What is the difference between CT and MRI: diagnostic features
The human body selectively blocks X-ray radiation, and the absorption capacity of tissues becomes a factor that affects the clarity of the image.
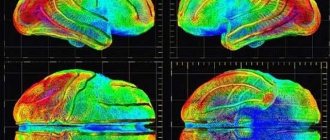
The rays are captured on film or other media - this is how we get an image. One of the main differences between MRI and CT is the way it affects the patient to identify pathologies and diseases. The effect of the magnetic resonance method is associated with the following feature of the structure of our body: the presence of hydrogen protons in the tissues, which are influenced by a strong field and release energy that is recorded by the device in the form of layer-by-layer images. The result is the most accurate visualization of muscles, brain, and ligaments.
MRI is recommended for detailed examination of tissues and blood vessels, joints and bones. In these cases it helps:
- determine whether there are tumors in these parts of the body;
- examine the nerves inside the skull, the structure of the connective tissues of the brain;
- study the condition of the spinal cord membranes;
- examine patients who have varying degrees of multiple sclerosis;
- examine ligaments and muscles;
- study the condition of the surface of the joints.
A CT scan can detect the presence of tumors, cysts, kidney stones or gall bladder stones. To make the study more effective and clear, doctors use a contrast agent, which is administered to the patient by injection. Once in the desired organ, it illuminates it, as it were, allowing you to study the required area in detail.
CT is prescribed if necessary:
- examine bone or tooth defects;
- find out to what extent the joints are affected;
- diagnose injuries and possible internal bleeding;
- study damage to the brain and spinal cord;
- examine the chest cavity (detect tuberculosis or pneumonia);
- check the genitourinary system;
- diagnose vascular diseases;
- examine hollow organs.
Computed tomography is performed using X-rays.
How does a CT scan differ from an MRI of the brain? The main difference between the methods is the principle underlying them.
- Computed tomography is performed using X-rays. During a conventional X-ray examination, they pass through tissue and are recorded on film in the form of a two-dimensional image. With CT, it turns out three-dimensional, since images are taken from different angles due to the ring-shaped contour.
- MRI uses electromagnetic waves rather than x-rays. Under their influence, hydrogen protons give one or another resonance, which is recorded by the scanner, processed and produced in the form of a three-dimensional image.
Thus, the methods will also differ in the list of contraindications. Computed tomography is an X-ray, which means it cannot be performed on young children (under seven years old), as well as women while they are expecting a child. Contraindications to MRI are dictated by the “magnetic” method of examination. The procedure is not performed if the body has metal or electronic structures - implants, knitting needles, pacemakers, vascular clamps and others.
There are two more significant differences between the methods:
- The CT scanner is not as sensitive to the patient's movements. During the examination, you must lie still, but the requirements for this immobility are not as strict as for MRI.
- CT allows you to obtain images in the shortest possible time - unlike MRI, which takes longer. Therefore, in emergency cases, when there is an acute disorder of brain activity or injury, a CT scan is usually performed.
Both methods are accurate, but there are situations when using a certain method will be more informative. In addition, there are some temporary and permanent individual contraindications and restrictions on the number of procedures.
Advantages of CT, MSCT:
- clear three-dimensional image of the studied area;
- the possibility of layer-by-layer study of the organ;
- painlessness of the diagnostic method;
- speed of research - exposure to rays lasts up to 10 seconds;
- less radiation than when using x-rays;
- effective for examining bone and muscle tissue, identifying bleeding and tumors;
- requires lower financial costs.
Magnetic resonance imaging also has a number of advantages, some of which are consistent with the advantages of CT. Pros of using MRI:
- high-precision information on a three-dimensional image;
- the ability to rotate the image into a convenient projection;
- layer-by-layer examination of the organ allows you to more accurately study the details;
- the best method of research for neurological problems - there are no more accurate diagnostic analogues in this field of medicine;
- safe for any age (used for children from birth);
- guarantees safety for pregnant women - does not affect the mother and fetus; no influence of radiation.
- there are no contraindications for frequent use, it is painless;
- it is possible to save data in electronic form (convenient for studying pathology over time);
Despite the manufacturability of the processes, their effective use is limited by certain nuances. In order to choose the most suitable method for studying pathology, you need to take into account the disadvantages of each method.
Disadvantages of CT, MSCT:
- radiation exposure (which is more harmful than the influence of electromagnetic waves);
- It is forbidden to use by pregnant women and children;
- it is impossible to obtain information about the functioning of organs; one can only consider anatomical changes in the structure.
Disadvantages of MRI:
- not suitable for precise examination of hollow organs (gall and urinary bladders, blood vessels);
- before the procedure, it is necessary to remove metal elements from clothing;
- the examination takes a long time - 30-40 minutes;
- not suitable for patients with claustrophobia;
- weight restrictions are possible - the devices are designed for a weight of up to 110 kg (few models - up to 150 kg);
- prohibited for use by people with fixed dentures and implanted elements - pins, clips, plates, pacemakers;
- To ensure the clarity of the resulting images, you need to remain motionless for a long time (anesthesia is used when diagnosing children).
