Lesions of the central nervous system: at what stages of pregnancy?
Damage to the central nervous system in a child occurs in two ways - in utero or during childbirth.
If developmental abnormalities occur in the fetus during the embryonic stage of intrauterine development, they often turn into defects that are incompatible with life, or are extremely severe and cannot be treated or corrected. If a damaging effect was exerted on the fetus after the eighth week of pregnancy, this will not affect the child in the form of gross deformity, but may well cause minor deviations that will have to be treated after birth. The negative impact on the fetus in the later stages - after the twenty-eighth week of pregnancy - will not manifest itself in the form of defects at all, but can become a catalyst for the occurrence of diseases in a normally formed child.
It is very difficult to predict which specific negative factor and at what stage of pregnancy will cause irreparable damage to the fetus. Therefore, the expectant mother needs to be extremely careful and monitor her health even before the moment of conception. Preparing for pregnancy is an important stage of family planning, because the child’s health can be affected by both the bad habits of the mother and her chronic diseases, hard work and unhealthy psychological state.
How exactly he is born is also important for the child’s future life. It is at the moment of birth that there is a danger of damage in the second way - intranatally. Any incorrect intervention or, conversely, lack of timely assistance is highly likely to have a negative impact on the baby. At risk are premature birth, as well as birth at the scheduled time, but rapid or, conversely, protracted.
The main causes of central nervous system damage in newborns are oxygen starvation, which leads to hypoxia, and birth trauma. Less obvious and diagnosable causes are less common: intrauterine infections, hemolytic disease of the newborn, malformations of the brain and spinal cord, hereditary metabolic disorders or chromosomal pathology.
Doctors identify several syndromes of central nervous system pathology in newborns.
Mechanism of damage
Residual damage to the central nervous system is always caused by unfavorable factors that preceded it. In most cases, the basis for the pathogenesis of such symptoms is cerebral ischemia. In children, it develops during the period of intrauterine development. Due to insufficient blood supply to the placenta, the fetus receives little oxygen.
As a result, the full development of nervous tissue is disrupted, and fetopathy occurs. Significant ischemia leads to intrauterine growth retardation and the birth of a child before the gestational age. Symptoms of cerebral hypoxia can appear already in the first days and months of life. Residual organic damage to the central nervous system in adults often develops due to traumatic and infectious causes. Sometimes the pathogenesis of nervous disorders is associated with metabolic (hormonal) disorders.
One of all the “inconsistencies” of the disease is the fact that a disorder of this type belongs to neuropathology, but its symptoms may relate to other branches of medicine.
Due to an external factor, the mother experiences disruptions in the formation of the phenotype of cells that are responsible for the full list of functions of the central nervous system. As a result, fetal development is delayed. It is this process that can become the last link on the path to central nervous system disorders.
Regarding the spinal cord (this is also part of the central nervous system), corresponding lesions can appear as a result of incorrect obstetric care or inaccurate turns of the head when delivering the child.
Causes of central nervous system damage
The reasons why perinatal damage to the central nervous system may develop are quite varied, among the most popular:
- somatic disease of the mother, which is accompanied by chronic intoxication;
- the presence of acute infectious diseases or chronic foci of infection while the expectant mother was carrying the child;
- if a woman’s nutritional process is disrupted, or she is not ripe for pregnancy and childbirth;
- changes in metabolism or the presence of a hereditary factor also entail a disorder of the nervous system in the unborn child;
- in case of severe toxicosis, both at an early stage and at a late stage, or the appearance of other problems with bearing a child;
- the environment is an important factor in the development of the disease;
- the appearance of pathology during childbirth - this may be weak labor, accelerated labor;
- if a child is born premature, then his body is not fully developed, therefore, against this background, a disturbance in the functioning of the central nervous system may appear;
- Children who have a hereditary factor are at greatest risk of developing central nervous system lesions.
All other causes of PPCNS are situational and, to a greater extent, their occurrence is simply impossible to predict.
