Unpleasant whistling in the ears
Many people are familiar with the condition when they hear noise, whistling or ringing in their ears.
Sounds appear and disappear periodically in both adults and children.
Usually it does not cause any discomfort.
But when the noise continues for several hours, it is already an abnormal condition, which leads to hearing impairment and sleep disturbance. You don't have to run to the doctor to get rid of the problem.
Treating whistling in the ears at home is a great way to overcome the disease.
Causes
Noise, whistling or other sounds in the head will go away only after their exact cause is established. The following factors can provoke this condition:
- Presence of toxins in the body. For example, due to medication or food poisoning.
- Physical fatigue due to hard work or sports.
- Mental and emotional stress. Head noises often occur in people suffering from psychosis and depression.
- Skull trauma or concussion. So, if a person receives an injury or blow, its consequences will bother him for several weeks and intensify after physical stress.
- Taking certain medications. For example, long-term use of Aspirin, Citramon and some antibacterial drugs can cause ringing in the ears and head.
- Changes in the body that occur as a person ages. For example, in older people, the cause may be wear and tear of the hearing aid ossicles, high blood pressure, or vascular disorders.
- Abuse of coffee or chocolate.
- Smoking. This can especially happen during the period when a person decided to quit this bad habit, but after a while he took up a cigarette again. In addition to ringing in the head, a person may develop nausea and dizziness.
Cause: vegetative-vascular dystonia
Typically, the sensation of a hum or noise in the head associated with atherosclerosis is similar to the sound of the sea, that is, it has a low pitch and rhythmic structure. Sometimes this noise intensifies after sleeping in an uncomfortable position.
What to do?
It is necessary to undergo an examination by a neurologist as soon as possible, do an MRI or Doppler ultrasound of the brain vessels. If the diagnosis is confirmed, you should limit the consumption of animal fats, which cause deposits of atherosclerotic plaques on the walls of blood vessels. They are found in butter, meat, sausages, complex sweets, sour cream, and cream. The doctor will also prescribe medications that lower cholesterol levels and improve the condition of the vascular wall, vasodilators and other agents.
In this condition, the regulation of blood vessel tone is disrupted, and blood pressure often decreases. This may cause mild, steady or pulsating tinnitus, dizziness, and loss of coordination.
What to do?
See your doctor to confirm your diagnosis. If the problem is vegetative-vascular dystonia, move more: walk, swim, dance, bike. Cool douches and restorative massage are also useful. Make sure you get enough sleep. It is necessary that there is an influx of fresh air into the bedroom at night. Give up bad habits.
It is important to learn how to relieve stress. For example, before going to bed, you can lie on your back and imagine how all the muscles of the body relax one by one, starting with the toes and hands and ending with the muscles of the face, and a feeling of pleasant warmth appears in them. It can also help to take a few deep breaths and exhale slowly.
Constant whistling in the ears and head
Whistle in the head can be of two types:
- Constant.
- Temporary.
Reasons contributing to the appearance of constant extraneous sounds in the ears:
- hypertension;
- runny nose;
- vasoconstriction.
The eardrum moves under the influence of some external signal. The hammer records this movement and redirects it to the cochlea, in which the fluid moves. Fluctuations in the fluid irritate the receptors in the cochlea, which send an impulse to the sound nerve. Then this vibration is re-formed into sound.
Head trauma and regular listening to loud music can damage the receptors, resulting in impaired perception of sounds. Due to disturbances in the functioning of the hearing organs, the signal does not always reach the auditory nerve without distortion and is processed.
When the receptors are damaged, sensations may appear that cause discomfort. The nature of the whistle is a fundamental sign when making a diagnosis. Sounds are divided into:
- strong;
- vibrating;
- intense.
The feeling of ringing in the head should be included in a separate category.
Reason: severe stress
During emotional experiences, severe fear, and anxiety, a person’s temporal muscles tense. Constant tightness of these muscles can lead to compression of the vessels of the ear canal, which causes the sensation of noise, ringing, and buzzing in the ears.
What to do?
Acupressure will help - light massage of active points with your fingertips. It should be done in a circular motion with gentle pressure.
Press the point located in the dimple above the upper lip with your index finger for 7 seconds. Then, with medium force, press the point at the end of the root of the nose, near the eyebrows - also for 7 seconds. Repeat these techniques several times a day.
For 7 seconds, apply intense pressure with your ring finger to the place where your earlobe connects to your face. Then another 7 seconds - just in front of the tongue of the ear (there, if you touch, you will feel a small hole). And finally, another 7 seconds - at the beginning of the upper part of the cartilage of the auricle (you should also feel the hole there). After exercise, a pleasant warmth usually appears, which indicates improved blood circulation.
What complications can a ringing in the head cause?
As a result of this problem, a person begins to take analgesics, antidepressants, NSAIDs, muscle relaxants and nootropics. But I can’t get rid of the ringing in my head.
Along with this, dangerous consequences may develop, such as:
- Memory loss, partial or complete.
- Oxygen starvation of the brain, which leads to a decrease in intelligence.
- Wear and tear of blood vessels, which leads to stroke or heart attack.
- And the most dangerous consequences of untreated noise in the head can be disability and even sudden death.
Reasons for appearance
The reasons for the appearance of extraneous sounds in the ear are either an external stimulus or internal changes.
As a rule, the presence of dizziness and noise in the head is only a symptom of some disease in the body.
Therefore, it is important to see a doctor to have your ear tract examined.