Preparing and performing tomography
There is practically no difference between MRI and CT for a patient. The preparation is also indistinguishable. If an examination with contrast is performed, then you must refuse to eat 6-8 hours before it. CT and MRI of the intestine require more careful preparation, including cleansing the colon with an enema. Before examining the abdominal organs, it is recommended to avoid foods that contribute to gas formation.
The tomography procedure itself takes place in a lying position. After the person is positioned on the couch, the doctor leaves the room. As the series of images is completed, the patient is released, and after 20-60 minutes he is given an examination protocol. If a study with contrast is planned, the contrast agent is administered intravenously, drip, orally or rectally before the procedure.
The duration of a CT scan usually does not exceed 15-20 minutes, while an MRI can last from 10-15 minutes to an hour.
Diseases for which computed tomography is prescribed:
- Herniated disc
- Protrusion
- Osteochondrosis
- Fractures of bones or spine
- Hematomas and bleeding
- Osteoporosis
- Scoliosis
- Lung cancer
- Pneumonia
- Chronical bronchitis
- Asthma
- Tuberculosis of any organs
- Cancerous tumors of any location
- Neoplasms and areas of autoimmune thyroiditis of the thyroid gland
- Adenoma, parathyroid cancer
- Aneurysms
- Stomach ulcer
- Atherosclerosis
- Urolithiasis disease
Diseases for which magnetic resonance imaging is prescribed:
- Brain tumors
- Multiple sclerosis
- Stroke
- Inflammatory process in the brain
- Aneurysms
- Pancreatitis
- Cholecystitis
- Neuritis
- Thrombosis
- Thromboembolism
- Atherosclerosis
- Dropsy of the brain or abdomen
- Diseases of ligaments and cartilage
- Stagnation of bile
- Abscesses and cellulitis
- Hernias, etc.
It is almost impossible to answer the question which type of tomography is better. They have their own indications and contraindications. There is a difference between CT and MRI, but in terms of information content, these techniques are not inferior to one another.
The development of diagnostic medicine currently makes it possible to identify a disease or pathology at the very initial stage. This applies even to such a complex system of the human body as the human brain. The CT and MRI brain research methods are based on the principle of layer-by-layer scanning. This is their main similarity. Let's find out how CT differs from MRI of the brain, and also what is more effective and accurate than MRI or CT.
Difference between MRI and CT scan of the brain
Generally speaking, there is a fundamental difference between diagnosing the brain using CT and MRI, which consists in:
- technology of the device;
- degree of sensitivity of the device.
The operation of a computed tomograph is based on X-ray radiation aimed at tissue, giving an idea of the physical state of the substance and its density. CT scan – the installation rotates around the main axis – the patient’s body, reproducing an image of the organ being filmed (in this case, the brain) in different projections. The sections obtained during the shooting process are summed up, processed on a computer, and the final result is produced, which is interpreted by a specialist in the field.
MRI is different in that the machine uses fairly powerful magnetic fields. By influencing hydrogen atoms, they align these particles parallel to the direction of the magnetic field. The radiofrequency pulse produced by the device goes perpendicular to the magnetic field, the vibrations of the cells resonate, and this is what makes it possible to build multi-layer images. Modern MRI scanners have an open design, which is especially important for patients suffering from claustrophobia.
Indications for CT and MRI of the brain
For patients who are scheduled for a brain examination procedure, a very important question is: what is better than MRI or CT? Let's consider both diagnostic procedures from the perspective of a medical specialist.
Using MRI, it is better to study soft tissues (muscles, blood vessels, brain, intervertebral discs), and CT is more effective for studying dense tissues (bones).
MRI is preferable for:
- pathologies of the membranes of the brain;
- lesions of soft tissues;
- suspected tumor;
- inflammation of brain tissue as a result of sclerosis, etc.;
- negative changes in intracranial nerves, pituitary gland.
MRI is also prescribed if there is intolerance to the radiocontrast agent used in computed tomography. A significant advantage of MRI is that there is no radiation during the study. This is what makes the procedure safe for pregnant women (with the exception of the first trimester) and lactating women, as well as children of early and preschool age.
At the same time, MRI is contraindicated for persons who have metal plates, implants, spirals, etc.
CT provides more accurate information when diagnosing:
If we consider both procedures in terms of time costs, then a CT examination of one part of the body lasts within 10 minutes, while an MRI examination takes approximately 30 minutes.
There is also a difference in the cost of research. Computed tomography of the brain costs significantly less, and the fee for magnetic resonance imaging is correspondingly higher. Moreover, the more advanced and expensive the MRI machine, the higher the quality of the images, the more money you need to pay for the examination procedure.
Just a century ago it was impossible to look inside a person without penetrating the body with some kind of instrument. Doctors had to make most of the diagnoses almost at random, based only on clinical manifestations. Soon, X-rays were discovered, which greatly simplified the diagnosis of many pathologies. But the x-ray could not give a complete picture of what was happening in the body, since it showed the insides only in a two-dimensional projection: the organs were “superimposed” on one another, and it was difficult to make out what was what.
These difficulties prompted scientists to look for other ways. Thus, computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging were invented. These research methods have many advantages compared to radiography; they are increasingly being used in modern medicine. To determine when to choose which method, you need to know the difference between CT and MRI. In some cases, you can only get by with computed tomography, and sometimes it is better to use MRI to obtain reliable information.
