General information about the drug
Spitomin has an anti-panic effect and effectively reduces anxiety levels. In addition, it acts instantly and does not have most of the side effects characteristic of benzodiazepine anxiolytics.
Drug group, INN, scope of application
Spitomin belongs to the group of anxiolytic drugs that excite dopamine receptors (Dopaminomimetics) and interact with specific serotonin receptors (Serotonergic drugs). The international nonproprietary name is Buspirone. Used in psychiatry and neurology to eliminate anxiety and psycho-emotional tension.
Compound
One tablet of Spitomin contains 5 or 10 mg of buspirone hydrochloride. This active substance causes the anxiolytic effect of the drug. Due to the fact that the drug contains a substance with a non-benzodiazepine structure, the drug does not cause addiction and does not have a withdrawal effect.
To give Spitomin the necessary properties, the following auxiliary components are used:
- lactose monohydrate;
- MCC;
- sodium carboxymethylcellulose;
- magnesium salt of stearic acid;
- polysorb.
Action of buspirone
Thanks to the use of these auxiliary components, it is possible to create the most effective product.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
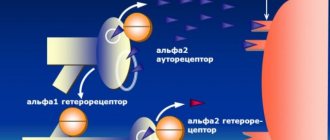
The drug has an antineurotic and thymoleptic effect, the mechanism of which is associated with the influence of the active component on the synthesis of serotonin and dopamine. Buspirone selectively blocks presynaptic autoreceptors that affect the synthesis and release of dopamine. The substance has virtually no effect on the functioning of GABAA receptors, does not have a negative effect on psychomotor functions, and does not enhance the effect of alcohol on the human body.
Positive dynamics of the disease are observed after 1-2 weeks of regular use of the drug. The maximum therapeutic effect is achieved after a month.
Absorption of buspirone occurs in the digestive tract. The substance undergoes first-pass metabolism, that is, liver enzymes participate in its biotransformation. In this regard, a small amount of unchanged substance enters the blood, and only 4% reaches the site of its action.
1-1.5 hours after entering the body, the substance reaches its maximum concentration. 95% of buspirone is bound to plasma proteins. 2-3 hours after a single dose of 10-40 mg of the substance, its concentration in the body decreases by 50%.
CYP3A4 isoenzymes take part in the biotransformation of buspirone. As a result, various active and inactive metabolic products are formed. The antineurotic effect of active metabolites is 4-5 times lower than that of buspirone.
Indications for use and side effects
If any food enters the body along with the drug, the absorption of buspirone slows down, but due to a decrease in first-pass metabolism, its bioavailability increases. As a result, the maximum concentration of the substance in the blood increases by 16%, and the total concentration by 84%.
2 days after the start of regular use, the rate of the forward reaction becomes equal to the rate of the reverse reaction. The apparent volume of distribution is 5.3 l/kg.
Patients with liver dysfunction often experience increased levels of buspirone in the blood. Since the unchanged substance is excreted into the bile, it is possible to achieve its maximum plasma concentration again. For patients with progressive liver diseases, the drug is prescribed in reduced doses.
In patients with impaired renal function, the clearance rate of buspirone may be reduced by 50%. Therefore, such patients should take the drug with caution.
Reviews about Spitomin
Based on patient comments, we can say that the drug does not cause addiction, but addiction to it is complicated by some unpleasant aspects:
- The doctor prescribed Spitomin + Finlepsin. The first week I felt very dizzy, I even fainted once. Towards the end of the second week, the condition completely improved, and at the end of the third I noticed an improvement.
- I started using Spitomin for anxiety due to social anxiety. It took a long time to get used to it and it was difficult: I felt sick for 2 weeks and had a headache. But this all covers up the effect that began to appear towards the end of the first month. I almost stopped suffering from panic attacks.
Cost of the drug
60 tablets of Spitomin in a pharmacy costs 550–650 rubles, depending on the city.
Indications and contraindications for taking Spitomin
Spitomin is a psychotropic medication that is used for various anxiety disorders, such as:
- anxiety neurosis;
- spontaneous panic attacks;
- violation of autonomic regulation of internal organs.
In addition, the drug is used as part of complex therapy for vegetative, somatic, neurological and mental disorders associated with prolonged use of alcoholic beverages. Also, in combination with other medications, Spitomin is used to treat various depressive disorders.
Depressive neurosis
The drug has certain contraindications for use:
- hypersensitivity to the components of the drug;
- various kidney pathologies;
- liver dysfunction;
- constant or periodic increase in eye pressure;
- damage to neuromuscular synapses.
In addition, the simultaneous use of the drug with substances that inhibit the activity of monoamine oxidase enzymes is prohibited.