A number of possible reasons causing noise and whistling in the head:
- sharp and strong noises: howling sirens, listening to music at high volume, emergency signals. Usually the effect after them is short-lived and goes away on its own, but in the case of regular exposure to the eardrums, the result will be disastrous - the hearing organs will be damaged;
- closing the ear canal with wax plugs. The whistling sound appears due to a violation of the patency of the auditory canal; the most common causes of buzzing in the ear are the appearance of pus as a result of an inflammatory process or injury to the ear. Sharp noise and congestion are characteristic signs of a serious illness;
- age-related changes that cause narrowing of blood vessels in the head, which provokes disturbances in the functioning of the hearing aid. Whistling caused by stress is a common occurrence in middle-aged and older people;
- problems with the functioning of the hearing organs can be caused by allergic reactions;
- the most difficult cause is a tumor of the brain or ear. In this case, one of the symptoms is pain, which is difficult for the patient to tolerate;
- Weather conditions also have a significant impact on the progression of tinnitus. The hearing organs can respond to changes in atmospheric pressure;
- people who tend to smoke several cigarettes a day become unwitting hostages of tinnitus, since tobacco contains substances that cause increased blood pressure and constriction of blood vessels;
- for the same reason, you should not drink large quantities of coffee, because it also negatively affects the condition of the hearing organs;
- overwork and severe psycho-emotional shock in some cases can be the causes of this illness. Stress contributes to the appearance of problems with blood vessels, and, consequently, with hearing;
- lack of iodine in the body.
general information
In fact, many people experience such phenomena as noise, humming or crackling in the head, as well as pulsating heartbeat in the ears.
However, not everyone attaches great importance to these symptoms, much less turn to specialists for help. And in vain, because for a healthy person such manifestations are not the norm and indicate the development of various kinds of pathologies. This is especially true for those people for whom noise effects have become constant companions in life. Of course, each person subjectively perceives different types of sounds.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=gR1DU-lerZY
Some people may sometimes be bothered by a buzzing or crackling sound in their head, some can clearly hear the beating of their own heart (pulsating noise in the ear), and some describe their sensations as if something is overflowing in their head. Various noises can disturb a person from time to time, for example, only at night or in silence, and do not affect his normal well-being or performance.
However, for some, such sound effects are a discomfort. In any case, according to experts, noise in the head is a good reason to see a doctor.
In what cases is the condition considered normal and when is it pathological?
Don’t be alarmed if you periodically experience ringing in your ears or head; this condition occurs in 90% of the planet’s inhabitants. The phenomenon is called tinnitus. It happens due to the functioning of the hearing organs, which is regarded as the norm.
But if noise in the head occurs regularly, then you may think that the person may have health problems. And sometimes these problems are serious, requiring immediate medical attention.
To have an idea of when ear ringing is considered normal and when it is not, you need to pay attention to the following points:
- the nature of the noise and whistle in the head;
- its intensity;
- duration;
- presence of accompanying symptoms.
Ringing Noise and Whistling in the Head - Why It Occurs and How to Get Rid of It
When a specialist examines a patient, he first records the symptoms of the disease and only then proceeds to order laboratory tests to clarify the medical history. If a person is bothered by extraneous noises, then it is important for the doctor to determine the nature of these sounds (squeaking, crackling, ringing, whistling, etc.), as well as establish their frequency and the circumstances under which they occur.
After all, patients complain not only of constant noise in the head, but also of periodically occurring sounds, for example, when changing body position or in the evening, when the overall noise level around them decreases. This type of extraneous noise, such as ringing in the head, is one of the most common sounds (according to statistics, up to 30% of the world's inhabitants have encountered this type), which signal the presence of a particular disease.
So, what are the causes of ringing in the head and ears? Experts say that this phenomenon is directly related to the degeneration of hair cells, otherwise they are called auditory receptors of the ear, which send a signal to the auditory nerve for no reason, which ultimately leads to the sensation of ringing in the ears or in the head. It is worth noting that such a noise effect does not always indicate deviations.
Absolutely healthy people can have ringing in the head if:
- a person has been in an excessively noisy room for a long time, for example, in a nightclub or at a concert. In addition, ringing may be a normal neuralgic symptom if you often listen to loud music on headphones. The thing is that our hearing aid simply cannot reconfigure instantly; it needs some time to adapt to silence after loud sounds. Although such ringing is not associated with any illness, it is still dangerous to human health. Constantly listening to loud music or being in noisy rooms sooner or later leads to loss of hearing acuity. It is for this reason that workers employed in extremely noisy industries or performing construction and installation work wear protective headphones;
- The ringing may be normal if you hear it from time to time in complete silence before going to bed. In fact, in this case, a person hears the noise of working internal organs, which resembles ringing.
In medical practice, ringing in the head is given the name tinnitus. If a person hears noises sometimes in silence, then this is not a reason for concern. It’s another matter if such sounds become constant companions of life. There are two main gradations that specialists take into account when examining a patient complaining of noise in the head:
- subjective noise, i.e. sounds that only the person himself can hear. The causes of such noise may be deviations of a psychogenic nature or damage to the hearing aid, in which distortion of sound perception occurs;
- Objective noise is the sounds that a doctor can hear with a stethoscope. As a rule, the causes of such sounds are muscle spasms or disturbances in the circulatory system.
Why does my head constantly ring? In fact, there are not a dozen diseases in which the patient may suffer from extraneous noise. However, it is ringing in the ears or in the head that a person hears in diseases such as:
- hypertension (high blood pressure);
- hypertensive crisis, i.e. a sharp rise in pressure, in which the indicators differ from the norm by more than 20 units;
- arterial hypertension, i.e. increased level of intracranial pressure;
- atherosclerosis is a common disease in which blood flow is impaired due to blockage of blood vessels;
- traumatic brain injuries, as well as damage to the hearing organs;
- infectious diseases;
- osteochondrosis, in which there is a gradual destruction of the integrity of the intervertebral discs, which negatively affects the condition of the nerve plexuses and blood vessels located in the spine;
- brain tumors, both malignant and benign neoplasms.
In addition, ringing can be a side effect of certain medications. Weather-sensitive people, i.e. Those who react painfully to changing weather often suffer from tinnitus due to pressure surges or vascular spasms. Professional risks cannot be written off either.
Acupuncture is one of the methods for treating tinnitus while taking medications.
For example, people who, due to their work responsibilities, are forced to spend a lot of time in noisy places often experience extraneous noise in their heads or ears, and also suffer from partial hearing loss. Ringing in the ears can also occur during sudden changes in pressure, for example, during takeoff or landing, as well as during scuba diving.
