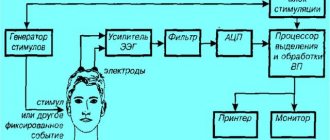
What is it prescribed for?
SCT (spiral computed tomography) of the chest organs is performed to study the condition of the lungs and mediastinal organs.
There are two types of procedure: simple and contrast.
In simple mode, images are obtained by passing the X-ray sensor in a spiral. During the procedure, a 1 mm thick slice is visible.
In the future, using automated software, you can obtain a 3D model of the chest organs. Such research is called virtual. In order to obtain it, it is necessary to place a person on a special diagnostic table of a computed tomograph.
The second type of SCT is a contrast examination. It is necessary for additional visualization of the pleural cavity or mediastinal organs. By introducing contrast into the free cavities, it is sometimes possible to identify additional shadows that are not detected during the usual procedure.
SCT of the chest is a qualitative research method that is prescribed for confirmatory diagnosis. When other methods are ineffective, SCT is prescribed.
Very often in inpatient medical institutions, using this method it is possible to identify tuberculosis foci, bronchiectasis cavities and bronchopleural fistulas. Computed tomography (spiral) allows you to accurately determine the location of the tumor, dissection or rupture of the vessel wall, the extent of the cancerous tumor, and also identify enlarged lymph nodes.
In oncology surgery, such X-ray diagnostics allows one to study the condition of a cancerous node, determine its boundaries and determine the size of the area for surgical intervention. Sometimes a computer examination of the chest cavity is prescribed to identify foreign bodies when it is urgently necessary to determine the cause of shortness of breath or difficulty swallowing.
SCT of the eyes, facial fragments and sinuses is widely practiced. The device detects disturbances in the structure of these organs and foreign bodies that have penetrated them.
SCT of the spine shows cracks, fractures of the spine, infected areas in the spinal canal, abscesses, osteochondrosis, intervertebral hernias, arthritis, osteoporosis, neoplasms and metastases in the spine and other organs, congenital anomalies of the skeletal system.
For limb injuries and joint damage, tomography is prescribed to clarify the diagnosis.
SCT of the chest reveals diseases of the heart, lungs, coronary arteries, esophagus, larynx, and large blood vessels. With its help, tuberculosis, aortic aneurysm, and tumors are detected. It is not recommended to eat food 4 hours before the procedure. This is what a picture of the heart obtained during the examination looks like.
For more information about how and for what purpose the study of human internal organs is carried out using a multispiral tomograph, see the video.
Many people have to undergo tomography during their lives. Which one is better - regular, spiral, magnetic resonance, share your opinion on this topic in the comments, let's discuss this issue together.
The information presented in the article is for informational purposes only. The materials in the article do not encourage self-treatment. Only a qualified doctor can make a diagnosis and make recommendations for treatment based on the individual characteristics of a particular patient.
Cost of the study
Carrying out spiral tomography, taking into account the time spent on preparation, data processing, formation of orders and recommendations by a radiologist, takes no more than 4 hours. No special preparation is required. The patient is recommended to undergo a preliminary MRI and ultrasound, and should not eat, drink or smoke 4 hours before the examination.
Stages of SCT diagnostics:
- administration of contrast (intravenously or orally);
- placing the patient on a mobile table (since you will need to lie still, in some cases the doctor prescribes sedatives);
- the table moves inside the gantry - “pipe” (the irradiation source rotates along a spiral trajectory);
- a scan is performed (usually the procedure takes from 5 to 30 minutes);
- information is displayed on a computer monitor (if desired, it can be recorded on a portable device);
- The radiologist deciphers the diagnostic result and issues a referral for consultation with specialists.
Examination using SCT is absolutely painless and may cause minimal discomfort associated with being in a confined space.
In order for the interpretation of the study results to be as accurate and reliable as possible, you need to provide the radiologist with your medical card or a report from the attending physician indicating a preliminary diagnosis. Then the doctor will be able to take into account all previous diseases and injuries, as well as the individual structural features of the patient’s body.