The effect of the drug on the condition of the fetus during pregnancy has not been fully studied. The drug is prescribed to pregnant women only in extreme cases. If treatment is necessary during lactation, breastfeeding should be stopped. The medication is not prescribed to patients under 18 years of age, since there is no information about its safety for this group of patients.
Instructions for use of the drug Migrenol and reviews about it
Spitomin - contraindications, side effects
Contraindications.
Hypersensitivity to buspirone or other components of the drug. Acute congestive glaucoma, myasthenia gravis, severe liver disease, severe liver failure (prothrombin time more than 18 seconds); severe renal failure (glomerular filtration rate below 10 ml/min), epilepsy, acute intoxication with alcohol, hypnotics, analgesics and antipsychotics.
Concomitant treatment with monoamine oxidase inhibitors (MAOIs) and within 14 days after discontinuation of an irreversible MAO inhibitor or within 1 day after discontinuation of a reversible MAO inhibitor.
Adverse reactions.
Side effects usually occur at the beginning of treatment and usually decrease with long-term use. In some cases, a dose reduction is necessary. The most common adverse reactions were from the nervous system, such as dizziness, insomnia, nervousness, drowsiness, fainting, as well as from the digestive tract, such as nausea, as well as other effects, such as headache and fatigue.
Less commonly observed were anger and hostility, confusion, blurred vision, diarrhea, muscle and bone pain, numbness, paresthesia, incoordination, tremors and skin rashes, dry mouth, weakness, asthenia, excessive sweating, clammy skin.
Pharmacological properties
Pharmacodynamics
Spitomin is an anxiolytic drug (tranquilizer) of the non-benzodiazepine series, which also has an antidepressant effect. It differs from classical anxiolytics in the absence of antiepileptic, sedative, hypnotic and muscle relaxant effects.
The mechanism of action of buspirone is associated with its effect on the dopaminergic and serotonergic systems. Selectively increases the rate of excitation of midbrain dopamine neurons and blocks presynaptic dopamine receptors.
Buspirone is also a selective partial agonist of 5-HT1A serotonin receptors. Anxiolytic activity is approximately equal to benzodiazepines.
Spitomin does not have a significant effect on benzodiazepine receptors. Does not affect GABA binding, does not cause tolerance, withdrawal syndrome and drug dependence, does not have a negative effect on psychomotor functions, and does not potentiate the effect of alcohol.
Spitomin: instructions for use, analogues and reviews, prices in Russian pharmacies
Spitomin is an anxiolytic drug (tranquilizer) of the non-benzodiazepine series, which also has an antidepressant effect. Unlike classical anxiolytics, it does not have antiepileptic, sedative, hypnotic or muscle relaxant effects.
Selectively blocks presynaptic dopamine receptors and increases the rate of excitation of midbrain dopamine neurons, selectively excites (partial agonist) serotonin receptors of subtype 1A (5-HT1A).
Does not have a negative effect on psychomotor functions, does not cause tolerance, drug dependence and withdrawal symptoms. Does not potentiate the effects of alcohol.
Instructions for use Spitomin, dosage
The drug should always be taken at the same time of day, before or after meals, to avoid significant fluctuations in the concentration of the active substance in the blood plasma throughout the day.
The standard initial dosage according to the instructions is 1 tablet Spitomin 5 mg \ 3 times a day. If necessary, it can be increased by 5 mg/day every 2 or 3 days.
Daily dosage: 20–30 mg. The largest single dosage is 30 mg. The maximum daily dose is 60 mg.
It should not be taken occasionally for the treatment of anxiety, since the therapeutic effect develops only after repeated use and appears no earlier than after 7-14 days.
Use of the drug during pregnancy and lactation
Clinical trials regarding the safety of the drug Spitomin for pregnant women and the fetus have not been conducted, so tablets can be prescribed to expectant mothers only if there are serious indications and in the case where the expected benefit to the mother outweighs the possible harm to the child.
Women undergoing treatment with the drug should carefully protect themselves and prevent pregnancy; if conception does occur, treatment with tablets should be stopped immediately and consult a doctor.
The active ingredient of the drug is excreted in breast milk, so if treatment with Spitomin tablets is necessary for a nursing mother, the issue of ending lactation and transferring the child to artificial nutrition should be decided.
From application practice
Having studied the reviews, we can draw the main conclusion that most often Spitomin is not addictive, but in some people it may become addictive.
Among the advantages of the drug are: quick assistance in treatment, effectiveness in the fight against anxiety and panic. Among the disadvantages of the medicine, it is noted that it acts slowly on the human body, its price and a large number of negative effects on the human body.
Doctors' opinions vary, but more often they are positive. Most agree that the drug is well tolerated by patients, inexpensive and effective. Next is direct speech.
I would like to say right away that the drug is quite strong and serious and you simply cannot prescribe it to yourself. This drug is a tranquilizer and was prescribed to me to reduce the symptoms of anxiety.