Treatment of ringing in the head begins with a visit to an otolaryngologist, who must rule out ENT diseases in which noise occurs due to damage to the hearing organs. As a rule, after an initial examination and hearing test, the doctor prescribes a number of additional tests for the patient (blood test, urine test, MRI, and so on).
After a comprehensive examination, the doctor prescribes treatment. As a rule, in the treatment of ringing in the head or ears, medications, physical therapy, massage, physiological procedures (magnetic therapy, electrical stimulation, acupuncture), as well as calming and relaxing techniques used by psychotherapists are used.
Since noise is a symptom of a disease, the basis of its treatment is methods that help cope with the cause of extraneous sounds. In addition, prevention and the patient’s subsequent lifestyle take an important place in therapy. This means that noise can be cured, but the long-term effect depends on the person himself, who must change his habits, for example, start eating right and playing sports, giving up bad habits, and so on, so as not to encounter this ailment again in the future. .
I know many people who have these problems - ringing, noise and whistling in their heads. The poor fellows suffer for years, try all sorts of treatment methods, but in the end they come to terms with the constant noise and simply stop paying attention to it. The symptoms remain, but the reaction to them is dulled. However, unpleasant sounds can be eliminated! Let's figure out how this can be done.
Noise in the head can be caused by various reasons. Problems in the functioning of the endocrine system are one of these reasons. Pay attention to the functioning of the thyroid gland. Feed it with iodine. Very often this is enough. There is a lot of iodine in seaweed, for example.
This also includes whistling from fatty foods; I have also recorded such cases. The woman could not consume even a drop of oil - she was immediately overcome by extraneous sounds in her ears.
What does it mean if a kettle whistles in your head? Another reason that causes ringing and noise in the head is vascular sclerosis in the brain. But we hear the sound, of course, not in our heads, but in our ears. The blood vessels are narrowed, hence the whistling sound that our eardrum feels.
There are two solutions: either inject a course of vascular medications, or monitor your diet very strictly. By the way, a course of IVs and injections helps some, but not others. If it doesn’t help in your case, then you have bad blood vessels. So the reason is in the diet.
Let us examine in more detail the probable and most common causes of extraneous sounds that a person can hear.
High blood pressure is one of the most common causes of ringing in the head and tinnitus. Symptoms may appear when blood pressure rises above 140 over 90 when the norm is 120 over 80.
A hypertensive crisis is a sudden increase in pressure by more than 20 units from normal. This also causes noise or ringing in the ears.
Arterial hypertension - unpleasant noise in the ears can occur with increased intracranial pressure, and can also be accompanied by severe headaches.
Age-related changes - noise and ringing in the head can appear in older people as a reaction to natural age-related changes in the hearing organs.
Atherosclerosis - deposits and plaques appear on the inner walls of blood vessels, which can disrupt the normal flow of blood and create turbulent turbulence, which causes tinnitus. It pulsates in time with the contraction of the heart muscle.
Weather sensitivity - some people react poorly to changes in atmospheric pressure. For them, a change in weather can cause changes in blood pressure, vasospasm, and ringing in the head.
Injuries to the head, ear, or eardrum can lead to hearing impairment and the appearance of ringing and noise in the head.
Osteochondrosis - with this disease, the intervertebral cartilaginous discs are gradually destroyed, which can cause damage to the blood vessels and nerve plexuses located in the spine.
In naturopathy terms, of course. After all, official medicine does not recognize the concept of acidification in relation to the human body. But supporters of natural medicine put this indicator at the forefront.
It is believed that over the years our body becomes acidic, lymph, and indeed all liquid environments inside our body, are at the lower permissible pH values. And this, in turn, provokes many diseases. The most varied - from joint pain, to noise in the head and headaches. I will discuss the topic of acidification and alkalization in my next publications in more detail.
Traditional medicine, human experience, advises drinking in the morning, on an empty stomach, one glass of water with lemon juice and soda. Squeeze half a medium-sized lemon into a glass.
Take half a teaspoon of soda.
Moreover, first pour soda into an empty glass, then pour boiling water, a third of the glass, the soda should hiss, then pour a third of the glass with water at room temperature, and then lemon juice.
Drink 30 minutes before meals. Carry out the procedure daily, throughout your life, as an alkalizing detoxification program. Your health will improve and extraneous noises will no longer bother you. The method works and has been tested by many in practice.
It is also recommended to drink a glass of plant decoction for unpleasant sounds in the head. The collection is as follows: equal parts of currant leaves, linden blossom, strawberry leaves or fruits, clover, St. John's wort, oregano. Add a mixture of herbs to boiled water (two glasses), simmer over low heat for 20 minutes, then let cool.
Possible diseases and warning signs
Quite often, hissing and whistling in the ears appear as symptoms of diseases of other organs. Among the diseases and pathological conditions that cause these manifestations are:
- disorders of the kidneys;
- slow or accelerated metabolism;
- pathologies of the inner ear and capillaries;
- mental illness;
- viral diseases;
- acute or chronic otitis media;
- hepatitis;
- migraine;
- osteochondrosis;
- hypertension.
Even if the irritating sound stops, the sensation of tinnitus continues. General malaise is accompanied by dizziness, which only intensifies over time;
- the whistling in the ear canals increases, while the patient’s physical condition worsens;
- after prolonged manifestation of symptoms, partial or complete hearing loss occurs;
- additional symptoms appear more and more strongly: sharp pain in the ear, discomfort, the appearance of liquid and purulent discharge, an inflammatory reaction that occurs in an acute form;
- dizziness intensifies, the person is practically unable to move independently. This condition is accompanied by weakness, migraine, blurred vision, and insomnia. Possible sudden fainting
If a person experiences such symptoms, it is necessary to seek help from a doctor as soon as possible, as they indicate pathological changes in the body. Vascular dysfunction, brain tumors and other diseases in the later stages are incurable.
