Can meningitis occur without fever? In certain cases this occurs, but with such symptoms of the disease one should talk about the viral nature of this pathological process. Children at an early age do not develop a fever, and signs of meningitis include lethargy, irritability, decreased appetite, and vomiting. There are cases where, during the development of this disease, patients experienced a decrease in body temperature. Bacterial forms of the disease are always characterized by a significant increase.
Why meningitis occurs without fever, we will understand in this article.
What is meningitis?
Meningitis is an acute infectious disease that leads to the development of inflammation of the membranes of the brain and spinal cord. It can be provoked by viruses, fungi and various bacteria, for example: enteroviruses, meningococcal infection, Haemophilus influenzae and tuberculosis bacilli. There is a possibility of this pathology appearing at any age, but most often people with weak immunity, head injuries, central nervous system lesions, and premature babies get sick.
With adequate and timely treatment, vital human systems and organs do not suffer. An exception to this rule is reactive meningitis, which is characterized by extremely severe consequences. If treatment is not started within the first day of the onset of severe symptoms, the patient may become blind or deaf. Often this disease leads to coma and even death. As a rule, symptoms of meningitis without fever in adults and children form immunity to the effects of pathogens, but this is not always observed.
Causes of the disease
What causes meningitis? The disease is caused by various bacteria, viruses and fungi. The launch of a pathological process can be triggered by:
- herpes viruses, syphilis, HIV;
- mycoplasmosis;
- tuberculosis;
- metastasis of malignant cells;
- trauma to the brain and spinal cord.
In case of traumatic brain injury, pathogenic microorganisms are transferred into the cranial cavity through the bloodstream. The entrance gate can also be the oral cavity in case of weakened immunity.
Meningitis causes of the disease and risk groups:
- premature babies;
- children with nervous pathologies;
- history of brain and spinal cord injuries (therefore, they are treated with antibacterial therapy).
Forms of the disease
The disease comes in primary and secondary forms. The first type of infectious lesion is diagnosed when the meninges are immediately affected when the disease occurs. The secondary form of meningitis manifests itself against the background of the underlying disease (otitis media, leptospirosis, mumps, etc.). The disease develops gradually, but eventually also affects the membranes of the brain.
A distinctive feature of these types of infection is the acute nature of the pathological process. The disease develops over several days and requires immediate treatment to prevent serious consequences. An exception to this rule is tuberculous meningitis, which often does not make itself felt for a long time. How does meningitis manifest without fever?
Routes of infection
What causes meningitis? Viruses and infections enter the body through mucous membranes, through airborne droplets (by sneezing), and if basic hygiene rules are not followed.
The disease affects children under seven years of age. In this category of patients, the serous form is most often diagnosed. This type of meningitis can be contracted through unwashed vegetables and fruits, water, dirty hands, and underwear. Maintaining hygiene is one of the main preventive measures.
What causes meningitis: another reason is an advanced form of tuberculosis. Any type of disease does not occur without fever, so the answer to the question of whether meningitis occurs without fever is clear: this is extremely rare. Even a slight increase is always observed.
Characteristic symptoms
It is known that the main signs of meningeal infection are severe headaches and a rise in thermometer readings. Doctors state that in almost 90% of cases the disease develops acutely, and an increase in temperature indicates the activity of the inflammatory process in the membranes of the brain or spinal cord.
This symptom is due to the active production of special biological substances in the body - pyrogens. They are synthesized as a response of the immune system to pathogens entering the body. However, if there are no signs of hyperthermia, this indicates a weakened immune system that cannot fight off the disease.
Viral form
In addition, meningitis without fever is often a sign of a viral form of the pathological process. Such an illness may be a consequence of concomitant diseases - mumps, influenza, rubella. Moreover, it is characterized by a short incubation period (2-4 days). During this period of time, the virus actively spreads throughout the body, but does not manifest itself in any way, in particular, there is no feverish syndrome. The patient feels lethargic and may be bothered by a cough, abdominal pain, or runny nose. Due to the absence of a high temperature, doctors often confuse such symptoms with ordinary ARVI, which significantly complicates the timely diagnosis and treatment of the disease.
