If the baby feels normal and there are no abnormalities in neuropsychic development, the specialist may suggest simply regularly visiting a neurologist to monitor the little patient’s condition. With a pronounced clinical picture of brain damage, pronounced neurological symptoms and a significant deviation in the size of the ventricles from the norm, treatment is necessary, which is prescribed by a neurologist.
Normal cerebral ventricles in a newborn
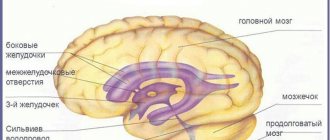
Normally, a person has four ventricles in the head: two lateral, they are located symmetrically, the third and fourth, located in the middle. The third is conventionally anterior, the fourth is posterior. The fourth ventricle passes through the cisterna magna, connecting to the central canal (spinal cord).
Why are doctors concerned about enlarged ventricles of the brain? The main function of the lateral structures is the production of cerebrospinal fluid and regulation of the volume of cerebrospinal fluid. A large release of fluid and a violation of its excretion provokes disruption of brain function.
The depth of the third ventricle should normally not exceed 5 mm, the fourth ventricle – 4 mm. If the lateral ventricles of the brain are considered, the norm for a newborn is calculated as follows:
- Anterior horns – from 2 mm to 4 mm.
- Occipital horns – from 10 mm to 15 mm.
- Lateral bodies - no deeper than 4 mm.
The standard depth for a large tank is 3-6 mm. All brain structures should grow gradually, the size of the ventricles should be linearly consistent with the size of the skull.
Anatomy of the ventricular system of the brain
The structure of the human brain is heterogeneous; it consists of several parts, each of which is responsible for a specific vital function.
In any healthy person, the brain consists of four ventricles, which are interconnected by vessels, channels, openings and valves. The brain consists of the lateral ventricles, the third and fourth. The side ones also have their own numbers: the left one is designated by the first number, and the right one by the second. 3 and 4 have a different name - front and rear, respectively. The lateral ventricles have horns - anterior and posterior, and a body of the ventricles. Cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) constantly circulates around all ventricles.
A change in the size of one or all ventricles entails a deterioration in the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid. This can have serious consequences: it leads to an increase in the volume of fluid in the spinal cord and a deterioration in the functioning of the body. Asymmetrical ventricles are not normal in babies and children under one year of age.
The ventricular system consists of 4 cavities located in parts of the brain. Their main purpose is the synthesis of cerebrospinal fluid or cerebrospinal fluid, which performs a large number of tasks, but its main function is to cushion the brain matter from external influences, control intracranial pressure and stabilize metabolic processes between the blood and the brain.
The movement of cerebrospinal fluid occurs through channels connecting the common 4th ventricle and the subarachnoid space formed by the membranes of the spinal cord and brain. Moreover, its main volume is located above significant fissures and convolutions of the cortex.
The largest lateral ventricles are located equidistant from the midline below the corpus callosum. The first ventricle is considered to be the cavity located on the left side, and the second - on the right. They are C-shaped and wrap around the dorsal parts of the basal ganglia. They produce cerebrospinal fluid, which enters the third ventricle through the intergastric openings. Structurally, segments I and II of the ventricular system include the anterior (frontal) horns, body and inferior (temporal) horns.
The third ventricle is located between the visual tuberosities and has the shape of a ring. At the same time, gray matter is located in its walls, which is responsible for regulating the autonomic system. This section is connected with the midbrain aqueduct, and through the interventricular foramen, located behind the nasal commissure, with the I and II ventricles.
The most important IV ventricle is located between the cerebellum and the medulla oblongata, with the vermis and medullary velum located above it, and the medulla oblongata and pons below it. This cavity was formed from the remains of the posterior medullary vesicle and is common to the rhomboid region. At its bottom lie the nuclei of the V-XII cranial nerves. In this case, the posterior lower corner communicates with the spinal cord through the central canal, and through the upper anterior part with the aqueduct.
Sometimes, when examining a newborn, the fifth ventricle is detected, which is a feature of the structure of the brain. It is located in the anterior midline, below the corpus callosum. Usually its closure occurs by 6 months of age, but if the gap is more than 10 mm, then we are talking about a pathology of the liquorodynamic system.
If an ultrasound revealed asymmetry of the lateral ventricles in a child, the prognosis depends on the degree of pathology and the depth of damage to brain tissue, as well as the reasons that provoked the development of the disease. Thus, a significant increase interferes with normal circulation and production of cerebrospinal fluid, which entails neurological problems.
Causes of enlarged ventricles of the brain
It is believed that changes in ventricular structures in infants are genetically determined. Pathological changes in the brain develop due to chromosomal abnormalities that occur in pregnant women. There are other factors that provoke asymmetry of the ventricles and excessive enlargement of parts of the brain:
- Diseases of infectious etiology that a woman suffered during pregnancy.
- Sepsis, intrauterine infections.
- Entry of a foreign body into the brain structures.
- Pathological course of pregnancy caused by chronic diseases of the mother.
- Premature birth.
- Intrauterine fetal hypoxia: insufficient blood supply to the placenta, increased placental blood flow, umbilical cord varicose veins.
- Long waterless period.
- Rapid birth.
- Birth trauma: strangulation by the umbilical cord, deformation of the skull bones.
