Organic mental disorders account for one third of the total number of diagnosed mental disorders.
Such a high percentage is due to frequent cases of injuries , domestic, industrial, as a result of road accidents, as well as adverse environmental impacts.
How do these disorders manifest themselves, what are their symptoms and treatment prognosis?
What is transient personality disorder? Read about it here.
Clinical picture
Patient complaints of increased fatigue during mental activity are typical. Memory impairment (difficulty in memorizing and reproducing new material), impaired thinking (difficulty in formulating general and abstract ideas), general confusion, and impaired concentration are noted. There may be difficulty understanding speech and choosing words.
Symptoms of the disease increase with intense intellectual stress, their manifestations disappear or decrease after rest.
Symptoms
At the beginning of its course, these diseases are characterized by the following signs :
- sharpening the most striking character traits inherent in a given person,
- viscosity of thinking, slow comprehension of the current situation, inhibition of mental processes,
- prolonged tension, a melancholy state, subsequently discharged by a flash of anger,
- elevated mood, a state of euphoria for no significant reason.
At later stages, the following manifestations are observed:
- apathy and indifference to what is happening in the outside world,
- changeable mood without good reason,
- low affective threshold, rage and aggression are caused by insignificant reasons,
- loss of control over impulses, pronounced impulsiveness,
- inability to predict one's own behavior in relation to other people,
- paranoid behavior traits,
- flat jokes, monotonous statements, impoverished associative series.
Subsequently, there may be a disturbance in motor activity, and significant difficulties with memorizing new material and its subsequent reproduction.
Treatment of mild cognitive impairment
- Drug therapy (nootropics, melatonin preparations).
- Individual psychocorrection.
- Stimulation of mental activity.
Treatment is prescribed only after confirmation of the diagnosis by a medical specialist.
Essential drugs
There are contraindications. Specialist consultation is required.
- (nootropic drug). Dosage regimen: orally with liquid at a dose of 2.4-4.8 g/day. in 2-3 doses.
- (neurotransmitter). Dosage regimen: orally, 15-30 minutes. before meals in a dose of 1.0 g 2-3 times a day.
- (metabolic, nootropic agent). Dosage regimen: orally, during or after meals, 2 tablets. or 2 teaspoons of suspension 3 times a day (600 mg/day).
- Melatonin (adaptogenic, hypnotic, antioxidant). Dosage regimen: orally at a dose of 1.5-3 mg 1 time/day. in 30-40 minutes. before sleep.
- (a drug that improves cerebral circulation). Dosage regimen: orally, during meals, with 1/2 glass of water, 1 tablet. 3 times a day. The course of treatment is at least 3 months.
Important! Be sure to check out this material! If after reading you still have any questions, we strongly recommend that you consult with a specialist by phone:
The location of our clinic in the park has a beneficial effect on the state of mind and promotes recovery:
This category includes mixed conditions that are causally related to brain disorders due to a primary brain disease, a systemic disease secondary to the brain, exposure to exogenous toxic substances or hormones, endocrine disorders, or other physical diseases.
Excluded: related to:
- delirium (F05.-)
- dementia classified under F00-F03
due to the use of alcohol and other psychoactive substances (F10-F19)
Diagnosis F 06.0 Organic hallucinosis
A disorder characterized by persistent or recurrent hallucinations, usually visual or auditory, that occur during clear consciousness and may not always be recognized as such by the patient. A delusional interpretation of hallucinations may be noted, but delusions do not dominate the clinical picture; awareness of the surroundings can be maintained.
Organic hallucinatory state (non-alcoholic)
Excluded:
- alcoholic hallucinosis (F10.5)
- schizophrenia (F20.-)
Prevention
Prevention should consist of creating a positive climate in the family, first of all. All conflicts must be resolved without quarrels and loud shouting. Then the child will not be subject to stress and constant nervous tension, so the risk of developing a pathology such as organic emotional labile asthenic disorder will be minimized.
It is also recommended that all people maintain a healthy lifestyle, monitor their diet, and periodically take a break from work. It is important to maintain composure in difficult life situations.
Diagnosis F 06.2 Organic delusional [schizophrenia-like] disorder
A disorder in which the clinical picture is dominated by persistent or recurrent delusions. Delusions may be accompanied by hallucinations. There may be some symptoms that make you think you have schizophrenia, such as bizarre hallucinations or disordered thinking.
Paranoid and paranoid-hallucinatory organic states
Schizophrenia-like psychosis in epilepsy
Excluded: disorder:
- acute or transient psychotic (F23.-)
- persistent delusional (F22.-)
- drug-induced psychotic (F11-F19 with common fourth character.5)
schizophrenia (F20.-)
Diagnosis F 06.7 Mild cognitive impairment
A disorder characterized by decreased memory, difficulty learning, and decreased ability to concentrate on a task for long periods of time. There is often a pronounced feeling of mental fatigue when trying to solve a mental problem; learning new things seems subjectively difficult, even when objectively it is successful. None of these symptoms are severe enough to warrant a diagnosis of dementia (F00-F03) or delirium (F05.-). This diagnosis should be made only in connection with a specified physical disorder and should not be based solely on the presence of any mental or behavioral disorders classified in categories F10-F99. The disorder may precede, accompany, or follow a wide range of infectious and somatic diseases (both cerebral and systemic), but there does not necessarily need to be direct evidence of brain involvement. This disorder can be differentiated from post-encephalitic syndrome (F07.1) and post-concussion syndrome (F07.2) by its different etiology, more limited range of mostly mild symptoms and usually short duration.