Signs of meningitis without fever
The viral form of meningitis, which occurs without fever, differs in the nature of its symptoms from the bacterial type of this disease. This type of inflammation is characterized by serous damage to the meninges. The course of the pathological process itself is much easier, and the outcome is the most favorable.
Symptoms of meningitis without fever, the serous form, manifests itself in the form of an effusion (fluid accumulation) that permeates the meninges. It provokes their thickening, as a result of which the patient experiences signs of increased intracranial pressure. The serous form of meningitis does not contribute to the development of brain cell atrophy, so it often occurs without fever. This disease is less dangerous, unlike a bacterial one.
Let's take a closer look at the symptoms of meningitis without fever. When diagnosing, specialists have to focus on certain manifestations of the disease, which are usually expressed as follows:
- malaise, weakness, lethargy;
- constant nausea, vomiting;
- muscle pain;
- runny nose, nasal congestion, pain in the larynx;
- indigestion, refusal to eat, diarrhea;
- slight change in consciousness - desire to sleep, feeling dazed.
At the stage of the disease, when no increase in temperature is observed, other symptoms in most cases are also not recorded. Subsequently, after the end of the incubation period of the disease and when obvious symptoms occur, pronounced meningeal syndrome appears.
Signs of meningitis without fever can be difficult to determine.
This pathological condition is characterized by tonic tension in the muscles of the body, which is usually combined with general cerebral symptoms. This syndrome is accompanied by high sensitivity of the skin, painful human reactions to external stimuli (bright light, noise), and tedious pain in the head. What other signs of meningitis occur in an adult without fever?
The patient often lies on his side with his head thrown back, legs bent, pressed to his stomach. Brudzinski's and Kernig's signs may also occur. With this course of meningitis, the symptoms subside for about 3-5 days, but it is at this time that the temperature can rise to high numbers. The entire period of the disease lasts 1-2 weeks, the average duration of meningitis is estimated at 10 days.
As you can see, this disease is somewhat mysterious even for specialists, and it affects not only adults. And a child can have meningitis without fever.
Meningitis without fever, how it occurs in children and adults – Neurology
Why sometimes there is no increase in temperature and what signs to use to identify the pathology in this case - read our article.
Is there meningitis without fever?
It is known that the main signs of meningeal infection are acute headaches and rising thermometer marks. Doctors state that in almost 90% of cases the disease develops acutely, and fever indicates the presence of active inflammation in the membranes of the spinal cord or brain.
The increase in thermometer readings is due to the active production of special biological substances by the body, they are called pyrogens. They are produced as an immune response to the penetration of pathogenic agents into the body. But if hyperthermia (overheating of the body) is absent, this indicates a weakness of the immune system, which is not able to fight off infection.
Also, meningitis without fever can be a sign of a viral form of the disease. Viral meningitis often becomes a consequence of concomitant inflammatory processes - mumps, rubella, and influenza. It is characterized by a short incubation period (2-4 days).
At this time, the virus actively multiplies in the body, but does not manifest itself in any way, in particular, there is no fever. A person feels lethargic and is bothered by a cough, runny nose, and abdominal pain.
Due to the absence of high temperature, such symptoms are often confused with a banal ARVI, which makes timely diagnosis of the disease difficult.
Read about the classic course of meningitis with fever in our next article.
Signs of meningitis without fever
Viral meningitis, which occurs without fever, differs in symptoms from the bacterial form of the disease. This type of inflammation is characterized by serous damage to the meninges, and the course of the pathology itself is much easier. Also the outcome is more favorable.
Serous inflammation is manifested by the formation of effusion (fluid accumulation) that permeates the meninges. The effusion causes them to thicken, causing the patient to show signs of increased intracranial pressure. At the same time, the serous form of meningitis does not cause atrophy of brain cells, so it often occurs without fever and is not as dangerous as bacterial.
Doctors have to navigate meningitis without fever based on the patient’s symptoms:
- malaise, lethargy;
- muscle pain;
- vomiting, constant nausea;
- runny nose, pain in the larynx;
- refusal to eat, indigestion, diarrhea;
- slight change in consciousness - a feeling of stupor, a desire to sleep.