Experts also note that the ventricles of the brain in newborns may become enlarged due to the occurrence of hydrocephalus of unknown etiology. Congenital causes that provoke expansion of the ventricles of the head include the growth of neoplasms: cysts, benign and malignant tumors, hematomas.
A traumatic brain injury received by a child during childbirth, cerebral hemorrhage, ischemic or hemorrhagic stroke can also cause enlargement of the ventricles of the baby’s brain.
Causes of enlarged ventricles
Premature babies may have dilated ventricles immediately after birth. They are located symmetrically. Symptoms of intracranial hypertension in a child with this condition usually do not occur. If only one of the horns increases slightly, then this may be evidence of the presence of pathology.
The following reasons lead to the development of ventricular enlargement:
Fetal hypoxia, anatomical defects in the structure of the placenta, development of placental insufficiency. Such conditions lead to disruption of the blood supply to the brain of the unborn child, which can cause expansion of the intracranial collectors.
Traumatic brain injuries or falls. In this case, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted. This condition causes water to stagnate in the ventricles, which can lead to symptoms of increased intracranial pressure.
Pathological birth. Traumatic injuries, as well as unforeseen circumstances during childbirth, can lead to disruption of the blood supply to the brain. These emergency conditions often contribute to the development of ventricular dilatation.
Infection with bacterial infections during pregnancy. Pathogenic microorganisms easily penetrate the placenta and can cause various complications in the child.
Prolonged labor. Too long a time between the rupture of amniotic fluid and the expulsion of the baby can lead to the development of intrapartum hypoxia, which causes a disruption in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid from the dilated ventricles.
Oncological formations and cysts that are located in the brain. The growth of tumors puts excess pressure on intracerebral structures. This leads to the development of pathological expansion of the ventricles.
Foreign bodies and elements that are located in the brain.
Infectious diseases. Many bacteria and viruses easily penetrate the blood-brain barrier. This contributes to the development of numerous pathological formations in the brain.
Clinical manifestations of ventricular dilatation
The ventricles not only store cerebrospinal fluid, they also secrete cerebrospinal fluid into the subarachnoid space. An increase in fluid secretion and a deterioration in its outflow leads to the fact that the ventricles stretch and enlarge.
An increase in the ventricular structures of the brain (dilatation, ventriculomegaly) may be a normal variant if a symmetrical expansion of the lateral ventricles is detected. If there is asymmetry of the lateral structures, the horns of only one of the ventricles are enlarged, this is a sign of the development of a pathological process.
Not only the lateral ventricles of the brain can become pathologically enlarged; the normal production and excretion of cerebrospinal fluid may be disrupted in the third or fourth. There are three types of ventriculomegaly:
- Lateral: enlargement of the left or right part of the ventricular structures, expansion of the posterior ventricle.
- Cerebellar: the medulla oblongata and cerebellar region are affected.
- When pathological release of cerebrospinal fluid occurs between the visual tuberosities, in the frontal part of the head.
The disease can occur in mild, moderate, severe form. In this case, not only an expansion of the cavities of the ventricles of the brain is noted, but also a disruption in the functioning of the child’s central nervous system.
There is normal symmetrical oversizing of the lateral ventricular structures when the child is large, has a large head or an unusual skull shape.
Anterior horns of the lateral ventricles are normal at 3 months – myschool8.com
Sometimes a slight discrepancy between the size of brain structures and normal values is genetically determined. This feature is detected already during the initial examination of the baby and, as a rule, is not considered pathological.
At the same time, noticeable dilatation or asymmetry of the ventricles may be the result of a serious chromosomal abnormality that arose during the intrauterine development of the fetus.
Doctors have also identified a number of non-genetic factors that provoke the expansion of brain cavities. These include:
- infections suffered by the child's mother during pregnancy;
- pathologies of fetal development caused by chronic diseases of the parent;
- sepsis;
- entry of a foreign body into the liquor spaces;
- hydrocephalus of unknown etiology;
- the occurrence of tumors and other neoplasms in the brain;
- birth injuries and complications.
At the moment, many factors are known that influence the appearance of pathologies of the ventricles of the brain in children. All of them can be divided into two categories: acquired and congenital. Acquired causes include those reasons that could arise during the pregnancy of the child’s mother:
- Infectious diseases that a woman suffers from during pregnancy.
- Infections and sepsis inside the womb.
- Penetration of foreign bodies into the brain.
- Chronic diseases of the mother that affect the normal course of pregnancy.
- Delivery ahead of schedule.
- Hypoxia of the fetus inside the womb (insufficient or, conversely, increased blood supply to the placenta).
- Abnormal duration of the dry period.
- Injury to the baby during childbirth (suffocation by the umbilical cord or deformation of the skull).
- Stormy birth.
Congenital causes include a genetic predisposition to enlarged ventricles; abnormalities occurring in chromosomes, as well as various neoplasms (cysts, malignant or benign tumors, hematomas). Along with the listed reasons, characteristic changes in the size of the ventricles of the brain can be provoked by traumatic brain injury, cerebral hemorrhage, or stroke.
In what cases is NSG performed?