The price depends on the class of the clinic performing the scan, the model, the power of the tomograph and the area of the body being examined. The use of contrast increases patient costs. Average price in Russia: whole body - 13 thousand rubles, minimum price for one organ - 4 thousand rubles.
Pros and cons of SCT
This research technique is distinguished by its high efficiency and speed of diagnosis. However, it not only has numerous advantages, but also certain disadvantages with contraindications.
Spiral computed tomography has the following advantages:
- minimal diagnostic time (5-30 minutes), which makes the use of the SCT method relevant in diagnosing head injuries and brain damage, when it is important to make a diagnosis as quickly as possible;
- obtaining ultra-thin sections, which improves the quality of images;
- the ability to obtain important and extensive information in less than one second (up to 300 images per revolution of the tomograph drum);
- high degree of safety (irradiation of the body is 66% less than with conventional x-rays);
- the method allows you to obtain much more information than standard computed tomography;
- obtaining three-dimensional images, multiplanar design and the ability to reconstruct x-ray images.
SCT is ideal for diagnosing various disorders in the functioning of various body systems, however, this technique has certain disadvantages and risks, including:
- less significant, but still harmful to the body, radiation, the level of radiation received by the patient during SCT is on average comparable to the dose acquired by a person from the environment over the course of 3-5 years;
- it is inadmissible to perform the study in pregnant women and a ban on breastfeeding for 24 hours after the administration of a contrast agent;
- allergic reactions to contrast agents containing iodine may occur;
- The study cannot be conducted on children under seven years of age.
Before conducting the study, the patient should inform the doctors what diseases he has had in the recent past, whether he is currently taking medications, and whether he has allergies or not.
Who interprets the results and when can they be obtained?
The resulting SCT images must be examined by a radiologist (a doctor who specializes in CT, MRI, X-ray studies and has the appropriate certificate). It is necessary to “read” all the scans, study the provided medical information. documentation, compare it with the obtained CT image, describe the study, draw a diagnostic conclusion, shoot film with scans. On average it takes about 1-3 hours.
After the examination, you receive films with scans and a diagnostic report, which will be signed by a radiologist. Also, the diagnostic report may contain recommendations regarding your further actions (which doctor to contact with these results, what types of further examination are recommended, and so on).
Brain research
It is widely used in diagnosing head injuries in patients in severe and super-severe condition, symptoms of changes in blood circulation in the brain, high intracranial pressure, and various neurological disorders. We see changes in tissue density already in the early stages. The device detects pathology (abscesses, neoplasms, cavities) that may not be visible with a conventional tomograph. The procedure helps prevent and detect diseases such as stroke and heart attack.
The survey is used for:
- Determining the cause of headaches, systematic confusion, sudden onset of paralysis, impaired sensitivity of individual parts of the body, various visual disturbances. And also if there is a suspicion of a brain tumor, intracranial bleeding, or rupture of an aortic aneurysm.
- Diagnosis of inner ear dysfunction in hearing impairment.
- Developing a plan for an upcoming operation or assessing the success of an already performed brain operation.
- Determining damage to areas of the brain and providing assistance for stroke.
- Ensuring safe access and eliminating the possibility of brain injury during biopsy.
In some cases, the procedure is performed with the introduction of a contrast agent intravenously, which facilitates the detection of tumors, cysts, metastases, atherosclerotic plaques, and blood clots.
SCT of the brain does not require preliminary preparation of the patient.
The use of SCT for emergency and routine examination of the brain is very productive. All currently existing SCT devices make it possible to identify a clear picture of any structural change occurring in the brain.
Using such equipment, capable of performing layer-by-layer scanning of the brain, the doctor will be able to obtain a high-quality image of it, which will help identify various changes and diseases: tumors, strokes, injuries, etc.
