General description[ | ]
Sound echo
- reflected sound. An echo is noticed if one also hears direct sound from a source, when at one point in space one can hear sound from one source several times, arriving along a direct path and reflected (possibly several times) from surrounding objects. Since a sound wave loses energy when reflected, a sound wave from a stronger sound source can be reflected from surfaces (for example, houses or walls facing each other) many times, passing through one point, which will cause multiple echoes (such an echo can be observed from thunder ).
The echo is due to the fact that waves can be reflected by solid surfaces; this is due to the dynamic pattern of rarefaction and compaction of air near the reflecting surface. If the sound source is located near such a surface, turned to it at a right angle or at an angle close to a right angle, the sound, reflected from such a surface, like a wave reflected from the shore, returns to the source. Thanks to the echo, the speaker can hear his own speech, along with other sounds, as if delayed for some time. If the sound source is at a sufficient distance from the reflecting surface, and besides the sound source there are no additional sound sources nearby, then the echo becomes most distinct. An echo becomes audible if the interval between the direct and reflected sound wave is 50-60 ms, which corresponds to 15-20 m that the sound wave travels from the source and back, under normal conditions.
Echoencephalography of the brain
Echoencephalography of the brain is one of the modern hardware research methods based on ultrasound neurophysiology and allows one to assess the functioning of the central nervous system.
The brain is the actual control center of the entire body. Its condition affects the functioning of all organs and systems. It is very important to promptly identify any disorders of brain activity. This task is performed by modern diagnostic methods, including EchoEG.
Features of the procedure in children
Until the age of one and a half years in children, the fontanel in the bones of the skull has not yet healed. Thanks to this, EchoEG studies in children are the most accurate and informative.
The study of the brain using ultrasound through a non-overgrown fontanelle is classified as a separate type of EchoEG - neurosonography. If necessary, it is performed even on newborn babies.
As a rule, such a need arises in case of suspected dangerous diseases of the child, pathologies of fetal development, identified as a result of monitoring during pregnancy.
Along with echo research, an EEG is used - an electroencephalogram, which examines the biocurrents of the neural activity of the central nervous system. Compared to MRI and CT, this method is less informative. However, the advantage of echo diagnostics is its safety and painlessness.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=n68URHkQKCM\u0026list=PLvT-BS6OODhlXHMROt9iEXXQH-UpJ2v2P
EchoEG is performed for children in the following cases:
- deviations in the child’s behavior;
- long-term and serious sleep disorders;
- delayed development of speech, growth, movements, etc.;
- nervous tics;
- head bruises;
- enuresis (urinary incontinence);
- severe stuttering;
- increased muscle tone;
- suspected hydrocephalus (water on the brain).
Decoding the results
The result of an echoEG is an encephalogram, which is a graphic image. Only specialists have the right to decipher and interpret its data - a laboratory assistant in the hardware functional diagnostics room, a neurophysiologist, a neurologist. Usually, 15-20 minutes pass from taking readings from the EchoEG device to the doctor’s conclusion.
The main indicator is the size of the M-echo and its symmetry relative to the different halves of the brain (no more than 1-2 mm deviations; in children up to 3 mm is allowed). The decoding also takes into account three types of signals: primary, middle and final complexes.
- The primary complex is signals reflected from the muscles, skin, meninges and upper parts of the brain.
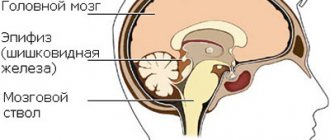
- The median complex is the reflection of signals from the middle part of the brain: third ventricle, cerebral peduncle, septum pellucidum, pineal gland, etc.
- The final complex of signals comes from the bones of the skull, the dura maters of the brain, and the soft layers of the brain matter.
The nature of the changes in waves as they pass through brain tissue makes it possible to detect existing diseases. For example, a signal shift of up to 3 mm indicates the presence of edema in the brain tissue, more than 3 mm indicates the formation of a cyst, and an increase in this value to 7 mm indicates hydrocephalus.
EchoEG helps to quickly identify diseases, many of which carry the threat of disability and even death. But disastrous consequences can be avoided if a diagnosis is made quickly and correctly and treatment is started in a timely manner. The use of echoencephalography, without a doubt, helped doctors save thousands of human lives.
Source: https://onevrologii.ru/metody-lecheniya/ehoentsefalografiya-golovnogo-mozga
The use of echoencephalography in childhood
The procedure is completely painless. This is the main advantage of EchoEG. The research process is not accompanied by unpleasant sensations or discomfort. This makes this type of examination convenient for diagnosing various pathologies in a child.
Echoencephalography is used in children with the following disorders:
- to assess the degree of hydrocephalus of the brain;
- with significant sleep disorders;
- with nervous tics;
- with delays in speech and physical development;
- with muscle hypertonicity;
- with urinary incontinence;
- for bruises and concussions.
In children under one and a half years old, it is possible to make a more accurate and complete diagnosis of all parts of the brain, since before this age the fontanel has not yet completely healed.
Also, to identify malfunctions in the brain in children, the EEG (encephalogram) method is used. This study captures biological neural currents and helps identify the causes of epilepsy in brain activity.
Preparation for the procedure and its implementation
Head echo does not require additional preparation. There is no need to drink a lot of fluids or follow a special diet, as is the case with an ultrasound. The examination is used for people of any age. There are no contraindications for normal pregnancy and breastfeeding after consultation with a doctor.
How is diagnosis carried out? First, the specialist must study the patient’s medical history and check the condition of the head to exclude subcutaneous hemorrhages and violation of symmetry.