Operating principle
Although both studies provide a three-dimensional image of internal organs, there are significant differences between them:
- According to the degree of sensitivity.
- According to the principle of action.
A CT scanner works using X-rays. This is a whole installation that, rotating around the patient’s body, takes pictures. All received images are then summed up and processed by a computer.
The difference between MRI and CT in the principle of operation is that there are no longer X-rays, but magnetic fields serve the person. Under their influence, the hydrogen atoms present in the patient’s body are aligned parallel to the direction of the magnetic field.
The device sends out a radio frequency pulse that travels perpendicular to the main magnetic field. Tissues in the human body come into resonance, and the tomograph is able to recognize these cell vibrations, decipher them and build multilayer images.
CT scan: what does it show and how does it differ from MRI?
The main advantages of the computed tomography method are:
- affordable price;
- the procedure lasts from 10 to 30 minutes;
- this study is necessary for diagnosing diseases and changes in bone structures, identifying kidney stones, calcification, pathologies, injuries and fractures.
In what cases is CT more informative? This procedure is most often performed when:
- detection of hematomas and neoplasms, brain injuries;
- damage to the bones of the skull, teeth;
- inflammation of the paranasal sinuses;
- diseases of the spine;
- changes in blood vessels as a result of the development of atherosclerosis;
- lung cancer;
- tuberculosis, etc.
Computed tomography differs from MRI in its greater accessibility with high information content of the examination of individual areas and affected organs.
However, this procedure also has one significant drawback - a large dose of X-ray radiation. That is why CT diagnostics cannot be performed on pregnant women. Another drawback is the impossibility of a full scan of the spine: the specialist exposes only a small area of it to the device.
We invite you to familiarize yourself with: Corrective osteotomy description, features of execution, possible complications
When conducting an examination using a CT scanner, the doctor cannot study the X-ray density of the examined tissues - it is this change that indicates the development of many serious diseases, including oncology. However, during magnetic resonance imaging, the specialist is also forced to perceive only a visual image, without obtaining the most complete clinical picture of the disease.
How are both of these methods different?
To understand the differences, you need to understand the technique.
Computed tomography is based on x-rays
. That is, CT is similar to X-rays, but the tomograph has a different way of recognizing data, as well as increased radiation exposure.
During a CT scan, the selected area is treated with X-rays layer by layer. They pass through tissues, alternating densities, and are absorbed by the same tissues. As a result, the system receives layer-by-layer images of sections of the entire body. The computer processes this information and produces three-dimensional images.
MRI diagnostics is characterized by the influence of nuclear magnetic resonance
. The tomograph sends electromagnetic pulses, after which an effect occurs in the area under study, which is scanned and processed by the equipment, then displaying a three-dimensional image.
From the above it follows that MRI and CT have a significant difference. In addition, computed tomography cannot be performed repeatedly due to the large radiation exposure.
Another difference is the research time. If 10 seconds are enough to obtain a result using CT, then during the MRI process a person is in a closed “capsule” from 10 to 40 minutes. And it is important to remain completely still. This is why magnetic resonance imaging is not performed on people suffering from claustrophobia, and why children are often given anesthesia.
Contraindications for procedures
Each of the procedures has contraindications that may interfere if you decide to undergo examination.
Computed tomography is not prescribed:
- Pregnant and breastfeeding women
- For children at an early age
- In case of frequent procedure
- If there is plaster in the examination area
- In case of renal failure. Magnetic resonance imaging also has its contraindications:
- Claustrophobia, schizophrenia
- The presence of a pacemaker, metal implants, clips on blood vessels, or other metal objects in the patient’s body
- Pregnancy in the 1st trimester
- The patient is overweight (over 110 kg)
- Renal failure (when using contrast agents).
It is imperative to consult a doctor before undergoing the test.
Magnetic resonance imaging device
CT and MRI are used to diagnose and prescribe treatment for a huge number of diseases. You need to know that the purpose of a particular examination method depends on what part of the person’s body is being examined.
If in some cases both methods are prescribed for research and give the same result, then MRI is, of course, preferable in terms of health safety. However, its price is higher.
In any case, it is important to always remember that health is, first of all, in your hands, and the most important thing is to promptly identify diseases using any diagnostic methods and begin proper treatment.
SHARE WITH YOUR FRIENDS AND VOTE
Despite their effectiveness, both devices have contraindications for use. Most often, patients refuse computed tomography due to fear of x-ray radiation. When answering the question of which is safer, MRI or CT, they tend to choose the first study.
Upon closer examination, it can be noted that both types have their own contraindications.
What makes MRI different from CT is its indications for use. Computed tomography is not indicated:
- Pregnant women (due to the risk of radiation exposure to the fetus).
- For young children.
- For frequent use.
- If there is plaster in the study area.
- In case of renal failure.
- While breastfeeding.
It also has its contraindications:
- Claustrophobia, when a person is afraid of closed spaces.
- The presence of a pacemaker in the body.
- First trimester of pregnancy.
- The patient is overweight (more than 110 kilograms).
- The presence of metal implants, for example in joints.