Sometimes, due to the presence of noise or ringing in the ears or head, people do not seek medical help. But there are a number of accompanying symptoms that should not be ignored, as they may indicate a serious illness. These include:
- temporary hearing loss, which can be complete or partial;
- the noises are sharp and increasing in nature;
- disruption of the hearing aid;
- ear pain;
- headache;
- ear congestion;
- noise or ringing in the head is prolonged and permanent;
- nausea and vomiting;
- asthenia;
- dizziness.
Determining the cause and treating ringing in the head will depend largely on the accompanying symptoms.
Squeaking in the head: causes and treatment
A squeak that occurs in absolute silence is a reason to think about the state of your health. There are many reasons for this ailment, among which it is worth highlighting the most common pathologies such as:
- deficiency of vitamins E and B;
- diseases of the nervous, cardiovascular and endocrine systems;
- anemia;
- ENT diseases;
- intoxication with toxic substances, for example, heavy metals;
- circulatory disorders;
- hearing injuries;
- traumatic brain injuries.
In addition, squeaking in the head can occur due to sudden changes in weather conditions, for example, when there is a difference in atmospheric pressure. In addition, extraneous noise is a common side effect when taking certain medications.
To treat squeaking in the ears and head, both medications and physiological procedures are used. It all depends on the cause of the ailment, which only a doctor can reliably determine. Therefore, if extraneous noise appears on a regular basis in your life, do not hesitate and seek help from specialists.
What diseases cause noise?
The causes and treatment of whistling in the head will be determined after identifying the disease that led to this condition.
Most often, this symptom accompanies a number of the following diseases:
- kidney pathologies;
- impaired metabolism;
- atherosclerosis and sclerosis of cerebral vessels;
- diabetes;
- capillary lesions;
- inner ear diseases;
- increased blood pressure;
- hypoglycemia;
- pathologies associated with the temporomandibular joint;
- psychological diseases;
- colds, especially flu;
- acute or chronic otitis media;
- carotid artery aneurysm;
- acoustic neuritis;
- hepatitis of various types;
- meningioma;
- feverish conditions;
- Meniere's disease;
- joint diseases, for example, osteochondrosis;
- perilymph fistula;
- migraine.
Prevention
To prevent the appearance of extraneous noise in the ears, you must:
- Do not listen to music at high volume, especially if using headphones;
- Monitor blood pressure levels;
- Set aside at least half an hour a day to be in a state of complete peace and quiet;
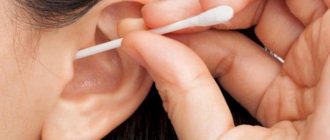
- Do not clean your ears with sharp or metal objects;
- Gently rinse your ears to avoid wax buildup;
- Treat inflammatory and infectious diseases in a timely manner;
- Avoid hypothermia.
Extraneous sounds in the ears are a phenomenon that may indicate the presence of serious pathologies. To prevent hearing loss, as well as deterioration of health, it is important to consult a doctor in a timely manner and treat the underlying disease.
Today, there are a huge number of people who, in one way or another, are faced with ear problems. This problem includes whistling in the ears. Whistling is a sign of a serious disorder that requires immediate treatment, since any abnormalities and sounds in the ear cavity can lead to insomnia, and subsequently to complete deafness.
According to statistics, every fourth inhabitant of the earth suffers from whistling in the ears. Basically, constant whistling in the ear cannot be an independent disease. But this sign may indicate a serious pathology.
Based on the nature of the sound, the following types of whistles are distinguished:
- the whistle is audible directly to the patient (high-frequency whistle with signs of hum, buzz, squeak);
- the so-called illusion of whistling and tinnitus, subjective whistling - in fact it is not there, but the patient thinks it is present;
- a strong whistle, similar to the sound of a click, usually corresponding to the rhythm of the heartbeat;
- a whistle that is heard by the patient and the people around him. Such a case is actually rare.
Today, this problem is familiar not only to the adult generation, but also to young people. As a rule, extraneous sounds in the ear may indicate the presence of some abnormality in the body. So, the causes of whistling in the ears:
- violation of the integrity of the eardrum (one of the main reasons);
- injury to the hearing aid (can cause much more serious complications);
- listening to music loudly on headphones (in the future this will definitely affect the acuity of sound perception);
- wax plug in the ear, which blocks the ear canal;
- ossification of the middle ear cavity;
- otosclerosis.
As for old age, the causes of whistling in the ear are senile changes. Against their background, the auditory nerve begins to gradually die, its functionality is impaired.
In addition, there are a number of diseases that can cause whistling in the ear:
- spinal injury;
- blood pressure surges;
- diabetes;
- thyroid dysfunction;
- allergic reactions.
It is worth noting that whistling is a symptom of Meniere's disease. There are also other signs that characterize whistling, which are worth paying close attention to. If you find yourself with one of the following symptoms, consult a doctor, otherwise your condition will only get worse every day.
Signs of whistling are:
- ringing, noise, buzzing;
- temporary hearing loss;
- soreness in the ears;
- feeling of stuffiness in the ear;
- frequent headaches.
Listening to music loudly with headphones can cause whistling in the ear.
Diagnostic methods
If you are worried about tinnitus, it is important to consult a doctor and find out why it occurred and how to get rid of it. Diagnosis of whistling in the ears is carried out by an otolaryngologist. However, if he suspects the presence of other diseases, he may prescribe examination by other doctors. The doctor conducts a study using the following diagnostic methods:
- examination of the ear canal using an otoscope;
- listening to the skull with a phonendoscope;
- measuring hearing acuity with an audiometer.
Drug treatment
Before you begin to treat whistling in the ear, its causes must be precisely established, since the choice of treatment method depends on this.
Since the appearance of various sounds is just a symptom of an existing or another problem, the first thing the patient needs to do is seek help from a doctor. He will conduct an examination and prescribe the necessary procedures and tests. Only after this will it be possible to begin treatment, which will be aimed at eliminating the cause that gave rise to the whistle.