Prevention
Prevention of pathologies from the central nervous system in a child is the task of the expectant mother. At risk are women who do not give up bad habits while carrying a baby - smoking, drinking alcohol or using drugs.
All pregnant women must be registered with an obstetrician-gynecologist in the antenatal clinic. During pregnancy, they will be asked to undergo so-called screening three times, which identifies the risks of having a child with genetic disorders from that particular pregnancy. Many gross pathologies of the fetal central nervous system become noticeable even during pregnancy; some problems can be corrected with medications, for example, disturbances in uteroplacental blood flow, fetal hypoxia, and the threat of miscarriage due to a small detachment.
This will avoid metabolic disorders in the baby. You should be especially careful when choosing a maternity home (the birth certificate that all pregnant women receive allows you to make any choice). After all, the actions of personnel during the birth of a child play a large role in the possible risks of traumatic lesions of the central nervous system in the baby.
After the birth of a healthy baby, it is very important to regularly visit the pediatrician, protect the baby from injuries to the skull and spine, and get age-appropriate vaccinations that will protect the little one from dangerous infectious diseases, which at an early age can also lead to the development of pathologies of the central nervous system.
In the next video you will learn about signs of a nervous system disorder in a newborn, which you can determine yourself.
Why do you need a tiny pocket on jeans? Everyone knows that there is a tiny pocket on jeans, but few have thought about why it might be needed. Interestingly, it was originally a place for storage.
9 Famous Women Who Have Fallen in Love with Women Showing interest in people other than the opposite sex is not unusual. You are unlikely to be able to surprise or shock anyone if you admit it.
What does your nose shape say about your personality? Many experts believe that you can tell a lot about a person's personality by looking at their nose. Therefore, when you first meet, pay attention to the stranger’s nose.
Charlie Gard Died A Week Before His First Birthday Charlie Gard, the terminally ill baby the world is talking about, died on July 28, a week before his first birthday.
15 Cancer Symptoms Women Most Often Ignore Many signs of cancer are similar to symptoms of other diseases or conditions, which is why they are often ignored. Pay attention to your body. If you notice.
13 signs that you have the best husband Husbands are truly great people. What a pity that good spouses don't grow on trees. If your significant other does these 13 things, then you can s.
Increased intracranial pressure: symptoms
Hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome is an excessive accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles and under the meninges. To identify this syndrome in an infant, an ultrasound scan of the brain is performed and data on increased intracranial pressure are recorded (according to echoencephalography - EEG).
In pronounced severe cases of this syndrome, the size of the brain part of the skull increases disproportionately. As is known, children are born with mobile bones of the skull, which fuse during development, therefore, with a unilateral pathological process of this syndrome, divergence of cranial sutures, thinning of the skin in the temporal lobe and increased venous pattern on the scalp will be observed.
If a child has increased intracranial pressure, he will be restless, irritable, easily excitable and whiny. Also, the baby will sleep poorly, roll his eyes and throw his head back. Graefe's symptom (a white stripe between the pupil and the upper eyelid) may occur. In more severe cases, there may also be a symptom of the so-called “setting sun”, in which the iris of the eye, like the sun at sunset, is half submerged under the lower eyelid. Convergent strabismus also sometimes appears.
With reduced intracranial pressure, on the contrary, the child will be inactive, lethargic and drowsy. Muscle tone in this case is unpredictable - it can be either increased or decreased. The baby may stand on tiptoes when supported, or cross his legs when trying to walk, while the baby’s support, crawling and walking reflexes will be reduced. Seizures can also often occur.
Classification and types of syndromes
The tendency to have seizures in the first months of a child’s life is due to immaturity of the brain. Convulsions occur only in cases where the spread or development of a disease process in the cerebral cortex occurs, and have many different causes.