At the stage when there is no increase in temperature, other symptoms, as a rule, are also not recorded. Further, at the end of the incubation stage of the disease and when obvious symptoms appear, meningeal syndrome appears. It is a tonic tension of the muscles of the body in combination with general cerebral symptoms.
Meningeal syndrome is accompanied by high skin sensitivity, a painful reaction to external stimuli (noise, bright light), and dull pain in the head. The patient lies on his side with his head thrown back, legs bent at the knees, pressed to the stomach and arms leaning against the chest.
Brudzinski's symptoms (the head bends, followed by the legs involuntarily) and Kernig's (the patient cannot straighten the leg bent at a right angle) are positive.
On days 3-5, the symptoms subside, but it is at this stage that the temperature may rise or remain within normal limits. The entire period of illness lasts 7-14 days, on average the duration of meningitis is estimated at 10 days.
Features of meningitis without fever in a child
Can meningitis occur without fever in children? Yes, and the clinical picture with the disease in an adult will be similar. For a child, the symptoms that doctors use when determining a diagnosis are as follows:
- diarrhea;
- regurgitation of food;
- lack of appetite, refusal to eat;
- whims, lethargy, constant crying;
- drowsiness or, conversely, excitement of the nervous system;
- tension in the back and pectoral muscles, which is why, when sitting on the potty, the child is forced to throw his head back and lean his torso forward;
- swelling of the fontanel - in infants.
The incubation period for meningitis lasts up to 10 days if the immune system is normal. If the body’s defenses are weak and the temperature does not rise, the pathology manifests itself within 1-2 days.
Parents should pay close attention to the symptoms exhibited by the child, even if at first glance they look like signs of a respiratory infection.
Timely diagnosis will help prevent the development of a bacterial infection, which often happens with weak immunity.
Diagnostics: how to recognize meningitis if there is no temperature
Having understood that meningitis actually occurs without fever, you need to consider ways to diagnose the disease. The diagnosis is tentatively made based on the patient's complaints.
Next, additional symptoms are assessed - the presence of meningeal signs, weakness, vomiting, muscle tension, depression of consciousness.
To confirm the viral form of the disease, in which hyperthermia may be absent, a lumbar puncture is performed and the cerebrospinal fluid (CSF) is examined.
Analysis of cerebrospinal fluid allows you to separate the viral nature of the pathology from the bacterial one. But the main problem is the isolation of the virus, since it is found in small quantities in the cerebrospinal fluid.
To establish an accurate diagnosis, a PCR study of the cerebrospinal fluid is performed - a polymerase chain reaction, which makes it possible to specifically identify which virus caused the disease.
Additional examinations of patients are as follows:
- clinical blood test;
- determination of the electrolyte composition of the blood for the content of the enzymes lipase, amylase, as well as creatinine, glucose;
- biochemical liver tests;
- electromyography.
If the course of meningitis is atypical, that is, without fever and severe symptoms, then doctors prescribe a computer or magnetic resonance imaging scan of the brain.
Treatment of meningitis without fever
There is no specific therapy against serous inflammation of the meninges of a viral nature, as such. An exception is a disease caused by the Epstein-Barr virus. In this case, the patient is prescribed the drug Acyclovir. In other situations, treatment is aimed at making the patient feel better and eliminating local symptoms.
The body must eliminate the virus on its own within 7-10 days, so it is not possible to speed up the healing process. You can only prescribe medications to alleviate the disease:
- analgesics – Baralgin, Analgin, Paracetamol to relieve acute headaches and muscle pain;
- anti-inflammatory non-steroidal drugs - Ibuprofen, Nurofen, Panadol, Nimesulide to eliminate pain in muscles and joints;
- diuretics - Veroshpiron, Furosemide, Torasemide to remove fluid from the body. Prescribed when necessary to reduce intracranial pressure, which increases due to swelling and thickening of the membranes of the brain.
Since the occurrence of meningitis without an increase in temperature is a sign of a weak immune system and a disruption in the production of pyrogens, the patient must be prescribed immunomodulatory drugs. These are immunoglobulins and interferon-type drugs - Viferon, Interferon, Cycloferon. They help strengthen the immune system's response to an invading virus.