Most often, neurosonography is prescribed for infants. There are a number of indications for performing this procedure. Among them:
- birth injuries that the child received;
- obstructed labor of the mother;
- resolution of the burden earlier and later than the due date, that is, prematurity and postmaturity;
- intrauterine infection;
- C-section;
- Rh conflict during pregnancy;
- a genetic disease that the mother suffers from;
- congenital defects detected in a newborn (unequal eye sizes, ears positioned at different heights, etc.);
- inflammatory processes diagnosed in an infant;
- a viral infection that the child suffered seriously. In this case, neurosonography allows us to exclude signs of meningitis and encephalitis.
There are symptoms that should alert you and prompt you to perform NSG even in the absence of the indications listed above. The procedure is recommended if:
- the baby behaves unusually - does not show activity, sleeps shallowly, shows poor appetite, often burps, arches its back, throws its head back;
- the newborn has a poor reaction to sound and visual stimuli - he does not respond to the voice of adults, is unable to look at his mother’s face without looking away, does not follow a moving toy;
- the child develops convulsions and fainting;
- he fell and hit his head hard.
Structure of the ventricular system of the brain
The ventricular system is a capacitive structure of the brain. Its purpose is to synthesize and store cerebrospinal fluid. This fluid, called cerebrospinal fluid, is responsible for a number of functions in the body.
It acts as a shock absorber, protecting the thinking organ from external damage, and helps stabilize intracranial pressure.
Without cerebrospinal fluid, metabolic processes between the brain and blood cells would be impossible.
| Ventricle | Shape, location | Function |
| 1 and 2 (left and right side) | Paired C-shaped structures, consisting of a body and horns (anterior frontal and inferior temporal) each, located behind the basaltic nuclei | Production of cerebrospinal fluid |
| 3 (conditionally front) | Ring-shaped structure located between the optic tuberosities | Regulation of the autonomic system |
| 4 (conditionally rear) | Diamond-shaped structure located between the cerebellum and medulla oblongata | Communication with the spinal canal |
Choroid ependymocytes
The surface of the ependyma is characterized by the fact that here the movement of the processous Kolmer cells, which are characterized by a well-developed lysosomal apparatus, occurs; it is worth noting that they are considered macrophages.
On the basement membrane there is a layer of ependymocytes, which separates it from the fibrous connective tissue of the soft shell of the brain - it contains many fenestrated capillaries, and you can also find layered calcified bodies, which are also called nodules.
Selective ultrafiltration of blood plasma components occurs into the lumen of the ventricles from the capillaries, which is accompanied by the formation of cerebrospinal fluid - this process occurs with the help of the blood-cerebrospinal fluid barrier.
There is evidence that ependymal cells can secrete a number of proteins in the cerebrospinal fluid. In addition, partial absorption of substances from the cerebrospinal fluid occurs. This allows it to be purified from metabolic products and medications, including antibiotics.
Normal ventricle sizes
Each ventricle has certain sizes that are considered normal. Deviation from them is a pathology. So, the normal depth of the third ventricle is no more than 5 mm, the fourth ventricle is no more than 4 mm. When taking side measurements, the following values are taken into account:
- Side cavities - depth should not exceed 4 mm.
- Horns in the occipital part – 10 – 15 mm.
- The horns in the front part are 2–4 mm.
The depth of a large tank is no more than 3–6 mm. All cavities and structures of the brain must have a gradual development, consistent and linearly dependent on the size of the skull.
The volume of each ventricle directly determines how much cerebrospinal fluid is synthesized or stored in it. If the size of the structure exceeds normal, there is a risk of overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid or problems with its removal, which cannot but lead to malfunctions in the functioning of the thinking organ.
What is the usual ventricular depth in newborns? According to the observations of neonatologists, normal values will be approximately as follows:
- 1st and 2nd ventricles - about 3 mm in the anterior and from 10 to 15 mm in the occipital horns, plus - no more than 4 mm in the lateral bodies;
- 3 ventricle – no more than 5 mm;
- 4th ventricle – no more than 4 mm.
Over time, as the newborn's brain begins to grow, the depth of its internal cavities will gradually increase. If the expansion of the ventricles occurs sharply, and their proportions cease to be linearly consistent with the size of the skull, this, like a congenital deviation from normal values, is a reason to sound the alarm.
Indicators indicating normality
First of all, the doctor performing neurosonography evaluates the shape and size of the cerebral hemispheres. Their symmetry is considered normal.
There should be no liquid in the space located between the left and right hemispheres of the brain.
The grooves and convolutions covering the cerebral cortex must be clearly defined.
Pathological changes in the meninges are unacceptable.
The ventricles of the brain - cavities containing cerebrospinal fluid - must have clear boundaries and not be dilated, and there should be no foreign inclusions in them.
The cerebral aqueduct is normally practically invisible on an echogram.
The cerebral peduncles, which are hypoechoic formations, are clearly visible.
The pulsating basilar artery is clearly visible.
The sizes of brain structures must lie in certain ranges:
- bodies of the lateral ventricles - up to 4 mm;
- the gap between the hemispheres of the brain is from 3 to 4 mm;
- anterior horns of the lateral ventricles - up to 2 mm (if the study is carried out at the age of 1 month), posterior horns - from 10 to 15 mm;
- cistern magna – up to 10 mm;
- third ventricle - from 3 to 5 mm;
- fourth ventricle - up to 4 mm;
- subarachnoid space - approximately 3 mm.