The most complex and expensive examination is positron emission tomography. This study allows doctors to obtain a clear color image of the layer-by-layer structure of the patient’s brain, which will make it possible to study this organ in minute detail.
In addition, with the help of SCT, they monitor the effectiveness of the treatment and analyze the results after the operation to determine the current state of the brain.
This study will also make it possible to diagnose some other diseases and formations in the brain, including: various types of tumors and cysts, hematomas, and heart attacks.
SCT is used to diagnose various types of injuries in the head in severe and super-severe patients, with significant changes in blood circulation, significant intracranial pressure, and in cases of complex neurological disorders.
Such research can identify and demonstrate unhealthy changes at an early stage. SCT can detect pathology that a conventional tomograph cannot detect. This brain examination will help to promptly identify many disorders in the brain.
This study is also used for:
- identifying the causes of headaches, with repeated cases of confusion, unexpected paralysis, loss of sensation in the limbs, visual impairment;
- during suspected brain tumors, intracranial bleeding, aortic rupture;
- to identify the cause in cases of hearing impairment, inner ear dysfunction;
- developing a plan for future surgery and its effectiveness on the brain;
- identifying damage to the brain and providing care for strokes and many other problems.
This type of examination may also be prescribed for patients with other types of diseases, such as multiple sclerosis. In certain situations, the study is performed using and introducing into the patient’s body a contrast agent that can facilitate the detection of tumors, atherosclerotic plaques, cysts and other pathologies.
This procedure does not require special preliminary preparation from a person.
Equipment for spiral computed tomography
Spiral computed tomography has become widespread. Since 1986, the technique began to actively spread throughout the world.
Over the 20 years of its existence, SCT has identified a new direction in development – oncology. The procedure is considered one of the highest quality. Layer-by-layer scanning allows you to study each layer of the chest structure separately through 1 mm.
To carry out the procedure, special equipment is required. It is a diagnostic table on which a person lies. A tube with an X-ray emitter moves along it in a spiral. It emits a thin beam, which is detected by a special sensor.
Rapid rotation of the tube in a spiral tomograph allows one to reduce the amount of radiation exposure to the spine. Directed examination of individual vertebral segments can further reduce radiation exposure. For these purposes, before performing SCT, radiography of the chest organs in frontal and lateral projections is prescribed.
In addition, modern equipment allows you to obtain high-quality images and 3D models.
The advantages of SCT include the rapid completion of the procedure and the receipt of reliable information - more than 98%. The manipulation allows for high-quality reconstruction of images. New perspectives in the development of the technique are offered by contrasting research. It complements the list of x-ray diagnostics and often allows you to save a person’s life.
Until about 20 years ago, there was a patient weight limit on CT scanners. If a person weighs 130 kilograms, there were limitations to the study. Modern equipment for SCT does not create such inconveniences.
Thus, spiral computed tomography allows us to identify things that are inaccessible to other x-ray methods. The research is highly reliable, but many medical clinics do not have enough money to purchase such equipment.
Ankylosing spondylitis and other autoimmune diseases
Back pain (dorsalgia)
Other pathologies of the spinal cord and brain
Other musculoskeletal injuries
Muscle and ligament diseases
Diseases of the joints and periarticular tissues
Curvatures (deformations) of the spine
Treatment in Israel
Neurological symptoms and syndromes
Tumors of the spine, brain and spinal cord
Answers to visitors' questions
Soft tissue pathologies
X-ray and other instrumental diagnostic methods
Symptoms and syndromes of diseases of the musculoskeletal system
Vascular diseases of the central nervous system
Spinal and central nervous system injuries
Irritable bowel syndrome (spastic colitis, mucous colitis)
It should be noted that defecation occurs at different frequencies for everyone. For some, the norm will be 3 times a day, and for others - 3 times a week. In essence, SRCT is not a serious disease. It is considered a functional disorder, because during the examination of the colon, no signs of the disease are detected. Quite often, SRCT is a consequence of stress, as well as fatigue or nervous stress. In addition, this disease is often associated with hemorrhoids.