In each specific case, the cause of the convulsive syndrome must be identified by a doctor. Effective assessment often requires a number of studies and manipulations: instrumental studies of brain function (EEG), brain circulation (Dopplerography) and anatomical structures (brain ultrasound, computed tomography, NMR, NSG), as well as biochemical blood tests.
From the point of view of localization, cramps are not the same - they can be generalized, that is, covering the entire body, and localized, which are associated with individual muscle groups.
Convulsions are also different in nature: tonic, when the child seems to stretch out and freeze for a short time in a certain fixed position, and clonic, in which twitching of the limbs and sometimes the entire body occurs.
Parents should carefully monitor their child in the first months of life, because... convulsions in children can become the onset of epilepsy if you do not immediately contact a specialist and do not carry out proper treatment. Careful observation and a detailed description of emerging seizures on the part of the parents will greatly facilitate the doctor’s diagnosis and speed up the selection of treatment.
Classification of the consequences of perinatal lesions of the nervous system in children of the first year of life (Russian Association of Perinatal Medicine Specialists, 2005) [8] is presented in Table. 1.
Table 1 - Classification of the consequences of perinatal lesions of the nervous system in children of the first year of life (Russian Association of Perinatal Medicine Specialists, 2005)
| Etiology and pathogenetic basis | Clinical course options | Main nosological forms | Outcomes |
| Consequences of perinatal damage to the central nervous system of hypoxic-ischemic origin (Cerebral ischemia of II-III degree) Intracranial non-traumatic hemorrhage in the fetus and newborn, grade II, III) (P91.0, P91.1, P91.2, P91.5, P91.8, P52.1-P52.9) P94.2 Congenital hypotonia Syndrome of nonspecific lethargy of the child | Perinatal persistent posthypoxic and/or posthemorrhagic damage to the central nervous system | G81.0 Flaccid hemiplegia G82.0 Flaccid paraplegia G82.3 Flaccid tetraplegia | Neurological abnormalities are not compensated for by the first year of life. Total or partial neurological deficit persists. |
PPCNSL is conventionally divided into several periods, depending on at what stage the disorder was identified and how it manifested itself.
The acute period lasts from 7 to 10 days, extremely rarely, but it can last up to a month. The period during which recovery occurs can last up to six months. If the child’s body recovers slowly, this period may take up to 2 years.
Pediatric neurologists distinguish the following types of perinatal lesions of the central nervous system, depending on the accompanying symptoms and syndrome:
- Violation of muscle tone, which is accompanied by a complex of disorders associated with breathing. This syndrome is diagnosed according to abnormalities depending on the age of the newborn. In the initial period of a child’s life, it is quite difficult to diagnose this syndrome, since in addition to this, physiological hypertonicity occurs.
- Syndrome associated with sleep disturbances and chin twitching. This syndrome can be diagnosed only when flatulence is excluded.
- Depression of the nervous system. This syndrome is diagnosed in children who are not active in the first months of their lives, they sleep a lot, and have decreased tone.
- An unfavorable prognosis for a child if intracranial hypertension syndrome develops. Its main signs are increased excitability and nervousness, and the fontanel begins to swell.
- One of the most dangerous and severe syndromes in PPCNSL is convulsive, which is one of the most serious manifestations of perinatal damage to the central nervous system. In addition, any attentive mother can notice deviations in her child’s health much faster than a neurologist, if only because she monitors him around the clock and more than one day.
In any case, a baby living for the first year with any (even minimal, but not passing) deviations in health requires repeated consultations with specialists (if necessary, additional examination), careful observation and therapeutic measures if necessary.
Clinical picture of acute hypertension
Organic diseases of the central nervous system in early childhood can only be detected by a specialist. In this case, the main signs are:
- the child is in a state of hypertonicity (increased muscle activity);
- disturbance of movements of the eyeballs;
- chaotic motor activity and involuntary head movement.
After one year of age, the following symptoms become evident in a child:
- Mental retardation. Manifests itself as a lack of attention to the environment. The child does not follow the toys and does not respond to requests, in most cases does not utter the first words.
