What is gastric neurosis
This problem occurs more often in women, between the ages of 20 and 40. Indigestion or gastroneurosis is perceived as an organ reaction to unfavorable events in a person’s life. It manifests itself in the form of various symptoms, which are often not at all associated with gastrointestinal problems. A concomitant disorder of this disease is irritable bowel syndrome.
Since neuroses have become an integral part of a significant number of people, the presented illness is common. This confirms the popular expression that all diseases are from nerves.
Stomach neurosis: psychological causes, signs, treatment
Gastric neurosis (irritable bowel syndrome, intestinal neurosis, esophageal neurosis) is a psychosomatic disease. In a fast-paced life, it is becoming more common, especially among people over 35 years of age. Every fourth person has experienced irritable bowel syndrome.
The essence of the problem
Gastric neurosis is a functional disorder of the gastrointestinal tract. This is the body's complex response to stress. Manifestations of neurosis intensify with a new psychological shock and are combined with mood swings.
Neurosis of the stomach reviews:
- “The psychotherapist prescribed pills, and after two days I noticed an improvement. Before that, I went to doctors for six months. I suffered just as much from pain,” Maria.
- “They prescribed the easiest sedative – valerian. Everything has passed,” Olga.
- “The psychiatrist told me that long-term stress is to blame. Constant tension and contraction of muscles causes digestive disorders over time,” Lyubov.
- “My neurosis is combined with panic attacks and vegetative-vascular dystonia. I was treated by a gastroenterologist for a year. Now they sent me to a psychotherapist,” Anna.
Analysis of reviews shows that the problem is very common. You can go to doctors for years, but without consulting a psychotherapist, neurosis cannot be cured.
Signs
Stomach neurosis symptoms:
- pain under the ribs, in the stomach, of unknown location;
- burning in the epigastric area;
- feeling of heaviness or chronic hunger, emptiness;
- bloating;
- white coating on the tongue;
- inability to taste and smell food, nausea, vomiting;
- changes in heart rhythm, chest pain, increased breathing;
- cephalgia;
- problems falling asleep and waking up, insomnia;
- heartburn independent of food consumed;
- loud belching of empty air;
- irritation, aggression, fears.
Over time, psychological manifestations expand. The patient is afraid that stomach problems will be found in the wrong place. Because of this, a person tries to leave the house as little as possible. The higher the anxiety and fears, the greater the risk of panic attacks.
It's not just the stomach that suffers due to stress. Functional disorders affect the entire gastrointestinal tract. The esophagus and intestines are often affected. These problems have their manifestations.
Violation Signs
| Esophageal neurosis | Heartburn, pain between the shoulder blades, increased sensitivity to hot, cold, spicy foods. In addition, there are problems with swallowing, a feeling of a lump in the throat, involuntary spasms that impede the passage of food or cause a gag reflex. |
| Intestinal neurosis | Diarrhea or constipation, simultaneous manifestation of diarrhea and constipation, cramping pain in the navel area, rumbling, feeling of fullness in the abdomen, night nausea, morning exacerbation of pain. |
Bottom line
It is better to prevent any problem. Psychological stress always affects the stomach first.
Try to do what you enjoy. Learn to throw out negative emotions, for example, beat a pear or dance. Increase your stress resistance, believe in yourself, take care of yourself.
Causes
Stomach neurosis is treatable. But in order to resist this disorder, it is necessary to become familiar with the possible causes. The root causes of neurosis are divided into two categories. The first includes both organic disorders of the stomach in the form of infectious, inflammatory processes, endocrine disorders, and mental disorders, which are accompanied by disorders of the human nervous system.
The next group includes only psychological changes that were provoked by external or internal reasons. The most common include:
- the presence of intrapersonal conflict;
- inadequate self-esteem, as a result, dissatisfaction with oneself in any manifestations, uncertainty;
- depression;
- dissatisfaction with various types of needs;
- character trait (accentuation);
- lack of sleep and rest.
Prerequisites for nervous dyspepsia
From the name of the disease alone it is clear that problems with the nervous system are to blame, but even doctors cannot name the exact catalyst. What exactly will lead to the development of this pathology, which can develop over several years, is difficult to guess: this does not always require going through a very severe emotional shock or prolonged depression - sometimes a minimal push in the form of a difficult working day or a quarrel with a loved one is enough to trigger process.
- People who have previously encountered gastroenterological diseases, have suffered gastritis or gastroduodenitis, or peptic ulcers are most likely to get nervous dyspepsia.
- A person may be at risk if his diet is disrupted, and there are constant “punches” in the menu (fast food, an abundance of simple carbohydrates, etc.). It is impossible not to mention people with alcohol and nicotine addiction, as well as those with weakened immune systems, who are often exposed to physical overexertion.
Symptoms of manifestation
The complex of symptoms that manifests itself in gastric neurosis depends on the cause of origin. Various clinical manifestations are observed in the digestive system. The most common include:
- vomiting after eating, which is often not accompanied by nausea;
- frequent belching, which occurs due to swallowing air during eating;
- heartburn that does not go away even when following a diet;
- a feeling of discomfort in the stomach (a feeling of emptiness or fullness);
- pain in the stomach, which soon migrates throughout the abdomen;
- changes in eating behavior and tastes;
- increased appetite or lack thereof.
These signs may also be accompanied by weakness with migraines and sleep disturbances. With gastric neurosis, symptoms are often ignored, since they are not always clearly expressed and are not perceived as a signal of a significant problem. Patients mainly seek help for another reason, since over time the condition worsens with manifestations of panic attacks, increased irritability, heart pain, frequent urination and other manifestations.
Complaints and symptoms
Neurosis most often affects women who have reached middle age. All characteristic signs of the disease are conditionally divided into two types:
- intestinal neuroses;
- severe pain in the abdominal area.
The characteristic symptoms of the appearance of neurosis in this case are:
- feeling of constant hunger;
- poor appetite;
- the smell of food causes nausea;
- heartburn;
- nervous colic;
- vomit;
- strong gas formation;
- constipation;
- diarrhea.
The symptoms are very similar to intestinal diseases. They have the same psychosomatic nature. This type of neurosis is distinguished by certain symptoms:
- constant migraines;
- dizziness;
- sudden change in pressure;
- insomnia;
- irritability;
- panic attacks;
- rapid pulse;
- heaviness in the chest;
- heart pain;
- frequent urination.
Therapeutic practice shows that it is quite rare to encounter such symptoms separately from intestinal tract disease. Usually they are of a mixed nature. As evening approaches, the pain intensifies. The pain becomes less as soon as the psycho-emotional state changes for the better.
Neurosis of this type is most often diagnosed in people diagnosed with:
- vascular dystonia;
- excess weight;
- mental disorder.
Most often, gastric neurosis appears in women who have reached the age of 35 years. Doctors divide signs of the disease into two types:
- Intestinal neuroses.
- Painful attacks in the abdomen.
The presence of the disease can be determined by the following symptoms:
- Constant feeling of hunger.
- Food and its smell are disgusting.
- Heartburn.
- Nervous colic.
- Nausea and vomiting.
- Increased gas formation.
- Problems with excretion of feces.
- Severe headaches and migraines.
- Pressure surges.
- Dizziness.
- Feeling of chest tightness.
- Heart pain and rapid pulse.
The most common symptom is vomiting caused by nervousness (aerophagia). This happens because when a person swallows food, he also swallows air. After which the latter begins to circulate between the cardiac section in the stomach and the pharynx, and then comes out with a loud sound and a strong unpleasant odor, which provokes vomiting.
It is difficult not to notice the manifestations when gastric neurosis occurs. The symptoms of the disease are so pronounced that they sometimes cause a lot of inconvenience. People constantly experience discomfort.
Important: doctors recommend seeking help at the first suspicion of gastric neurosis. Its symptoms are easy to recognize, as they are very pronounced.
The main “local” complaints “tied” to the stomach include a perverted feeling of hunger. It may appear as:
- nervous chewing, despite the absence of food in the mouth;
- constant thoughts about food;
- an obsessive desire to eat, despite the fact that you have just eaten a hearty meal.
So is its opposite - the feeling of disgust experienced from the smell of food (and even at one glance at it or at the thought of it).
The consequence of perverted anorectic thinking about food is the following physical anorectic symptoms of gastric neurosis:
- nausea followed by vomiting of eaten food;
- various pains and discomfort in the upper third of the abdomen;
- feeling of heaviness in the pit of the stomach;
- heartburn of varying intensity;
- “rumbling” and bloating in the abdomen;
- nervous colic-spasms.
Thus, with an objective look at the patient, the doctor can only note more or less pronounced asthenia, a pronounced reflex from the root of the tongue (not necessarily), the presence of plaque on the tongue (not always) and pain on palpation in the epigastric region that raises doubts about its reliability.