Despite the fact that Spitomin really helps get rid of anxiety quite well, it caused unbearable nausea and dizziness for me. After a few days, these side effects disappeared.
Alexey Valerievich, 42
I was prescribed to take Spitomin tablets. The doctor immediately explained that the medicine was quite serious and needed to be taken at the same time. After using the drug a few days later, I felt that my nervous tension had really disappeared and I felt better.
The only negative that I would like to note is its price - a little expensive.
Alina
Overdose and side effects
If you overdose, you may experience nausea, vomiting, and drowsiness. If an overdose occurs and the dose of the drug is large, then depression of the nervous system may occur (this is the case when a severe form appears).
In order to get rid of these symptoms, it is necessary to rinse the stomach with plenty of water.
But here we need to make a reservation - even in the case of an overdose, the patient may not always develop symptoms of intoxication.
Side effects after taking the drug do occur, but the medicine is almost always very well tolerated. Typically, the negative effects of the drug on the body begin to appear immediately in the early stages of therapy.
For some benefit and for some harm
Indications for use of Spitomin:
- a disorder that is caused by anxiety;
- panic disorder;
- autonomic dysfunction - a disruption in the functioning of blood vessels, the normal reaction to external factors disappears;
- in combination with therapy for depression;
- generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
Among other similar remedies, this one has a relatively small list of contraindications:
- age indicator – not younger than 18 years;
- if there is an individual intolerance to one of the components of the drug;
- if a person has problems with the kidneys and genitourinary system, then this drug is not prescribed;
- eye diseases such as glaucoma;
- This drug should not be used by nursing or pregnant women.
Since the drug is largely psychotropic, it is in no case compatible with alcohol. Regardless of the percentage of alcohol in the drink, you simply cannot drink it while taking the drug!
Overdose
During treatment, you must strictly follow the doctor's instructions, and in no case exceed the dose. Otherwise the following are possible:
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomit;
- increased fatigue;
- constriction of the pupils (miosis);
- loss of consciousness;
- problems in the digestive system.
If these symptoms appear, call a doctor immediately. As a treatment, the instructions for the drug recommend gastric lavage. There is no specific antidote. During this period, you need to monitor your blood pressure, breathing, and pulse.
Use of the drug, dosage
The tablets are taken at the same time. It is possible to take the product both before and after eating; you should choose one option and always stick to it.
The drug is not suitable for occasional use when anxiety occurs, since the therapeutic effect is not detected immediately, but after some time. Repeated use of Spitomin is required.
The required dose is determined for each patient separately. “Spitomin” is presented in customer reviews as a drug, the dose of which at the initial stage of treatment in most cases does not exceed 15 mg of medication per day. Increasing the dose is possible every 2-3 days. However, its increase should be gradual, no more than 5 mg at a time. Daily use of the product is recommended in 2-3 doses. Typically, the dosage per day is 20-30 mg. The maximum dose available for use at one time is 30 mg, the maximum possible daily dose is 60 mg.
Impaired kidney function requires the implementation of therapy based on a reduced dose. If you have liver problems, special care is needed during treatment with Spitomin; the dosage should also be reduced. For this purpose, the doctor usually reduces some doses, while increasing the intervals between taking the drug.
Pharmacokinetics of the drug
According to the data obtained when using the drug, the following can be distinguished. After use, the drug is almost immediately eliminated from the gastrointestinal tract.
It passes well through the liver, but when analyzed, its residue is found in the blood. If the drug is used together with food, the absorption process into the body begins to slow down. If you take the drug after a meal, then in this case its effect increases by 84%.
The presence of the drug in plasma can only be detected two days after the start of its use.
The drug is prohibited for nursing mothers, since the drug remains in the mother's milk and, accordingly, will reach the baby.
If there are disturbances in the liver, the level of the drug in the plasma may be increased. The drug can be used in such patients, but its dosage should be less than in a person who does not have liver problems.
In case of documented kidney problems, it is better not to prescribe the drug or take it in a minimal dosage. When using the drug, the pharmacokinetics do not change in older people.
Pharmacodynamics and pharmacokinetics
Buspirone hydrochloride belongs to the group of anxiolytics - psychotropic drugs that reduce fear, anxiety, irritability, and emotional tension. The mechanism of action of the drug differs from the effect on the body of drugs from the group of benzodiazepines, which are characterized by sedative, hypnotic, anticonvulsant, and sedative properties.
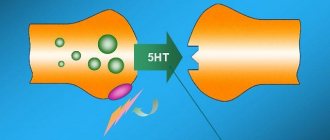
Buspirone is a partial 5-HT (serotonin) receptor agonist. Its action is directly related to the neurotransmitter serotonin, through which signals are transmitted between nerve cells (neurons) through the synaptic space. The more popular name for serotonin is the “happiness hormone”, since it affects mood and eliminates depression. In addition, the neurotransmitter reduces pain, eliminates inflammation, allergies, and regulates the functioning of the digestive system.
