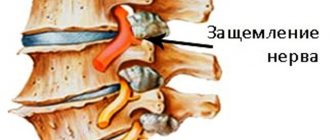
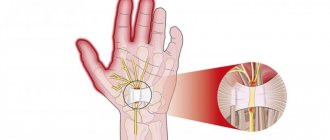
The radial nerve is one of the longest radial plexuses that supplies nerve cells to the muscles and skin of the shoulder, forearm and hand. It is considered a kind of hybrid due to the fact that it not only conducts sensitivity to the tissues and muscles of the human hand, but also has motor endings. A pinched nerve in the hand (radial neuropathy) is considered a pathological condition and occurs quite often in everyday life. It manifests itself as painful sensations when extending, for example, the wrist, fingers or forearm. This may occur due to compression of the radial nerve during sleep (with severe alcohol intoxication), fractures of the humerus, infections and intoxications of the body, long walks on crutches, or occupational diseases. Pinching of the hand can be classified as an occupational disease; this occurs due to the fact that the hand takes a forced position for quite a long time. As a rule, these are hairdressers, artists, programmers, etc.
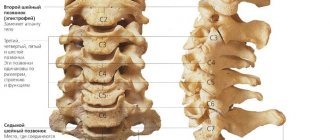
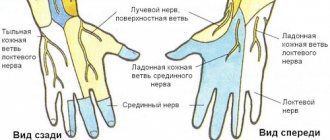
The distribution of nerves in the arm originates from the posterior bundle of the brachial plexus. The radial nerve has fibers that are part of the brachial plexuses. For the most part, it is part of the upper humeral trunk and, to a lesser extent, the middle and lower ones. Its widest part is at the level of the armpit, and in the area of the middle of the shoulder it becomes narrower, as it carries innervation to the hand, wrist and forearm. This nerve has branches such as the articular, posterior cutaneous and inferior lateral cutaneous nerve of the shoulder, muscular, posterior cutaneous of the forearm, superficial and deep branches. The nerve of the human hand forms many connections with neighboring nerves.
Pathologies
Risk factors are usually:
- fractures of the shoulder and sometimes forearm;
- intoxication of the body with alcohol or lead;
- pinched nerve during sleep;
- long-term stay of a person on crutches;
- there is “honeymoon palsy”, in which case the radial nerve is pinched from the fact that the partner lies on the inside of the shoulder for a long time.
- Infringement also occurs when hugging a person sitting on the next seat, if the hugger’s hand is pinched between the back of the seat and the partner’s back directly;
- Dislocations of the radius can lead to pinching;
- radial neuropathy develops due to prolonged wearing of tight bracelets or handcuffs;
- pathology can develop due to compression by benign neoplasms located on neighboring tissues; malignant tumors in such places are rare;
- pinching of a nerve in the hand occurs during operations, pressure with hooks, or during surgery in the place where the radial nerve passes;
- pinched nerve endings in the hand are also quite common and are considered an occupational disease.
This type of pathology can be primary or secondary. Primary - in case of fractures or dislocations, secondary - this is, for example, edema, tumors growing in neighboring tissues.
Possible consequences of pinching
If you do not contact a neurologist in time, the disease can develop serious complications that will take a long time to treat. Without effective treatment for pinched cervical spine, the following occurs:
- increased symptoms of the disease;
- atrophy of nerve endings and muscles;
- hand atony (impaired functioning);
- involvement of nearby tissues in the inflammatory process;
- development of inflammation;
- the appearance of swelling.
Complications impair the quality of a person's daily life. But when the pinching is advanced, it is more difficult for specialists to fully restore the functions of the musculoskeletal system.
We recommend reading similar articles:
Symptoms
If compression occurs in the shoulder area, the extension function of the shoulder, forearm and hand is immediately impaired. The hand hangs like a whip, the fingers take a forced bent position. If compression occurs in the lower part of the shoulder and in the upper forearm, then the triceps muscle retains its functions, but paralysis of the phalanges of the fingers occurs. Swelling of the tissues and blue discoloration of the hand can occur due to damage to the triceps muscle, due to pinching in the area of the wrist joint. But this happens quite rarely. Symptoms of pinching in the wrist joint include numbness of the hand or, conversely, sharp pain.
The human condition is characterized by weakness in the muscles of the hand, the shoulder joint may also hurt, burning and tingling in the fingers, difficulty in moving and abducting the thumb, numbness in the back of the hand. It is difficult to straighten the forearm, the shoulder constantly hurts. If you palpate the area of pain, you will feel an increase in pain along the nerve. Muscle atrophy is observed.
Symptoms of a pinched nerve in the hand: pain and numbness in the fingers
Clinical symptoms of a pinched nerve in the hand manifest themselves in the form of impaired sensitivity and motor function. In the first case, the signs are expressed in a feeling of numbness of the skin in a certain part of the hand. Limitation of mobility or the inability to bend fingers or clench them into a fist is also a manifestation of damage to motor axons.
As a rule, pain in the hand due to a pinched nerve is localized at the site of pathological changes and in distant areas that suffer from impaired innervation. A complex pathogenic mechanism is at work here:
- when a nerve is pinched in the elbow joint, two innervation branches are immediately affected;
- pain in the elbow area may be due to the disease that caused the pinching (arthrosis, arthritis, bursitis, tendovaginitis, etc.);
- pain in the elbow area may also be associated with the primary point of nerve damage;
- distant (distal) areas of pain can be located in the fingers, the back of the hand, or the wrist joint;
- this is due to the fact that the innervation of the vascular wall is disrupted, due to which the process of impaired blood microcirculation develops;
- stagnant and trophic changes cause acute pain in those tissues that do not receive an influx of fresh blood;
- compression syndrome with tissue necrosis may develop.