This is not a complete list of signs of normal anatomy of the newborn’s brain. Doctors know a whole range of such indicators.
In addition, the specialist performing the NSG takes into account the weight, height and other characteristics of the child, stating the normality of the anatomy or making a diagnosis.
That is why parents do not need to try to interpret the results of an ultrasound examination on their own - this is a job for professionals.
Main types of ventriculomegaly
Normally, the size of the cerebral ventricles should not be more than 10 mm. This indicator is considered borderline. Its excess is a cause for concern for the health of the unborn baby. However, not all cases of ventriculomegaly lead to irreversible consequences in the development of the nervous system. It is no coincidence that this disease is divided into three types:
- mild, in which the enlargement of the cerebral ventricles varies between 10-12 mm;
- medium, if the size of the pathology is up to 15 mm;
- severe if the enlargement of the lateral ventricles of the brain in the fetus exceeds 15 mm.
Depending on the type of disease, a treatment strategy is developed.
Symptoms of the disease in an infant
Since the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is impaired, it remains in large quantities in the head, while the intracranial pressure in the newborn increases, and swelling of the tissues, gray matter, and cerebral cortex increases. Due to pressure on the brain, blood supply is disrupted and the functioning of the nervous system deteriorates.
If the growth of the horns of the ventricles of the brain is accompanied by hydrocephalus, the child’s skull bones move apart, the fontanel bulges and tenses, the frontal part of the head can significantly exceed the facial part in size, and a network of veins protrudes on the forehead.
When the ventricle of the brain is enlarged in a newborn or pathological asymmetry of the lateral ventricles is noted, the child experiences the following neurological symptoms:
- Impaired tendon reflex, increased muscle tone.
- Visual impairment: inability to focus, squint, constantly downturned pupils.
- Trembling of limbs.
- Walking on tiptoe.
- Low manifestation of basic reflexes: swallowing, sucking, grasping.
- Apathy, lethargy, drowsiness.
- Irritability, loudness, capriciousness.
- Poor sleep, jumping up in sleep.
- Poor appetite.
One of the most striking symptoms is frequent regurgitation, sometimes vomiting. Normally, a child should burp only after feeding - no more than two tablespoons at a time. Due to the fact that when intracranial pressure increases (it is provoked by excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cavity of the cranium), the vomiting center in the fourth ventricle at the bottom of the rhomboid fossa is irritated, the frequency of regurgitation in a newborn increases significantly (more than twice after feeding and later).
The acute, rapid development of the disease provokes severe headaches, which is why the child constantly screams loudly and monotonously (brain scream).
Diagnostic methods
For the first time, a doctor can pay attention to deviations in the size of brain structures from the norm during an intrauterine ultrasound examination of the fetus. If the head size does not return to normal, a repeat ultrasound is performed after the baby is born.
Enlargement of the ventricles of the brain in newborns is diagnosed after neurosonography - ultrasound performed through the skin of an undeveloped fontanel. This study can be carried out until the child’s skull bones have completely fused.
If the disease develops chronically, the doctor may pay attention to the fact that the ventricles of the brain are larger than normal when examining the child with an ultrasound scan at three months of age. To clarify the diagnosis, it is recommended to undergo additional examination:
- Ophthalmological examination - helps to identify swelling of the eye discs, indicating increased intracranial pressure, hydrocephalus.
- Magnetic resonance imaging can be used to monitor the growth of the cerebral ventricles after the bones of the child’s skull have fused. MRI is a long procedure, the time spent under the machine is 20-40 minutes. In order for the child to lie motionless for such a long time, he is immersed in medicated sleep.
- When undergoing a CT scan, you do not need to remain motionless for a long time. Therefore, this type of study is suitable for children for whom anesthesia is contraindicated. Using CT and MRI, you can obtain accurate images of the brain, determine how much the size of the ventricular system deviates from the norm, and whether there are neoplasms or hemorrhages in the medulla.
It is recommended to undergo an ultrasound of the brain for children in the first month of life if pregnancy or childbirth was accompanied by complications. If the ventricles are enlarged but there are no neurological symptoms, it is recommended to be re-examined after three months.
Symptoms of dilatation of the lateral ventricles
In an adult, clinical symptoms are rarely observed. Symptoms of dilatation in children:
- Dizziness;
- Nausea and vomiting;
- Apathy;
- Feeling of constant anxiety;
- Impaired walking coordination.
The clinical picture is nonspecific, so manifestations vary from person to person. In more rare cases, pathology of sensitivity, muscle paresis, cognitive disorders, and problems with head tilt occur.
Manifestations in newborns
The clinical picture in newborns is determined by the severity of the pathology. Immediately after birth, a number of external signs are noted:
- Frequent regurgitation;
- Tendency to throw the head back;
- Low muscle tone;
- Tremor;
- Paralysis;
- Nervous excitability;
- Decreased peripheral sensitivity;
- Constant crying;
- Refusal to eat.
Identification of any symptom requires an ultrasound scan of the brain. Ultrasound rays penetrate well through unclosed fontanelles.
Hydrocephalus in a baby is determined by the appearance of the skull. The increase in head size is caused by excess accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid. Liquor causes dilatation (expansion) of the ventricles (lateral, third, fourth).