The functioning of many organs and systems depends on serotonin, so its deviation from the norm causes various pathologies, including changes in the emotional background. A lack of neurotransmitter leads to depression, obsessive disorders, and migraines. An increased amount causes serotonin syndrome - hallucinations, schizophrenia, mania, increases anxiety, and causes insomnia.
Spitomin acts by modulating (changing) the serotonergic system. Under its influence, serotonin renewal is inhibited and the frequency of inflammation of 5-HT neurons in the dorsal raphe nuclei is reduced. The result is a decrease in anxiety and depression.
Unlike benzodiazepines, it does not have an anticonvulsant effect, does not reduce the tone of skeletal muscles, and most importantly, does not cause addiction. Buspirone does not have an immediate effect, so it cannot be used once. The medicine manifests itself gradually, so the first signs of the drug's effect appear between the first and second weeks. The maximum effect is observed after a month.
After absorption into the blood, 95% of the active substance binds to plasma proteins: 86% to albumin, the rest to acidic α1-glycoprotein. Buspirone undergoes major transformation in the liver almost immediately. The main metabolite, 5-OH-buspirone, is not active. The action is exerted by the dealkylated metabolite 1-(2-pyrimidinyl)-piperazine, 1-PP.
The maximum concentration of the drug is observed an hour and a half after taking the drug, the required therapeutic level in plasma is two days after repeated use. From 30 to 65% of the substance leaves the body in urine during the day, 20–40% is excreted in feces. If the patient has problems with the liver or kidneys, the period of elimination of buspirone from the body slows down.
Method of administration and dosage regimen of the drug
It is recommended to take the tablets at the same time, regardless of meals, with plenty of water.
The dose of the drug and the duration of the course of therapy are determined individually for each individual patient. The initial dose of the drug is 15 mg per day (divided into 3 doses), if necessary, it is increased daily by 5 mg, the maximum daily dose of the drug should not exceed 60 mg. The therapeutic effect of the drug develops gradually over 7 days, which patients should be warned about.
Patients with impaired liver and kidney function require individual dose selection and adjustment.
Side effects of Spitomina
“Spitomin” does not always receive a positive review, and this is due to its ability to cause some unwanted reactions in the body. Usually the drug is well tolerated by the patient, but sometimes side effects may occur. If they develop, this usually happens at the very beginning of therapy; side effects disappear on their own. A reduction in the prescribed dosage is rarely required.
A person may experience sleep problems, a significant increase in nervous excitability and headaches. In very rare cases, extrapyramidal disorder may occur. Changes in the functioning of the digestive system are possible, these are various dyspeptic phenomena, for example, nausea with vomiting, poor appetite.
In case of an overdose of the drug "Spitomin", the review of many specialists confirms the need to perform gastric lavage and provide therapy aimed at eliminating this condition. There is no antidote, there is no effect from dialysis.
Reviews, analogues of the drug "Spitomin"
The drug "Spitomin" price, reviews make it a profitable and effective remedy for the treatment of conditions indicated in the instructions. Patients' opinions about the drug contain some unpleasant aspects. For example, a medicine when combined with Phenlepsin can lead to a deterioration in health, which can manifest itself as fainting and dizziness, but such side effects disappear over time. When treating anxiety with Spitomin, headaches and nausea may appear, but later they also disappear, and the result of therapy becomes noticeable. Undesirable reactions of the body to Spitomin are rare cases.
Doctors confirm the effectiveness of the drug when used to combat certain pathological conditions of the body. In their opinion, with proper use of Spitomin, recovery always occurs.
The only analogue of the drug is Buspirone Sandoz, this option is cheaper. A specialist can select a drug substitute without buspirone in the composition; usually these are tranquilizers that make up the benzodiazepine series. Such tasks are performed on an individual basis, taking into account the disease and its severity, and general health.
special instructions
Liver failure
Metabolism of the active substance occurs in the liver; when 20 mg of the drug is administered at a time to a patient with cirrhosis, the concentration of buspirone in the blood increases, the drug takes longer to be eliminated from the body. Since the substance can enter the bile unchanged, a repeated peak in the level of the active ingredient in the blood is possible.
Kidney failure
Regarding treatment with Spitomin, doctors' reviews show that if deficiency is moderate or severe, the clearance of the active component may become half as low. Severe insufficiency, in which GFR does not exceed 10 ml/min., its moderate form when the indicator is around 10-30 ml/min., and mild when the indicator is more than 30 ml/min., are those conditions for which treatment with Spitomin is possible ", but in a reduced dose and with extreme caution.