- Delayed physical development. With this diagnosis, the child does not hold his head up and does not attempt to crawl or walk.
In older childhood, suppression of brain activity does not allow one to study well on a par with peers. The child quickly gets tired and exhibits symptoms of emotional instability (mood variability). In some cases, the psychoemotional state is disrupted, manifesting itself as psychopathy and depression.
Symptoms in adults develop gradually. Initially, this manifests itself as absent-mindedness, the patient’s memory deteriorates, and the ability to remember text and current events decreases.
List-list of the main symptoms of organic damage to the central nervous system in adults.
| Number in order | Type of manifestation | Short description |
| 1 | Headache | Depending on which lobe of the brain the affected area occurs, intense spastic pain appears (temporal, frontal or parietal). |
| 2 | Excessive nervousness | In some situations, the feeling of calm is sharply changed by a sudden surge of aggression. The patient's behavior becomes antisocial. |
| 3 | Abrupt increase in intracranial and blood pressure | May lead to headaches, as blood pressure readings may be critical. |
| 4 | Movement disorders | Uncertainty of gait occurs (becomes shaky). Fine motor skills of the hands become impaired, and the ability to hold a book, spoon, or writing utensils is lost. |
| 5 | Epilepsy | Attacks of varying duration and severity occur. |
Most often, symptoms of residual organic damage to the central nervous system appear some time after exposure to an unfavorable factor. With perinatal fetal hypoxia, disturbances can be noticeable already in the first month of life. Depending on the extent of the damage, the following symptoms may be observed:
- Minor damage to nervous tissue: tearfulness, poor sleep, memory loss. At school age, a child may experience attention deficit hyperactivity disorder, a tendency to hysterical states, and phobias.
- Damage to the central nervous system of moderate severity has such manifestations as constant crying, breast refusal, convulsive syndrome, and enuresis.
- In severe cases, focal neurological symptoms are observed. This includes muscle weakness, paresis and paralysis of the limbs, delayed physical and mental development, generalized convulsions, etc.
There are practically no specific symptoms that appear with organic brain damage. This is due to the fact that any manifestation depends on the underlying disease, which led to brain damage.
You can identify symptoms that will be characteristic of almost all concomitant pathologies:
- decreased activity;
- apathy, lack of interest in something;
- sloppiness appears.
Memory loss is a rarer symptom, but also occurs. Patients may forget the names of their relatives or friends, or their appearance. There is a violation of counting and people will not be able to list the numbers from 1 to 10 or remember the sequence of days of the week.
Violations of writing and speech are manifested in the rearrangement of syllables and words. In the most severe cases, a person will not be able to speak independently, but will only be able to repeat a small phrase that he hears. Emotionally, there are several possible outcomes.
Or the person becomes kind of unemotional, reacting to everything too calmly, which can’t help but be noticeable. Or, on the contrary, the manifestation of emotions is inadequate and perverted. Hallucinations may occur.
Criteria for assessing the quality of medical care
Not every mother who does not have a medical education will be able to distinguish and determine at first glance that her child has a perinatal lesion of the central nervous system.
But, neurologists accurately determine the disease by the appearance of symptoms that are not characteristic of other disorders that are characteristic of the youngest patients.
Symptoms of PCNSL:
- When examining the baby, muscle hypertonicity or hypotonicity may be detected;
- the child is excessively restless, anxious and excited;
- the occurrence of shaking in the chin and limbs (tremor);
- the appearance of seizures;
- when examined with a hammer, there is a noticeable loss of sensitivity;
- the appearance of unstable stools;
- heart rate changes;
- the appearance of irregularities on the child’s skin.
As a rule, after a year these symptoms disappear, but then appear with renewed vigor, so this situation simply cannot be neglected.