But the patient’s neuropsychic sphere is represented by a much greater wealth of manifestations:
- dizziness;
- “jumps” in blood pressure;
- constantly “covering” migraines;
- various sleep disorders (inability to fall asleep, waking up in the middle of the night in a state of severe anxiety);
- hyperirritability, leading to panic attacks and phobias;
- palpitations, pain in the heart and a feeling of a “heavy heart”;
- frequent diuresis.
With intestinal neurosis, symptoms can vary significantly. This disease is characterized by a chronic course with periods of exacerbations and remissions.
The pain syndrome can vary in intensity: from mild discomfort to severe cramping pain. Triggered by food intake. The release of gas or bowel movements helps the pain subside.
Associated symptoms include:
- feeling of incomplete bowel movement;
- feeling of a lump in the throat when swallowing;
- migraine-like headaches;
- urination disorders (frequent urge to urinate, feeling of a full bladder, feeling of incomplete emptying of the bladder, etc.);
- heartburn, belching;
- pain in the lumbar region.
Intestinal neurosis is characterized by a number of features:
- Long history of the disease.
- Variable nature of symptoms.
- A clear connection between psycho-emotional factors and intestinal symptoms.
- No symptoms during sleep at night.
Most often, people with dyspepsia complain of a burning sensation, a feeling of emptiness, fullness and pain in the stomach. In most cases, such sensations occur after eating food. Discomfort in the abdominal area is not the only symptom that accompanies gastrointestinal neurosis. Signs of the disease also include:
- rumbling in the stomach;
- nausea (regardless of food intake);
- flatulence (bloating);
- loss of appetite;
- colic;
- food rejection;
- loud belching;
- heartburn;
- diarrhea;
- constipation;
- migrating pain in the abdominal and iliac space, etc.
In addition to symptoms that indicate the source of the problem, the patient may experience other signs of dyspepsia. These include:
- headache;
- sleep disorders;
- sense of anxiety;
- increased excitability;
- cardiopalmus;
- increased sweating (hyperhidrosis);
- irritability;
- apathy, etc.
Forms of gastric neurosis
The most common signs of gastric neurosis allow us to distinguish several of its varieties:
- aerophagia - the disease manifests itself through frequent, often loud belching. The patient is also bothered by flatulence;
- stool disorder - frequent diarrhea, mainly in the morning. Changes to constipation, accompanied by poor appetite;
- loss of appetite - a dangerous manifestation of this type is anorexia or bulimia, which leads to vomiting, dehydration, and, in extreme cases, death.
Diagnostics
Correct diagnosis increases the likelihood of a quick recovery for the patient. It is worth carrying out a set of diagnostic measures to separate gastric neurosis from pancreatitis with ulcers, gastritis and other gastrointestinal diseases.
- A general blood test can detect signs of inflammation and anemia, and a biochemical test will indicate existing metabolic disorders.
- Urinalysis is also aimed at detecting inflammation and metabolic disorders.
- The coprogram is used to analyze stool for the presence of blood and undigested fibers. Cultures for intestinal infections are also carried out.
- Ultrasound examination is aimed at studying the gastrointestinal tract and its possible pathologies.
- Colonoscopy is performed if pathology in the colon is suspected.
- Sigmoidoscopy allows you to examine the sigmoid colon for problems.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy examines the stomach for the presence of ulcers, necrosis, and signs of gastritis.
- Magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography are performed to detect organic abnormalities in the brain.
In addition, consultation with a gastroenterologist, neurologist, psychotherapist, or psychiatrist is necessary.
How to treat
After conducting a diagnostic complex and making an accurate diagnosis, therapy is prescribed. It includes not only classical drug treatment, but also physiotherapy, the use of alternative medicine methods and, of course, psychotherapy. Also an important component of the treatment of gastric neurosis is diet.
Medications are aimed at eliminating signs of indigestion, bloating, heartburn and other manifestations. Relief from spasms occurs by taking No-shpa. Simetic with Espumisan helps with flatulence. You can cope with diarrhea with Loperamide.
Irritable bowel syndrome and gastric neurosis require taking enzymes. Creon is often used for this. Intestinal motor abilities are restored when using Lactulose.
In addition to the medications presented, doctors prescribe sedatives like Persen and valerian tincture. If necessary, specialists prescribe a course of antidepressants. Also, treatment cannot be done without taking vitamins.
Prevention
Preventive measures involve following the following recommendations:
- avoid stressful situations;
- monitor your diet;
- to walk outside;
- communicate with people, do not withdraw into yourself;
- work through psychological problems immediately, without waiting until they develop into neurosis or more serious disorders;
- To exclude the possibility of organic damage, it is worth undergoing a medical examination annually.
Stomach neurosis is eliminated using an integrated approach. To avoid complications, you should pay attention to your own feelings in time, and also consult a doctor in a timely manner.
Gastroneurosis, or stomach neurosis, is often confused with ulcers or other diseases in the abdominal area. Having characteristic symptoms similar to gastroenterological pathologies, for example, burning, abdominal pain, nausea and vomiting, gastric neurosis is considered a psychosomatic disorder of the digestive system. As a rule, pain symptoms bother people with nervous disorders or living in a state of constant stress.
Features of the course in children
Pain in the abdominal area of neurotic origin occurs among children with a frequency of 15-30% in the general population. When it comes to psychosomatic pathology in a child, it is important to find out the reasons, which are:
- Situational (stressful effects).
- Personal (change in the type of psychological response).
- Psychopathological (genetically determined changes in the formation of emotions).
- Cerebral (caused by organic and traumatic lesions of the brain substance).
- Somatic (defect of regulatory functions and executive mechanisms involved in the control of visceral organs).
Manifestations of neurotic disorders in children, in addition to traditional symptoms (vomiting, nausea, bloating), include hiccups, loss of appetite, and rumination (repeated reflux of food from the esophagus into the oral cavity). In 52% of children, the typical clinical picture of gastrointestinal neurosis is supplemented by symptoms such as nail biting, hair pulling, body swaying, rhythmic head tilting, and thumb sucking.
Nervous pain in the stomach - causes of concern
Low resistance to stress, emotional overstrain and other psychosomatic factors can cause burdensome pain in the digestive system. Gastrointestinal neurosis is the result of a nervous system reaction to prolonged, intense stress, chronic anxiety or depression, or traumatic events or sensations. Nervous stomach upset is extremely difficult to diagnose because laboratory and imaging tests reveal no changes. Atypical symptomatic signs of nervous stomach are often confused with other abdominal diseases.
Symptoms of gastric neurosis
Typically, nervous indigestion occurs in people who are afraid of an important event or challenge. Symptoms of neurosis of the digestive tract are unpleasant and have typical complaints:
- abdominal pain;
- nausea and vomiting;
- bloating;
- heartburn and belching;
- choking and difficulty swallowing.
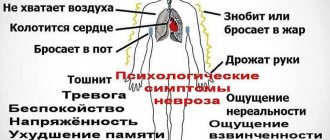
Often, nervous stomach pain is accompanied by diarrhea and flatulence. In addition, a stressful situation can cause constipation. Even with little food consumption, a person feels a feeling of oversaturation in the stomach. Symptoms of gastric neurosis are complemented by other patient complaints. Problems with sleep arise, the constant feeling of anxiety does not disappear and the feeling of emotional overstrain does not go away. In addition, patients complain of typical neurotic symptoms, such as palpitations, a feeling of weakness, increased sweating, tightness in the chest, trembling of the hands and the whole body.
The symptoms of these diseases are somewhat similar. Since stomach ulcers are more common, when there is pain in the abdomen, first of all, a suspicion of this disease arises. Naturally, taking into account the psychosomatic characteristics of neurosis, peptic ulcer disease has a completely different condition. The disease is an actual disorder of the digestive system, characterized by defects in the mucous membrane of the stomach or intestines.
Burning and severe pain in the abdomen may be accompanied by nausea and heartburn. Characteristic is increased discomfort immediately after eating. Peptic ulcer disease, like gastric neurosis, can be the result of stress, which stimulates the production of acids that destroy the epithelium in the digestive system. Additionally, gastrointestinal ulcers can be caused by Helicobacter pylori infection.
Clinical manifestations
Symptoms of neurosis of the intestines, stomach, and other organs of the gastrointestinal tract are characterized by polymorphism, which implies the need for a thorough diagnosis and an individual approach to treatment. The pathology is characterized by the stability and diversity of gastrointestinal disorders in the absence of a morphological basis for their development. Neurotic manifestations play an important role in the clinical picture:
- Asthenic syndrome (increased fatigue, general weakness).
- Decreased ability to work.
- Deterioration of cognitive abilities (memory, mental activity).
