We will select a clinic or diagnostic center for free. Call 8(499) 116-77-86
Find a clinic
Sign up for an MRI
Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive medical diagnostic method that allows diagnosing various brain diseases.
MRI uses a powerful magnetic field, radio frequency pulses, and a computer processes the information received, converting it into detailed images of soft tissues and structures (including the brain). Images can be displayed on a computer monitor, transmitted electronically, printed on film, or burned to a CD. MRI does not use ionizing radiation (X-rays).
Currently, MRI is the most informative method for visualizing the head (especially the brain) and is often used in clinical practice, allowing one to determine morphological changes in the brain and skull.
Brain MRIs are performed for a variety of symptoms, which can be either acute or chronic. These are symptoms such as headache, nausea, vomiting at the height of headache, visual impairment, hearing impairment, endocrine disorders, impaired motor functions in the limbs, neurological symptoms of central origin (memory impairment, cognitive impairment, etc.).
Progress of the procedure: how does an MRI of the brain with contrast work?
The NMR tomography method allows you to examine and study human organs based on the saturation of tissues of various structures with hydrogen atoms. The characteristics of their magnetic properties are also important. This procedure is most often prescribed in difficult clinical situations: for cancer patients, for a detailed and clear examination of the tumor and the affected organ, for demyelinating diseases, for some types of strokes.
During the procedure, the condition of all parts of the brain is monitored, as well as the cerebellum, basal ganglia, ventricles, the ratio of gray and white matter and other structural indicators.
The method is safe, since the patient is not exposed to x-rays during diagnosis.
The contrast agent is injected into a vein using a syringe system. Within 10-30 seconds, the substance penetrates all vessels and tissues and illuminates the areas necessary for diagnosis.
The implementation consists of several stages:
- Before administering the drug, a native study is performed, without the use of contrast;
- After this, the patient is given an injection with a contrast agent in the required volume;
- Then you need to re-set the scanning programs.
Most patients do not notice any deterioration in their health or side effects.
How to prepare for the procedure
Special preparation is required only when examining the abdominal cavity and pelvic organs. Three days before the examination, you will need to follow a low-carbohydrate diet, and a day before - eat light food, and also not drink strong tea and coffee, so that the doctor can determine what the MRI of the patient’s head shows. The patient is not yet allowed to drink water or food 5 hours before the event.
Why is an MRI of the brain done with contrast agent?
MR contrast agents are used to detect tumors, autoimmune inflammation and other pathological changes. Most often used in neurosurgery and neurology to enable more informative and high-quality research.
The substance allows you to visualize the exact boundaries, structure and localization of the tumor, the activity of the demyelinating process, the severity of the blood supply to the area under MRI observation.
The advantages of MRI of the brain are that it preserves a clear picture of all structures, even if the tissues are at different depths, and also provides the opportunity to examine all areas of the brain that are covered by the skull.
Differences in imaging with contrast-enhanced MRI
How to determine
An MRI of the head is a study that shows changes in the human body that a doctor may not notice with other research methods. The very principle of operation of magnetic resonance equipment is based on the characteristics of the human body.
Each cell of the human body contains water molecules, which, in turn, consist of hydrogen atoms (2 atoms) and oxygen (1 atom). If we consider them from a physical point of view, then these atoms are magnets. This means that when these atoms find themselves in an intense magnetic field, their electrons begin to rotate along the axis of the external field.
At this moment, a so-called deviation from the orbit in which they were moving before occurs. When such a system is exposed to radio waves, the angle of inclination of the moving particles changes.
When the external influence stops, the electrons inside the atoms return to their previous orbit and begin to emit electromagnetic waves. At this moment they are recorded by a tomograph. As a result, the device generates a clear three-dimensional image based on the received data.
An MRI of the head shows the water content in the cells and other parameters. Based on them, it is possible to make a more accurate diagnosis, assess the quality of treatment and select the most optimal course of therapeutic measures for the patient.
