Due to its high information content and safety, MRI is gradually becoming a routine examination method; it is prescribed to patients more and more often. In order for the scan to be informative, you need to know in advance how to prepare for it and what to expect from the process itself, how the MRI procedure goes and what recommendations need to be followed before and after it.
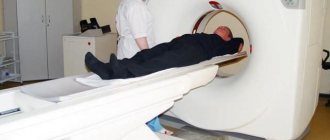
In the MRI room
MRI of the brain allows you to diagnose conditions such as:
- Brain tumors
- Strokes
- Infections (meningitis, encephalitis)
- Developmental defects
- Hydrocephalus
- Diagnose the cause of epilepsy
- Brain hemorrhages due to certain injuries
- Some systemic nervous system diseases, such as multiple sclerosis
- Problems with vision or inner ear function
- Pituitary gland dysfunction
- Vascular disorders such as aneurysms, arterial occlusions or venous thrombosis
- Dementia, which may be associated with both developmental anomalies and involutional changes in the brain
To whom is it assigned?
Diagnosis is carried out on an outpatient basis in special medical centers and on an inpatient basis. Resonance tomography can be done with the direction of a doctor or without a prescription in the following cases:
- Constant pain in the head, dizziness.
- Suspicion of the presence of a neoplasm.
- Before and after brain surgery.
- Inflammation of the brain.
- A sharp decrease in vision or hearing.
- Cerebral apoplexy or heart attack.
- Pituitary gland diseases.
- Unreasonable loss of consciousness.
- Noticeable memory impairment, decreased attentiveness.
- Congenital abnormalities of brain development.
- Multiple sclerosis.
- Injuries, bruises to the head.
- Epilepsy (including alcoholic).
- Monitoring the cancer during treatment.
- Impossibility of performing computed tomography.
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain vessels is performed regularly:
- With increased intracranial pressure.
- Patients who have suffered a stroke.
- With congenital heart disease.
- Persons engaged in intense physical activity involving blows to the head (athletes).
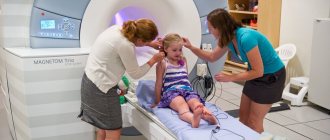
For children, MRI of the brain has the following indications:
- Developmental delay.
- Speech delay (logoneurosis).
- Suspicion of mental disorders.
- Convulsive seizures, freezing (absences).
- Fainting.
Preparing for an MRI examination
During an MRI examination, the patient may be asked to wear special clothing or may be allowed to wear his own clothes during the examination if they are loose and do not have metal fasteners (zippers, fasteners, etc.).
Food intake is generally not a factor in brain MRI. But if you plan to conduct a contrast study, it is better to refrain from eating a few hours before the study, which will avoid unwanted side effects such as nausea and vomiting. In addition, when performing an MRI of the brain with contrast, the radiologist needs information about the presence of allergies to contrast and the presence of asthma.
The contrast agent that is most often used for MRI studies contains metal elements (gadolinium) and causes allergic reactions much less frequently, unlike iodinated contrast agents that are used in CT (MSCT).
The presence of chronic kidney disease requires laboratory tests before MRI with contrast.
Women should always inform their radiologist about the possibility of pregnancy. MRI has been used to scan patients since 1980, and no side effects have been reported in pregnant women or children born after the study. However, the presence of the fetus in a strong magnetic field has not been studied, and therefore MRI is not recommended in the first trimester of pregnancy. MRI should only be performed in cases where there are strong clinical indications and the risks of misdiagnosis outweigh the risks of harmful effects of the magnetic field on the fetus. But the introduction of contrast during MRI for pregnant women should be carried out in exceptional cases.
If you have claustrophobia (fear of closed spaces), sedatives may be recommended, or, if claustrophobia is severe, the study can be done with an open MRI.
All objects containing metal must be removed before MRI is performed. These are items such as:
- Jewelry, watches, credit cards and hearing aids that may be damaged
- Pins, hairpins, metal zippers and similar metal objects that may distort the MRI image
- Removable dentures containing metal
- Pens, pocket knives and glasses
- Body piercing
In most cases, MRI is safe for patients with metal implants (such as teeth). But the presence of certain implants or electronic devices in the body is a contraindication for MRI examination.