- Obsessive states, hysterical disorders.
The main symptom of neurosis of the stomach and intestines is algia (unpleasant, painful, often painful sensations that are not associated with objective reasons). The causes and signs of algia cannot be determined using instrumental examination, which complicates the treatment of neurosis, despite the obvious symptoms of gastric dysfunction:
- Heartburn, belching.
- Feeling of fullness, fullness.
- Nausea, attacks of vomiting.
Symptoms of gastric neuralgia are usually combined with signs of an anxiety disorder. If the clinical picture is dominated by symptoms of a functional intestinal disorder, the pathology is often combined with cancerophobia (an irrational fear of getting cancer). Abdominal pain with intestinal neurosis is complemented by algia, diffuse flatulence, and increased peristalsis (wave-like contraction of the walls) of the intestine.
With neurasthenia, manifestations of mental disorders usually increase. Dysmorphophobia often develops (the patient's pathological belief that he has a disease or defect). Such patients are convinced that they are unable to retain gases in the intestines and are afraid of emitting an odor that is unpleasant to others. It is typical for patients to demonstrate problems in the digestive system.
Some vividly and colorfully describe the symptoms, ask the doctor to find out the cause of the discomfort and make a diagnosis. Others strive to exclude serious diseases, ask to schedule repeat examinations, and strictly adhere to a strict diet, deliberately excluding unhealthy foods (fatty, sweet, spicy, fast food).
More often, the pathology is accompanied by viscero-vegetative seizures, which are caused by disruption of the activity of cortical structures. Viscero-autonomic disorders affect the organs of the gastrointestinal tract. Main manifestations: a feeling of discomfort, tightness, burning, emptiness, pain in the abdominal cavity or epigastric zone, less often in the mouth and throat.
The occurrence of such sensations correlates with the appearance of other symptoms of neurosis of the esophagus and stomach - nausea, rumbling in the gastrointestinal tract, increased salivation, flatulence. In some cases, uncontrolled swallowing and chewing movements are observed. The sensations arising in the stomach area spread higher, radiating to the neck and head, which is associated with transmission along the ascending pathways of nervous excitation.
Darkness and subsequent loss of consciousness often occur. Functional dyspepsia develops due to nervousness (discomfort in the upper abdominal segment, which is recurrent). Patients complain of delayed digestion of food, increased gas formation, and a feeling of early satiety while eating.
In parallel, effects such as belching, nausea, stool upset (constipation, diarrhea), pain in the epigastric region and abdominal cavity appear. Most often, a breakdown in the regulatory activity of the autonomic system is manifested by syndromes - irritable stomach and irritable bowel. The syndrome, manifested by stomach irritation, is characterized by:
- Psychogenic halitosis (the patient’s false belief about the unpleasant odor he is spreading, while excluding all probable reasons for such conclusions).
- Dysgeusia (taste disorder).
- Glossodynia (tongue sensitivity disorder).
- Feeling of a lump in the throat area.
Halitosis often turns into an obsessive condition. Patients concentrate, become fixated on false sensations, and avoid contact with others. With dysgeusia, patients feel a foreign taste in the mouth, often bitterness, not associated with food intake. Nausea is accompanied by a feeling of dry mouth or excessive salivation. Glossodynia is manifested by a burning sensation, tingling sensation in the tongue area and nearby areas.
There are types of vomiting of neurotic origin - hysterical and habitual. In the first case, gagging correlates with psycho-emotional tension, stress, and accompanies emotions of a certain type. Habitual vomiting can occur in any environment, regardless of the current emotional state. Vomiting attacks often resolve easily without a preceding prolonged feeling of nausea.
Autonomic components (excessive salivation, increased sweating, blanching of the skin) are weakly expressed or completely absent. Repeated vomiting attacks can lead to dehydration (dehydration), hypokalemia (decreased potassium concentration in the blood), and deficiency of other substances. Psychogenic esophagospasm (spastic contraction of the smooth muscles of the esophagus against the background of dyskinesia, disruption of the flow of esophageal contents) is combined with persistent dysphagia (impaired swallowing function).
Liquid food moves through the esophagus more difficult than solid food. Typically, onset esophagospasm occurs as a result of severe emotional shock during the period of eating. Then every meal is accompanied by esophagospasm. Spasmodic contraction of the esophageal muscles can occur regardless of food intake. Without a relationship with food, the disorder manifests itself as pain, a feeling of compression, tension in the chest area.
In this case, differential diagnosis for angina is necessary. Provoking factors for the development of esophagospasm are fear and anxiety associated with the process of eating. The disorders correlate with motor and sensory dysfunction of the esophagus. In case of dysphagia of neurotic origin, differential diagnosis is carried out in relation to iron deficiency (sideropenic syndrome).
The syndrome, manifested by intestinal irritation, is characterized by dyskinesia (impaired flow of contents) of the intestine, pain in the intestinal area of a neurotic origin of a burning, bursting, cramping nature. Painful sensations become more intense against the background of emotional stress and stress. Symptoms of intestinal crises:
- Sharp, cutting pain in the abdominal area.
- Flatulence (bloating, excessive accumulation of gases inside the intestines).
- Rumbling in the stomach.
- Feeling of need to pass gas, urge to defecate.
Neurotic disorders that affect the functioning of the gastrointestinal tract often cause chronic constipation or psychogenic diarrhea. Imperative (unobjectionable, commanding) urges to defecate often occur in inappropriate conditions (outside the home, under uncomfortable circumstances), which negatively affects the psychological state and further aggravates the severity of the pathology.
An eating disorder is a component of the development of neurotic conditions. For example, chronic overeating as a kind of compensation for a lack of positive emotions leads to the development of obesity. Refusal to eat according to the type of anorexia neurotic is accompanied by physical and nervous exhaustion, weight loss, often life-threatening.
Diagnosis and treatment of gastric neurosis
The diagnosis of a nervous stomach requires the exclusion of other diseases of the digestive system that present similar symptoms, such as gastric reflux, gastritis, peptic ulcer. Instrumental diagnosis involves performing colonoscopy and gastroscopy. Only after laboratory tests can one confidently recognize gastric neurosis, excluding other diseases of the digestive system.
Treatment of gastric neurosis involves taking sedatives and anxiolytics, including, for example, herbal medicines. Since the treatment of gastric neurosis is multifaceted, psychotherapy may be required. The patient needs to eliminate the stress factor. In this case, a relaxation technique is prescribed, which gives excellent results in treating the disease. The suffering person needs to change their lifestyle and learn to cope with stress.
The best solution is to sign up for yoga classes or relaxation techniques courses. Properly selected relaxation and rest in combination with yoga will improve the functioning of the body and alleviate the unpleasant symptoms of gastric neurosis. If the disease is the result of past traumatic events, then you will have to seek help from a psychiatrist or psychologist. Also, an integrated approach to the treatment of nervous indigestion requires not only eliminating the cause of the disease, but also changing eating habits. Herbal and aromatherapy will help relieve the painful symptoms of the disease.
In addition to the therapeutic measures prescribed by specialists, home therapy is very effective. First of all, you should pay attention to your lifestyle. It is no secret that alcohol, smoking and taking certain medications increase discomfort and symptoms of neurosis. Therefore, they should be replaced with herbs with a calming and relaxing effect. For people suffering from gastric neurosis, herbal treatment can be very beneficial.
Soothing medicinal plants, for example, lemon, linden, lavender, valerian, ginseng, will help solve the problem of indigestion due to nervousness. In addition, herbal treatments are recommended to relieve the symptoms of the disease, that is, abdominal pain and cramps, nausea, heartburn and so on. Chamomile and mint have relaxing properties. Hops stimulate digestion and reduce smooth muscle tone.
Since pharmacological drugs cannot be taken for more than 12 weeks, the patient should learn to relieve stress on their own. Abdominal massage can help with this, as it not only improves your mood, but also gives you a feeling of relief. To combat stress, a bath with the addition of medicinal herbs or essential oils is also recommended. This relaxing activity can be accompanied by relaxing music. Remember that all forms of movement improve your mood and reduce stress. Therefore, moderate physical activity is necessary.
Gastric neurosis is not a life-threatening condition, but it makes it very difficult. The symptoms of the disease are unpleasant and tiresome. Without treatment, the disease can lead to social anxiety disorder and depression, so gastric neurosis should not be underestimated. What is needed is an integrated approach to treatment, including a review of nutrition.
Stomach neurosis - what is it, causes, symptoms, treatment, prevention
A feature of the gastrointestinal tract is the location of a large number of nerve endings in it.