Treatment of pathology:
- If the cause of the noise is infectious and inflammatory diseases of the throat, nasopharynx, and other diseases, most often the doctor prescribes sulfonamide drugs. It is imperative to listen to the recommendations of doctors, because some antibiotics have an ototoxic effect.
- For disorders associated with tumor formation, only surgery can help. The easiest way to deal with the presence of a foreign body in the ear. For children, these are usually toys and small objects, but sometimes the cause of discomfort can be an insect that gets into the ear canal. Removing all this from the ear on your own is very dangerous, you can damage the eardrum and cause great harm to your health. This manipulation can be easily and quickly performed by an ENT doctor.
- The presence of wax plug requires immediate attention. If it is not too large, you can soften it by instilling it, followed by careful cleansing of the ear canal. If this does not help, you need to go to the doctor and he will wash the plug with a special device. Usually after this all extraneous sounds in the ear disappear.
- Whistling associated with arterial hypertension will completely disappear or significantly decrease after the use of special medications aimed at reducing blood pressure.
Age-related changes are not so easy to cure, and sometimes it is simply impossible. Typically, general health supplements, vitamins and minerals, a special diet and supportive medications are prescribed, and for hearing loss, hearing aids are prescribed.
Instrumental diagnostics
Not only the causes and treatment of whistling in the head are important, the correct diagnosis also plays a special role. If there are frequent noises in the head, it is necessary to undergo an instrumental examination:
- Ultrasound of the vessels of the cervical spine. This study allows you to detect pathologies of the arteries, narrowing of the vascular bed.
- Angiography of cerebral vessels. This diagnosis reveals the presence of atherosclerosis.
- EEG (electroencephalography). It is carried out when, along with ringing in the head, convulsive reactions and clonic seizures occur.
- CT scan of the brain. The study determines pathological foci in the brain, the presence of neoplasms, cysts, and ear pathologies.
- MRI (magnetic resonance imaging) of the head. This method is important for determining the functioning of the vegetative-vascular system.
- MRI of the cervical spine is performed to clarify the diagnosis of osteochondrosis, determine the exact location of damaged vertebrae, and examine intervertebral discs.
- Audiogram. The method determines how much a person’s hearing has decreased due to constant whistling in the head.
- Hearing test.
Cause: osteochondrosis
This disease can compress the nerves connected to the auditory part of the brain. This often happens during sleep if you have taken an uncomfortable position. The result is an unpleasant high-pitched continuous hum of varying intensity in the head. It can be similar to the sound of a refrigerator running or the sound of cars honking during a traffic jam on the highway.
If the buzz in the head is associated with osteochondrosis, it should decrease or disappear altogether when taking a vertical position.
What to do?
Pay close attention to your sleeping conditions. The pillow should fit you exactly, not too high and not too low.
After waking up, it’s good to do a little gymnastics for the cervical spine. Rotate your head, stretch your ear to your shoulder, push an imaginary ball under your chin towards your chest.
How to get rid of annoying sounds
Before you get rid of constant whistling in your ears, it is important to understand why it appeared. Diagnosis and treatment are carried out only by a doctor. If the appearance of noise was caused by viral diseases that affected the maxillary sinuses or caused otitis media, the otolaryngologist prescribes antibiotics and local treatments.
If the cause is a foreign body, then the only option is surgery. This often happens in children, as they may accidentally push a foreign object into the ear canal.
Under no circumstances should you try to get it out yourself, as there is a high probability of damaging your eardrum. Only an experienced otolaryngologist can perform the operation efficiently and safely.
If the noise is caused by osteochondrosis, then massage can help relieve discomfort. To do this, use your fingertips to massage your neck towards your head. The muscles relax, blood flow increases, and the whistling in the ears disappears.
If the cause of the disturbances lies in listening to loud music, then the acoustic trauma goes away on its own in silence.
One of the most popular treatments for tinnitus is physical therapy. It includes laser therapy, electrophoresis and air massage of the eardrum.
If whistling in the ears signals us about the presence of another disease, then, depending on its nature, either psychotropic drugs, or drugs from the group of antihistamines to relieve swelling of the mucous membrane, or anticonvulsants are prescribed.
If none of the medications used gives the desired effect, then you should consult a doctor again, because there are also other pharmaceutical drugs that may help relieve discomfort in the ear in just a few days.
Reasons for whistling
There are several reasons why there is whistling in the ear. This feeling can be caused by prolonged exposure to a noisy place, overwork, that is, it is not a symptom of any disease.
People whose work involves loud sounds especially often suffer from ringing. These are DJs, road builders, factory workers. However, the causes of whistling in the ear can be serious diseases of the nervous system and hearing aid.
The main health problems associated with noise in the head are:
- Otitis.
- Stuck and swollen wax plug.
- Diseases of the peripheral nervous system: multiple sclerosis, vestibular neuralgia, herpes infection.
- Diseases of the hearing aid.
- Meniere's disease.
- Motion sickness.
- Lack of vitamins.
- Polyneuropathy caused by intoxication and taking certain medications.
- Diabetic neuropathy.
- Hypertension.
Head injuries
A blow to the skull can damage the temporal bone, which contains important hearing organs and sensory nerves. When they are affected, the patient loses a sense of balance, feels a noise in the head, a hum or a whistle. Nausea and vomiting are also possible. If you have a traumatic brain injury, you should immediately seek medical help.
Otitis
Inflammation of the middle and inner ear, auditory tube is a common cause of ringing in the head. Often occurs after hypothermia or against the background of nasopharyngeal infections in children. Otitis requires treatment with anti-inflammatory drugs: Otinum, Otipax, Sofradex. Sometimes treatment with antibacterial or antifungal drugs by an ENT specialist is necessary. For otitis media, camphor alcohol, which is instilled into the ears, will help relieve inflammation. Timely antibacterial treatment as prescribed by a doctor will prevent complications.