All of the listed contraindications are absolute, but before carrying out the procedure you should consult your doctor; perhaps there will be special recommendations in your case.
Is it harmful to have a CT scan?
The dose of radiation received during a CT scan is small. However, you can do the examination no more than 2 times a year - six months after the previous procedure. Such a limitation is not strict and unambiguous: firstly, it will depend on the scale of the procedure performed and the specific radiation dose, which is always indicated in the study protocol. Secondly, if absolutely necessary, CT can also be performed earlier.
Computed tomography is harmful for pregnant women, because even minimal doses of X-rays have a negative effect on the fetus. Also, X-rays are undesirable for use in nursing mothers, and in this case you will have to stop breastfeeding for at least a day.
Other contraindications to CT mainly relate to examinations with contrast. They are as follows:
- Kidney failure.
- Pathologies of the thyroid gland.
- Multiple myeloma.
- Severe heart disease.
- Diabetes.
With a body weight of more than 200 kg, the patient is unlikely to be able to fit on the tomograph table, so there are also weight restrictions. CT is less sensitive to movement than MRI, but in case of severe pain or mental abnormalities, the study cannot be performed qualitatively.
MRI: what is the advantage of the procedure
- Rays that are hazardous to health are replaced by radio waves. This feature makes it possible to diagnose all patients, including children and pregnant women. Along with the need for restrictions, the need to organize the training necessary to protect doctors and subjects disappears.
- The clarity of the image depends on the concentration of hydrogen protons in tissues and organs. The difference in performance ensures contrast and high quality three-dimensional projection.
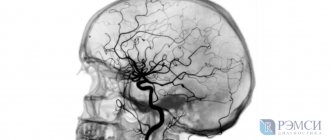
- The magnetic resonance method allows you to visualize longitudinal and transverse sections, obtaining an accurate image of the vessels of not only the brain, but also the spinal cord with determination of blood flow parameters.
This method of research has established itself as one of the most effective methods used in diagnosing pathological changes in:
- central nervous system (brain and spinal cord);
- joints;
- spine;
- adrenal glands, liver, spleen, ureter;
- work of the heart and blood vessels.
One of the main features of MRI, which can be confidently called an advantage of this method, is the high level of soft tissue contrast, which allows you to examine the necessary areas without the use of expensive drugs and the direct injection of a special substance.
The basis for obtaining a detailed image when performing magnetic resonance imaging is two main components:
- powerful magnetic field;
- radiofrequency pulses.
The study is carried out as follows: the patient enters a special installation tunnel, open on both sides, with a diameter of 70 to 80 cm, which allows him to maintain a horizontal position during the procedure. Ventilation and unobtrusive lighting are provided especially for maximum comfort of the examinee.
What diseases can CT detect?
- diseases of the bronchi and lungs (tuberculosis, neoplasms, pleurisy, pulmonary abscess, thromboembolism, abnormal development of the chest organs)
pathologies of joints and bones (osteoporosis, arthritis, arthrosis, osteochondrosis, tumors of bone and cartilage tissue), as well as injuries - fractures, cracks, dislocations, etc.
diseases of the spine (inflammatory processes, tumor neoplasms, consequences of injuries)
liver diseases (cirrhosis, hepatitis, hemochromatosis)
diseases of the kidneys and adrenal glands, pancreas, spleen, damage to the abdominal lymph nodes
pathologies of the blood vessels of the neck, brain, upper and lower extremities (varicose veins, thrombosis, aneurysms, heart defects, thrombophlebitis)
head injuries, increased intracranial pressure, hydrocephalus, stroke, etc.
ENT diseases.
In addition to diagnostics, CT is used for minimally invasive operations, biopsies, determining therapy in oncology and monitoring the results of surgical treatment.
Advantages of magnetic resonance imaging
To figure out which is better - MRI or CT, it is necessary to consider the advantages of each type of study.
Magnetic resonance imaging has a lot of positive aspects:
- All information received is highly accurate.
- This is the most informative research method for lesions of the central nervous system.
- Accurately diagnoses spinal hernias.
- It is a safe examination for pregnant women and children.
- You can use it as often as you need.
- Absolutely painless.
- Three-dimensional images are obtained.
- It is possible to save information in the computer's memory.
- The likelihood of receiving erroneous information is almost zero.
- No exposure to x-rays.
Considering the features of the device and its operating principle, loud knocking noises are possible during the study, which you do not need to be afraid of; you can use headphones.
Video: Which diagnostic MRI or CT is better?
MRI and CT scans of the brain are prescribed for various pathologies not only of the central nervous system, but also of surrounding tissues and bones of the skull. They are used for emergency or routine diagnostics in the following conditions:
- traumatic damage to the bones of the skull with suspected traumatic brain injury;
- the presence of symptoms of ischemic damage to the central nervous system (paralysis, impaired speech clarity, anisocoria, severe weakness of the upper or lower extremities);
- benign and malignant neoplasms;
- inflammatory processes of the central nervous system (meningitis, encephalitis);
- degenerative changes in the brain;
- congenital abnormalities of the vascular system (aneurysms);
- endocrinological pathologies of the pituitary gland;
- symptoms of increased pressure in the ventricular system of the central nervous system (hydrocephalus);
- atherosclerotic damage to cerebral vessels;
- disturbance of consciousness of unknown origin;
- headaches that do not respond to drug therapy.