Severe stress, depression, fear through the release of stress hormones often leads to severe irritation and malfunction of the entire digestive system. It is impossible to control the emerging gastroneurosis through willpower. Sometimes it is accompanied by irritable bowel syndrome. The disorder most often occurs in children and women under 40 years of age before important or fear-inducing events, immediately after stress, or has a delayed effect. In the latter case, disturbing moments could have happened in the past or accumulated in small portions gradually. However, at some point in time, under the influence of disturbing events, they managed to manifest themselves.
Pathology in its external manifestations does not differ from diseases caused by organic causes. However, the diagnostics carried out do not allow us to see any anatomical disorders.
Types of neurosis
The leading symptoms make it possible to distinguish several types of gastric neurosis. The pathology can manifest itself as severe heartburn. It happens all the time. It cannot be relieved with medications or diet.
The disorder is accompanied by aerophagia. A distinctive feature of this type of gastroneurosis is constant belching. She comes out making loud noises and screaming. Occurs due to involuntary swallowing of air. Additionally, a person is bothered by flatulence.
Intestinal neurosis is manifested by stool disorders. Often accompanied by diarrhea. Without any objective reason, loose stools appear up to four times a day. Occurs mainly in the morning.
On the contrary, when acidity decreases, constipation, poor appetite, and frequent abdominal pain appear. This disorder manifests itself in different ways. Sometimes constipation gives way to diarrhea.
In other cases, stool is regular, but even after defecation there is a feeling that there is still feces in the intestines.
Gastroneurosis also manifests itself as appetite disturbances. With anorexia, a person experiences an aversion to all foods, even his favorite ones. Prolonged neurosis of this type leads to death.
Sometimes the disorder is characterized by increased appetite. The patient experiences constant hunger. He eats a lot, but the food masses immediately come out with vomiting. It occurs involuntarily and is not accompanied by pain or nausea.
Causes
Intestinal neurosis often manifests itself in vulnerable people, weakened by illness, fatigue and anxiety. However, it often attacks a completely healthy person who is accustomed to sending his worries and worries into the depths of his consciousness.
The mechanism of occurrence of the pathology is associated with increased release of cortisol and adrenaline in situations that are perceived as stressful or actually are so.
Stress hormones affect the vagus nerve, under the influence of which gastric juice is produced in small quantities or, conversely, too much.
This leads to impaired digestion of food masses, the appearance of ulcers, and stool upset.
The causes of neurosis can be divided into several groups:
- Mental. Neurosis is caused by irritability, psychological trauma, increased anxiety, internal conflicts, and constant worry. Hyper-responsibility and constant dissatisfaction with oneself increases the likelihood of a violation.
- Eating disorder. This group of reasons includes frequent consumption of spicy, fatty foods, overeating or, conversely, malnutrition, and lack of fluid. The appearance of neurotic disorders is promoted by infrequent, rich meals, and eating too cold or hot food. In adults, this is alcohol consumption.
- Gastrointestinal pathologies. Neurosis is caused by intoxication, infectious and inflammatory diseases, and endocrine diseases.
- Voltage. Pathology is caused by constant stress, chronic fatigue, frantic pace of life, mental and physical fatigue, and lack of sleep.
Symptoms of thermoneurosis in adults and methods of treating psychological problems
Symptoms
Manifestations of neurosis of the stomach and intestines are quite diverse. They are associated mainly with discomfort, pain in the gastrointestinal tract, and its dysfunction. Rumbling, nausea, and belching appear.
The feeling that the stomach is full does not disappear, the stomach is bursting, bloated, and colitis appears. Often accompanied by loss of appetite. A person constantly wants to eat or, conversely, experiences an aversion to food.
In many cases, repeated diarrhea occurs, in others the patient complains of constipation.
Another group of symptoms is associated with autonomic disorders. These are tachycardia, frequent urge to urinate, headache, pressure surges. The patient complains of sweating and cold extremities. In some cases, the temperature rises.
The third group of symptoms includes psychological signs. Noteworthy are anxiety, irritability, bad mood, hypochondria, restlessness. A person suffers from sleep disorders and fears.
Most symptoms appear only during the day. At night they disappear.
Diagnostics
The main goal of all diagnostic measures is to determine the correct diagnosis. It is important to differentiate gastric neurosis and irritable bowel syndrome from gastritis, ulcers, pancreatitis, and other pathologies of the gastrointestinal tract.
The patient is prescribed:
- Blood tests. General allows you to detect signs of inflammation and anemia. Biochemistry indicates metabolic disorders.
- Urine examination. Detects metabolic disorders and inflammatory processes.
- Stool analysis. They diagnose the presence of hidden blood and remains of undigested dietary fiber. Cultures are carried out to detect pathogens of intestinal infections.
- Ultrasound of internal organs. The study allows you to see the structural features of the gastrointestinal tract and its pathology.
- Colonoscopy. Detects pathologies of the large intestine.
- Sigmoidoscopy. Prescribed to exclude pathologies of the sigmoid and rectum.
- Esophagogastroduodenoscopy. Eliminates tumor processes, allows you to see ulcers, manifestations of gastritis, tissue necrosis.
- MRI, CT. Studies are carried out to obtain a clear picture of the anatomical changes.
Diagnostic measures include consultations with a neurologist, psychiatrist and gastroenterologist.
Treatment
The diagnostic results and symptoms of gastric neurosis determine the treatment and its tactics. Usually complex therapy is carried out, based on the relief of gastrosymptoms and normalization of the psycho-emotional background. Medicines, psychotherapy methods, physiotherapy, and folk remedies are used Diet plays an important role.
Medications
To relieve spasms and stomach pain, No-shpu is prescribed. Espumisan and Simethicone help to cope with flatulence and bloating. With diarrhea - Loperamide.
If there are symptoms of intestinal and stomach neurosis, treatment includes enzymes, for example, Creon. Lactulose improves intestinal motor functions.
Drug treatment includes sedatives. This is valerian tincture, Persen. They are treated with antidepressants – Grandaxin. Vitamins are prescribed.
Psychotherapy
An important part of the treatment is the use of psychotherapeutic methods. They help to understand the cause of neuroses and reduce anxiety.
One of the main purposes of their use is to teach a person to cope with stressful situations, to establish barriers between oneself and traumatic circumstances.
Physiotherapy
For stomach neurosis, periodic massages, Charcot showers, baths with essential oils or herbal decoctions are recommended. Ultraphonophoresis and electrotherapy are performed.
Folk remedies
Treatment with folk remedies is aimed at reducing mental stress, relieving anxiety, and restoring normal sleep. It is recommended to use them as prescribed by a doctor:
- A bath of yarrow (1 tbsp), wormwood (1 tsp), lemon balm (1 tbsp) and mint (3 tsp) helps to relax. The broth is boiled for half an hour, filtered and mixed with water. It is recommended to take such a bath every day.
- You can get the necessary vitamins by eating, drinking vegetable juices or rosehip tincture.
- Oregano tea will help you calm down. Treat depression with a decoction of St. John's wort.
Forecast
It is believed that the treatment suppresses the symptoms of gastroneurosis and effectively prevents the onset of the disorder and the deterioration of the condition of patients. It is enough to follow the recommendations of a psychologist or psychotherapist. Hearing this, many patients are ready to refuse treatment.
It is worth remembering, however, that in advanced cases and if the patient does not want to be treated or engage in prevention, neurotic manifestations intensify.
Prevention
The occurrence of any pain in the gastrointestinal tract is the basis for a thorough diagnosis and exclusion of organic lesions. A set of preventive measures aimed at preventing the development of gastric neurosis includes an active lifestyle, proper nutrition, and walking.
It is better to try to work through anxious thoughts, fears, and anxiety immediately on your own or with the help of a psychologist. You shouldn’t just forget about them, you should try to understand their causes, consequences and ways to prevent them from appearing again.
Conclusion
Stomach neurosis is manifested by stool disturbances, vomiting, and severe belching. To determine it, diagnostic measures are required. The prognosis is favorable, but requires corrective medicinal and psychotherapeutic measures. In some cases, it is enough to use folk remedies and diet.
Source: https://neuromed.online/nevroz-zheludka/
Stomach neurosis - diet
First of all, you should review your diet, which should be regular - 5 times a day every 2-3 hours, and easily digestible. In this case, portions should not exceed a total weight of 150-200 grams. Changing your diet during periods of emotional stress is especially important. The patient should not overeat. Fried food should be replaced with boiled food. It is necessary to reduce the amount of fats and sugars that cause bloating, as well as avoid highly processed foods.
The diet should be enriched with fiber, which is abundant in vegetables and fruits. The patient needs to drink at least two liters of water a day, replacing alcoholic and carbonated drinks with regular mineral water. People with stomach and intestinal problems, among others, should limit their intake of stimulants. Experts recommend completely giving up coffee and strong tea. Since the source of the problem lies in the nervous system and not the digestive system, diet will mainly affect the symptoms and not the cause. Therefore, it is worth it to alleviate the suffering of the patient. Take care of yourself and always be healthy!