Sulfur plug
Whistling in the ears after swimming is a consequence of wax swelling. In this case, auditory perception is impaired. An ENT doctor will help you pull out the plug with a hook or wash it with a Janet syringe and water. There is a drug on sale for dissolving traffic jams at home, Acerumen.
Nerve diseases
There are many diseases that cause dysfunction of the auditory nerves. This is a herpes infection, and other reasons leading to constant whistling in the ears. A thorough examination is necessary, because the disease can also lead to complete deafness.
In multiple sclerosis, nerve fibers become scarred due to the body's own immune system being overly aggressive against its own tissues. Diagnostics – allowing to visualize foci of connective tissue. For treatment, immunoglobulins, immunosuppressants, interferons, and glucocorticoid hormones are used.
Herpetic infection affects nerve fibers. To identify it, PCR tests and serology are required. Antiviral drugs (Acyclovir, Valacyclovir), interferons, and immunostimulants are used in treatment.
Meniere's disease
The pathology is caused by an anomaly in the structure of the vestibular apparatus, as a result of which the pressure of the fluid – endolymph – increases in the auditory labyrinth. In this case, the patient complains of whistling in the ears and imbalance. The problem can lead to deafness. Treatment: use of Betahistine, and, if necessary, surgery.
Motion sickness
When traveling by plane, train, ship and other types of transport, the vestibular system suffers increased load. To relieve whistling and a feeling of congestion, passengers are given sour caramel or before the trip they are prescribed anticholinergic drugs (Aeron) and homeopathic remedies (Aviamore).
Avitaminosis
Polyneuropathy
Occurs with metabolic diseases (diabetes mellitus), intoxication with heavy metals, for example, lead. Taking ototoxic drugs contributes to the appearance of whistling. These are contraceptives that can cause otosclerosis, aminoglycoside antibiotics (Gentamicin), Metronidazole, Fluoroquinolones. Unpleasant symptoms may require discontinuation of medications and replacement with others.
Useful information about why: causes, diagnosis, solutions to patients' problems.
Note: reasons and... When a symptom becomes dangerous.
Everything about the feeling: main causes, symptoms, diagnosis, what the symptom says.
Hypertension and cerebrovascular accident
High blood pressure often causes hearing impairment, including whistling. Taking antihypertensive medications will relieve these symptoms. Beta blockers, calcium antagonists, and diuretics are used. Doctors prescribe a diet that limits salt.
Poor blood circulation in the head occurs with neuroinfections (meningitis), hypertension, atherosclerosis of the carotid arteries and cerebral vessels. For inflammatory diseases, antibiotics and diuretics are used to relieve symptoms of intracranial hypertension.
In atherosclerotic processes, blood circulation is restored with the help of vasodilators that dilate blood vessels: Cavinton, Betagistin, Stugeron. A diet excluding refined, floury foods is also prescribed to reduce cholesterol levels. Vitamin therapy will help reduce the level of homocysteine - the culprit of vascular diseases.
Preventing whistling in the ears
To prevent whistling in the ears, the patient should reduce the intake of foods high in salt, listen to music at a moderate volume to prevent hearing damage, set aside a couple of free minutes every day to be in silence, and drink a glass of water with lemon juice every day.
Whistling in the ears is often just a manifestation of another ailment, so you should never self-medicate. When the first unpleasant sensations appear, consult a doctor who will make the correct diagnosis and prescribe the appropriate treatment.
Treatment
If you feel whistling in your ear, immediately contact your doctor, who will prescribe treatment in accordance with all rules and regulations. The doctor will conduct an examination (X-ray, general blood test, coordination, etc.) and prescribe the necessary treatment.
For people who constantly have whistling in their ears, doctors recommend:
- limit salt intake, as salt impairs blood circulation;
- normalize blood pressure;
- do not listen to loud music;
- do not drink coffee, alcohol, tobacco;
- get more rest.
In some cases, treatment may include surgery. Surgical interventions can be divided into two groups:
- impact on the nerves of the tympanic cavity, on paravertical nerve endings;
- impact on various structures of the hearing organs.
It is not uncommon for hearing-improving surgeries such as tympanoplasty to help eliminate whistling and tinnitus. In cases where whistling and tinnitus do exist, the doctor prescribes special ear medications that have a beneficial effect on the ear and the entire body.
Whistling in the ears and head - treatment
The causes of the ringing in the head are clear, but there is no treatment yet. Treatment for this condition will depend on the specific illness that caused the whistling in the head. In addition to treating the underlying disease, the doctor will prescribe medications to normalize cerebral circulation. A course is often carried out using nootropic medications and antihistamines.
Physiotherapy also plays an important role. It is based on the following procedures:
- laser treatment;
- the use of electrophoresis;
- air massage in the area of the eardrum.
Treatment of noise in the head with cervical osteochondrosis involves physical exercise. In addition, you will probably have to take chondroprotectors.
For atherosclerosis, it is recommended to normalize the level of cholesterol in the blood and strengthen the blood vessels of the brain. For these purposes, the following medications are prescribed:
- Calcium antagonists help strengthen blood vessels, make them more flexible and improve metabolism in the body.
- Herbal preparations, such as Ginkgo biloba, which can improve the nutrition of gray cells, accelerate blood microcirculation, and prevent platelet aggregation.
- Nicotinoids dilate blood vessels and have a general strengthening effect.
Determining the causes and treating whistling in the ears and head is important for a person’s future life, because the phenomenon not only worsens the quality of life, but is also fraught with its consequences.
Ear whistling is not an independent disease, it is only a symptom of some pathology. The following tips will help as auxiliary methods in treatment:
- Reduce salt intake in your diet.
- Lemon juice diluted with water is beneficial.
- Food must contain sufficient amounts of iodine.
Before treating whistling in the ears and head, it is necessary to discover its root cause. This can only be done by a doctor specializing in this field. After diagnosis, the patient must follow the following rules:
- You should not be in a place where there is constant hum and rumble, or listen to loud music;
- for hypertension, it is necessary to constantly monitor blood pressure, avoid eating salt and be in complete silence for an hour;
- Be sure to perform exercises that normalize blood circulation;
- do not drink drinks such as tea, coffee, alcohol;
- quit smoking;
- set aside more time for rest.