One of the most dangerous manifestations and consequences of PPCNSL in the absence of a response to symptoms is the suspension of the development of the child’s psyche. The speech apparatus does not develop, and there is a delay in the development of motor skills. Also, one of the manifestations of the disease may be cerebrasthenic syndrome.
There are several ways of development of perinatal damage to the central nervous system in newborns, depending on the cause and subsequent symptoms, the analysis of which allows us to make an initial diagnosis:
- If a lack of oxygen is clearly detected while the baby is inside the mother’s body (hypoxia), then hypoxic ischemic damage to the central nervous system is diagnosed.
- During childbirth, the baby's tissue structure may be damaged (this can be either the brain or the spinal cord). In this case, we are already talking about a traumatic lesion of the central nervous system, resulting in changes in the functioning of the brain.
- In case of metabolic disorders, metabolic and toxic-metabolic lesions may appear. This may be due to the use of alcohol, medications, drugs, or nicotine during pregnancy.
- Changes in the central nervous system in the presence of infectious diseases of the perinatal period.
Table 2 – Organizational and technical conditions for the provision of medical care.
| Type of medical care | Specialized medical care |
| Conditions for providing medical care | Inpatient / day hospital |
| Form of medical care | Planned |
Table 3 – Criteria for the quality of medical care
| № | Quality criteria | Level of evidence | Convincing Level of Recommendations |
| 1. | Completed rehabilitation courses using physical factors, including kinesiotherapy | WITH | 1 |
| 2. | Consultation with a neurologist and/or ophthalmologist and/or educational psychologist and/or neuroorthopedist and/or nutritionist was performed | WITH | 1 |
Rehabilitation period
Damage to the central nervous system in newborns during the recovery period has the following syndromes:
- increased excitability;
- epileptic;
- motor disorders;
- mental retardation.
With prolonged violation of muscle tone, mental development delays and the presence of motor function disorders often occur, which are characterized by involuntary movements provoked by contraction of the muscles of the trunk, face, limbs, and eyes. This prevents the child from making normal, purposeful movements.
When mental development is delayed, the baby begins much later to hold his head up on his own, sit, walk, and crawl. He also has poor facial expressions, decreased interest in toys, a weak cry, and a delay in the appearance of babbling and humming. Such delays in the development of a child’s psyche should definitely alert parents.
Where does regurgitation and tendency to constipation come from?
Autonomic-visceral dysfunction syndrome is characterized by impaired thermoregulation in a child (body temperature rises or falls for no apparent reason), exceptional whiteness of the skin associated with vascular dysfunction, and gastrointestinal disorders (regurgitation, vomiting, a tendency to constipation, insufficient weight gain compared with indicators accepted as the norm).
All these symptoms are most often combined with hypertensive-hydrocephalic syndrome and are directly related to disturbances in the blood supply to the posterior parts of the brain, where all the main centers of the autonomic nervous system are located, which controls the life-supporting systems of the body - digestive, thermoregulatory and cardiovascular.
Complex of therapeutic measures
If a child develops an acute period of illness, he is first sent to the intensive care ward. Diuretics are used in case of suspected cerebral edema - dehydration therapy can be carried out.
Depending on what symptoms the baby has, with the right treatment, you can get rid of seizures, disorders of the respiratory tract and cardiovascular system, and muscle disorders.
If the disease is complicated, the child is fed through a tube. To restore the basic functions of the central nervous system, as well as to reduce the manifestation of neurological symptoms, the baby is prescribed a whole range of drugs:
- to relieve seizures, a course of taking Radodorm, Finlepsin, Phenobarbital may be prescribed;
- if the child periodically regurgitates, Motilium or Cerucal is prescribed;
- if there are disorders of the musculoskeletal system, Galantamine, Dibazol, Alizin, Proserin are prescribed;
- In order to reduce possible hemorrhages, it is recommended to use the drug Lidaza.
Nootropic drugs can also be used in treatment, which can restore trophic processes in the brain - Piracetam, Cerebrolysin, glutamic acid.