The difference between CT and MRI indications is determined by the type of pathology that is suspected in the patient.
When should a CT scan not be prescribed?
CT scan of the brain uses X-ray radiation; therefore, contraindications to its use are common to these research methods. Therefore, it cannot be used in the following situations:
- the patient's pregnancy;
- use of metformin for type 2 diabetes mellitus;
- presence of decompensated heart failure;
- functional kidney failure (increased concentrations of creatinine and urea in the blood plasma);
- exacerbation of bronchial asthma;
- presence of seizures;
- the patient is unable to move;
- allergy to contrast (if it is necessary to use it);
- the presence of multiple myeloma.
Before conducting a CT scan, the doctor must evaluate the patient’s condition, his concomitant pathologies and the severity of the condition. This study should not be carried out too often due to the negative effects of X-ray radiation on the patient’s body.
Contraindications for MRI
How does MRI differ when it comes to possible contraindications? This study has fewer of them. In general, MRI of the brain is considered a safer test than CT. However, this study has one serious limitation that limits its use in some patients.
Also, MRI should not be prescribed for brain pathologies if the patient has had electronic devices implanted - pacemakers, middle ear implants, ferromagnetic devices. Contraindications also include the patient’s inability to remain motionless for a long period of time, since MRI is performed for more than 15 minutes. Therefore, children and patients at risk of seizures are advised to undergo the study using medical sedation.
For some patients who suffer from claustrophobia and fear of enclosed spaces, staying in a tomograph for a long time also brings a lot of unpleasant sensations. Therefore, it is preferable for them to give preference to rapid diagnosis using CT.
In addition, all tomographs have restrictions regarding the maximum patient weight (usually more than 150 or 200 kg).
How to prepare for a CT or MRI?
It is rare that the doctor asks the patient to do something before the CT scan begins.
This is typical only for some cases when the patient needs to be injected with contrast. In such a situation, a specialist may prohibit the consumption of drinks and food for several hours.
If you decide to take sedatives before the procedure, your doctor will also tell you not to eat or drink anything.
Remember that it is up to you how comfortable you feel during the diagnosis. Do not wear tight or tight clothes. If you have hearing aids or dentures, take them out for a few minutes while the examination lasts.
Be sure to warn doctors that you are taking any medications or are allergic to any components.
If you are afraid to leave your child alone in the treatment room, then with the permission of the staff and after putting on a gown, you can be with him.
In terms of duration, this diagnosis falls into the short-term category. In just 15 minutes everything will be completed and you can go home. However, if you have been given sedatives, it is best not to leave the medical facility until their effect wears off.
We suggest you read: Which doctors treat arthrosis Who is best to contact?
When you return, try to drink as much fluid as possible for several days in a row. This will remove the contrast agents from the body.
Usually there is no preparation. But, if you need to diagnose a disease that is presumably located in the abdominal organs, the doctor will recommend that you avoid eating foods that cause gas formation. For example, vegetables, fruits or flour products.
It is not forbidden to take the medicine if you experience pain and cramps in the stomach, liver, and so on.
If problems are detected in the pelvic organs, the fullness of the bladder is important.
The duration of the magnetic resonance examination procedure does not exceed half an hour. The patient must be prepared to spend this time in a confined space, listening to the somewhat loud tapping and whistling noises that occur as a result of the operation of the device.
Often, in order to relax the patient, specialists suggest that he listen to music using headphones at this moment.
If this method does not help, a person can always stop the diagnosis by pressing a special button, which he will hold in his hand throughout the entire examination. Using this button you can communicate with a doctor and tell him about your feelings.
Magnetic resonance and x-ray computed tomography
Such research methods are considered the most informative among specialists. They reflect the patient’s real state of health, which is why CT and MRI diagnostics are prescribed more often than other procedures. The choice of a specific technique depends on the following factors:
- the area being examined;
- characteristics of the patient’s body;
- doctor's opinion.
This diagnostic method is based on the ability of the human body to absorb ionizing radiation at varying intensities. Thus, fabrics with increased density absorb significantly more rays than those with reduced density. In fact, CT, like radiography, is performed using x-rays and is accompanied by radiation. However, unlike the first method, the study displays not a two-dimensional, but a three-dimensional image, which simplifies the diagnostic process.
Computed tomography is a manipulation that helps to see:
- even the smallest pathological changes in internal organs;
- foci of inflammation and their spread;
- condition of the blood vessels of the circulatory system and bone tissue;
- neoplasms.
There are the following types of computed tomography:
- A method involving the use of a contrast agent - iodine-containing preparations are more often used. They are delivered to the body through the bloodstream, intravenously. A contrast agent helps to see differences between internal organs and identify even the slightest pathological changes.
- Research involving the use of 2 radiation sources. This method involves a quick scan. It is used to study organs that are constantly in motion.
- Angiography is a study that helps to check in detail the condition of the circulatory system. During this procedure, a dye is injected into an artery or vein, which helps to detect the smallest pathological change in the structure of blood vessels.
- Multispiral is a diagnostic method in which shooting is performed in a spiral. The procedure itself does not last more than 7 minutes.