If the disease proceeds without complications and is treated outside the hospital, the patient is prescribed strict bed rest. The patient is also prohibited from watching TV, going to the computer, or reading, so as not to overload the eyes.
Treatment of meningitis at home is acceptable in case of illness in an adult, but children in most cases are hospitalized due to weak immunity, the possibility of a bacterial infection and a high risk of complications.
Consequences and complications
In most recorded cases, the pathology in an adult passes without complications, and recovery occurs after 7-14 days. However, meningitis without fever can cause a number of consequences in an adult patient.
In 10% of cases, the following phenomena may develop: sleep disturbances, loss of performance, lethargy, headaches, deterioration of coordination in space, mild impairment of memory and attention.
These symptoms go away on their own within a few weeks or months.
For children, meningitis without fever is more dangerous. Due to the risk of late diagnosis, when the disease is confused with ARVI, the following consequences may develop:
- hearing loss;
- inability to concentrate on simple tasks;
- memory impairment;
- strabismus;
- developmental delay.
Since the absence of fever during inflammation is a sign of weak immunity, a recurrence of the disease cannot be ruled out. To prevent it, a course of immunomodulatory drugs is prescribed not only during therapy, but also after it.
Conclusion
Meningitis is a dangerous disease. Its occurrence without an increase in temperature in most cases indicates a viral form, which has a favorable prognosis.
If suspicious symptoms appear that have not previously been noted with ARVI or influenza (severe headaches, repeated vomiting, photophobia, muscle aches), you should immediately consult a doctor.
Meningitis without fever is not a reason to consider the pathology not dangerous; without timely diagnosis, the risk of complications increases.
Source:
Meningitis without fever, can it happen, how long does it last in a child and an adult?
At least once, every person, one way or another, has encountered meningitis. Often, people suffering from meningitis may not be aware of this or confuse it with a regular migraine. Many people believe that the main symptom of this disease is fever. But meningitis without fever also occurs.
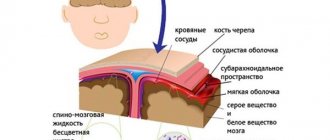
This is an inflammation of the meninges surrounding the brain and spinal cord with an increase in the number of cells in the cerebrospinal fluid.
The brain and spinal cord are surrounded on the outside by protective membranes of connective tissue called the meninges. These membranes can be contaminated by various pathogenic microorganisms.
The inflammatory process is called meningitis. If the infection touches the brain itself, meningoencephalitis occurs.
The incubation period of the disease ranges from 2 to 10 days. Most often, the infection begins acutely with a rise in temperature, which can reach 42˚. In a period of several hours to several days, an intensely growing headache appears.
You should not endure pain and fever, but it is also not recommended to lower your temperature on your own. It is best to call an ambulance or consult a doctor immediately. Since the temperature in most cases rises due to inflammation, its decrease does not mean recovery.
In addition, it is not always possible to reduce the temperature at home.
Meningitis should always be treated as an emergency. Without treatment, it can lead to death of the patient.
Both as a result of the infection and as a result of carriage, a stable immunity to the disease is formed.
There are different forms of this infection. It can be primary or secondary, developing against the background of an existing disease. They mainly differ due to the reason of infection.
- Bacterial or purulent meningitis
This type is caused by bacteria. It is severe and often life-threatening. This type of infection always requires emergency medical attention.
This form refers to a syndrome of acute onset of meningeal symptoms with high fever and an increased number of cells in the cerebrospinal fluid.
This is one of the forms of aseptic meningitis. It is easier than bacterial. If this type of infection is limited only to the meninges and inflammation does not occur, then the disease can often resolve spontaneously on its own, without the intervention of specialists.
In young people, harmless forms of viral meningitis are more common. in the elderly - bacterial, more severe forms.
The most common pathogens are bacteria and viruses, less often fungi and parasites. Germs are usually transmitted through airborne droplets, sneezing or coughing. Many people carry infection-causing organisms without developing the disease itself, meaning they are simply carriers.