Let's talk about a disease that is difficult to diagnose and self-diagnosis - gastric neurosis, or gastroneurosis. It is difficult to distinguish it from ordinary diseases of the digestive system, however, the principle of treating gastric neurosis has a fundamental difference - cure is possible only through correction of the psychological state.
Stomach neurosis symptoms and treatment + 10 valuable tips – On the nerves
The modern world brings people more and more stress, which ultimately affects the performance of the body. The situation where psychological factors influence the occurrence of physiological disorders has become quite commonplace these days. Nerve endings are located in all tissues: muscle, connective, epithelial.
And since there are a lot of them in the gastrointestinal tract system, it is extremely sensitive to the influence of external and internal factors. Therefore, various forms of the disease arise here, including neurosis of the stomach and intestines.
To understand how gastric neurosis manifests itself, let’s move on to an in-depth consideration of the topic “Gastric neurosis, symptoms and treatment.”
Symptoms of gastric neurosis
Psychosomatic phenomena usually do not lead to severe stomach upsets. However, pain in the stomach during neurosis is felt extremely realistically, which significantly reduces the quality of life. The pain varies from very mild to extremely severe, so it is difficult to believe in its psychological source.
But it is worth remembering that a prolonged depressed state still leads to a general decrease in immunity, and this in turn, for example, can easily provoke the development of infectious diseases. Malfunctions in the nervous system manifest themselves in a wide variety of symptoms.
It all depends on the initial makeup of the individual’s psyche and the depth of its single shock or monotonous loosening.
However, gastric neurosis has specific signs:
- Increased or decreased appetite
- Nausea, which often precedes vomiting.
- Diarrhea and constipation
- Gas formation, leading to bloating, flatulence and colic.
- Heaviness in the stomach and heartburn.
- Compression in the esophagus, which in the upper part is sometimes perceived as swelling or enlargement of the thyroid gland.
- Aerophagia is frequent belching caused by swallowing air during meals.
- Significant change in food preferences.
In this topic, “Gastric neurosis, symptoms and treatment,” it is important to pay attention to the presence of signs of the disease, which seem to be mutually exclusive. Constipation, quickly replaced by diarrhea, lack of appetite alternating with its increase. Or the symptoms are vague. For example, pain without localization in the stomach or outside it without clear reasons.
Stomach neurosis sometimes manifests itself as back pain. During palpation, pain points are sometimes not detected at all. Or, as it seemed to the patient, a specific pain point upon examination is not such at all.
Since gastric neurosis is often characterized by a deterioration in general well-being, it is necessary to pay attention to accompanying symptoms that require separate treatment, such as weakness and drowsiness, with poor sleep at night with sudden abrupt awakenings, headaches, temperature within 37.5 and frequent urination, as well as involuntary muscle contractions leading to tremors (shaking) and tics. The spectrum of such manifestations can include all external signs that are not related to the structure of the body (organs, tissues, bones) and manifest themselves in a decrease in its performance.
The likelihood of gastric neurosis in different categories of the population
How dangerous the appearance of such an ailment as gastric neurosis, which will require further treatment, can be understood by considering neurosis in the general sense of the word.
This disease is a neurotic disorder that manifests itself in a person regardless of gender, age, and social status. Neurosis occurs even in newborn children who experience the shock of being born.
At such a moment, the child needs to be surrounded with care so that he feels safe. However, there are specific risk groups.
The first includes persons who are at a certain stage of natural biological development (puberty, menopause) or persons susceptible to the influence of various diseases (vegetative-vascular dystonia). The second group contains people whose pathological state of mind is caused only by external oppressive circumstances or internal unresolved conflicts.
IMPORTANT: This disease negatively affects the entire body, so it is worth considering your well-being comprehensively, excluding other manifestations of neurosis, including heart neurosis, since its consequences are very negative.
Diagnosis and methods of treatment of gastric neurosis.
In order to have a clear understanding of the issue raised in the article “Gastric neurosis, symptoms and treatment,” it is necessary to understand the process of diagnosing the disease.
Unfortunately, the process of diagnosing Gastric Neurosis involves more than just an initial appointment with one doctor. In this case, you will have to follow the method of exclusion and, by visiting a therapist or immediately a highly specialized gastroenterologist, rule out all organic causes of the disease. First of all, these are gastritis, peptic ulcers, pereduadenitis, colitis, and infectious diseases.
In the process of making a diagnosis of Neurosis, possible stomach cancer will also be checked. If, after taking tests and undergoing other examinations, the doctor concludes that there are no physiological disorders in the functioning of the stomach, then the question is raised about the psychological causes of the existing pain. After this, a visit to a neurologist or psychiatrist is recommended.
It is worth noting that much depends on the qualifications of the first doctor visited in this chain and his attentiveness to patients. Stomach neurosis, as well as intestinal neurosis and their initial causes, as we found out earlier, still lead to a real disruption in the functioning of the organ, which will be revealed after the examination.
Therefore, in these circumstances, the gastroenterologist needs to find out what the nature of the problems found is. Whether it is exclusively organic or combined with personal factors. Otherwise, treatment will only be prescribed, in which the prescribed medicine will not have an effect on the stomach neurosis, or it will only smooth out the symptoms and solve the problems temporarily.
Therefore, you should always listen to your feelings and consider the problem from a variety of perspectives.
Perhaps the most difficult case for the diagnosis of gastric neurosis is a long-term depressed state of mind, in which the symptoms manifest themselves quite clearly, and the treatment is protracted.
Causes of neurosis:
- Constantly being in a tense environment
- Lack of fulfillment in any area
- Intrapersonal conflicts
- Unsatisfied basic needs
- Low self-esteem
- Hypochondria or suspiciousness
- Tendency to hysteria or apathy
When concentrating on a problem for a long time, obsessive states occur.
As a result, such psychosomatic cases in advanced cases work like a vicious circle, since the emotional background of the patient worsens due to his thoughts about a possible terrible disease.
Taking the form of obsessive states, experiences provoke the emergence of new physiological manifestations of the disease. In this case, the pain may intensify or appear in other areas.
When gastric neurosis is diagnosed, medication is prescribed with support from physiotherapeutic procedures, folk remedies and optimization of lifestyle. As for medications, sedatives with a mild effect that work with the nervous system are prescribed. For example, phenibut and phenazepam help with stomach neurosis.
Rudotel is also prescribed for stomach neuroses. In addition, medications are prescribed to improve gastric activity, such as Motilium, Imodium, etc. As for physiotherapy, it will help fight muscle contractions that are characteristic of a depressed state of the nervous system.
Such contractions lead to compression of the nerve endings and further to painful sensations. In this case, procedures such as exercise therapy, ultraphonophoresis, electrotherapy, darsonvalization, and magnetic laser therapy are indicated. In addition, medications can be prescribed that are suitable specifically for your case of neurosis, solving specific individual problems.
For example, the problem of high acidity resulting from neurosis.
In addition, when a person is faced with the question voiced here, “Stomach neurosis, symptoms and treatment,” then a desire arises (including) to solve it independently.
Stomach neurosis and treatment with folk remedies is a separate point worthy of attention. Such treatment methods are aimed at working with the nervous system and relieving inflammation. A RECOMMENDATION in this case would be the use of tea and decoctions.
Soothing teas with chamomile, lemon balm, lavender, as well as herbal infusions of valerian, motherwort, and oak bark. To eliminate pain, you can use a decoction of flax seeds, which envelops the mucous membrane. In addition, mint and angelica roots have antiseptic and bactericidal properties.
And marshmallow root and cudweed herb help relieve symptoms of stomach fullness.
TOP 10 tips on how to get rid of stomach neurosis.
1. Naturally, first you need to consult a doctor to clarify the diagnosis, since there may be various reasons behind your health condition. When a diagnosis of Gastric Neurosis is made, all the symptoms characteristic of this particular disease will be listed and treatment will be prescribed.
2.Follow your doctors' instructions and remember that treating gastric neurosis can be a long process. Be patient and tune in to a positive outcome, purposefully protecting yourself from stress.
3. Introduce a work regime that would minimize emotional and physical stress. At the same time, the manifestation of activity is not excluded if it is aimed at normalizing the functioning of the nervous system. For example, visiting the pool.
4. Provide yourself with passive rest, including a sufficient number of hours of sleep.
5.As a calming procedure, you can take relaxing baths at night with pine infusions, valerian root, motherwort, tansy, and St. John's wort. Or visit, for example, a massage room from time to time.
6. It is imperative to follow a diet, which will also be useful with concomitant reduced immunity. In addition, if there are real malfunctions in the gastrointestinal tract, a specific diet for gastric neurosis should be developed. The diet will take the load off the stomach and help avoid vomiting and other reactions.