These are devices such as:
- Cochlear implants
- Some types of clips on vessels
- Stents in blood vessels
- Metal joint endoprostheses
- Artificial heart valves
- Implanted insulin pumps
- Implanted electronic devices, including a cardiac defibrillator, pacemaker, or pacemaker
- Implanted nerve stimulators
- Metal pins, screws, plates, stents, or surgical staples
Recently, endoprostheses used in orthopedics contain little metal and an MRI is possible, but before performing it it is necessary to take an x-ray, which will allow the identification of metals in the body. In addition, radiography is necessary if there are bullets or shrapnel in the body, since MRI can lead to the displacement of metal objects and tissue damage. This is especially true if there are metal objects in the eye area. The dyes used in tattoos may contain iron and may become hot during an MRI, but this is generally rare. Dental fillings and braces do not usually affect the magnetic field, but they may distort images of the face or brain and should be reported to your radiologist. Parents who accompany children to the MRI scan area should also remove any metal objects and notify the radiologist if there is any metal or electronic devices in the body.
What does an MRI look like?
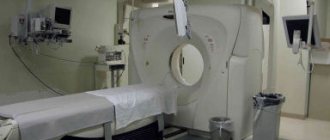
A traditional closed-type MRI machine is a cylindrical tube surrounded by a circular magnet. The patient will lie on a movable examination table, which will be located in the center of the magnet. But there are also open-type devices, where the magnet does not completely surround the patient, but is open on the sides. Open-type MRI examinations are indicated for patients with claustrophobia and overweight patients. Until recently, the disadvantage of open-field devices was the low magnetic field, which significantly reduces image quality. But recently, open-type devices with a high magnetic field (1 or more T) have appeared, which has made it possible to conduct research in patients with claustrophobia with high resolution.
Operating principle of the equipment
Before getting acquainted with the step-by-step steps of the study, it is worth paying attention to the physical and technical essence of magnetic resonance imaging as a method that allows you to explore previously unexplored corners of the human body.
The basis of the operating principle of MRI is magnetic nuclear resonance, which is the ability of a substance to absorb certain radio waves.
Without delving into the terms of physicists, its effect can be explained by a change in the energy state of neutrons and protons of non-zero magnetic nuclei, due to the small distance between which radio emission is formed.
If we draw a parallel between the method of x-ray radiation, radio waves have minimal energy that cannot harm molecules.
After the body begins to absorb radio waves, the nuclei begin to emit them, moving to an even lower energy level, which is easy to detect during a detailed study of the process. These emission spectra are affected by the magnitude of the magnetic field.
In order for the image to be transmitted to the screen, a kind of antenna transmitter and radio wave receiver are used.
At this moment, the transmission wavelength changes at different points, which also affects the degree of signal reception.
Next, the computer processes the received information and generates a three-dimensional image, the quality of which allows specialists to make reliable diagnoses.
Closed-type devices are the most accurate and powerful among similar units for MR examination
MRI procedure
Unlike conventional X-rays and computed tomography (CT), MRI does not use ionizing radiation.
The magnetic field in most MRI machines (with the exception of open-type machines) is created by passing current through the wires of the coils. Other coils, located inside the machine and in some cases located around a part of the patient's body, send and receive radio waves, producing signals that are detected by the coils.
The computer then processes the signals using a special program and generates a series of images that form a visualization of a thin section of body tissue. Images can be obtained from different angles and different thicknesses, depending on the tasks facing the radiologist. Differentiation of pathological tissue from healthy tissue using MRI of the brain is better than using other neuroimaging methods such as X-ray, CT or ultrasound. When performing an MRI of the head, the coil is placed around the head.
The duration of the study when conducting an MRI of the brain is 20-25 minutes, but if the study is carried out with contrast, the duration of the study can be 45 minutes.
Most MRI scans are completely painless. However, in some cases, patients experience discomfort while inside the device. Others may experience a feeling of fear (claustrophobia). During the examination, the patient may feel warm in the area being examined, but this is a normal sensation. During the examination, it is necessary to remain motionless, as movements can lead to distortion of the images. During examinations, the patient can hear the hum and knocking of the operating device and this should not frighten the patient. In some cases, the patient may be advised to use earplugs to reduce hearing loss. As a rule, the patient is alone in the equipment room during the MRI examination. However, the radiologist can see, hear and talk to the patient at all times using a two-way intercom. Often, in clinics where MRI is performed, relatives or parents are allowed to be with the patient in the control room, especially when it comes to conducting the study on children. MRI scanners are air conditioned and well lit. In addition, music can be played through headphones, which allows you to better pass the time. MRI with contrast may cause some discomfort and patients may experience a temporary metallic taste in the mouth after the contrast injection. There is no recovery period required after the examination, and the patient can perform normal activities and eat normal food immediately after completing the MRI examination. In very rare cases, patients experience significant side effects from the contrast agent, including nausea and local pain in the area where the contrast was injected. Also, quite rarely, patients may have an allergy to the contrast agent, in the form of urticaria, itching in the eye area or other reactions. In such cases, it is necessary to report such a reaction to a laboratory assistant (doctor) or radiologist to provide medical assistance. The interpretation of MRI results is carried out by a radiologist (MRI doctor), who analyzes the obtained images and issues a conclusion about the detected morphological changes.