What are the most common symptoms of SRCT? First of all, it is pain in the abdominal area. Bloating and gas formation are also common. Intestinal problems such as constipation or diarrhea may occur.
How can you help yourself with SRCT? Let's start with the fact that it is important to eat the right foods. To be more specific, fatty foods, especially meat and poultry skin, whole milk and butter, whipped cream and margarine, are strictly prohibited. Avocado is a harmful fruit. Also, don't eat chocolate. Increasing the amount of fiber in your daily diet will be very useful; bread is great, as are legumes and vegetables. You need to eat little, but quite often. It helps to reduce pain and spasm in the intestines. A very important point is to reduce stress and strain; if you are nervous, then take the appropriate medications. If you have a fever, you should consult a doctor. The same should be done if you have blood in your stool or if you are seriously losing weight in a short period of time.
A very important point - in women during menstruation, symptoms appear more clearly; it should be noted that if you take sex hormones, they are quite capable of causing an exacerbation of the disease.
Other forms of colitis
We have put a lot of effort into making sure you can read this article and would welcome your feedback in the form of a rating. The author will be pleased to see that you were interested in this material. Thank you!
(1 ratings, average: 3.00 out of 5)
gemor.su
What is SKT? What is the essence of the procedure and is it worth doing?
Preparation for the SCT procedure of the brain obliges the patient to refuse to eat 4 hours before the examination. Besides this, it's not worth it
Tomograph Somatom Ssensation-64
smoke, drink strong tea or coffee. It is advisable to take the results of previous studies (MRI, ultrasound, CT) with you to the examination.
It is worth warning doctors in advance about the presence, if any, of allergic reactions, chronic diseases and other similar problems.
On average, the procedure lasts no more than 30 minutes. During this procedure, the patient is placed on a convenient mobile table, on which the subject will be moved inside the tomograph. During the entire examination, the tomograph ring will rotate around the table with the patient.
The person must lie still during the procedure. At this time, the medical staff monitors the examination, and if the patient feels some discomfort, he can notify the doctors about it using the communication system.
The result of the examination with its detailed description is available to the patient a short time after its completion. Often the results are recorded on a CD. With the acquired data, the patient must come to his treating doctor, who will write out a detailed treatment program for him or send him for a consultation with another specialized specialist.
Today, the price of spiral computed tomography of the brain in clinics in the Russian Federation starts from 5,000 rubles.
The price is influenced by the name of the clinic, the level of service and equipment used, whether the patient needs to use a contrast agent during the examination, and other factors.
Consultation and interpretation of the obtained data are either included in the cost of MSCT or can be paid separately.
4 hours before the examination procedure, food and water intake is stopped.
Before examining some organs, the patient must undergo preparation - drink a contrast agent (urografin). Detailed instructions for preparing for the procedure will be given by the specialist who will conduct the examination.
The dinner before the procedure is light; for breakfast it is better not to eat solid food, preferably liquid porridge and juice.
The patient lies down on a movable table that slides into a special tunnel - a scanning device. For the patient’s comfort, the table is equipped with special pillows and belts; they help limit his movements during the procedure so that the photographs are clear and not blurry.
Patients who cannot lie still for a long time and hold their breath for a short time (children or nervously excited patients), or are susceptible to claustrophobia, are given a sedative.
In another office there is a computer station with a doctor-technologist working on it, controlling the scanner using the screen. During the procedure, he talks to the patient and gives the necessary instructions.
The spiral computed tomography procedure is completely safe. Although the patient receives a small dose of X-ray radiation, it is so insignificant that it does not cause any harm to the body. There is a risk when administering a contrast agent or sedatives. The patient must inform the doctor about any allergic reaction he has to medications or iodine, which is part of the dye.
If the person being examined has diabetes, asthma, kidney failure, heart disease or thyroid disease, you should also tell the doctor about this.