A high frequency of pathology formation is observed with cysts, intracranial hemorrhages, hematomas, and neoplasms.
Inflammatory processes in the cerebral parenchyma provoke bacterial and viral infections that newborns contract in utero (syphilis, chlamydia, mycoplasma, cytomegalovirus, herpes).
Treatment
When a child has enlarged ventricles of the brain, only a neurologist or neurosurgeon can prescribe the necessary treatment.
Drug therapy
Enlargement or asymmetry of ventricular structures does not always require treatment. If the child develops correctly, eats and sleeps well, it is considered that enlargement of the ventricular horns is an acceptable deviation from the norm.
If pronounced neurological symptoms occur, the baby is prescribed special medications:
- Diuretics (Diacarb, Furosemide) - to reduce cerebral edema, speed up urination, and normalize fluid excretion from the body.
- Potassium preparations (Panangin, Asparkam) - to replenish potassium deficiency, which occurs during accelerated work of the urinary tract.
- Vitamins (Multitabs, B6, D3, Magne B6) - to prevent rickets and accelerate regeneration processes in the body of a newborn.
- Nootropic drugs (Cavinton, Vinpocetine, Noofen, Ecephabol, Cerebrolysin) - to normalize cerebral circulation, strengthen blood vessels, improve microcirculation in brain tissue.
- Sedative medications (Glycine) – help reduce nervous symptoms: tearfulness, moodiness, irritability; stabilize the process of falling asleep, normalize sleep.
If the provoking factors that caused the pathological growth of the ventricles of the brain are identified, they are also eliminated: viral and infectious diseases are treated. If the cause of the pathology is brain damage or the growth of a tumor, surgical intervention is performed: the cyst is excised, the cancerous tumor is removed.
When enlarged ventricles of the brain are diagnosed in a child, treatment takes a long period of time. Newborns need to undergo massage courses and constantly perform physical therapy exercises to restore muscle tone and prevent atrophy.
Possible consequences and complications
Probably due to the wide availability of information and the opportunity to consult with other parents, an unhealthy trend has been observed recently. Parents refuse to treat their children for hydrocephalus; they attribute constant crying to capriciousness and stubbornness, and lethargy to character traits. People are frightened by serious medications and contraindications, and they decide that the disease will go away on its own.
But asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain, their significant increase can lead to serious consequences:
- Delayed mental, physical, mental development.
- Loss of vision: complete or partial.
- Hearing loss.
- Paralysis of limbs, complete immobilization.
- Pathological head growth.
- Inability to regulate bowel movements and urination.
- Epileptic seizures.
- Frequent loss of consciousness.
- Comatose state.
- Lethal outcome.
It’s good if the doctor notes a slight deviation from the norm during the ultrasound and suggests only observing the patient. This is possible if there are no symptoms of the disease: the child is calm, eats well, sleeps, and develops normally.
A diagnosis of “Dilation of the lateral ventricles of the brain in a child” has been made, but you doubt the professionalism of the doctor, and do not want to give your newborn medications in vain? Contact several independent specialists and get a complete examination. Do not refuse treatment, since the actions of the parents determine how fulfilling the child’s life will be.
Date of publication: 02/17/2017
Author of the article: Shmelev Andrey Sergeevich
Neurologist, reflexologist, functional diagnostician
33 years of experience, highest category
Professional skills: Diagnosis and treatment of the peripheral nervous system, vascular and degenerative diseases of the central nervous system, treatment of headaches, relief of pain syndromes.
The newborn's brain is not yet fully adapted to life outside the mother's body.
There are often situations when the ventricles of the brain enlarge in an infant. This can happen for various reasons.
What is the brain
The brain is the most complex organ in all animals. In addition to the cortex, it has internal structures, for example, ventricles. There are 4 of them in total, two paired and two unpaired. They are designed to collect and store cerebrospinal fluid, or cerebrospinal fluid. The ventricles end in cisterns, which are a reservoir for cerebrospinal fluid.
The largest ventricle, the fourth, collects all the fluid, so it is the one that dilates most often. The ventricles communicate through the foramina of Monroy, which is necessary to reduce the pressure in one of them. Fluid collects in the brain space and leaks from the surrounding veins. The higher the pressure in them, the more liquid will accumulate.
If too much brain fluid collects, dilatation of the ventricles of the brain occurs. Most often, one unpaired one is enlarged. Dilatation of the lateral ventricles, left or right, is less common.
What are the ventricles of the brain, their role
The ventricles of the brain are strips of tissue necessary for the deposition of cerebrospinal fluid. External and internal factors can lead to their increase in volume. The lateral ventricles are the largest. These formations are involved in the formation of cerebrospinal fluid.
Asymmetry is a condition in which one or both cavities are enlarged to varying degrees.
Lateral . The ventricles are the most voluminous, and they contain cerebrospinal fluid. They connect to the third ventricle via the interventricular foramina. Third . Located between the visual tuberosities. Its walls are filled with gray matter. Fourth . Located between the cerebellum and medulla oblongata.
Why does fluid accumulate?