Consultation with a specialist
An MRI of the brain is usually prescribed by a doctor if he suspects problems in the functioning of the organ. There are different indications for the session. These may be alarming general or
neurological symptoms, poor tests, a history of a number of diseases or previous head injuries. Using the technique, changes in the patient’s condition with a tumor, vascular damage, and the risk of arterial thrombosis are monitored. Increasingly, the approach is used to test the body's response to the therapy used.
Commercial medical centers and paid clinics perform MRIs if the client does not have a referral from a doctor. Even in such cases, consultation with a medical professional is required first. This could be a general practitioner, a neurologist, or a therapist. If technical questions arise, it is better to discuss them in advance with a radiologist. Neglecting a preliminary conversation with a professional, even for a healthy person, can lead to unpleasant consequences.
Benefits and Risks of MRI
Advantages
- MRI is a non-invasive imaging technique that does not use ionizing radiation
- MRI images of the brain and other cranial structures are clearer and more detailed than images obtained using other imaging methods. This detail makes MRI an invaluable tool in the early diagnosis and evaluation of many diseases, including tumors.
- MRI allows doctors to evaluate brain structures and, in some cases, can also provide information about the functional state of the brain
- MRI can detect brain abnormalities that may not be visible due to bone overlay with other imaging techniques
- The contrast agent used in MRI scans is much less likely to cause allergic reactions than the iodine-based contrast agents used in X-rays or CT scans.
- MRI is the most sensitive method for imaging brain tumors
- MRI of the cerebral vessels (MR angiography) provides detailed images of the blood vessels in the brain, often so high quality that they do not require additional contrast injection
- MRI can detect strokes at a very early stage by mapping the movement of water molecules in tissue. This movement of water (diffusion) is disrupted in most cases of stroke, often within a very short period of time from the onset of symptoms
Risks
MRI does not pose any risk to the average patient when proper safety precautions are followed.
- If sedation is used, there is a risk of oversedation
- Although a strong magnetic field is not harmful in itself, implanted medical devices that contain metal may malfunction or break during an MRI scan.
- There is an extremely small risk of an allergic reaction if a contrast agent is injected. Such reactions to contrast are usually minor and easily controlled with medication.
- Nephrogenic systemic fibrosis is now a proven rare complication of MRI and is thought to be caused by high-dose gadolinium injections in patients with impaired renal function. Therefore, when contrast is administered, careful assessment of renal function is necessary to avoid such complications.
- Manufacturers of intravenous contrast recommend that breastfeeding mothers not breastfeed their infants for 24 to 48 hours after contrast administration.
MRI of the brain must be performed on devices with a high field, as this allows you to obtain the necessary high-quality image.
If you have claustrophobia, then MRI can be performed on an open-type device (mostly low-field). But taking into account the fact that open-type devices with a high field have recently appeared, the possibility of high-quality visualization of brain structures has increased significantly.
Carrying out studies with high-field devices, in addition to better-quality images, requires less time for research and is less sensitive to patient movements than low-field devices.
But in cases where emergency medical care is necessary and quick diagnosis is necessary, it is better to use other imaging methods (for example, MSCT).
results
The radiologist examines the data, describes the images and draws up a conclusion. The diagnosis is made by the attending physician based on the obtained indicators.
Normal tomography results:
- There are no tumors in the brain.
- No pathologies were found in the soft tissue structure.
- No inflammatory processes were detected.
- No blood clots, bulges or bleeding.
- The sizes of the ventricles correspond to normal values.
Deviations from the norm indicating abnormalities in the organ:
- A tumor neoplasm has been identified (sizes are indicated down to millimeters).
- There is swelling.
- There are significant signs of infection or inflammation.
- Vascular abnormalities, bleeding, aneurysm, or bulges are noted.
Also in the image, the specialist can see tumors and cysts in the maxillary sinus, disturbances in the eye orbits, and increased cerebrospinal fluid pressure. The image shows metastases, the presence of blood clots, and areas damaged by ischemia.
A blurred clinical picture, a lack of symptoms indicating problems with the brain, pituitary gland, and blood vessels are the main indications for MRI of the brain. The examination can be carried out in any clinic equipped with the device, by appointment.