Treatment is carried out depending on the factor that caused whistling in the ears:
- The sulfur plug is washed out using a solution of Remo-Vax or A-cerumen.
- Otitis media is treated with antibacterial drops, along with which painkillers and antipyretics are prescribed. This therapy helps to get rid of discomfort in the head.
- For tinnitus resulting from influenza or other infectious diseases, as well as inflammation of the throat, medications that have antibacterial properties are prescribed. In this case, it is necessary to carefully follow all the recommendations of doctors regarding the use of antibacterial agents, since most of them have an ototoxic effect.
- Along with drug therapy, the patient is prescribed physiotherapeutic procedures such as:
- electrophoresis;
- laser therapy;
- air massage.
- The discomfort associated with headaches due to hypertension can be relieved with medications that lower blood pressure.
There are situations when a patient is prescribed surgical intervention, most often this occurs with a head injury. In this case, the nerve endings in the eardrum or other structures of the hearing organs are affected. Very often, after such an operation, the whistling disappears immediately. If this symptom remains unchanged, then medications are prescribed to help restore not only hearing, but the entire body as a whole.
Foreign bodies in a child’s ear, and this could be a small part of a toy or an insect, cannot be removed independently. Such actions can only harm the baby by damaging the eardrum. To prevent this from happening, such an operation should be performed by an otolaryngologist.
Treatment
The treatment method directly depends on the provoking factor or cause of the disease that could provoke whistling in the ears:
| Cause of whistling in the ears | Treatment method |
| Diseases of the otolaryngological organs of an inflammatory and infectious nature | Depending on the form and severity of the condition, the patient is prescribed antibiotics (Levomycetin, Ceftriaxone, Ampicillin), immunomodulators (Immunal, Cycloferon, Arbidol) and vitamins |
| Tumor neoplasms | Surgical intervention with complete resection of the tumor causing whistling in the ears |
| Foreign bodies in the ear canal | Special tools are used to remove foreign objects. The procedure is only allowed to be performed by doctors, as there is a risk of damage to the eardrum |
| Sulfur plug | To get rid of a plug that has partially or completely blocked the ear canal, rinsing is carried out with special solutions. At home, you can use a syringe without a needle and clean water. |
| Blood pressure surges | Taking medications aimed at normalizing blood pressure |
| Cerebrovascular accident | Complex therapy with vascular drugs |
| Osteochondrosis of the cervical spine | Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs, massage |
| Headache | Analgesic and antispasmodic drugs |
| Vasospasm | Taking vasodilators and sedatives |
The table does not include the names of medications for some cases, since independent use of these groups of drugs can aggravate the situation. Medicines used to treat the heart and blood vessels should only be prescribed by a specialist.
To get rid of whistling in the ears, folk methods are used. You can eliminate hissing and other unpleasant sounds:
- Special massage. It is recommended to carry out circular movements in both directions, placing your palms to your ears. At the end of the procedure, you should firmly press your ears to your head with your hands and sharply move them away.
- Tampons soaked in a solution of olive oil and propolis in a ratio of 4:1. It is recommended to insert them before bed and remove them the next morning.
- Infusion of dry dill. To prepare the medicinal product, take 2 tbsp. l.raw materials in powder form, pour a liter of boiling water and leave to infuse for 1 hour. The resulting drink should be drunk 2 times a day, half a glass.
- A mixture of garlic, cranberries and natural honey. You will need 200 g of garlic, 1 kg of cranberries and 500 g of honey. The first two components are ground in a blender and left to brew for a day in the refrigerator. Then honey is added to the resulting mixture, everything is mixed and consumed 30 minutes before meals, 2 times a day.
To get rid of unpleasant sensations, treatment with folk remedies alone is not enough. It is imperative to consult an ENT doctor to determine the exact causes.
If you ignore the problem, there is a risk of developing serious consequences. Over time, hearing loss may appear on the left or right side, or hearing may completely disappear. This is especially observed when tumors reach an inoperable size.
A phenomenon such as whistling in the ear is not a disease, but a symptom indicating that there is a pathology in the body. The whistle can be true or false. A false whistle occurs in a person who is very nervous or under stress, but it only seems to him that there is a whistle in his ears. This phenomenon also occurs in people suffering from mental illness. But a true whistle resembles a buzzing or hissing, which quite often turns into a squeak or hum. A true whistle is also a pulsating one that is combined with the blood pulse.
A loud sound that affects the hearing for a long time can cause a whistle. Over time, whistling in the ears, the causes of which have been eliminated, goes away on its own, but if the source of the loud sound is not removed, the whistling will continue. This is evidence that the auditory analyzer is affected.
Another cause of true whistling is due to otitis media or trauma, as well as damage to the middle or inner ear. In this situation, whistling in the ears is complicated by pops or clicks. The cause of the whistling can also be a sulfur plug or a foreign object blocking the passage.
In old age, in people with vascular diseases, the auditory nerve is destroyed. In this case, whistling in the ears is accompanied by hearing loss, and otosclerosis may develop. In hypertensive patients, when pressure increases, an uneven, two-way whistle appears against the background of hissing, coinciding with the pulse. A high-frequency and constant whistling sound that exhausts a person may be evidence of a tumor that has formed in or in the auditory analyzer of the brain. Whistling in the ears is accompanied by migraine-like pain, a person experiences weakness and fatigue, as well as nausea accompanied by vomiting.
Whistling can be caused by diseases such as influenza, ARVI, sinusitis, pneumonia, and meningitis. This phenomenon disappears when the disease is cured, but before treating the causes of whistling, you need to consult a doctor and undergo an examination. But there are general recommendations that must be followed:
The ears need maximum comfort, that is, no loud sounds, music or noise.
If you have hypertension, you need to monitor your blood pressure and treat the disease.
Three times a day, give your ears the opportunity to completely rest for at least fifteen minutes.