Liquor can accumulate and cause dilatation of the ventricles of the brain for various reasons:
- the size of the ventricles and cisterns is too small compared to the large volume of cerebrospinal fluid. Their greatest length is 4 cm and width is 2 cm. With improper distribution, dilation of the ventricles occurs in newborns. This process is not a pathology, but it needs to be controlled;
- Ventriculomegaly is an increase in the size of the ventricles as a result of a birth defect. If everyone is evenly enlarged, then this is normal. This condition is not a pathology and will not affect the child’s condition. You should be wary if one ventricle is enlarged, especially if it is severe. In this case, hydrocephalus develops. It is caused by enlargement of the ventricles of the brain in newborns. More often, pathology affects the occipital horns as the weakest;
- pressure on the channels from the outside as a result of birth trauma, hematoma, brain tumor. The liquid cannot flow out completely, since the lumen of the tank is narrowed. Its walls expand, and the ventricle enlarges. The most common type is dilatation of the lateral ventricles. Only a neurosurgeon can cope with this condition, and urgently.
The causes of the pathology can be:
- complicated pregnancy or childbirth;
- acute intrauterine fetal hypoxia;
- developmental defects;
- premature birth;
- birth injury.
A competent obstetrician will promptly notice a condition in which the ventricles of the brain are enlarged.
In this case, urgent treatment is needed.
Manifestations of the disease
The expansion of the ventricles of the brain in a child is accompanied by an increase in intracranial pressure. In newborns, it is difficult to notice alarming symptoms in time:
- decreased appetite;
- decreased muscle tone;
- trembling of limbs;
- enlarged veins on the forehead, temples and back of the head, as the outflow of blood in them is impaired;
- slow reaction of the child. He has difficulty moving and grasping;
- eyes can look in different directions;
- the protrusions of the skull and other irregularities of the head are visible;
- The baby spits up frequently.
An older baby may complain of weakness, nausea, dizziness and pallor.
Normal and brain abnormalities on ultrasound in infants
Ultrasound examination allows us to study the work and structure of internal organs. By reflecting the waves, the finished data is sent to the monitor.
Ultrasound of the brain in infants is a mandatory preventive examination procedure. Thanks to the data obtained, it is possible to judge the structure of the brain and the functioning of the vascular system.
The examination is carried out quickly and painlessly and does not pose any danger to the child..
How is the procedure performed?
NSG (neurosonography) allows you to determine disturbances in the functioning and structure of all brain structures, as well as evaluate the functioning of the central nervous system.
NSG is carried out through the fontanel, which is located between the unfused bones of the skull. Thanks to this, the result will be accurate and correct. The fontanel is soft to the touch, pulsation is palpable. Normally it should be at the level of the surface of the head. Swelling indicates health problems.
The NSG procedure does not require additional preparation - it is enough to free the child’s head from the cap. The result is not affected in any way by the child’s condition, even if he cries, is capricious, or calmly examines the situation. The procedure is also carried out when the child is sleeping.
What is the reason for this study?
Ultrasound is a mandatory scheduled procedure every month. In other cases, indications for performing NSG before the first month of life are the following cases:
- the child was born early or late;
- the child’s weight at birth is less than 2800 g;
- pathology of the external structure of the body;
- swelling (tension) of the fontanelle;
- lack of screaming in the first seconds of life;
- birth injury;
- the child has a seizure disorder;
- disruption of labor;
- if during pregnancy disturbances in the development of the brain in the fetus were discovered;
- Rhesus conflict.
NSG is mandatory in one month in the following cases:
- children who were born by caesarean section;
- irregular head shape;
- conduct research to monitor the condition;
- with developmental disorders such as torticollis, strabismus, paralysis;
- The baby spits up frequently.
For children older than one month, NSG is performed for the following indications:
- evaluate the effectiveness of treatment for injuries or neurological diseases of the brain;
- after infectious diseases (encephalitis, meningitis);
- genetic and gene disorders;
- head injury.
In some cases, an MRI of the brain is indicated, which is performed under anesthesia.
Diagnosis of the disease
You should not hope that the dilated ventricles of the brain in a newborn will decrease on their own. A neurosurgeon or neurologist should prescribe treatment.
In order to choose the right therapy, you need to make an accurate diagnosis. Radiation studies are recognized as the best diagnostic methods.
But they are recommended only for a child over one year old, after all the fontanelles have closed.
- MRI (magnetic resonance therapy). Excellent display of soft tissues. But it has contraindications, especially for children. It is almost impossible to properly assess a restless child. The procedure requires remaining still for 20 minutes. If a child is awake and moving during an MRI, there is a chance of getting a false result. The problem can be solved with the help of anesthesia, but it will have a bad effect on health.
- CT scan. The most preferred research method if there are dilated ventricles of the brain in an infant. It is carried out much faster and does not require anesthesia. The dimensions of the lateral and posterior ventricles can be determined. The disadvantage compared to MRI is lower quality. CT does not allow obtaining high-resolution images, especially on small objects. Tomography best shows hemorrhages in the interthecal spaces. This allows you to quickly diagnose the disease and begin treatment.
- Additionally, the condition of the fundus is assessed. It clearly shows dilated vessels, which are an indicator of increased intracranial pressure.
- Neurosonography. Determines the size of the lateral ventricles, but does not visualize them. Sizes up to 3-4 mm are considered normal. The device does not show less than 1 mm.