Types of MRI
The most accurate images are obtained if the machine can cut very thin sections. This parameter depends on several things - the tomograph model (how modern it is) and the type of MRI.
There are several types of magnetic resonance therapy:
- Standard. The specialist receives the necessary amount of information. No contrast agent is administered. In this case, the patient spends about 20-30 minutes in the tomograph.
- With contrast. This type of examination produces a clearer image. To do this, a special drug containing gadolinium salts, Omniscan or other means is injected into the patient’s vein to enhance the contrast of the image. Solutions of this type enter the bloodstream and begin to illuminate when the rays of a tomograph hit them. This allows you to decipher data better and promptly pay attention to various anomalies in the structure of the brain. As a rule, this method is used for vascular diseases, multiple sclerosis, and cancer.
The dose of the contrast agent is determined by the doctor individually, depending on the data of a particular patient. If a contrast agent is used, the duration of the procedure can be increased to 1 hour. In addition, this type of procedure differs from the standard form of MRI in that after the contrast is administered, a person may feel a metallic taste in the mouth. This is a completely normal reaction. There are usually no other unpleasant sensations. Therefore, people tolerate scans using contrast quite easily.
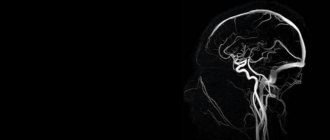
- MR angiography. A type of procedure that is performed when it is necessary to evaluate the condition of the vascular system if it is suspected that the patient is suffering from atherosclerosis, an aneurysm, or there is a fear of blood clots.
- MRI of the pituitary gland. In this case, special attention is paid to the appendage, which is an endocrine gland. Thanks to the pituitary gland, hormones are synthesized, which determine the quality of performance of the body's reproductive system. MRI of the pituitary gland is recommended for suspected benign tumors, hormonal system failures, gigantism, and obesity. Also, this type of procedure allows you to confirm or exclude so-called pituitary formations.
What does a brain MRI with contrast show?
There are many symptoms of brain disorders, in which it is better not to postpone a visit to specialists and get a tomography. If you observe: atypical behavior, movement disorders, general health, often neurologists or other clinicians after examination will advise you to do an MRI as the most revealing diagnostic method. MRI of the brain with contrast is prescribed when making a diagnosis is difficult and additional examination is required.
Indications for MRI:
- tumors;
- acute vascular diseases of the nervous system;
- epilepsy;
- severe headaches;
- multiple sclerosis;
- pathology of cerebral vessels;
- bruises and injuries of the skull and brain and their consequences.
As a result of the procedure, inflammatory processes can be detected, indicating their exact location. Examinations are also prescribed after brain surgery. An MRI can help determine whether the tumor has shrunk or recurred.
For a clear and detailed image, the doctor prescribes the injection of a special substance that will help to examine the patient’s problem in more detail. It is worth noting that the contrast agent is safe for health, since it is eliminated from the body within 3-4 hours.
The main advantages of contrast in brain MRI include:
- minimum contraindications;
- obtaining slices in any plane;
- high contrast and image resolution;
- the ability to obtain images of all brain structures covered by bone tissue;
- good tolerability of the drug.
This technique uses several types of substances; they differ in composition and method of application. Most often, doctors prescribe a contrast agent, which is administered intravenously and contains the rare earth paramagnetic metal gadolinium.
The procedure has no contraindications, the exception may be a peculiarity of the body with individual intolerance. In some cases, side effects are possible: rash, nausea, slight dizziness. Complications are observed in less than one percent of clinical cases.
Preparing for an MRI with contrast
What is research and what is its purpose?
Magnetic resonance imaging of the brain is performed to diagnose various pathological conditions.
Most often it is prescribed if there are suspicions of the following diseases:
- tumors, both benign and malignant;
- aneurysms and other vascular anomalies;
- strokes;
- pathology of the inner ear and organs of vision;
- injuries;
- pituitary diseases;
- multiple sclerosis and other diseases of the nervous system with a chronic course;
- severe and persistent headaches of unknown etiology;
- Diagnosis of brain pathology in dementia.