The examination is contraindicated for pregnant women. If there is an urgent need, it is still performed, but the uterus is covered with a lead screen. Patients with pacemakers, ferromagnetic implants, and patients weighing over 130 kg are also not examined.
Next, the radiologist conducts a thorough analysis of the images.
Spiral computed tomography is one of the modern methods for diagnosing many diseases of different parts of the human body. Now we will try to figure out what SCT is and what the essence of its action is.
Relatively recently, a completely new method of diagnostic examination of various parts of the body has appeared in medicine. We are talking specifically about spiral computed tomography. Not long ago in 1986, the first spiral tomograph passed all the necessary tests and two years later began to be actively used in hospitals for diagnosing many pathologies, the identification of which had previously caused many difficulties.
It should be noted that Siemens and TOSHIBA, which are still actively working in the medical equipment market, began to produce such tomographs. Each of their new tomographs has a larger number of detectors, up to 5000, and conducts a full examination in a shorter time. The fourth generation device takes less than a second to scan a patient’s turnover.
Indications and contraindications for use
Due to the high speed and information content of the examination, the relative simplicity of the procedure and the absence of the need for special preparation of the patient, SCT is prescribed for:
- examinations of victims with various brain injuries;
- detection of brain diseases and control over their course (spiral computed tomography of the brain);
- determining pathologies of internal organs in patients with breathing disorders;
- examination of patients with whom contact is impossible or difficult;
- making a diagnosis in those patients who experience severe pain in a horizontal position;
- in some cases when children are examined;
- identifying pathologies of the cardiovascular system;
- creating graphic models of internal organs, including in non-standard planes;
- virtual endoscopic examination;
- for the purpose of modeling operations in the process of training medical specialists.
Find out what triplex scanning of head and neck vessels is: indications and procedure.
Read who is prescribed an EchoEG of the brain, and for what diseases the study is indicated.
Physical properties
To obtain images, a spiral computed tomograph (SCT) uses classical X-rays. SCT is a special X-ray installation that, rotating around the patient’s body, takes pictures from all angles and allows you to obtain sections of a separate area of study. The resulting sections are processed by the server, summarized, and the diagnostician receives a three-dimensional image of a part of the patient’s body. With this research method, radiation exposure is present.
A magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scanner does not emit x-rays to produce images. The patient is placed in a high-intensity magnetic field, this is necessary so that the hydrogen atoms in the human body line up parallel to the vector of the magnetic field strength. At the same time, the device generates an electromagnetic signal, perpendicular to the static vector of the magnetic field, while hydrogen atoms, which have the same frequency as the signal, go into an excited state, generating their own signal, which is received by the device.
They've been through it
I recently had an SCT of the brain done in one of the clinics in St. Petersburg, everything went quite quickly, under the supervision of specialists and generally at a high level, the price is acceptable, especially when you realize the importance of this study.
Marina, July 2020
Lately I have been tormented by constant headaches and often had high blood pressure. My doctor advised me to do an MSCT of the brain, thanks to which he was able to see the problems that had arisen and prescribe an effective comprehensive treatment.
I am absolutely satisfied with the examination, I am very glad that I carried it out in a timely manner and eliminated the ailments at their early stages of development.
Mikhail, Nizhny Novgorod, September 2016
Sensitivity
If you take a picture of a regular X-ray machine, even a non-specialist will be able to best distinguish the bones in it. MSCT, using X-ray radiation, will also “see” bone tissue better. Therefore, SCT is very well suited for diagnosing bone injuries and damage. Moreover, in the SCT image, the doctor accurately sees open bleeding, so computed tomography is used to study patients with injuries to the head, chest, abdominal cavity and pelvic organs, as well as in the early stages of stroke.
Magnetic resonance imaging is focused on the study of human soft tissues (brain, muscles, ligaments, cartilage, etc.). As an example, MRI is prescribed in cases of suspected ligament rupture and to exclude or diagnose intervertebral hernias. For neurology and neurosurgery, MRI is the main tool for reliable diagnosis of diseases and pathologies (long-term traumatic brain injuries, late stages of stroke, suspected brain tumors).