Lactose intolerance
Since the tablets contain lactose, this factor should be taken into account when prescribing Spitomina to patients.
Effect on reaction speed and attention
Usually the drug does not have such an effect, but its presence should be determined individually.
Switching from benzodiazepines
The use of the drug is possible only after discontinuation of benzodiazepines by gradually reducing the dosage.
Predisposition to drug dependence
After treatment with Spitomin, patient reviews confirm the lack of addiction to the medication. But if the patient has a predisposition to dependence on drugs, he requires careful supervision by a specialist.
Recommendations for patients
Avoid drinking alcohol and grapefruits. It is forbidden to drink grapefruit juice in large quantities. These products help increase the concentration of the active substance in the blood. In addition, they increase the likelihood of side effects, the severity of their occurrence, and the frequency of occurrence.
Spitomin
Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Due to the lack of properly controlled clinical trial data, the use of buspirone during pregnancy is only possible if the expected benefit of therapy for the mother justifies the possible risk to the fetus.
Women of childbearing potential should use adequate contraception during treatment with buspirone, since the safety of buspirone during pregnancy has not been proven.
Buspirone is excreted in breast milk. There is insufficient data from clinical studies of the use of buspirone during breastfeeding, so the drug should not be prescribed to nursing mothers.
Use for liver dysfunction
Contraindication: severe liver failure (prothrombin time > more than 18 seconds).
Use for renal impairment
Contraindication: severe renal failure (GFR < 10 ml/min).
Use in children
The use of the drug is contraindicated in children and adolescents under 18 years of age (the safety and effectiveness of buspirone for this age group has not been proven).
Use in elderly patients
In elderly patients, dose adjustment is not required, because The pharmacokinetics of buspirone do not depend on age.
special instructions
Buspirone undergoes extensive metabolism in the liver. With a single dose of 30 mg in patients with liver cirrhosis, the concentration of buspirone in the blood plasma increases and the AUC increases with prolongation of T1/2 of the drug. Due to the release of unchanged substance into the bile, a second peak in the concentration of buspirone in the blood plasma is possible. The drug is contraindicated in patients with severe liver failure. Patients with liver cirrhosis should be prescribed the drug at lower doses or at the same doses at extended intervals.
In moderate to severe renal impairment, buspirone clearance may be reduced by up to 50%. The drug is contraindicated in patients with severe renal failure and GFR less than 10 ml/min. In case of mild (GFR more than 30 ml/min) and moderate (GFR 10-30 ml/min) renal failure, buspirone can be given, but care should be taken and the drug should be taken in reduced doses.
In elderly patients, no dose adjustment is required, but the drug should be used with caution, for example, due to a possible decrease in renal and/or liver function and an increased likelihood of side effects. For these patients, the drug should be prescribed in the minimum effective doses, and if the dose is increased, the patient should be closely monitored.
The drug should be used with extreme caution in patients with angle-closure glaucoma and myasthenia gravis.
Patients should be advised not to eat grapefruits or drink grapefruit juice in significant quantities, because these products may increase buspirone plasma concentrations and result in an increase in the frequency or severity of side effects.
Switching patients from benzodiazepines to buspirone: Buspirone does not relieve benzodiazepine withdrawal symptoms. If a patient is switched to buspirone after long-term benzodiazepine therapy, buspirone should be given only after the benzodiazepine taper period has been completed.
Buspirone does not cause addiction to the drug, but its administration to patients with an established or suspected predisposition to drug dependence requires careful medical supervision.
Since the anxiolytic effect appears after 7-14 days of taking the drug, and the full therapeutic effect develops in approximately 4 weeks, patients with severe anxiety require careful medical supervision during the initial period of therapy.
Patients should avoid drinking alcohol throughout the course of treatment with buspirone.
In case of lactose intolerance, when preparing a diet, the lactose content in the tablets should be taken into account (55.7 mg in 5 mg tablets and 111.4 mg in 10 mg tablets).
Impact on the ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery
The results of clinical studies showed that buspirone monotherapy does not affect the psychomotor performance of patients. Despite this, at the beginning of the course of treatment, transient undesirable effects are possible, and therefore patients should be warned that driving vehicles and operating machinery is possible only if the patient is fully confident in his psychomotor functions. The patient's ability to drive vehicles and operate machinery should be determined individually depending on the patient's response to treatment and the use of concomitant therapy.
Pharmacological profile
The drug is a tranquilizing drug, but can also have an antidepressant effect on the body. Its main difference from similar ones in
Buspirone hydrochloride formula
that it is not a sedative and hypnotic. The drug does not have a negative effect on psychomotor functions.
The effect of using the drug appears after only 7–14 days, the maximum effect is recorded in the patient only after four weeks.