In order to stimulate general reactivity, a newborn baby is given a course of therapeutic massage and special gymnastics.
If parents detect at least one of the signs of central nervous system damage, they should immediately consult a doctor. Do not forget that the development of each child is an individual process.
Such individual characteristics of each newborn child in each specific case play an important role in the process of restoring the functions of higher nervous activity.
Therapy
To successfully treat CNS ROP, it is necessary to use complex therapy. It includes the prescription of medications and the additional use of physical rehabilitation methods.
The following medications are prescribed:
- Nootropic drugs (Piracetam, Nootropil, Encephabol, Actovegin).
- Drugs that improve blood circulation (Trental, Pentoxifylline).
- Peptide hydrolysates (Cerebrolysin, Cerebrolysate).
- Tranquilizers Phenazepam or Sonapax - in order to prevent psychopathy, in which depression of consciousness occurs, a feeling of anxiety and emotional indifference appears.
- Sedatives (Afobazol, Novo-passit, Phenibut, Pantogam).
- Synthetic sedatives are prescribed for increased irritability and anxiety, when herbal medications do not have the desired effect. In this case apply:
- Glycine or Adonis bromine;
- Adaptol or Glutalite;
- Seroquel or Zyprexa.
- To improve overall well-being, it is recommended to use multivitamin complexes (Undevit, Complivit, Aevit).
In the treatment of organic damage to the central nervous system, massage, physiotherapeutic treatment, and a set of gymnastic exercises will have positive dynamics. Many practitioners advise using measured loads in a swimming pool.
Danger and consequences
There is an opinion among experts that if the central nervous system of the fetus has been damaged, it cannot be completely restored. But practicing neurologists say the opposite. They say that if the disease is treated correctly, it is possible to achieve partial or complete restoration of the functions of the nervous system.
But even despite such an optimistic forecast, if you look at all diseases associated with the nervous system, then 50% of their total number leads to disability, while about 80% of it is allocated to perinatal damage to the central nervous system.
Overview of the pathological process
Organic damage to the central nervous system does not have a code according to ICD -10. Practitioners use a generalized concept using the G96.9 label. In the case of diagnosing certain psychiatric disorders (with damage to the central nervous system), a type of code for psychiatric diseases is used.
Organic damage to the nervous system in the medical literature is otherwise called encephalopathy or residual organic damage (ROD) of the central nervous system. It can occur both in childhood and in adults (most often after 65 years).
In a child, the disease often manifests itself in the form of cerebral palsy. Organic damage to the central nervous system can cause speech, mental and epilepsy disorders in adults.
Treatment of a child with central nervous system damage
Accurate diagnosis and timely correct treatment of CNS pathology is extremely important. The child’s body is very susceptible to external influences at the initial stage of development, and timely procedures can radically change the future life of the child and his parents, allowing at the earliest stages to get rid of problems with relative ease that can become very significant at a later age.
As a rule, children with early age pathologies are prescribed drug therapy in combination with physical rehabilitation. Therapeutic exercise (physical therapy) is one of the most effective non-drug methods of rehabilitation of children with central nervous system lesions. A properly selected course of exercise therapy helps restore the child’s motor functions, using the adaptive and compensatory capabilities of the child’s body.
Establishing diagnosis
Diagnosis of organic focal diseases of the brain is important both at the earliest stages and at later stages with already prescribed treatment. Early detection of the disease will allow you to take action and prescribe medications that can stop its progression or even reverse it.
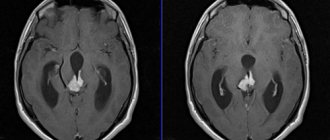
Foci of organic brain damage are shown by arrows
Anamnesis allows you to determine the duration of the disease, its course, and its connection with heredity. A neurological examination is mandatory to identify the causes. Tomography identifies atrophic lesions that cause symptoms.