- The composition of the cerebrospinal fluid can tell about changes in the body. To do this, a puncture of the lumbar spine is performed.
Dilatation of the lateral ventricles is treated with medication. If the child is under 2 years old, treatment should take place in a hospital. Older children are treated on an outpatient basis.
The neurologist prescribes:
- diuretics. They increase urine excretion by the kidneys. At the same time, the volume of blood in the vessels and intercellular fluid decreases. From them liquor is formed. If there is less blood, intracranial pressure will not increase. Therefore, fluid will not leak into the ventricles and cause their dilatation.
- nootropic drugs. Brain fluid is formed for different reasons, but it affects surrounding tissue in the same way. Their swelling and compression occurs. The blood vessels of the brain are compressed. This leads to hypoxia and death. Nootropic drugs improve cerebral circulation, help eliminate hypoxia in the nervous system and reduce the amount of cerebrospinal fluid. Their use in combination with diuretics helps ensure that fluid from the ventricles returns to the blood and is excreted by the kidneys. The child’s condition improves;
- sedatives. Despite the weakness, the child is worried. Any little thing can trigger stress. When stressed, adrenaline is released, which constricts blood vessels and increases blood pressure. The outflow from the brain further decreases, and hydrocephalus progresses. Sedatives relieve this effect. They should be used only as prescribed by a doctor and should not exceed the prescribed dose. Overdose may have life-threatening consequences;
- drugs that improve muscle tone. As a rule, it is reduced at high blood pressure. The muscles do not regulate the stretching of the veins, and they swell. To normalize tone, medications or massage and gymnastics are used. With physical activity, tone increases. A trained person's blood pressure decreases. All treatment methods can be used only with the permission of a doctor and gradually. No harsh effects should be allowed.
For some, hydrocephalic syndrome occurs as a complication of a bacterial infection. First of all, it is necessary to cure it, getting rid of the cause of dilatation of the lateral ventricles.
If the condition is physiological and the child’s life is not in danger, for example, when the baby is large, then there is no need to treat. As a preventative measure, massage and physical therapy are recommended.
Modern medicine does not recognize the effectiveness of acupuncture, homeopathy and similar things. If used incorrectly, they can harm the child.
Taking vitamins has a general strengthening effect, but it does not fight the cause of the disease.
Neurosonography of the brain of newborns: 6 reasons for prescribing, interpretation of the results
Neurosonography is a method for diagnosing hydrocephalus. Neurosonography is an ultrasound of the brain with a mandatory assessment of blood flow in various parts. Analysis of these parameters is necessary for reliable diagnosis of developmental defects or pathologies accompanied by dysfunction of the central nervous system.
What is neurosonography
NSG is used primarily in pediatric practice. This is a modern, reliable, fast way to obtain information about the structure of the brain. The method is absolutely safe and painless. Therefore, neurosonography is the gold standard for diagnosing congenital and acquired intracranial pathologies.
Every child is recommended to undergo a routine examination. Early detection and timely treatment improve the outcome of almost any disease.
Watch the video with a specialist’s explanation of why neurosonography is necessary for a newborn:
Indications for the study
Ultrasound of the brain is performed on children under one year of age. This is explained by the fact that by the age of 8 months the processes of ossification begin, by the year the fontanelles close, visualization of the brain becomes impossible. A routine study is carried out in the first month of life. The examination is carried out in combination with ultrasound of the heart, abdominal cavity, and thymus.
Main indications for research in children:
- physiological immaturity;
- pathological childbirth;
- hypoxia or asphyxia during childbirth;
- neuroinfections;
- diagnosed diseases of other organs;
- impaired consciousness (less than 7 on the Apgar scale);
- chromosomal diseases or suspicions of them;
- the presence of neurological symptoms (delayed psychomotor development, convulsions, weakness of the limbs, nystagmus, strabismus);
- violations of the structure of the head or facial skull;
- abnormal size or shape of the head;
- increased epileptiform readiness.
When pathology is detected, the neurosonogram, along with other research results, is studied by a pediatric neurologist and neurosurgeon. In the future, the management tactics and method of treating the patient are determined.
Preparation for the procedure
Transcranial neurosonography does not require special preparation. The procedure is performed without anesthesia or other medication.
Before neurosonography, doctors recommend feeding the child tightly and letting him sleep during the examination itself. In this case, the study will go unnoticed and will not cause stress.
How is NSG carried out?
NSG is a harmless and painless procedure. Its duration does not exceed 15 minutes.
The area of the large fontanelle is examined. In children under one year old, it consists of cartilage, so ultrasound easily penetrates the tissue, allowing detailed visualization of the anatomy of the brain.
A conductive gel is applied to the crown and a sensor is placed. The temporal and occipital regions are also examined, which helps to fully evaluate these parts of the brain.
Decoding the results
After the study, parents receive a protocol with a functional diagnostic doctor’s conclusion. In the future, you need to visit a neurologist who interprets the neurosonogram.
All anatomical structures should be clearly visible on the image. Bone elements are hyperechoic (white). The brain tissue itself has medium echogenicity (gray color). An important element is the interhemispheric space. On neurosonography it looks like a hyperechoic strip with grooves.