Treatment
If the radial nerve is pinched, treatment must be timely and professional. First you need to find out the cause and area of the pinching. Treatment is divided into conservative and surgical methods. The conservative method is to relieve pain and restore the damaged area itself. Before prescribing medications, or better yet at the first sign, avoid physical activity. The healing and restoration process takes a long time. Treatment should begin with the very first signs of pinching.
During drug treatment, anti-inflammatory drugs, decongestants and painkillers, vitamin therapy, and drugs that prevent scar formation are prescribed. Physiotherapy, acupuncture, and massages are often added to the treatment complex.
If within three months there is no effectiveness from the drug treatment, then a decision is made to undergo surgery.
If the ends of the nerve tissue are torn, it is stitched together. If a tumor is detected during pinching diagnosis, it is recommended to remove it. Surgeries are carried out with the release of scars, that is, the nerves are isolated, released and, due to better conditions, restored, this method is called neurolysis. Neuroraphy is a surgical method of treatment; its essence lies in the fact that the ends of the nerves are compared and sutured using microneurosurgical techniques. During surgery, adhesions adjacent to the tissues may be detected. In this case, their dissection and prevention of pinching of the nerve in the arm are indicated.
A pinched hand can be treated at home, but always after consulting a doctor. To do this, the doctor may prescribe exercises to restore the functionality of the arm. Physical exercises will be aimed at flexing and extending the fingers. Massage as the pain progresses; you can rub in warming ointments. You can take herbal baths based on sage, Jerusalem artichoke and oregano. But before that, you should make sure that you are not allergic to herbs. Dates are good for neuralgic ailments; you need to take them in small quantities after meals for a month. But remember, dates have a lot of fructose, so this option may not be suitable for everyone.
Nerve pinching of the hand is a fairly common occurrence and at the first symptoms you should pay attention to it and consult a doctor as soon as possible.
If treatment was carried out adequately and on time, the following results can be achieved:
- first of all, relieving pain at the pinched site and along the nerve;
- absence of relapses or long remission;
- increased performance, physical activity;
- improvement of blood circulation at the site of infringement;
- complete or at least partial restoration of impulse transmission through nervous tissue;
- if there was an inflammatory process, then completely exclude it.
Causes of the disease
The radial nerves most often suffer from pinching due to their location. They are located quite close to the surface of the skin, and also consist of different types of fibers, which leads to their instability in the face of damaging factors.
The following causes of pathology are distinguished:
- “wedding night syndrome,” in which a temporary nerve is pinched due to pressure on the shoulder (often occurs in a man if a woman sleeps on his shoulder all night);
- traumatic injury to the relevant area (we are talking about a wide variety of injuries, ranging from fractures to bullet wounds);
- a consequence of improper long-term use of crutches or, as this pathology is also called, crutch injury;
- oversaturation of the body with lead due to large amounts of it at home or contacts at work;
- a consequence of surgical intervention performed not entirely correctly;
- muscle strain due to intense exercise (one of the most common causes of the development of the disease);
- prolonged stay in a position that does not correspond to anatomical norms with pressure on the corresponding physiological areas;
- injections performed with nerve trauma.
Causes of brachial nerve entrapment disease
Diagnostics
The first diagnostic decision when a hand is pinched is a neurological examination. The doctor conducts tests to determine the general performance of the arm and muscle strength, and examines the sensory sphere. To diagnose hand drop syndrome, the doctor asks the patient to stand and extend his arms parallel to each other in front of him. You may be asked to move your thumb to the side to identify supination - the arms are lowered along the body, and the hands are turned so that the palms “look” forward. Sensitivity testing and functional tests are performed to differentiate radial nerve neuropathy from ulnar and median nerve neuropathy.
When diagnosing a pinched nerve, electromyography is used; it is based on a study of the bioelectrical activity of muscles and neuromuscular transmission. Another method for studying radial nerve neuropathy is electroneurography, which examines the slowing of nerve impulse transmission.
When diagnosing, it is imperative to identify why the hand is pinched; consultations with an orthopedist, traumatologist, and endocrinologist are prescribed. An x-ray of the shoulder, forearm and hand is required. Laboratory tests of blood and urine are prescribed.
Diagnostic methods
A pinched radial nerve in the hand is diagnosed by a surgeon. The doctor finds out the cause of the condition, the presence or absence of previous injuries or bone diseases, and evaluates motor functionality. To make an accurate diagnosis, the doctor prescribes a number of diagnostic procedures such as:
- computed tomography or magnetic resonance imaging;
- radiography;
- electromyography;
- Nerve conduction test.
The study will determine the condition of soft and bone tissues.
Using these methods you can get the following results:
- condition of the joints on the hand;
- the nature of the damage to the surrounding soft tissues, which could lead to pinching;
- speed of movement of nerve impulses;
- muscle contractility.
Prevention
Measures to prevent neuropathy include the following:
- First of all, you need to monitor your weight. The BMI (body mass index) of a healthy person should not exceed 25; if the index exceeds this mark, then obesity is already diagnosed. You should immediately bring your weight back to normal, otherwise excess body weight may be a potential cause of neuritis;
- An active lifestyle is also a guarantee of health. This also has a direct bearing on preventing infringement. This is especially true for people who have sedentary work at a computer;
- avoid drafts and sudden temperature changes, dress appropriately for the weather. Prevention of influenza and acute respiratory infections;
- the sleeping area must be equipped with an orthopedic mattress and pillows;
- avoid unilateral compression, for example, if you carry a bag on one side for a long time, this can also lead to pinching;
- timely seeking medical help.
The disease must always be prevented rather than treated later!