Preventive actions
In order for the baby to be healthy, it is necessary:
- completely give up alcohol, drugs, smoking;
- avoid infectious diseases during pregnancy;
- if indicated, carry out heat treatment, which improves blood flow and warms the tissues;
- As soon as the baby is born, you can attend an underwater shower-massage course, which is carried out in warm water and has a beneficial effect on the development of the baby’s muscle tone; if this is not possible, you can perform a manual massage under water.
Design features of a centrifugal pump
If you look at the equipment in cross-section, you can identify the main structural elements:
An electric motor that acts as a drive.
A shaft that transmits rotation from the engine to the operating pulley.
A pulley with blades that move liquid inside the working chamber.
Bearing unit ensuring easy rotation of the shaft and wheel.
Seals that protect the structure from the negative effects of liquid media.
The snail-shaped body is equipped with two pipes.
Keywords
- hypoxia
- prematurity
- cerebral ischemia
- intracranial hemorrhage
- intraventricular hemorrhage
- muscle hypertonicity
- muscular dystonia
- delayed motor development
- psychomotor development delay
- hemiparesis
- hemiplegia
- diplegia
- tetraparesis
- tetraplegia
- ataxia
Bibliography
Cerebral palsy - cerebral palsy
CT – computed tomography
CPK - creatine phosphokinase
MRI - magnetic resonance imaging
NBD – hereditary metabolic diseases
LBW – low body weight
NSG – neurosonography
VLBW - very low body weight
USDG – Doppler ultrasound
Ultrasound - ultrasound examination
ALP – alkaline phosphatase
ENMG – electroneuromyography
ELBM – extremely low body weight
- Baranov A.A., Namazova-Baranova L.S., Ilyin A.G., Konova S.R. etc. Multi-level system of providing comprehensive rehabilitation assistance to children with chronic pathologies and disabled children. Methodological recommendations M.: NTsZD RAMS. 2012. 29 p.
- Baranov A.A. The state of health of children in the Russian Federation as a factor of national security. Ways to solve existing problems. Pediatrician's Handbook. 2006; 3:9-14.
- Baranov A.A., Namazova-Baranova L.S., Volynets G.V., Ilyin A.G., Konova S.R. etc. Determination of disability in children of different ages based on the international classification of functioning, disability and health. M.: Pediatr. 2013. Barashnev Yu.I. Perinatal neurology. M.: Triad -H. 2001. 640 p.
- Barashnev Yu.I. Features of the health of children born using assisted reproductive technologies. Ross. Vestn. perinatol and pediatrician. 204; 49(5): 12
- Bombardirova E.P., Yatsyk G.V., Zainitdinova R.S. Non-drug methods of restorative treatment of children with perinatal damage to the nervous system. Ross. pediatrician. and. 2011; 3:55-56.
- Diagnosis and comprehensive rehabilitation of perinatal pathology of newborns. Ed. G.V. Yatsyk. M. Pediatr 2012.156 p.
- Keshishyan E.S., Sakharova E.S. Psychomotor development as a criterion for the neurological development of health in a premature baby. Physician 2004; 5: 21-57.
- Classification of perinatal lesions of the nervous system and their consequences in children of the first year of life. Guidelines. M Federal State Educational Institution "VUNMC Roszdrav". 2007.88 p.
- Mitish M.D. Long-term consequences of perinatal brain damage in children. Abstract of dissertation. doc. honey. Sci. M.2004 25 p.
- Neonatology. Ed. T.L.Gomelog, M.D. Cunnigum. Per. from English M.: Medicine 1995. 640 p.
- Neonatology: national guidelines. Ed. N.I. Volodina. M.: GEOTAR-Media. 2007. 848p.
- Palchik A.B., Fedorova L.A., Ponyatishin A.E. Neurology of premature babies. M.: Medpress. 2011. 352 p.
- Palchik A.B., Shabalov N.P. Hypoxic-ischemic encephalopathy of newborns. SPb.: Peter.2000. 224s.