In a child of any age, the corpus callosum should be visualized on ultrasound. It is represented by a set of nerve fibers that support the connection of symmetrical sections with each other. It is also necessary to assess the condition of the liquor system, which consists of the ventricles and cisterns. They appear as anechoic (black) cavities filled with fluid.
The cisterns are gaps between the meninges. Particular attention should be paid to the large tank. Its expansion is often a harbinger of pathologies in the posterior cranial fossa.
Normally, neurosonography reveals:
- symmetry of brain structures;
- no displacement of trunks;
- clarity of convolutions, furrows;
- homogeneous structure of the liquor system;
- echogenic (gray) nuclei and thalamus;
- hyperechoic (white or light gray) choroid plexuses;
- anterior horn of the lateral ventricle up to 2 mm;
- lateral ventricle depth 4 mm;
- the distance between the hemispheres is about 2 ml, there is no liquid in it;
- a transparent septum is square in shape and filled with liquor;
- third ventricle up to 4 mm;
- large tank 3–6 mm.
Indicators depend on the age of the child. When making a diagnosis, the neurologist compares the initial data with values that correspond to the age norm.
Table of normal NSG indicators:
| Structures | Newborns, mm | 3 months, mm |
| Lateral ventricles | Anterior 2–4, occipital 10–15, depth up to 4 | Anterior up to 4, occipital up to 15, depth 2–4 |
| Third ventricle | 3–5 | up to 5 |
| Fourth ventricle | up to 4 | up to 4 |
| Interhemispheric region | 3–4 | 3–4 |
| Large tank | no more than 40 | 6 |
| Subarachnoid space | until 3 | until 3 |
Watch the video about ultrasound anatomy of the newborn’s brain:
What does neurosonography show in case of illness?
The causes of changes detected during NSG are neuroinfections, intrauterine development disorders, and oncological diseases. Neurosonography reveals only syndromes that are characteristic of diseases of various natures.
NSG helps to identify the following anomalies:
- Hydrocephalus. This condition is characterized by excessive accumulation of fluid in the cranial cavity. Upon examination, you can see dilated and shapeless ventricles and cisterns filled with black (hypoechoic) fluid. The subarachnoid space also changes. It takes on the appearance of a thickened black stripe.
- Holoprosencephaly is the non-division of the forebrain into hemispheres.
- Porencephaly is a developmental defect in which cavities are found in the middle parts of the hemisphere. On neurosonography they appear as oval shadows with clear boundaries.
- Tumors. If the tumor is located in the central regions, then displacement of brain structures may occur. Signs of tumors also include calcifications, hemorrhages and cysts. On the NSG you can see rounded shadows with clear or unclear (depending on the type) contours. The echogenicity of formations can also vary. An inflammatory shaft is often found around the formation, which differs from normal tissues by increased echogenicity (lighter than healthy areas).
- Hemorrhages are another asymptomatic pathology that is reliably determined by NSG. The most common is subarachnoid hemorrhage. This type of pathology is typical for weak, premature children. Hemorrhage is characterized by an increase in the pattern of the brain (furrows), the appearance of light shadows, without clear boundaries (bruises).
- In the case of all these pathologies, neurosonography is the fastest and safest diagnostic method.
- Watch a professional examination of a child with a cyst in the brain:
Contraindications for NSG
This study has no contraindications. It does not require pharmacological preparation or anesthesia. Neurosonography is performed even on children in serious condition. The procedure itself does not affect the baby’s well-being in any way, so the technique is suitable for both screening and targeted diagnostics.
How much does the research cost?
The cost of neurosonography depends on the clinic and the doctor’s qualifications. The average price for large regions of Russia is 2,500 rubles. In Moscow, a study costs from 1,500 to 6,500 rubles. In St. Petersburg and Kaliningrad, the cost varies from 1200 to 3500 rubles. In Novosibirsk, neurosonography will cost 2,000 rubles.
Neurosonography is a new and extremely progressive direction in the diagnosis of intracranial pathologies. At the moment, it is possible to perform NSG even in utero. Such technologies help to start treatment in a timely manner and stop the progression of the disease.
Source: https://rdbkomi.ru/simptomy/nejrosonografiya-golovnogo-mozga-novorozhdennyh-6-povodov-dlya-naznacheniya-rasshifrovka-rezultatov.html
Consequences of the disease
Most often, the disease itself is not fatal. It can lead to other complications that will be much more severe. The most severe consequence is rupture of the wall of the veins or ventricles. It is an irreversible condition that causes instant death or coma.
In some cases, the optic and auditory nerves are damaged and irreversible deafness develops. If the nerve is simply compressed by fluid, then the blindness is temporary. Vision will return when the swelling subsides.
Epilepsy attacks. They occur when the brain is damaged. Their cause and mechanism of development are not exactly clear, but prolonged dilatation of the lateral ventricles can provoke an attack.
Unpleasant but less dangerous complications:
- developmental delays;
- urination and defecation disorders;
- periodic blindness and deafness.
The younger the child with hydrocephalus, the greater his chances of a favorable outcome. Over time, the condition may return to normal.
A mild disease may not be treated, but no one guarantees the absence of complications. Hydrocephalus in infants is common, so a lot of experience has been accumulated in its treatment. A favorable outcome depends on prevention and care, which parents should take care of.