The drug has a relaxing effect on the body, but taking it does not cause drowsiness. In addition, it is an excellent sedative aimed at reducing the development of an antidepressant state.
Spitomin (buspirone). A new “classic” in the treatment of anxiety disorders
Introduction to the problem
According to large-scale epidemiological studies conducted in the United States and European countries in 2005 and 2010, anxiety disorders of varying severity are observed in 21-30% of the population1.
According to WHO, the problem is among the top 10 most significant health problems2. It has been proven that anxiety disorders are characterized by a chronic course3 and a high degree of comorbidity with other mental and behavioral disorders. First of all, this concerns depression, which in more than 50% of cases4 accompanies panic disorder or generalized anxiety disorder. Often, the combination of anxiety and depressive disorders leads to a more severe course of the disease and resistance to standard treatment.
Treatment of anxiety and depressive disorders, which include generalized anxiety disorder (GAD), panic disorder with agoraphobia, post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD), obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD), social phobias, usually long-term and combined, requires careful selection of doses , their episodic correction and monitoring of side effects.
Complex therapy should be aimed at:
- elimination of mental and somatic symptoms (anxiety, restlessness, muscle tension, sleep disorders, pain, blood pressure fluctuations, arrhythmias, etc.),
- treatment of comorbid conditions,
- improving quality of life,
- achieving complete remission (preventing relapses).
Among the means of pharmacotherapy today, combinations of tricyclic antidepressants, antidepressants of the SSRI and SNRI groups, and benzodiazepines are most often used.
Current problems in classical treatment of anxiety disorders
Antidepressants
The therapeutic effect of SSRIs, like other antidepressants, is realized mainly from the 2-3rd week of therapy, and the 1st week may be marked by increased anxiety, which is subjectively difficult for patients to tolerate5. In addition, there is the possibility of developing, despite a generally favorable tolerability profile, potentially dangerous side effects (serotonin syndrome), as well as withdrawal syndrome6.
Benzodiazepines
It is a generally accepted fact that tranquilizers of this group have pronounced undesirable effects: muscle relaxant, sedative, excessive hypnotic, amnestic, negative effects on psychomotor functions, a high risk of developing addiction and withdrawal syndrome7.
Pregabalin
Recently, the psychotropic activity of the drug pregabalin, a structural analogue of GABA, has been discussed in the literature. It reduces the stimulation of postsynaptic neurons, causing anxiolytic, anticonvulsant and analgesic effects. However, when using the drug for 8 weeks, only 52% of patients showed a 50% reduction in symptoms on the Hamilton Anxiety Scale (HAM-A)8.
Taking into account the goals of therapy and existing problems, a list of requirements was determined that the main clinical and pharmacological characteristics of anxiolytics must meet:
- a distinct anxiolytic effect, both in relation to the mental and somatic components of anxiety;
- lack of sedative, muscle relaxant and additive properties;
- the effect of the drug should be aimed not only at eliminating the mental symptoms of the disorder, but also at treating comorbid conditions;
- reduction of maladjustment;
- improving quality of life.
The drug Spitomin (buspirone), the only representative of the class of serotonergic anxiolytics, azapirones, perhaps best meets these criteria.
Spitomin (buspirone): mechanism of action
Buspirone differs in its chemical structure from all other previously known anxiolytics and belongs to the azaspirone class.
Its anxiolytic effect is associated with stimulation of presynaptic serotonin autoreceptors, and, unlike SSRIs, does not depend on the nature of the basal release of serotonin9. Buspirone has proven to be an effective pharmacotherapy for the most difficult to treat forms of anxiety disorders, and was the first non-benzodiazepine anxiolytic approved by the FDA in 1986 for the treatment of patients with GAD10.
Spitomin (buspirone) occupies a special place among all neuropharmacological agents and can be considered as a drug that combines the properties of an anxiolytic and antidepressant, which is of great value in the treatment of mixed anxiety-depressive disorders.
Spitomin (buspirone) affects:
- Serotonin neuromediation system. When it is hyperactive, it stimulates presynaptic 5-HT1A receptors, which block the release of serotonin into the synapse (antiserotonergic effect). When it is weakened, it stimulates postsynaptic 5-HT1A receptors (activates serotonergic processes)11.
- Dopamine neurotransmission system. By selectively blocking pre- and post-synaptic D2 receptors, it increases the rate of excitation of midbrain dopamine neurons12 and enhances its independent antidepressant effect.
- Norepinephrine neuromediation system. Active metabolites of buspirone have adrenergic effects13. The associated general uplift in mood explains the antidepressant effect in patients resistant to SSRIs.
Spitomin (buspirone) does not affect either GABA or benzodiazepine receptors, and therefore does not have the side effects of such tranquilizers. However, in terms of its effectiveness by 7-14 days of therapy, the drug is comparable to typical benzodiazepines.