7. For the general strengthening of all life support systems, you should take useful microelements and vitamin complexes, including in the form of vegetables and fruits.
8. Work with such personality traits as suspiciousness and fixation on a certain issue, as well as perfectionism, which are often characteristic of people suffering from gastric neurosis. By redirecting them in the right direction for self-improvement, you can achieve personal growth.
9. Apply all the listed measures comprehensively, and not separately and one by one.
10.To avoid a relapse, after completing treatment, follow all prescribed regimens, continuing to protect yourself from stress as much as possible.
Conclusion
Having considered the topic “Stomach neurosis, symptoms and treatment,” naturally, doubt arises about the possibility of completely eliminating stress from life. This is extremely difficult to achieve. However, it is worth remembering that any negative situation can provoke gastric neurosis, which will result in another treatment.
RECOMMENDATION: It is very important to learn to switch to positive emotions. Listen to your subconscious dissatisfaction and promptly change unsatisfactory life circumstances. In this case, it is necessary, without fanaticism, but in a timely manner, to listen to the reactions of the body.
If you again feel like you have a stomach ache, then perhaps this is a newly emerging neurosis. But in this situation, it is necessary to calmly analyze the situation, remembering what neurosis of the stomach and intestines is and their symptoms.
Perhaps, by conducting an internal dialogue, your pain will disappear.
Source: https://na-nervah.ru/nevroz/nevroz-zheludka-simptomy-i-lechenie
What it is?
Stomach neurosis is a psychosomatic disease that occurs against the background of neurasthenic, hysterical or psychasthenic neuroses. Refers to autonomic neuroses. Includes symptoms that are usually mistaken for signs of gastrointestinal diseases. However, it differs from somatic diseases in the presence of concomitant nervous disorders.
It is quite difficult to distinguish gastric neurosis from diseases caused by organic causes. A comprehensive examination is required, including gastroenterological and psychological diagnostics.
Symptoms of gastric neurosis
They are divided into two groups - at the level of body and soul. Physiological symptoms include the classic list:
Psychologists say that in the case of three or more symptoms in a patient, most likely gastric neurosis; the symptoms and treatment in this case are different from ordinary diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, since psychological and vegetative manifestations will be present:
- poor sleep – insomnia, frequent awakenings at night;
- general anxiety and restlessness;
- fixation, obsessive states;
- hypochondria (a meticulous search for illnesses and confidence in one’s ill health);
- irritability, causeless aggression;
- headache and dizziness;
- weakness;
- unstable blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- frequent urination;
- pain and heaviness behind the sternum;
- migraine.
The difficulty of diagnosis lies in the fact that psychological manifestations can be present for a long time, and only after months and years does intestinal neurosis appear - the symptoms are difficult to connect together, so the patient can treat gastrointestinal diseases for a long time and unsuccessfully, without knowing about the psychological causes of his condition.
Neurosis of the intestines, stomach (gastrointestinal tract): symptoms, treatment – Harmony within
Let's talk about a disease that is difficult to diagnose and self-diagnosis - gastric neurosis, or gastroneurosis. It is difficult to distinguish it from ordinary diseases of the digestive system, however, the principle of treating gastric neurosis has a fundamental difference - cure is possible only through correction of the psychological state.
What it is?
Stomach neurosis is a psychosomatic disease that occurs against the background of neurasthenic, hysterical or psychasthenic neuroses. Refers to autonomic neuroses. Includes symptoms that are usually mistaken for signs of gastrointestinal diseases. However, it differs from somatic diseases in the presence of concomitant nervous disorders.
It is quite difficult to distinguish gastric neurosis from diseases caused by organic causes. A comprehensive examination is required, including gastroenterological and psychological diagnostics.
Symptoms of gastric neurosis
They are divided into two groups - at the level of body and soul. Physiological symptoms include the classic list:
- nausea and vomiting immediately after eating;
- chest pain;
- frequent loose stools;
- flatulence;
- heartburn;
- lack of appetite;
- hunger that occurs soon after eating;
- belching;
- pain in the intestines (colic);
- constipation;
- feeling of fullness in the intestines;
- rumbling;
- constant feeling of a “full stomach”;
- pain radiating to other parts of the body;
- aversion to food.
Psychologists say that in the case of three or more symptoms in a patient, most likely gastric neurosis; the symptoms and treatment in this case are different from ordinary diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, since psychological and vegetative manifestations will be present:
- poor sleep – insomnia, frequent awakenings at night;
- general anxiety and restlessness;
- fixation, obsessive states;
- hypochondria (a meticulous search for illnesses and confidence in one’s ill health);
- irritability, causeless aggression;
- headache and dizziness;
- weakness;
- unstable blood pressure;
- tachycardia;
- frequent urination;
- pain and heaviness behind the sternum;
- migraine.
The difficulty of diagnosis lies in the fact that psychological manifestations can be present for a long time, and only after months and years does intestinal neurosis appear - the symptoms are difficult to connect together, so the patient can treat gastrointestinal diseases for a long time and unsuccessfully, without knowing about the psychological causes of his condition.
Types of gastric neurosis
Several of the most common types of gastroneurosis can be distinguished based on the predominant symptom.
- Neurosis with severe heartburn, which cannot be relieved with medications. Heartburn exhausts the patient and reduces the quality of life, but examination does not reveal any organic disorders or pathologies.
- Anorexic form - aversion to food, inability to eat even previously favorite dishes. This form of neurosis is very dangerous, since if prolonged, it can lead to general weakness, emaciation and even death from exhaustion.
- Bulimic form. A person experiences severe hunger and eats with increased appetite, but immediately after eating he throws up what he has eaten. Vomiting can occur involuntarily or be caused intentionally. It is impossible to cure such a neurosis of the stomach on your own; treatment should begin as soon as possible and only by specialists!
- Aerophagic disorder is characterized by swallowing air, belching and flatulence.
- Neurosis with low stomach acidity. In this case, food is poorly digested, the person feels a weak appetite, experiences pain, and constipation.
- Intestinal neurosis with frequent loose stools that occur for no reason, pain (irritable bowel syndrome).
Intestinal neurosis
It is a branch of gastroneurosis, although it is rarely isolated as a separate disease. Most often, neurosis of the stomach and intestines manifests itself in the patient simultaneously. The symptoms are listed above: stool disorders, flatulence, pain in the soft part of the abdomen, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen.
Usually, disturbances in the functioning of the stomach and intestines due to nervousness accompany each other, but in some cases intestinal neurosis occurs without gastric symptoms.
We are not talking about intestinal neurosis if the symptoms appear episodically and in connection with isolated stressful situations. Almost every person has experienced indigestion at least once before an exam, a date, or speaking in public.
But such “nervous” diarrhea and stomach turmoil do not require treatment and go away on their own. Now imagine a similar condition that does not go away for months.
Regardless of what worries the patient—an upset stomach due to nervousness or intestinal neurosis—the treatment is the same: symptom relief plus psychotherapy.
Causes of gastroneurosis
The main cause of gastroneurosis is a violation of the nervous regulation of the gastrointestinal tract.
In a broader sense, this condition is caused by stress in which a person remains for longer than he can bear. Stress becomes chronic, the body is constantly “preparing for battle”, the adrenal glands secrete the stress hormone – cortisol.
The psyche, like a hundred thousand years ago, reacts to stress with the desire to fight or flee, but a person living in the civilized world is forced to block these desires. The vagus nerve is overstimulated by cortisol and adrenaline.
Since it is responsible for the secretion of the stomach, the production of gastric juice decreases or increases, food is poorly digested, or, conversely, the acidic environment causes the development of stomach ulcers. Similar processes occur with the intestines, which react to stress with frequent loose stools or constipation.
A protracted difficult situation with work, money, personal and professional relationships can lead to neurosis.
Chronic stress is often caused by the loss of a loved one or a painful breakup. Prolonged overwork, poor nutrition and regular lack of sleep also lead the body to a state of stress.
Also, intestinal neurosis often manifests itself against the background of an existing chronic neurosis. Thus, the saying “All diseases come from nerves” is confirmed.
A person can literally be “sick of life”; it is difficult for him to “digest” it.
Neurosis of the intestines and stomach, constipation and heartburn with VSD - how to treat
If you suffer from constant nausea or even vomiting, you are tormented by heartburn and heaviness in the stomach, and treatment does not bear any fruit, it is possible that you have a food neurosis or, as I call it differently, intestinal neurosis. This problem is the result of abnormalities in the nervous regulation of this organ and, as a rule, it affects middle-aged people whose nervous system is subject to high stress.
Before moving on to considering treatment methods for this disease and its symptoms, it is necessary to find out what contributes to its occurrence and how it develops.