Reasons for the development of pathology
Organic emotionally labile asthenic disorder (f 06.68 in ICD-10) can develop for many reasons. In medicine, it is generally accepted that the disease develops as a result of a serious illness that has lasted a long time, hypertension, cerebrovascular accident, dyscirculatory encephalopathy, and cerebrovascular diseases. Pathology can also appear due to prolonged overexertion and conflicts. Typically, such a disease in medicine is considered one of the first signs of the development of psychoneurological pathologies.
In this case, organic emotional labile asthenic disorder can be observed for several months or even years. It requires therapeutic intervention, since it does not go away on its own even after the person has had a good night's sleep.
The main reasons for the development of the disease include:
- Disorder of metabolic processes in the body.
- Overstrain of the central nervous system.
- Insufficient intake of vitamins and nutrients into the body.
- Hypertension and arrhythmia.
- Neurological disorders.
- Infectious diseases.
- Various injuries.
- Degenerative changes in the body.
- Severe diseases of vital organs.
- Prolonged physical and mental stress without rest.
- Constant lack of sleep.
- Epilepsy, HIV.
- Neuroinfections.
- Benign or malignant brain tumors.
- Encephalitis, chronic depression.
- Repeated use of anesthesia.
Organic emotionally labile asthenic disorder in children may appear for the following reasons:
- Hereditary predisposition.
- Severe stress or emotional distress.
- Lack of proper sleep and rest.
- Poor family environment.
- Heavy workload at school.
Symptoms of organic asthenic disorder
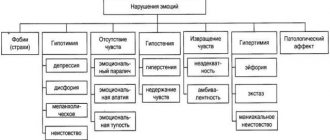
People with the disorder are characterized by tearfulness, emotional irascibility, frequent and severe mood swings, and a storm of emotions, often over a minor issue. All reactions are spontaneous (occur without a serious reason or reason) and uncontrollable.
A person reacts painfully even to minor events; emotions, as a rule, are negative (anger, irritation, resentment).
He perceives troubles as “the end of the world”, constantly having outbursts of anger and irritability towards loved ones and surrounding people.
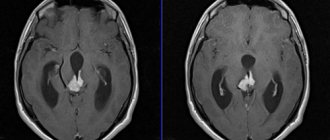
Diagnosis of organic emotionally labile disorder - examination by a psychiatrist and neurologist. Additionally, the attending physician may prescribe a pathopsychological examination, blood tests and instrumental methods (EEG, CT, MRI).
A person complains of regular and severe headaches, dizziness, decreased or blurred vision, increased blood pressure, and tinnitus. These complaints indicate a brain disease that has led to an organic emotionally labile disorder. They interfere with a person’s life and work, and because of them he goes to the doctor.
Hypersensitivity is characteristic - pain sensitivity in response to a slight touch on the skin, excessive auditory or light sensitivity, when ordinary sounds are perceived as very loud (up to the development of pain), and sunlight causes severe lacrimation and pain in the eyes.
General weakness, rapid fatigue, decreased performance, a feeling of powerlessness - all these are integral companions of organic asthenic disorder.
Organic emotionally labile asthenic disorder in children occurs due to severe pregnancy of the mother (toxicosis, threatened miscarriage, eclampsia), complications during childbirth or severe diseases of early childhood.
An experienced psychiatrist can make a diagnosis during the first examination. The main manifestations of asthenic disorder include excessive moodiness, frequent tearfulness, disobedience, irritability, and inability to concentrate for a long time. Such children may develop sudden lethargy and lack of initiative. It is necessary to differentiate an emotionally labile disorder from character traits and age-related changes.
The prognosis for adults and children is favorable if the recommendations of the attending physician are followed.
Characteristics and description of the problem
Organic emotional labile asthenic disorder (asthenia) is a neurological disease that is associated with severe exhaustion of the body, loss of the ability to perform physical activity and mental work. The pathology is also manifested by increased fatigue and irritability. This condition is accompanied by the appearance of somatic diseases and mental disorders.
The disease is characterized by decreased performance, fatigue, aggressiveness, sleep disturbance, lack of self-control, as well as an increased reaction to bright lights, strong smells and loud sounds, pain in the muscles or throughout the body. Code in ICD-10 - F 06.68 - organic emotionally labile asthenic disorder
Symptoms of the pathology can appear in absolutely healthy people as a result of prolonged mental or physical stress. It occurs in the form of a persistent feeling of weakness, chronic fatigue. Fatigue is felt constantly. From the moment of awakening, a person feels exhausted, he becomes irritable, moody and tearful.
In fact, there are many reasons for the development of the disease. Most often this is prolonged overexertion, stress, and conflicts.