What is the essence of SCT?
The first spiral tomograph appeared in 1988 and became an indispensable assistant for doctors.
This method is based on scanning the body with X-rays, which are converted into electrical signals and further processed by a computer. It allows you to quickly obtain an accurate result with an unprecedented error of only 1 mm.
During a session in the clinic, the table with the patient moves, but around the patient, as if in a spiral, the X-ray tube with the surface on which the detectors are located additionally rotates.
The device recognizes tumors up to 1 mm in size. This is extremely important in oncological diseases for the timely detection and elimination of the source of the disease. One anatomical area is scanned on an outpatient basis within 3-5 minutes. The laser camera takes wide-format photographs.
Amazing results can be obtained on modern 64-slice (multi-slice or multi-slice) high-speed tomographs - quickly obtaining two-dimensional and three-dimensional images of excellent quality with a low level of radiation.
SCT in medicine is a relatively new phenomenon. It is based on conventional computed tomography, but with some differences. This feature consists of the simultaneous rotation of the X-ray emitter and the table - the conveyor on which the subject is located.
This double rotation is ensured by a special so-called “sliding ring”. In which the X-ray room is located. When the tomograph is turned on, the tube begins to emit X-rays in one clockwise or counterclockwise direction. At the same time, the patient’s table begins to move and thanks to this, in one approach the tube makes not a circle around the examined person, but a kind of spiral.
Another feature of SCT is that it does not make one topographic slice, but scans the entire examined area. For example, if you conduct an SCT scan of the brain, you will get not one image, but several, which will show the state of almost all the structures of this organ.
The main characteristics of a spiral tomograph are the speed of movement of the conveyor table and the slice thickness. Moreover, the accuracy of the shooting depends on the speed of movement of the table; the faster it moves, the less clear the reconstruction will be.
What is SCT?
The article will focus on spiral computed tomography: what is SCT, are there any differences between SCT and MSCT, what place does SCT occupy in modern medicine, a little history, the essence of the method, its advantages, indications, contraindications, prices, reviews.
Computed tomography is a modern way of diagnosing diseases of various organs and systems, one of the types of which is spiral computed tomography. The beginning of its use in clinical practice dates back to 1988. SCT belongs to the methods of radiation diagnostics that are based on X-ray radiation.
Its peculiarity is the simultaneous rotation of the X-ray tube and the movement of the tomograph table on which the patient lies. Thanks to this, the X-ray source moves in a spiral, which is the key to quickly obtaining detailed longitudinal and transverse sections of areas of interest in increments of 0.5 mm. The technique allows you to identify pathology at an early stage and detect formations up to 0.1 cm in size.
Multislice, or multi-slice, computed tomography (MSCT), like SCT, allows you to analyze information based on the ability of the tissues of the human body to absorb X-rays. It began to be used in medical practice later - in 1992. The main difference between MSCT is the increase in the number of detectors located around the circle.
Advantages of the newest diagnostic method
SCT has a number of differences and advantages over conventional computed tomography:
- High speed of information collection (scanning). In a short period of time (up to 20 seconds), an image of one anatomical area (abdomen, lungs) is formed. The quality of the pictures is very high.
- Obtaining more accurate spatial 3D images. Three-dimensional models more accurately show the nature and location of the pathology. The use of spiral scanning techniques made it possible to use angiography, i.e. examination of the arteries, to identify vascular aneurysms, narrowing, and their extent.
- Non-invasiveness in comparison with ventriculography, myelography.
- There are no blood flow artifacts in the image.
- Reduced X-ray exposure to the patient compared to conventional tomography. Even when studying several anatomical zones simultaneously, radiation doses are not summed up.
As already mentioned, spiral tomography is a new generation in the field of medical diagnostics. So what is the difference between SCT and MRI. The following paragraphs show not only the differences between these two types of diagnostics, but also the advantages of spiral tomography over magnetic resonance imaging.