Preparing for an MRI of the brain with contrast
No special preparation is required before administering contrast, but experts advise avoiding heavy meals, regardless of which organ is being scanned. This will help avoid side effects such as nausea and vomiting.
During the procedure, you should remove all products made from ferromagnetic alloys. It is also necessary to remove any metal, even non-magnetic, from the face and head (earrings, chains, etc.) to avoid interference.
Women are advised to remove make-up from their face as some dyes contain metallic particles which may distort images.
The question of the frequency and frequency of MRI depends primarily on the disease for which this examination is prescribed. It is worth addressing this issue individually with your doctor, neurologist or neurosurgeon. The MRI procedure, regardless of the frequency of use, is completely safe and can be performed as often as necessary.
Indications for the study
Any doctor who diagnoses a patient can refer you for an MRI. However, most often neurosurgeons, endocrinologists, vascular surgeons and other highly specialized doctors refer for this examination. The patient, in turn, comes to them by referral from a therapist.
MRI of the head shows a variety of abnormalities, so the doctor may refer the patient for this examination if he suspects:
- neoplasm of malignant or benign type;
- stroke;
- the injury received;
- single or multiple type cyst;
- pathologies that affect the pituitary gland;
- diseases of the vascular system of the brain;
- the presence of parasites in the patient’s body that could penetrate the brain, moving along the vascular bed;
- development of pathology that entails deterioration of hearing or vision;
- multiple sclerosis;
- dementia.
Also, a similar study is carried out if the patient complains of frequent headaches, but any other diagnostic measures carried out did not help to give him an accurate diagnosis. Therefore, MRI is prescribed for migraines, as well as in the case of thrombosis and adenoma.
MRI of the brain is also performed for:
- The occurrence of metastases. As a rule, in this case the patient complains of simultaneous problems with hearing, vision, smell, and touch. He may have hallucinations, reading difficulties and other symptoms of brain damage.
- Epilepsy and other pathologies that manifest themselves in the form of confusion and speech. Also, MRI is mandatory for those who suffer from convulsions and other seizures.
- Meningitis, myelitis, encephalitis and other inflammations that affect the brain and are extremely dangerous to human life. MRI is also prescribed for lesions that could be caused by measles, tuberculosis, or toxoplasmosis.
- Rehabilitation after a traumatic brain injury or stroke. Thanks to the examination, the doctor can assess how quickly the recovery is progressing and whether he has chosen the right drug therapy.
- Degenerative processes that may indicate the development of pathologies such as multiple sclerosis, Alzheimer's disease and other diseases.
- Congenital pathologies or signs of hydrocephalus in children.
Indications for anesthesia during MRI
As a rule, during the examination the person is conscious. He is asked to lie still while he is in a special tomograph chamber. However, in some situations, the patient is physically or psychologically unable to lie quietly in a confined space and keep his body motionless.
General anesthesia is indicated in the following cases:
- Claustrophobia. This is a pathological condition that is characterized by a fear of closed spaces. In this case, the patient will be in a state of extreme stress and panic if asked to take a horizontal position in the tomograph. In this case, it is impossible to conduct diagnostic studies. In addition, the patient himself can harm himself, so it is recommended to conduct the examination under general anesthesia.
- Presence of mental disorders. If it is impossible to predict how the patient may behave inside the tomograph chamber, then it is better to use anesthesia. In addition, if a person is constantly in uncontrolled movement, this will blur the resulting image, and it will still not be possible to make a diagnosis.
- Nervous tics and other uncontrollable physiological characteristics. In this case, the patient also cannot take a calm and motionless state.
- Epilepsy and other pathologies that are accompanied by seizures. In this case, only intravenous anesthesia is indicated.
- Early childhood. A small child is also unable to follow doctors' recommendations and is unable to remain still. Therefore, for young patients it is sometimes recommended to use a light anesthesia, which has an effect through the short use of a mask.