Do exercises that involve alternately tensing and relaxing the ear muscles.
Whistling in the ears can also be treated with folk remedies:
1. Pour a tablespoon of lemon balm into one glass of boiling water, leave for thirty minutes, filter and take half a glass three times during the day. You need to drink lemon balm for three weeks.
2. Make a hole in the peeled onion, pour a teaspoon of cumin seeds into it, cover with cotton wool and bake in the oven. The resulting juice should be instilled five to seven drops at least twice a day.
3. Grind a clove of garlic, add three drops of camphor oil to it, wrap it in gauze in the form of a small tampon and place it in the ear for about fifteen minutes before going to bed.
4. Boiled beets are grated and squeezed, and the juice is dripped into the ears two or three times a day, three drops each. This procedure can be combined with drinking fresh beet or cranberry juice, which should be taken in three or four tablespoons.
5. Finely chopped raw potatoes with honey are wrapped in gauze and placed in the ears for one hour before going to bed.
It should be remembered that no medicine should be prescribed independently. Without the recommendation and consultation of an experienced doctor, you can irreversibly damage your health.
Each of us has at least once experienced the sensation of noise and whistling in the ears. The whistling can last from a few seconds to several days or even weeks.
When it does not disappear for a long time, a person’s sleep is disturbed, performance deteriorates and hearing decreases.
There are many reasons that can cause whistling in the ears:
- inflammatory processes in the ear;
- blockage of the ear canal;
- use of certain medications;
- damage to the auditory analyzer;
- barotrauma;
- hypertonic disease;
- tumor of the middle ear or central auditory analyzer;
- influenza, ARVI, meningitis, allergic diseases;
- narrowing of the blood vessels of the head and neck.
Preventive actions
It is clear that the causes and treatment of whistling in the head are interconnected. But here's what to do with prevention. If you are a sensitive person or have a history of tinnitus, you should wear headphones or earplugs in noisy areas. When listening to music, do not play it too loudly; the sound should not exceed 40 dB.
If you are included in the category of hypertensive patients, as well as if you are diagnosed with atherosclerosis, you should give up foods such as chocolate and coffee, or at least reduce their consumption. Smoking is highly discouraged. To strengthen blood vessels and prevent ringing in the head, you need to more often include sea fish rich in Omega-3 acids and natural dairy products in your diet.
A calm environment during the day, the absence of stress, overwork and overexcitement will help you avoid evening noise in your head. It is necessary to get a good night's sleep and allocate sufficient time for rest.
To improve overall health, it is recommended to move more, walk in the fresh air and give up bad habits.
It is worth noting that noise and ringing in the ears most often bother older people. Therefore, for preventive purposes, after 40 years, you should undergo an annual medical examination at your place of residence. Such methods make it possible to identify diseases at an early stage and quickly eliminate them. Then a person will not have a question about how to get rid of the whistling in his head.
- What causes whistling in the ears
Physiological causes of the disease
Finding the causes of whistling in the ears and eliminating unpleasant symptoms is the primary task of the doctor and the patient. It is necessary to find out why sound phenomena and accompanying signs appeared. Whistling occurs for the following reasons.
Long-term sound exposure
Listening to music at full volume, a sharp loud beep, siren, music in headphones. The phenomenon goes away on its own.
After attending events with loud rhythmic music, there is ringing, whistling and other sound effects in the ear canal. The patient is diagnosed with acoustic injuries of varying severity. The symptoms go away on their own after some time. If the sensations continue to bother you for a long time, then it is better not to go to such events. The appearance of congestion in the ears, a persistent whistling indicates the beginning of inflammatory processes inside. Long and frequent exposure to aggressive sounds can result in deterioration in the quality of hearing.
It's not just loud music that causes symptoms. Consumption of energy drinks that overstimulate the nervous system. Accordingly, the nerve endings of the inner ear are irritated and auditory hallucinations occur.
Violation of the integrity of the tympanic cavity as a result of exposure to very loud sounds, sharp signals, and air pressure.
Occupational hearing loss causing buzzing sounds. Noise effects occur among workers in production, construction, wherever there is a constant loud hum.
Blocking a channel
The appearance of a foreign body or cerumen plug in the ear canal. It does not form on its own. As a rule, the cause is improper ear cleaning. Sulfur is designed to protect the internal cavity from external influences. Thanks to the movement of the jaw, the discharge moves independently through the ear canal. When cleaning with a cotton swab, part of the sulfur is removed, and the other part is driven deep into the eardrum.
First there is a feeling of stuffiness in the ear. If action is not taken to eliminate the cause, other symptoms appear: whistling, clicking, ticking, squeaking. Correcting the situation is best done with medical help to prevent internal damage and the occurrence of inflammatory processes.
Hearing diseases
More often caused by damage to the eardrum, rupture, inflammation and purulent processes. Ear diseases manifest themselves as pain. The noise is perceived in the form of a whistle, fluid transfusion, or congestion.
Otitis is a disease that causes ringing and whistling in the head. Inflammatory processes affecting the middle ear, inner ear, and tubes. The factors that caused otitis media are associated with hypothermia, infection in the child’s nasopharynx.
An inflamed auditory nerve causes a disease - neuritis. It contributes to various auditory phenomena from quiet noise to a sharp whistle.
Patient age
Older people are more likely to have hearing problems, blood circulation is impaired, and atherosclerosis occurs. The temporal part of the head suffers from pain and whistling in the ears due to liver or kidney failure.
Colds, allergies
The structure of the ENT organs suggests a close relationship between the nose, throat and ear. Infections that enter one of the organs move freely to others. The patient coughs, blows his nose, sneezes - these are signs of the virus in the body.
A cold causes nasal congestion, and a whistling noise appears when you blow your nose.
Eustachitis occurs when an infectious disease spreads to the entire ear-nose-throat system. With this pathology, patients experience heaviness in the head, the echo of their own voice is heard in the canal, extraneous sounds in the ear, and the quality of hearing decreases.