- SCT can diagnose a specific organ (liver, kidneys) separately, and not as part of the entire abdominal cavity or chest. The degree of differentiation in SCT is 1-2%, and in MRI – 15-20%.
- The research speed is much higher than in MRI.
- Makes it possible to obtain a clear cut of the organ under study, without unnecessary layers.
- The quality and resolution of the obtained images as a result of SCT are significantly higher than in MRI.
- Using SCT, you can learn about the exact sizes, features of various organs and pathological formations.
- Serious injuries to internal organs and brain;
- Examination of the chest cavity if a person is unable to hold his breath for a long time;
- Diagnosis of patients with whom close contact poses some difficulties;
- During the diagnosis of patients with acute pain, which significantly intensifies during prolonged lying down.
SCT is also recommended in cases where a minimum amount of x-ray exposure is required, namely:
- When children under twelve years of age need examination;
- When it is necessary to diagnose pathologies of blood vessels, especially the coronary arteries.
- If virtual endoscopy is necessary;
- If it is necessary to construct an accurate image in the frontal, sagittal and axial planes.
- During demonstration operations for the purpose of training young doctors.
What does SKT “dislike”?
First of all, these are movements. Any movements during scanning of the study area distort the resulting images, of course, reducing their information content for the doctor. If in a series of images obtained, even just 1-2 scans are distorted by motion artifacts, then subsequent 3D reconstructions will already have defects and their information content for the doctor, of course, will be reduced.
Secondly, metal. Metal is to X-rays what a mountain is to the sun—it leaves a “shadow.” A large amount of metal in the examination area can significantly distort the resulting images. But if the metal is located in any place other than the area being examined, it cannot in any way affect the quality of the scans.
Spiral computed tomography of the abdomen
The procedure creates a multi-layered image of organs (liver, spleen, pancreas, etc.). The indication for it is pain in the abdomen, pelvis, as well as a number of diseases of the small and large intestines, internal organs.
It is used in diagnostics:
- Appendicitis, pyelonephritis, kidney and bladder stones, diverticulitis, abscesses
- Pancreatitis, cirrhosis of the liver, inflammatory processes and polyps in the intestines, internal bleeding
- Cancer of organs located in the abdominal cavity
- Diseases of blood vessels and lymph nodes
Before the procedure, the patient must be prepared and a contrast agent is used.
How to prepare for a CT scan
As a rule, no special preparation is required before performing a CT scan, with the exception of the following cases:
- CT scanning using contrast agents is performed on an empty stomach;
- during examinations in the pelvic area, the bladder should be moderately full;
- When examining the abdominal cavity the night before, you must have a bowel movement using a laxative or an enema.
It is also necessary to try not to consume foods that can cause flatulence for several days before the procedure.
Tell your doctor if you:
- have chronic diseases;
- Have recently had an X-ray using barium (this substance can interfere with the clarity of the resulting images);
- you suffer from claustrophobia (being inside the tomograph in this case may be unpleasant for you).
It is necessary to have with you information regarding the course of your illness, including: a referral, an extract from the medical history, photographs or results obtained through other examination methods.
At the end of the procedure, the patient receives pictures on his arm; in some cases, they may be accompanied by a CD with three-dimensional images. The doctor who issued the referral makes a decision on further treatment depending on the results obtained.
If you were examined on your own initiative, you can consult with the specialists of the diagnostic center about further actions.
Renal tomography
This method of kidney examination is used:
- For timely detection of benign and malignant formations in the kidneys, stones, anomalies of kidney development, abscesses, polycystic disease.
- To diagnose kidney injuries.
- During a kidney biopsy to monitor the correctness of tissue sampling.
- After a kidney transplant or removal, to monitor the condition of the operated area.
During the procedure, a contrast agent is used to improve the clarity of the image. The day before the examination, the patient is prepared according to the generally accepted scheme.