Symptoms in children
Many parents are concerned about the question: can meningitis occur in a child without fever? The answer to this is positive, and the clinical picture of the pathological process in children and adults is quite similar. For a child, the symptoms that doctors use when making a diagnosis are as follows:
- diarrhea;
- refusal to eat, lack of appetite;
- regurgitation of food;
- drowsiness or, conversely, excessive nervous excitement;
- whims, constant crying, lethargy;
- pronounced tension in the pectoral and back muscles, as a result of which, in a sitting position, the child often throws his head back and leans his torso forward;
- in infants - swelling of the fontanelle.
Diagnostics
You can make a diagnosis and identify meningitis by conducting a number of examinations:
- Blood testing for general and biochemical parameters.
- Laboratory examination of cerebrospinal fluid.
- Determination of specific antibodies in blood serum.
- Magnetic resonance and computed tomography.
- Electroencephalogram.
- Electroneuromyography.
Incubation period
The incubation stage of meningitis in a child with a normal state of immunity lasts on average up to 10 days. With a weakened protective reaction of the body, when no increase in temperature is observed, the pathological process manifests itself in the first 1-2 days. Parents should pay close attention to the symptoms of the disease, even if at first glance they look like signs of a respiratory disease. Timely diagnosis helps prevent the development of a secondary bacterial infection, which is often observed with weak immunity.
Unfortunately, doctors had to observe the symptoms described above, and medical practice has shown that meningitis without fever can also occur in children.
Treatment
Medical care should be provided to the patient even before hospitalization, since symptoms appear very quickly, this can lead to intoxication of the body, deterioration of heart function and, as a result, infectious-toxic shock cannot be ruled out.
On this topic
- Meningitis
How to prevent the development of purulent meningitis
- Ekaterina Nikolaevna Kislitsyna
- March 26, 2020
Before sending the patient to a medical facility, the arriving ambulance team:
- For fulminant meningitis, adults are given intravenous hormones (Dexamethasone, Prednisolone) along with glucose and Euphyllin.
- To prevent cerebral edema, Lasix and Furosemide are administered.
- Treated with antibiotics .
- To prevent shock, therapy is carried out with saline solution with hormones and vitamin-containing preparations. For low blood pressure, Polyglucin and Reopoliglucin are administered.
- of Seduxen is given . At high temperatures, Diphenhydramine, Amidopyrine and others are co-administered.
Next, the patient is sent as soon as possible to the infectious diseases department for inpatient treatment, where he is prescribed:
- Antibacterial treatment.
- Detoxification therapy.
- Anti-inflammatory drugs.
- Symptomatic treatment to stabilize body functions.
- Elimination of purulent formations (if any).
Since it is not always possible to immediately determine the cause of the infection, broad-spectrum antibiotics (Ceftriaxone, Vancomycin, Tobramycin) are prescribed.
Penicillin, Ampicillin, and carbapenems have worked well for treatment, as they have a good effect on almost all bacteria and microbes that are present during the development of meningitis. In the most difficult situations, complex therapy is prescribed.
Antibiotics in tablets are not prescribed; they are usually injected intramuscularly, sometimes intravenously (Ceftriaxone). A lumbar puncture is performed every three days; if there is no improvement, then the antibiotic must be changed.
On this topic
- Meningitis
What are the dangers of reactive meningitis?
- Ekaterina Nikolaevna Kislitsyna
- March 26, 2020
Most often, the full course of treatment lasts ten days; in more complex situations, the period increases.
Infusion treatment is carried out:
- To eliminate infectious-toxic shock, it is necessary to restore blood. This is done by introducing plasma, albumin, crystalloid and colloid solutions.
- To relieve edema , diuretics (Mannitol) and oxygen treatment are used.
- Restore body functions and acid-base balance.
As additional methods of therapy, medications are used to eliminate fever, seizures, and neurological pathologies; anti-inflammatory and antihistamines.
If a diagnosis of a secondary form of the disease is made, then action on the primary focus (pneumonia, otitis media, sinusitis) is necessary. If a complication such as a brain abscess occurs, surgical intervention is necessary.