With gastric neurosis, unpleasant sensations manifest themselves in a slightly different way than with gastroenterological diseases.
For example, a patient may, having barely risen from the dinner table, complain that he feels a feeling of emptiness in his stomach or, conversely, a feeling of fullness even after the most modest meal.
For some reason, treatment with well-proven drugs also does not produce results.
The matter is further complicated by the fact that many patients do not consider this problem serious enough, thinking that everything will go away on its own.
Alternatively, they begin to treat the disease on their own, using actively advertised (but far from safe) enzyme preparations and painkillers.
In such cases, we can say with almost one hundred percent certainty that the problem is of a psychological and not a gastroenterological nature.
It may seem that the digestive and nervous systems have nothing in common, however, both are closely related. Moreover, all processes, reactions, as well as sensations that occur, including in the abdominal cavity, are controlled and provided by the nervous system. Therefore, any failure will certainly affect the overall health, including the digestive system.
To be convinced of the correctness of the above, it is enough to recall various difficult life situations when even healthy people begin to experience heartburn, nausea, a lump in the throat, etc.
Symptoms and causes
The main cause of this disease is a modern completely unhealthy lifestyle.
Insignificant physical activity, multiplied by constant nervous tension, insufficient rest in general and poor sleep in particular, leads to the development of vegetative-vascular dystonia and its variety such as intestinal and stomach neurosis. In addition, this disease develops much more often in those who have a corresponding hereditary predisposition.
Often, the development of neurosis of the stomach and intestines is preceded by strong emotional experiences and psychological trauma. However, VSD is rarely associated with serious mental illness.
Particularly susceptible to this disease are those prone to self-hypnosis, suspicious people who relate to their health with an increased sense of anxiety.
It should be noted that among people actively involved in sports, there are almost no patients with VSD.
Most often, food neurosis makes itself known through the following symptoms:
- Malaise, lethargy, general depression, poor sleep, low performance.
- Frequent heartburn, even with a perfectly healthy diet.
- Insufficient or excessive appetite.
- Unreasonable changes in gastronomic preferences, up to aversion to once favorite dishes.
- Frequent pain in the stomach area, which can spread to neighboring organs.
- Discomfort caused by a feeling of fullness or emptiness in the stomach.
The above symptoms are often supplemented by signs typical of other conditions of a neurotic nature:
- Depression.
- Migraine.
- Sudden and frequent mood changes.
- Irritability, etc.
Often they help to distinguish food neurosis of the stomach and intestines from diseases of a gastroenterological nature and, accordingly, to use the help of a psychologist and neurologist.
Types of gastric neurosis
Several of the most common types of gastroneurosis can be distinguished based on the predominant symptom.
- Neurosis with severe heartburn, which cannot be relieved with medications. Heartburn exhausts the patient and reduces the quality of life, but examination does not reveal any organic disorders or pathologies.
- Anorexic form - aversion to food, inability to eat even previously favorite dishes. This form of neurosis is very dangerous, since if prolonged, it can lead to general weakness, emaciation and even death from exhaustion.
- Bulimic form. A person experiences severe hunger and eats with increased appetite, but immediately after eating he throws up what he has eaten. Vomiting can occur involuntarily or be caused intentionally. It is impossible to cure such a neurosis of the stomach on your own; treatment should begin as soon as possible and only by specialists!
- Aerophagic disorder is characterized by swallowing air, belching and flatulence.
- Neurosis with low stomach acidity. In this case, food is poorly digested, the person feels a weak appetite, experiences pain, and constipation.
- Intestinal neurosis with frequent loose stools that occur for no reason, pain (irritable bowel syndrome).
Neurosis of the stomach. Description of the disease
With timely (and adequate cause) treatment, complications and consequences of gastric neurosis are not observed.
However, both with complete ignorance of the processes occurring in the body, and with excessive enthusiasm for “examinations”, untested methods of “folk” magic and healing, as well as due to uncontrolled or excessive use of medications, the following are possible:
- further neuroticization of the patient’s personality (up to severe mental pathology);
- the appearance of truly serious diseases of the body (and not only the gastrointestinal tract) with severe anorexia, leading to the cessation of the body’s intake of the vitamins and minerals it needs.
Neurotics are “closed-minded” people who do not see a way out of their life situation. Their life is like a circle: you cannot quit your job because there is “no time” to think about another, and “there is no time” because all the time is carried away by the performance of official duties and the desire to live up to the “high trust placed in them.”
These are people with an exaggerated sense of duty, and only a strong-willed effort designed to make the rhythm of their lives tolerable can help them part with it. It’s not their effort – it’s someone else’s, from a side they don’t even look at!
In addition to relaxation, qigong techniques and other “foreign” practices, those suffering from gastroneurosis should be given a helping hand by their parents, whom their grown-up children still hate, resenting them, continuing to be afraid and avoiding communication with them. After all, nothing can warm up a heart and mind “frozen” by resentment and fear like a peaceful and cozy tea party in the evening on the veranda in your parents’ house!
After all, just by looking at the terrifying “monster” up close, you can understand that it is just a tall bush menacingly stretched out in the night.
- balanced diet containing proteins, fats and carbohydrates;
- adherence to diet;
- timely diagnosis and treatment of inflammatory processes in the intestines;
- timely detection of hidden anxiety and depressive diseases;
- adequate physical activity during the day;
- rejection of bad habits.
Digestive problems often arise from poor diet. Food on the go, in large quantities, with a huge content of poorly digestible fats and carbohydrates are factors that contribute to the occurrence of gastrointestinal diseases. Sudden weight loss or gain, belching, a feeling of heaviness in the stomach, nausea are symptoms that indicate disturbances in the functioning of the digestive system.
Stomach neurosis is an exacerbation of existing gastrointestinal diseases. It is most often caused by stress, severe emotional shock or overwork of the body. Gastric neurosis is characterized by severe, spasmodic pain throughout the entire abdominal area. An exacerbation can occur not only due to disruption of the nervous system.
Characteristic symptoms:
- Heartburn, vomiting and nausea. If these unpleasant sensations do not go away after switching to a light diet, then this means that the problem is deeper. Vomiting can cause dehydration, so in cases where it does not go away for a long time, you need to call an ambulance.
- Feeling of fullness in the stomach. At the same time, a person may be hungry. There may also be a feeling of insatiability.
- Severe pain in the abdominal area during a long break between meals. They can become generally intolerant if a person is in a stressful situation.
- Drowsiness, fatigue, lethargy, bad mood, loss of appetite.
Neurosis of the digestive system is a dangerous disease that can lead to very unpleasant consequences - stomach ulcers, gastritis, obesity, anorexia, cancer, etc. At the first sign of problems with the gastrointestinal tract, you should consult a doctor. Only a qualified specialist will be able to correctly assess the situation, diagnose and prescribe adequate treatment.
In this case, neurosis also occurs on the basis of problems with the functioning of the nervous system, eating disorders, and abuse of bad habits. Symptoms that indicate intestinal disease:
- Unpleasant sensations in the lower abdomen. They can be caused by intestinal gas. This causes colic or rumbling.
- Abnormal stool. Frequent urge to urinate or constipation may occur. Intestinal neurosis provokes dysbacteriosis and diarrhea. Constipation may also cause hemorrhoids and anal fissures. Symptoms such as vomiting or nausea appear less frequently with intestinal diseases, but also indicate problems.
- Exacerbation of pain during nervous shock. Nervousness is caused by a disruption in communication between the brain and the digestive system.
Symptoms may not be acute. Problems with bowel function may not be noticed immediately. Therefore, it is important to undergo a routine annual medical examination. It is better to start treating intestinal neurosis at the initial stage, in principle, like all diseases.
Intestinal neurosis
It is a branch of gastroneurosis, although it is rarely isolated as a separate disease. Most often, neurosis of the stomach and intestines manifests itself in the patient simultaneously. The symptoms are listed above: stool disorders, flatulence, pain in the soft part of the abdomen, a feeling of fullness in the abdomen.
Usually, disturbances in the functioning of the stomach and intestines due to nervousness accompany each other, but in some cases intestinal neurosis occurs without gastric symptoms.
Treatment
First of all, it is necessary to alleviate the symptoms of the disease. Treatment is carried out comprehensively:
- General restorative measures - correction of sleep and wakefulness, spa treatment, prescription of a vitamin complex, walks, recommendation to spend less time on TV and computer. Sports (simple morning exercises or yoga are suitable), vitamins, water and sun are very effective means in treating any type of neurosis.
- Relief of physiological symptoms - selection of a gentle menu, proper diet, prescription of medications depending on the main symptom. For example, drugs that reduce or increase stomach acidity, bacteria to improve microflora, drugs that relieve spasms.