- The presence of severe pain syndrome. If the patient is literally writhing in pain, he will also not be able to take an even position.
Contraindications
There are relative and absolute contraindications. In the first case, research is possible under certain conditions, in the second it is unacceptable.
Absolute contraindications:
- pacemaker;
- middle ear implants;
- metal body prostheses made of ferromagnetic alloys;
- presence of insulin pumps;
- pregnancy in the early trimester;
- Ilizarov apparatus.
Relative contraindications:
- claustrophobia;
- mental disorders in the patient;
- prosthetic heart valves;
- Bracket system;
- patients under 5 years of age.
The examination is performed as prescribed by a doctor to clarify the diagnosis, as well as to monitor the dynamics of treatment. In most cases, MRI of the brain makes it possible to correctly diagnose and identify diseases at an early stage.
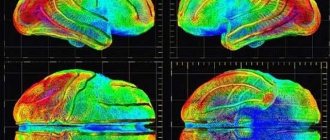
Decoding the results
An MRI of the head shows a large amount of information, but it is very difficult for someone who is far from medicine to understand it. Of course, in no case should you make a diagnosis for yourself based on your own assumptions or by comparing your picture with those images that are on the Internet.
MRI of the head. What does normal show?
However, it is possible to roughly estimate several parameters that may indicate possible deviations from the norm.
| MRI indicators | Decryption features |
| Fabrics | In normal condition, fabrics have a characteristic gray tint, which should be lighter or darker depending on the specific area. |
| Cerebral fluid | It looks like peculiar streams of light gray color. |
| Intracerebral sinuses | They should look like cavities of the same black color. In this case, the signal intensity of the sines should be the same. |
| Tumors | In the image they appear as light spots with uneven outlines. |
| Atrophy | Due to the too hidden development of the pathology, it is impossible to determine its presence. However, if you have some knowledge in the field of medicine, it is worth paying attention to dying cells. |
| Vessels | Should be evenly illuminated. |
| Atherosclerosis | The image clearly shows that the vessels are narrowed. You may also notice the presence of plaques. |
| Aneurysm | The vessels are dilated, and the walls of the vessels, on the contrary, look thinner. |
| Hypertensive angiopathy | Near the vessels you can see small round cavities. |
| Hydrocephalus | The ventricular cavities are greatly expanded. |
| Stroke | In the case of such a lesion, the brain suffers greatly from oxygen starvation. In the image, you can determine the area that is more affected by hypoxia by its lighter shade. Vascular ruptures will also be visible on the image. They are darkened areas with peripheral stripes. Gradually, these rings may begin to disappear, so it is important to have an MRI scan immediately after a stroke attack. |
| Multiple sclerosis | With pathology, the myelin layer disappears on the nerve fibers. In the picture you can see lesions that can be of different shades. It all depends on the volume of chemical components in the tissues. Foci of such lesions can be found in a variety of areas of the white matter. At the initial stage of multiple sclerosis, there may be several foci, but their number rapidly increases as the pathology progresses. |
It is better to entrust the interpretation of analyzes to a specialist, since only he can pay attention to the nuances. It is also worth considering that the same pathologies and abnormalities can manifest themselves differently depending on a huge number of factors, including gender, age and other patient data. Other pathologies from which the patient suffers are also taken into account.
MRI of the brain with or without contrast
The difference between the procedures is the information content of the image, because the use of contrast allows a detailed examination of the pathological focus under study. Standard MRI is performed without enhancing substances. There is no preparation before the usual procedure.
MRI with the drug takes longer than tomography without enhancement, since after the end of the umbrella tomography it takes about 15 more minutes to complete the contrast protocol.
The difference in price is noticeable - the cost of the substance increases the cost of scanning. The required amount of medicine is calculated based on the patient’s weight and varies between approximately 2500-5000 thousand rubles.
The substance is completely safe for the body - scientists have proven the low toxicity of gadolinium, which is part of the drug. This drug does not cause an allergic reaction and leaves the body without difficulty. The drug plays a significant role in identifying malignant tumors.