Indications for use
Spitomin (buspirone) has shown its clinical effectiveness in the treatment of the following diseases:
- Generalized anxiety disorder (GAD).
- Panic disorder.
- Autonomic dysfunction syndrome.
- Alcohol withdrawal syndrome (as an auxiliary therapy).
- Depressive disorders (as an auxiliary therapy).
Clinical effectiveness
Based on numerous clinical studies (Murphy, Owen and Tyrer; Schramm et al., Pato et al., Goodman et al., Jenike et al., Robinson et al. et al.), buspirone has been proven to be a very promising and safe treatment for long-term mono- or combination therapy.
For generalized anxiety disorder
The anxiolytic effect of buspirone does not differ from that of diazepam (after use for 3 or more weeks)14. Buspirone is much more effective than benzodiazepines in reducing depressive symptoms associated with anxiety disorder. Adverse effects of sedation with buspirone occur much less frequently than with benzodiazepines15.
For anxiety and depression
The effectiveness of buspirone in the treatment of GAD in combination with depressive symptoms is 1.3 times greater than placebo in reducing anxiety and 1.6 times greater than placebo in reducing depressive symptoms16. Tolerability of buspirone is comparable to placebo.
For obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD)
- Clomipramine and buspirone show similar results on the OCD scale and the depression scale.
- Buspirone added to fluoxetine therapy for OCD increases the effectiveness of treatment.
- The simultaneous use of buspirone and antipsychotics is well suited for patients who are not amenable to therapy with selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors.
When treating depression
Numerous open studies have clearly demonstrated the positive effect of buspirone on depressive symptoms, including resistant depression. When buspirone was added to antidepressant therapy, there was a significant improvement in the condition compared with the placebo group. Some symptoms, such as depressed mood, reluctance to work, and lethargy, decreased after the first week of taking the drug.
Buspirone, already an effective antidepressant in itself, when added to enhance treatment with classical antidepressants, presumably through the serotonergic and noradrenergic systems, can improve treatment outcomes17. Buspirone is an effective and safe drug for improving the results of antidepressant therapy.
In the treatment of panic disorder
Buspirone significantly reduces the severity of generalized anxiety, agoraphobia, panic attacks and depression in the short term18. The positive effects of buspirone have been demonstrated on both the cognitive and somatic components of anxiety.
For anxiety disorder in elderly patients
Use of buspirone in older adults with anxiety disorders is more beneficial than treatment with benzodiazepines. Often, when treating such patients, a long-lasting anxiolytic effect is achieved while maintaining muscle tone, normal breathing, and the speed of cognitive and psychomotor reactions. In addition, it is important that buspirone improves mood.
For alcohol addiction
In the buspirone group, compared with placebo, there was a significant improvement in the following psychopathology measures: anxiety disorder, depression, irritability, interpersonal relationships, and global psychopathology score. A meta-analysis showed that buspirone improves the effectiveness of treatment for alcohol dependence and anxiety disorders. The researchers concluded that the main effect of buspirone in patients with alcohol dependence is not a reduction in alcohol consumption, but a positive effect on psychopathological symptoms. It improves mood, which is very important in the treatment of anxiety disorders, does not cause addiction, and does not have a negative effect on the psychomotor reaction.
Conclusion
Thus, Spitomin (buspirone) can successfully replace classical drugs that cause intolerance or side effects, or complement therapy to achieve a more complete and rapid effect.
Buspirone is a powerful serotonergic selective anxiolytic, which, due to its pharmacodynamics, has a pronounced anxiolytic effect without impairing cognitive functions and the speed of psychomotor reactions, ideal for both elderly and active business people.
1 Kessler RC, Chiu WT, Demler O et al. Prevalence, severity and comorbidity of 12-month DSM-IV disorders in NCSR. Arch Gen Psychiatr 2005; 62: 617–27; Terrie E, HonaLee H, Avshalom C et al. Depression and generalized anxiety disorder: cumulative and sequential comorbidity in a Birth cohort followed prospectively to age 32 years. Arch Gen Psychiatry 2007;
2 Barlow DH. Anxiety and its disorders: the nature and treatment of anxiety and panic. NY: Guilford Press 2002; European Status Report on Alcohol and Health 2010. WHO Euro, Copenhagen;
3 Hirschfeld RM. Placebo response in the treatment of panic disorder. Bull Manning Clin 1996; 60 (2): 76–86;. Keller MB. The clinical course of panic disorder and depression. J Clin Psychiat 1992; 53(Suppl.): 5–8;
4 Kalinin VV / Anxiety disorders – Rijeka: In Tech, 2011 – 323p;
5 Nutt DJ. Overview of diagnosis and drug treatments of anxiety disorders. CNS Spectr 2005; 10 (1): 49–56;
6 Schatzberg AF, Haddad P, Kaplan EM et al. Serotonin reuptake inhibitor discontinuation syndrome: a hypothetical definition. Discontinuation consensus panel. J Clin Psychiat 1997; 58(Suppl. 7): 5–10;
7 Avedisova A.S., Yastrebov D.V., Kostacheva E.A. and others. Pharmacoepidemiological analysis of outpatient prescription of benzodiazepine tranquilizers in psychiatric institutions. Ross. Psychiatrist. magazine 2005; 4: 10–2;