- Multislice CT is performed using a device in which detectors are located along its entire circumference.
When trying to figure out which is more effective than CT or MRI, one should not lose sight of the advantages of each method. For example, computed tomography has the following advantages:
- obtaining an accurate and high-quality image of a specific department or organ;
- the technique is indicated for use by persons susceptible to mental disorders and claustrophobia;
- high scanning speed;
- no overlays on pictures;
- high accuracy, allowing to detect pathology at the initial stage of its development.
This examination method is considered informative and safe. Magnetic resonance imaging is a non-invasive research method that is based on measuring electromagnetic fields. This method is mainly used to study soft tissues and diagnose their pathologies. Considering the advantages of the latter method will help you understand which examination is better - CT or MRI. The following advantages are considered key:
- obtaining high-quality layer-by-layer images without contrast agents;
- no radiation exposure;
- the possibility of timely detection of neoplasms;
- provides detailed information about the structure and functional parameters of the organ under study (for example, the speed of blood flow).
A CT scan uses X-rays. They affect the area under study from different angles. The procedure looks like this:
- When X-rays hit sensitive sensors, they are converted into electrical impulses.
- Computer processing of information is carried out.
- The result is displayed on the monitor.
A detailed examination of what a computed tomography shows will help you understand how a CT scan differs from an MRI. This procedure helps:
- study bone density;
- identify the presence of stones;
- determine the boundaries of tumor spread;
- diagnose congenital defects;
- study the patency of blood vessels;
- identify pathological changes.
The mechanism of action of MRI is based on the phenomenon of nuclear physical resonance. Its essence is that all cells of the body are saturated with hydrogen, so the human body emits radio signals. Moreover, healthy cells emit some signals, and pathologically altered ones – others. All of them are processed by a computer and displayed in 3D projection on the monitor.
When trying to figure out which is better: CT or MRI, it would be useful to consider what the latter shows. This procedure allows you to identify:
- brain damage;
- inflammatory processes occurring in the body;
- neoplasms;
- vascular lesions;
- joint deformation;
- changes in soft tissues.
Only a doctor can choose the optimal research method. It is important to remember that although the indications and contraindications for MRI and CT are almost similar, they have differences. For this reason, only a specialist can choose the optimal diagnostic method. He knows the difference between CT and MRI.
Computed tomography has the following indications:
- lung pathologies;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- internal bleeding;
- frequent fainting;
- convulsions;
- complaints of headaches;
- pathologies of the reproductive system;
- disorders of the spine and pelvic organs;
- examinations before the upcoming operation.
MRI helps identify:
- damage to joints and ligaments;
- neoplasms in fat and muscle tissues;
- pathological changes in the brain;
- disorders in the spine.
Such diagnostic methods are not always acceptable. CT has the following contraindications:
- pregnancy (even a small dose of radiation is dangerous for the fetus);
- age less than 14 years;
- weight 120 kg or more;
- kidney dysfunction;
- decompression diabetes mellitus.
Magnetic resonance imaging has the following contraindications:
- presence of a pacemaker;
- the first months of pregnancy;
- mental illness;
- implanted insulin pump implant;
- the presence of metal prostheses.
A computed tomography scan is a test that uses x-rays. According to experts, the safe dose is 15 mSv per year. However, the intensity of radiation exposure depends on the equipment used and the area of study. For example, with head tomography, the dose received is 2 mSv.
Computed tomography and magnetic resonance imaging differ in the mechanism of the procedure. Unlike CT, MRI has no restrictions on the frequency of procedures. However, this diagnostic method should not be abused either. The frequency of studies is determined by the doctor, and it depends on the patient’s pathology. For example, to prevent complications in multiple sclerosis, such a study is prescribed once every 1 or 2 years.
We suggest you read: Therapeutic blockade for hernia of the lumbar spine
The doctor decides on the advisability of combining these diagnostic procedures. In certain situations, he may decide that they can be performed on the same day or explain to the patient how long after a CT scan an MRI can be done. However, there are also limitations to research procedures.
In appearance, both tomographs are very similar. The result of their work also comes down to obtaining thin sections of the studied areas in the picture. Without a detailed study, it is very difficult to say how MRI differs from CT.
The advantages of computed tomography include the following facts:
- A three-dimensional image of the studied area is obtained.
- Clear photographs of the skeletal system.
- There is no pain during the procedure.
- The entire study takes a few minutes.
- Simplicity and reliability of information.
- A tomograph produces a lower dose of radiation than an X-ray machine.
- You can be examined if you have metal or electrical devices in your body.
- Provides truthful and accurate information in case of internal bleeding and detection of tumors.
- Lower cost compared to MRI.
As you can see, a computed tomograph is in no way inferior in its advantages to a magnetic resonance scanner, therefore, which is better - MRI or CT, must be decided in each specific case.
Indications for tomography
When assessing the difference between CT and MRI, you need to know the exact indications for both techniques. The fact is that some problems of the body are visualized better by MRI, others by CT. Magnetic resonance imaging is a good method for diagnosing the condition of soft tissues, and computed tomography is a good method for assessing the health of bones and other hard structures.