- Pediatrics. Edited by J. Graefe. M.: Praktika.1997. 912 pp.
- Principles of staged nursing of premature babies. Ed. Corresponding member RAMS, prof. L.S. Namazova-Baranova. M. 2013. p.172-204
- Pshenisnov K.V. Diagnosis and intensive treatment of multiple organ failure in newborns requiring interhospital transportation. Author's abstract. diss. Ph.D. honey. Sci. St. Petersburg, 2009.24 p.
- Guide to Pediatrics. Neonatology. Edited by G.V. Yatsyk, G.A. Samsygina. M.: Dynasty. 2006. 464 p.
- Modern medical and social problems of neonatology. Ed. A.A. Baranova, G.V. Yatsyk. M.2015. Pediatrician S 225-301
- Shabalov N.P. Asphyxia of newborns. M.: Medicine. 1990. 310 p.
- Shabalov N.P. Neonatology. M.: Med-press-inform. 2004.T.1.608 p.
- Shilko V.I., Zelentsova V.L., Popova N.P. Experience in the rehabilitation of premature infants with perinatal brain damage. Ross. Vestn. perinatologist. and pediatrician. 2003;2:43-47.
- Shmakov A.N., Konchno V.N.. Critical conditions of newborns (technology of remote consultation and evacuation). Novosibirsk: Kosta.2009.165 p.
- Yatsyk G.V. Nursing of very premature babies. Medical newspaper. No. 66. August 26, 2005 (electronic version).
- Yatsyk G.V., Bombardirova E.P. Selected lectures on pediatrics. Edited by A.A. Baranova, R.R. Shilaeva, B.S. Kaganova. M.: Dynasty. 2005.P.57-67.
Terms and Definitions
Extremely low body weight (ELBW) – birth weight from 500 to 999 grams
Very low body weight (VLBW) – birth weight from 1000 to 1499 grams
Low body weight (LBW) – birth weight from 1500 to 2499 grams
The consequences of perinatal damage to the central nervous system with muscle hypotonicity syndrome are damage to the brain during a certain period of its development with the subsequent formation of pathological muscle tone of the hypotonic type.
Most often, the disease is the outcome of perinatal damage to the central nervous system of hypoxic-ischemic origin (Cerebral ischemia P91.0, Intracranial non-traumatic hemorrhage in the fetus and newborn II, III degrees P52, Periventricular cysts (acquired) in a newborn P91.
In premature infants, especially those born with ELBW, VLBW, muscle hypotonia is recorded during the first six months of life. And subsequently, muscle tone may change with the formation of hypertonicity.
Also, muscle hypotonia is a symptom of toxic-metabolic dysfunctions of the nervous system (P 04 - P 04.4), with connective tissue pathologies (congenital ligamentous dysplasia, Ehlers-Danlos and Marfan syndromes, osteogenesis imperfecta syndrome), with metabolic diseases (hypercalcemia, rickets, phenylketonuria ) and endocrine (hypothyroidism) disorders.
Appendix B: Patient Information
Consequences of perinatal damage to the central nervous system with muscle hypotonicity - a disease that is the outcome of perinatal damage to the central nervous system of hypoxic-ischemic origin (Cerebral ischemia P91.0, Intracranial non-traumatic hemorrhage in the fetus and newborn II, III degrees P52, Periventricular cysts (acquired) in a newborn P91 .
In premature babies born with ELBW, VLBW, during the first 6 months of life, often o. For children born full-term, prematurely with low body weight, the gradual development of persistent motor disorders is characteristic. Neurological symptoms appear as the child's nervous system matures.
Apoptosis (delayed programmed death of neurons) can be reversible, so the doctor has time to prevent neuron death - the so-called “therapeutic window”.
The prognosis depends on the severity of the damage to the central nervous system and the effectiveness of the treatment.
Conducting early, staged restorative treatment/rehabilitation determines a more favorable prognosis and improves the quality of life of children, in some cases preventing their disability.