Preparing and conducting analysis
Before performing a brain scan using a tomograph, it is important to consult with a specialist. Recommendations for preparing for the examination may vary depending on your specific situation.
If we talk about standard preparation recommendations, it is worth considering the following tips:
- Before the examination, it is important to choose the right clothing. Since you should not keep metal objects near a powerful magnet, you need to carefully choose clothing for the examination. It should not have metal zippers, buttons, rivets or other decorations. In this case, you should give preference to comfortable, loose clothing, since you may have to stay in the tomograph for up to 1 hour. Some modern clinics have disposable sets of clothes for MRI, but this issue should be clarified in a specific medical institution.
- It is recommended not to wear jewelry, watches or other accessories. Or you can remove them immediately before the study, but it is better to think about this in advance, since there is a risk that, while in the medical center, a person may forget to remove one or another metal element. It is also worth checking if there are coins, keys and other things in your pockets.
- Before an MRI, you should avoid drinking alcohol. If the examination involves the use of a contrast agent, then you should not eat anything 3 hours before the MRI. If a patient eats a heavy lunch before an MRI, he may begin to experience severe discomfort during the tomography.
In some cases, before performing an MRI, it is necessary to introduce additional solutions that will further increase the contrast of the image. The doctor may also pre-inject the patient with a very small dose of a contrast agent to determine whether the person is allergic to the selected drug.
If an allergic reaction begins directly during the scanning procedure, this will distort the result and will have to be repeated. However, most often no prior administration of contrast is required.
Carrying out MRI
MRI of the head shows the presence of brain lesions and developing pathologies. Since the procedure is a type of magnetic resonance imaging, this means that all metal objects must be removed before the examination. In addition, the patient must even remove dentures, if any.
After this, the person is asked to take a horizontal position on a moving table, which will then be directed into the tomograph itself. Additionally, the patient can be secured using belts so that he does not move during the examination. After this, a special device with wires is placed on the person’s head. It is necessary in order to transmit and receive signals.
The patient is also recommended to use earplugs, since during the operation of the tomograph, not very pleasant clicking sounds are constantly emitted, which can tire you during a rather long stay inside the research apparatus.
When the patient is fixed on the table and is ready for research, the table moves into the tomograph, and the medical staff moves into the next room. The doctor monitors the progress of the study using a computer. Already during the procedure itself, the specialist can evaluate the data and draw preliminary conclusions about the patient’s condition.
During operation of the unit, layer-by-layer images are taken. Their quality and information content depend on which MRI method is used.
After the MRI, the patient can immediately go home and lead a normal life. This type of examination does not have any side effects or cause pain. Some discomfort can only come from being in one position for a long time.
The results of the study can also be obtained immediately. In some medical centers, I copy the received images to a disk, flash card, or can send them by e-mail. As a rule, the doctor who conducts the examination can indicate certain deviations from the norm, but the final diagnosis is made by the attending physician. He should be shown the MRI results.
When to see a doctor
Regardless of whether the patient was able to decipher the results himself, he must make an appointment with an MRI diagnostician. Only this doctor will be able to fully assess the person’s health status.
In order to understand why decoding can only be done by a specialist, it is enough to know that before starting to engage in MRI diagnostics, a person must not only receive an education at a medical institute, but also obtain the specialty of a radiologist.
After this, the doctor takes additional courses (lasting from 3 to 6 months, depending on the candidate’s qualifications). Next, the specialist spends another 2 years conducting and interpreting MRI under the supervision of more experienced colleagues, and only after that he can independently begin diagnosing.
An MRI diagnostician will make a diagnosis, but he is not involved in prescribing treatment. Therefore, after visiting a specialist, you need to go to the attending physician and present him with the results of the study and the diagnostician’s conclusion. Which specific doctor to contact depends on the specific pathology identified in the image.
You may need to talk to a neurosurgeon or cardiologist. A diagnostician can tell you who is best to contact.