If it is necessary to examine the intestine, MRI is usually recommended, although both techniques will give similar results and should be used with the introduction of a contrast agent. The intestine is a hollow organ, and good visualization of it will be possible by staining the walls with a contrast agent.
MRI when examining the brain is an indispensable research method that allows you to accurately determine a number of pathologies of the meninges, the actual brain tissue and blood vessels, as well as the nerve plexuses. A CT scan of the head is usually done to evaluate the health of the hard membranes, bones of the skull, the junction of the base of the skull and the spine, and facial bones.
A doctor can accurately answer which of the two types of tomography is better, depending on the specific indications. CT and MRI will differ in the preferred area of examination, although in many cases they can still replace each other. Main indications for CT:
- Any diseases of the intestines and stomach
- Pathologies of the lungs and kidneys
- All diseases of bones, joints, spine
- Finding damage sites in case of trauma
- Damage to jaws and teeth
- Problems of the thyroid and parathyroid glands
- Vascular diseases
What is the difference between CT and MRI: magnetic resonance imaging is usually recommended for examining the nervous system, blood vessels, soft tissues - ligaments, muscles, internal organs, brain. MRI is indicated for all diseases of the abdominal and pelvic organs, retroperitoneal space, as well as the larynx and trachea, and lymph nodes.
What is safer and more informative – CT or MRI?
Of course, it is impossible to say that one method is more informative than another. They both do a great job in different occasions and situations.
If we summarize everything we talked about before, we can conclude that computed tomography is well suited for studying bones, muscles, tumor formations in internal organs, lesions of cartilage and other structures.
Magnetic resonance imaging can also monitor the condition of the entire body. It is especially good at identifying advanced stages of pulmonary diseases such as tuberculosis and emphysema.
If we take safety into account, then, as we noted before, during CT diagnostics the patient is exposed to X-rays, but now the devices are designed in such a way that the radiation exposure becomes minimal and does not injure the patient’s condition at all. It doesn’t matter whether it’s a child or an adult.
During an MRI examination, nothing can harm the patient’s health. It is considered absolutely safe for people of all ages.
Contraindications
Considering that computed tomography is nothing more than radiation, it is not recommended for pregnant women or during lactation
.
Magnetic resonance imaging is not performed in the following situations:
- the presence of metal parts
in the human body and on the human body; - claustrophobia
; - pacemakers
and other electronic devices located in tissue - patients suffering from nervous pathologies
who, due to illness, are unable to remain motionless for a long time; - patients weighing from 150-200 kg
.
Disadvantages of each type of study
Currently, almost all types of examinations have both positive aspects and certain disadvantages. Tomographs are no exception in this regard.
The disadvantages of MRI diagnostics include the following facts:
- Hollow organs, for example, the urinary and gallbladder, and lungs, are difficult to study.
- Metal parts in the human body will become an obstacle to the procedure.
- It takes a lot of time to conduct research.
- To obtain a true and accurate result, the patient must remain in a stationary position for a long time.
The disadvantages of computed tomography are as follows:
- The study does not provide information about the functional state of organs and tissues, but only about their structure.
- Harmful effects of X-rays.
- Contraindicated for use in pregnant women and children.
- This procedure cannot be carried out frequently.
If both methods of examination are recommended for you, then in this case it does not matter how MRI differs from CT.
What is the difference between MRI and CT? Let's take a closer look at the features of these diagnostic methods.
A diagnostic research method based on the use of x-rays. Unlike a conventional X-ray, the resulting image of the organ being studied will be three-dimensional and not two-dimensional. This effect is achieved through the use of a ring-shaped circuit that distributes the X-ray beams around the installed couch with the patient.
During the session, a series of images of internal organs are taken from different angles. This makes it possible to combine them later and obtain a computer-processed three-dimensional image. CT makes it possible to examine the organ layer by layer - “slices” on the most accurate devices reach 1 mm. Multislice or spiral CT (MSCT) - the technique involves continuous rotation of the device, which makes the image more detailed.
Brain examination
A diagnostic technique that allows you to obtain a three-dimensional image of the organ being studied. The research method is based on the use of electromagnetic waves. Nuclear magnetic resonance affects hydrogen in the human body - it forces it to change position, this data is recorded by the device and compiled into a three-dimensional picture - a tomogram.
Differences between diagnostic tests
Magnetic resonance imaging is an examination that allows you to obtain three-dimensional images. This result is achieved by passing electromagnetic waves through the body. Different tissues react to the passage of waves in different ways; these responses are recorded by a special device and transformed into a three-dimensional image. Next, the image is displayed on a computer screen or printed on special material.
To understand what a CT scan is, you need to know how radiography works. Because during a CT scan, X-rays are also used. But unlike a regular X-ray, which makes it possible to see the insides in a two-dimensional image, a CT scan produces a three-dimensional image. This is due to the design of the tomograph: rays are supplied from all sides. The subject lies on a table inside the apparatus. During the examination, doctors receive images that are processed on a computer.
Such diagnostic methods allow you to examine each organ layer by layer, which is especially important when determining the location. So what is the difference between MRI and computed tomography? Some pathologies are better visualized under the influence of X-rays, while the use of electromagnetic waves will be more acceptable for diagnosing others.