8 Instructions for use of pregabalin (Lyrica).
9 Baldwin D, I Anderson, D Nutt et al. Evidence-based guidelines for the pharmacological treatment of anxiety disorders: recommendations from the British Association for Psychopharmacology. J Psychopharmacol 2005; 19:567–96
10 Loane C, Politis M. Buspirone: what is it all about? Brain Res. 2012 Jun 21; 1461: 111-8
11 Anon A. Buspiron bei Angst und Depression // Pharm Ztg. – 1996. – Vol. 34. – P. 43.
12 Instructions for medical use.
13 S.G. Burchinsky, Buspirone: new possibilities for the treatment of anxiety and depressive disorders in neurological practice. Institute of Gerontology of the Academy of Medical Sciences of Ukraine, Kyiv
14 RickelsK., Wiseman K., Norstad N., et al. Buspirone and diazepam in anxiety: a controlled Study//J.Clin.Psychiatry, 1982, 43(12), 81-86;
15 BY HAROLD L. GOLDBERG, MD, AND RICHARD J. FINNERTY, PH.D. he Comparative Efficacy of Buspirone and Diazepam in the Treatment of Anxiety. m J Psychiatry 136:9, September 1979.
16 Sramek JJ1, Tansman M, Suri A, Hornig-Rohan M, Amsterdam JD, Stahl SM, Weisler RH, Cutler NR. Efficacy of buspirone in generalized anxiety disorder with coexisting mild depressive symptoms. J Clin Psychiatry. 1996 Jul;57(7):287-91. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8666569
17 Dimitriou, Evangelos C. MD; Dimitriou, Christos E. MD. Buspirone Augmentation of Antidepressant Therapy. Journal of Clinical Psychopharmacology: December 1998 - Volume 18 - Issue 6 - pp 465-469.
18 Cottraux J, Note ID, Cungi C, Légeron P, Heim F, Chneiweiss L, Bernard G, Bouvard M. A controlled study of cognitive behavior therapy with buspirone or placebo in panic disorder with agoraphobia. Br J Psychiatry. 1995 Nov; 167(5):635-41;. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pubmed/8564320
Instructions for use of tablets
Instructions for use contain the necessary information on how to take the medicine correctly. It notes that treatment must take place over a course of at least 14 days. Single use of the drug is not recommended.
Since food intake affects the concentration of the substance in the blood plasma, the drug should be taken before or after meals. The tablets must be swallowed whole with a small amount of liquid. To make it easier to swallow, you can split the tablet in half.
Description of the drug
The dosage of the drug depends on the type and degree of the disease and is prescribed to each patient individually. It is recommended to start treatment with 15 mg of the substance per day. If necessary, the dose is increased by 5 mg every 2-3 days. The maximum therapeutic effect is achieved with 20-30 mg of buspirone per day.
Important! You can take no more than 30 mg of buspirone at a time, and no more than 60 mg per day.
For patients with liver and kidney diseases, the drug is prescribed in lower doses. If the medication is used in combination with strong protease inhibitors, its initial dose should be reduced. Subsequent increases in dosage should take place under the supervision of a physician.
Composition and release form
Spitomin is produced by a Hungarian pharmaceutical company in the form of white round flat tablets. According to the instructions for use, the drug contains the following substances:
| Components | Dosage |
| Active substance | |
| buspirone hydrochloride | 5 or 10 mg |
| Additional substances | |
| microcrystalline cellulose, lactose, sodium starch (type A), magnesium stearate, colloidal silicon dioxide | |
Drug interactions "Spitomina"
The drug cannot be combined with MAO inhibitors. Its use during the period of taking antidepressants, oral contraceptives, and antipsychotics should be done with caution. The same applies to cardiac glycosides and hypoglycemic and antihypertensive drugs.
Sources
- https://Pilyule.com/obzor/nervnaya/trankvilizatory/spitomin/
- https://www.neboleem.net/spitomin.php
- https://bezboleznej.ru/spitomin
- https://NeuroDoc.ru/lekarstva/spitomin.html
- https://fb.ru/article/221056/preparat-spitomin-otzyivyi-vrachey-instruktsiya-po-primeneniyu-sostav-i-pokazaniya
- https://www.medcentre24.ru/medicamenty/spitomin.html
[collapse]