Gradual development
A feature of tuberculous meningitis is its gradual development. The first symptoms are nonspecific. The patient may experience general malaise, weakness, insomnia at night and daytime drowsiness, apathy, and decreased appetite. In most cases, the body temperature does not increase, but sometimes low-grade fever (up to 37.5 C) can be observed, and often this occurs only in the evening. Gradually, the patient begins to lose weight, vomiting appears, interest in the outside world disappears, and behavior changes.
Progression of the disease
As the pathological process progresses, the severity of the headache increases, insomnia intensifies, nightmares occur, attention and memory deteriorate. This stage is called the prodromal stage and lasts approximately 2-8 weeks. Next comes the height of the infectious process. At this stage, the clinical picture consists of symptoms of damage to the meninges and certain areas of the brain, nerves, and may differ slightly in different patients. The patient exhibits specific signs affecting the brain region - Kernig's sign, neck rigidity, Brudzinski's sign. Such meningitis without fever can occur in an adult.
At this stage, indicators may fluctuate at the low-grade level, but a significant increase may also be noted. Hyperthermia in older people is sometimes absent. Cephalgia is quite intense, greatly exhausts the patient and does not bring relief when changing body position.
Children often experience generalized epileptic symptoms, which manifest themselves in the form of loss of consciousness and the development of seizures throughout the body. Unpleasant sensations can be caused by any tactile influence (touching, stroking).
The cranial nerves are also affected, and if several of them are involved in the pathological process (3, 4, 6 pairs), then strabismus occurs. The patient may experience a split silhouette. Hearing loss and dizziness develop when the 8th pair of such nerves is damaged. And if the visual ones are affected (2 pairs of cranial nerves), this is fraught with complications. One of the dangerous consequences of meningitis is atrophy, which is characterized by irreversible loss of vision.
During the height of the disease, cerebral blood supply is disrupted, which leads to focal symptoms: weakness (paresis) in the legs or arms, impaired speech reproduction and understanding, dulling of sensitivity.
Symptoms
Meningitis appears at any time of the year, but with the onset of winter, along with ARVI and influenza, the incidence increases sharply. Symptoms of the disease can vary, and early diagnosis is very important for successful treatment.
The first thing that accompanies meningitis is an increase in temperature, which indicates an infectious process. When the membranes of the brain are damaged, it rises to high values.
What is the temperature for meningitis:
- febrile temperature - from 38 to 39 degrees;
- pyretic – 39-40 degrees;
- hyperpyretic - above 40-41 degrees.
Additional signs:
- repeated vomiting and nausea that do not bring relief;
- dizziness;
- confusion;
- headaches of varying intensity;
- a typical posture for meningitis is in a horizontal position: the head is thrown back, the legs are bent, brought to the stomach, while the stomach is retracted;
- rashes in the form of small dots all over the body, appearing after a rise in high temperature;
- redness of the throat, tonsils.
Without treatment, new symptoms appear:
- loss of consciousness;
- delirium, behavioral disorders due to temperature fluctuations and general intoxication of the body;
- convulsions.
After a few days, without treatment, the condition becomes extremely severe:
- coma;
- complete or partial paralysis;
- constant cramps;
- paralysis of the respiratory muscles, which can lead to the death of the patient.
The infection spreads throughout the body, this process is accompanied by:
- decreased blood pressure;
- shortness of breath;
- increased heart rate;
- dark rash.
At this stage, it is very difficult to save the patient, but still possible. Late diagnosis and treatment lead to irreversible changes in the body: the surviving patient inevitably becomes disabled.
Early seeking qualified medical help and proper treatment lead to recovery within a few weeks.
Spinal shape
The occurrence of symptoms of spinal cord damage indicates the spinal form of tuberculous meningitis. In this case, the functions of the pelvic organs are primarily affected in the form of urinary and fecal incontinence, severe weakness in the legs.
The course of the tuberculous form of meningitis can be lightning fast, which leads to the death of the patient without treatment within 4-8 weeks, or it can be sluggishly progressive, which can become a chronic type of disease with the development of pelvic disorders, dementia, and hydrocephalus.
The article provided comprehensive information about whether meningitis can occur without fever. We hope that it will be useful for you and will protect you from a dangerous illness.