It is believed that the use of CT is not always justified, since radiation exposure occurs. However, SCT helps solve the problem. To understand what spiral computed tomography (SCT) is, you need to imagine a regular tomograph, the movements of which will differ from the standard ones. The ring itself rotates around the patient, and the couch constantly makes translational movements inside the device. This technique allows you to significantly reduce the time of exposure of x-rays to the patient’s body.
How much do MRI and CT scans cost?
It should be noted that both procedures are significantly more expensive than ultrasound or x-rays. That is why they try to prescribe them only after the rest of the diagnostics have been carried out. All this is aimed not only at optimizing patient costs, but also at obtaining the most complete results.
If we talk about prices, they differ depending on the clinic, its location and the scope of research. The average cost of diagnosing one organ is approximately 5,000 rubles. If you want to examine the whole body, then get ready for high expenses. This can cost you 80,000 rubles on average.
Is MRI examination harmful?
This diagnostic method is considered absolutely harmless, because it does not provide radiation exposure at all. But in the first trimester of pregnancy, even an MRI is done only according to strict indications, because it is believed that electromagnetic waves can provoke problems in the condition of the fetus or cause an increase in the tone of the uterus.
Other contraindications to MRI are as follows:
- The presence of metal implants in the body, especially endoprostheses, as well as various electronic devices (pacemakers, defibrillators, insulin pumps, vascular stents)
- Patient weight more than 160-200 kg (depending on the specific tomograph model)
- Claustrophobia and mental disorders
For children and people who, due to health reasons, are unable to lie still during the procedure, it can be performed under anesthesia or sedation.
Information content of methods
After visiting the doctor, you will be prescribed an examination, which, in the doctor’s opinion, will give a more truthful and accurate result.
If you decide not to wait for recommendations, then it is worth knowing in which cases which device is better to choose.
If you don’t know which is more accurate – MRI or CT, then keep in mind that magnetic resonance imaging will give a more accurate and informative result in the presence of the following pathologies:
- Brain tumor, stroke and multiple sclerosis.
- All pathologies of the spinal cord.
- Pathologies of intracranial nerves and brain structures.
- Damage to muscles and tendons.
- Soft tissue tumors.
If you have serious impairments in vital functions, you should additionally consult a doctor.
A computed tomograph will provide more accurate information if there are:
- Suspicions of intracranial hemorrhage, trauma.
- Damage and diseases of bone tissue.
- Pathologies of the respiratory system.
- Atherosclerotic vascular lesions.
- Lesions of the facial skeleton, thyroid gland.
- Otitis and sinusitis.
Preoperative examination will provide an accurate picture of the area of the upcoming surgical intervention.
If you are firmly convinced of the proposed diagnosis, then you can choose the research method yourself.
| Operating principles of CT | Difference between low-field and high-field magnets |
When to do a CT scan and when to do an MRI?
The choice of which is better for diagnosis: MRI or computed tomography depends on the purpose of the examination. The use of X-rays is justified in the following cases:
- examination of the brain for damage;
- diagnosis of vascular diseases (atherosclerotic changes);
- examination of the organs that make up the human genitourinary system (kidneys, ureters, bladder, urethra);
- examination of the chest organs makes it easy to diagnose tuberculosis, pneumonia, and other diseases of the lower respiratory tract;
- diagnosing pathology in hollow organs (intestines, gall bladder, stomach);
- examination of teeth and bone tissue;
- finding joint damage;
- diagnosis after injuries, detection of hidden but fresh bleeding;
- examination of the spinal column allows you to see osteoporosis, scoliotic changes, hernias.
Using computed tomography, cysts, tumor formations, and stones can be detected. The anatomical features of internal organs and their damage are also diagnosed. To obtain more complete information, in some cases the examination is carried out using X-ray contrast agents (see).
Find out what it is and when the examination is prescribed.
Indications for and examination procedure.
What health myths are preventing you from deciding to get tested?
Magnetic resonance imaging is used in cases where it is necessary to examine in detail the soft tissues of the body, joints or cardiovascular system:
- soft tissue tumor;
- examination of muscles and ligaments;
- examination of patients who have suffered ischemia of a region of the brain (stroke);
- study of the meninges and nerves.
CT scans are most often prescribed to diagnose injuries to internal organs, during bleeding, as well as to examine the condition of internal organs. MRI is used when it is necessary to determine the location of the tumor process in the body or to conduct a control examination during treatment to identify various inflammations, hernias, and abscesses.
Main differences between the methods
Despite such a large number of similarities, there is still a difference between CT and MRI. If in several points, then we can say the following:
- The most important difference between these two research methods is their operating principle. MRI uses a magnetic field, and CT uses x-rays.
- Both methods can be used to diagnose a huge number of pathologies.
- If the result is the same, you may be inclined to choose MRI, since this study is safer, but its cost is more expensive.
- Each procedure has its own contraindications, so they must be taken into account before making the final choice.
Remember, your health is in your hands, and sometimes it doesn’t matter what diagnostic method you use, the most important thing is to get an accurate and truthful result and start treatment in a timely manner.
Tags: computer, magnetic resonance imaging, tomography, good
About the author: admin4ik
« Previous entry