- Elimination of stressful situations and psychotherapy. Without it, it is difficult to get rid of such a complex disease as gastrointestinal neurosis. After all, the cause of painful sensations and unpleasant conditions lies in the mind, and often even at the subconscious level - that is, a person does not even realize that he is tormented. Therefore, no pills, herbs or dietary supplements will bring complete recovery.
- Drug correction of neurosis using psychotropic drugs. Must be used in severe cases such as anorexia and bulimia.
- Physiotherapeutic treatment aimed at normalizing nervous processes: warming up, baths, massage. It is useful even for completely healthy, but slightly tired people.
Esophageal neurosis: symptoms and treatment
Three specialists can participate in the treatment of psychogenic dyspepsia: a gastroenterologist, a neurologist, and a psychotherapist. The main role here belongs to the psychotherapist, but in order to fully and quickly restore all functions of the body, it is sometimes necessary to eliminate some physiological disorders that were caused by neurosis. Before the patient receives a prescription, a series of diagnostic procedures must be completed.
Diagnostics
Depending on what symptoms the patient experiences of gastrointestinal neurosis, he may be prescribed certain tests. Let's consider the main series of diagnostic tests that a person who observes signs of a digestive system disorder should undergo.
- General blood analysis.
- General urine analysis.
- Blood test for biochemistry.
- Coprogram.
- Complex gastroenterological diagnostics.
Based on the research obtained and consultations with specialists, the patient is prescribed a number of restorative procedures, which may include various methods.
Psychotherapy
The doctor conducts sessions with the patient during which the true psychogenic causes of neurosis are searched, then they are worked through and eliminated. A person learns to look and react differently to situations that put pressure on him. If internal conflicts are detected, the doctor helps resolve this dispute.
Along with psychotherapy, the patient may be prescribed sedatives, antidepressants, and tranquilizers.
The drug Teraligen has proven itself very well for gastric neurosis, reviews of which are mostly positive. This medicine not only calms the nervous system, but also has antispasmodic properties. Also effective are: Paxil, Fluoxetine, Atarax, Phenibut, Citalopram.
READ MORE: Existing drug could treat triple negative breast cancer
Gastrotherapy
To eliminate the symptoms of gastrointestinal neurosis, treatment may include taking antispasmodics, analgesics, carminatives, choleretic, antidiarrheal or, conversely, anticonstipation drugs and other medications to improve bowel function. These medications are prescribed by a gastroenterologist.
In some cases, the doctor may recommend dietary nutrition, temporarily eliminating foods that cause flatulence from the diet, and prescribing vitamins, bacterial and enzyme preparations.
Physiotherapy
Physiotherapy can have a good effect as part of complex procedures. When experiencing negative emotions, the muscles of the body spasm, pinching the nerve endings. This leads to pain, malaise, weakness, and poor circulation.
Physiotherapy may include the following procedures:
- Hydrotherapy (swimming, relaxing baths with herbs and salt, Charcot shower)
- Massage aimed at relaxing muscles.
- Electrotherapy.
- Darsonvalization.
- Magnetic laser therapy.
- Ultraphonophoresis with drugs and sedatives.
- Exercise therapy.
Traditional methods
Often, good results are obtained from treating gastric neurosis with folk remedies in combination with psychotherapy sessions.
| Tea with mint | Mint has sedative, carminative, antispasmodic properties, calms the nervous system, and normalizes sleep. |
| St. John's wort decoction | The herb has antibacterial properties and is a natural antibiotic. Kills harmful bacteria in the intestines and helps restore healthy microflora. |
| Tea with oregano | Oregano normalizes intestinal dysfunction, fights pathogenic microflora, calms nerves, and improves immunity. |
| Oak bark decoction | Effective for diarrhea, dysbacteriosis, relieves inflammation, has astringent and bactericidal properties. |
| Chamomile tea | Chamomile has soothing and powerful anti-inflammatory properties. |
A person suffering from psychosomatic diseases is also recommended to reconsider his lifestyle: add more activity, switch to a healthy diet, and eliminate bad habits.
In general, neuroses respond well to therapy, and even in the most severe conditions, recovery can be achieved quickly. The speed and effectiveness of treatment largely depends on the patient himself, how willing he is to perceive information and actively work in tandem with a psychotherapist.
No matter how good and professional the specialist is, there are times when the patient does not at all perceive the assertion that all his physical ailments are caused by the psyche. He is closed and not ready to work with a psychiatrist, listen and change his lifestyle.
In this case, exclusively drug treatment can produce results, but, as a rule, the remission remains short-lived and after some time the problems return. Complete recovery of eating neurosis occurs when its cause is discovered, realized, processed and eliminated.
Good time everyone!
Problems with the gastrointestinal tract began for me after a neurosis, which I had the good fortune to catch. This condition is also called vegetative-vascular dystonia, but I prefer a simpler and more appropriate term – neurosis. For those who are not in the know, this is a very strong stress, as a result of which psychosomatic symptoms appear.
In my case, the intestines were the first to rebel. Spasms, strange pains here and there, sudden urges and many other special effects. Actually, I won’t go into neurosis and all its charms, fortunately, I got rid of long ago. I'll tell you about my experience with Meteospasmil.
READ MORE: How to treat hidradenitis at different stages of the disease
It was recommended to me by a doctor, a neurologist, but I’ll immediately make a reservation that at that moment I took a bunch of tests and did all sorts of examinations, and no diseases were found. That is, it was necessary to treat the nerves and eliminate painful symptoms. The digestive system is the most sensitive to nerves, so most often it is what fails during neurosis. I was simply diagnosed with irritable bowel syndrome.
I bought Meteospasmil in the hope that it would calm down my gastrointestinal tract. The medicine is not cheap, there are 30 capsules in a package. It contains simethicone to eliminate gases and alverine citrate, which is an antispasmodic. It was prescribed 1st 3 times a day before meals or immediately after. The capsules are drunk normally, the taste is neutral. I drank as prescribed.
To be honest, I didn’t feel much of an effect, although I had hopes for these pills. The intestinal turmoil has not become less, except that perhaps the spasms have decreased a little. Without feeling any obvious relief after a couple of days, or after a week, or after two.
Espumisan, which I bought myself without a prescription, also did not give much effect. It became better only when I got rid of the neurosis and put my nerves in order. Everything took more than six months. During this time, no medications helped calm the gastrointestinal tract.
My conclusion is this: healthy nerves, healthy intestines. In general, during self-psychotherapy I learned a lot of interesting things about the metaphysical causes of diseases. But that is another story. As for Meteospasmil, it didn’t help me. I practically didn’t feel its effect. There were no side effects. There were no changes at all. The fact that the spasms slightly reduced, well, in this case it will be much cheaper to buy Spazmalgon.
I can’t recommend drinking or not drinking, but if your doctor prescribed it, it’s probably worth a try. And everyone’s cases are different. But I would recommend this to everyone to think about your psychological state and analyze how satisfied you are with your life, with your reality. All diseases are caused by nerves, that’s a fact.
Sources used: irecommend.ru
Video
We recommend watching an interesting video by a competent psychotherapist who talks about the main cause of intestinal neurosis and what unites all patients:
So, to summarize the above, we can say: it is necessary to treat a gastrointestinal disorder due to nervousness without delay. However, if you have recently noticed some symptoms of gastroneurosis, first of all try to harmonize your life and reduce the impact of stress. Perhaps soon you will not remember your past illness.
Why does the disease occur?
When we talk about the common causes of intestinal and stomach diseases, they are often caused by bacteria, hereditary predisposition, and acquired chronic pathologies.
But do not forget that the vagus nerve is involved in organizing proper gastric secretion. When it is at rest, secretion occurs normally and the person feels comfortable. But psychological shocks and past illnesses, as well as simply constant anxiety, can lead to serious problems.
Among the common causes of gastric neurosis are:
- Problems of a psychological nature. They arise when a person feels constant anxiety, is dissatisfied with himself, or experiences a tragic event. Psychologists note that neurosis can cause a break with a loved one, being in a negative environment in a team at work, or the loss of a relative.
- Wrong lifestyle. The nervous system suffers due to lack of sleep, poor work-rest balance, and constant severe stress.
- Nutrition problems. The gastrointestinal tract makes itself known when you eat a lot of fatty, heavy foods, consume a lot of sweets and starchy foods. Poor diet is another risk factor. To avoid getting sick, you should give up frequent snacking and balance your diet.
- Past illnesses. Many viral diseases, as well as problems with the stomach and intestines, quickly provoke neurosis. The problem appears against the background of gastritis, neoplasms, ulcers and other problems.
- Negative effects on the gastrointestinal tract. The disease can manifest itself after severe poisoning, as well as during intoxication, against the background of bad habits.