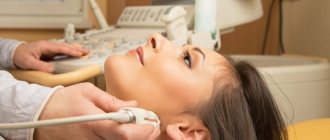
The patient is in a supine position, but sometimes the procedure can be performed while sitting. Before installing the sensors and starting the study, the specialist applies a special gel to certain areas of the head. This allows for a stronger connection between the sensor and the skin.
The gel is absolutely harmless and does not cause irritation, discomfort, deformation, etc.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=t3lVPg91Dqs\u0026list=PLvT-BS6OODhlXHMROt9iEXXQH-UpJ2v2P
The diagnosis begins on the right side of the skull, then on the left, moving from the frontal to the occipital part of the head. This examination option is used for urgent diagnosis. It is often used for emergency diagnostics. The small size of the device allows it to be portable, thereby speeding up diagnosis in bedridden patients.
One-dimensional echoencephaloscopy of the brain is usually performed in a clinic by the attending physician, but it can also be done in an ambulance, at home or on the street. To do this, the device must be equipped with a battery. The procedure lasts from 10 to 15 minutes.
Types of diagnostics
There are two types of EG echo:
- Transmission.
- Emission.
The transmission method uses two ultrasound sensors, which are installed along the same axis on both sides of the skull. The first probe sends electrical signals to the second.
This is needed to calculate the “midline of the head.” Normal - if it coincides with the midline, which should be smooth.
But if there were bruises, displacements or intracranial hemorrhages, the signal from the sensors does not coincide with the anatomical line.
With the emission diagnostic method, only one probe is used. It is installed at those points where the cranial bone is thinnest. Thanks to this, ultrasound penetrates better and gives a more accurate understanding of the state of the brain.
To make the image more accurate, the Echo EG apparatus is gradually moved along the surface of the skull. A projection of a cross section of the brain will appear on the monitor.
But if the foci of pathology are insignificant, this examination method will not be sufficiently reliable.
Decoding the research results
The results of interpretation of Echo EG of the brain in adults and children do not differ. The procedure is performed by a sonologist.
Normally, the examination consists of three bursts, which are called complexes. The initial burst is a signal generated by ultrasound. Ultrasound is reflected from the bone tissue of the skull, skin and brain tissue. The median burst (M-echo) is a complex that is obtained when ultrasound comes into contact with the structures of brain tissue located between the two hemispheres.
The final burst is a signal that comes from the tissues of the cranial bones and the dura mater of the brain on the other side of the probe. The connection between these three complexes is projected onto the monitor screen and represents a graph with axes. The specialist prints the results on paper and begins decoding.
Evaluation of indicators
The data decryption is as follows:
- M-echo. Such a signal usually occupies a middle position between two bursts. A displacement of 1.5 mm will be considered normal. If the indicator is higher, then you need to undergo additional diagnostics. After a stroke, a shift of more than 5 mm indicates the hemorrhagic nature of the disease. If there is no signal at all or it is no more than 2.5 mm, the disease is ischemic in nature.
- Burst from the third cerebral ventricle. Splitting or expansion of this indicator indicates intracranial hypertension.
- M-echo pulsation. Indicators should not exceed 10-30%. If they are higher, this may indicate hydrocephalus of the brain.
- SI (mid-sellar index). For adults, the norm will be 3.9-4.1 and above. If the results are lower, this indicates increased intracranial pressure.
Rice. 1.
Schematic representation of normal echoencephalograms: at the top - a frontal section of the head with ultrasound sensors located in the temporal regions (A, B), below are echoencephalograms (A - right, B - left); SS - midline structures, M - M-echo, ES - echo signal from various non-median structures of the brain, NK - initial complex, CC - final complex; Normally, distance a on the echoencephalogram obtained when installing the sensor on the right is equal to distance b on the curve obtained when installing the sensor on the left.
Rice. 2. Schematic representation of echoencephalograms with a space-occupying formation in the right hemisphere of the brain. In case of pathology (a space-occupying lesion in the right hemisphere of the brain is shaded), distance a on the right (upper) curve is increased due to the displacement of the midline structures of the brain, and the direction of displacement of the M-echo is opposite to the localization of the pathological focus.
Other results
Electroencephalography contains several more indicators:
- Third ventricle index. The norm is 22-24 points. If the result is less, this is a sign of hydrocephalic syndrome.
- Medial wall index. The norm is 4-5 points. A higher result indicates intracranial hypertension.
Each examination, be it Echo-EG, ultrasound or ECG, has errors. Only a doctor can interpret the results. After identifying the origin of the disease, he will prescribe the necessary treatment or additional diagnostics.
Where can I make an Echo Head?
This type of disease testing is offered by specialized clinics in many Russian cities. The study is prescribed by a neurologist.
Doctors have been using echo EG for many years. This is the only method of brain research that has no contraindications.
It allows you to identify pathologies when magnetic resonance or computed tomography are unavailable for one reason or another. The procedure does not cause discomfort and there are no side effects after it.
The only drawback of this diagnostic method is that it does not detect small pathologies, unlike CT or MRI, which help diagnose the disease in the early stages.
Source: https://neuromed.online/eho-eg/
Practical application[ | ]
Since sound waves travel at a constant speed in air (about 340 meters per second), the time it takes for sound to return can provide information about the removal of an object. To determine the distance to an object in meters, you need to measure the time in seconds before the echo returns, divide it by two (the sound travels the distance to the object and back) and multiply by 340 - we get the approximate distance in meters. This principle is the basis of echolocation, which is used mainly to determine the position of an object using the delay time of the returns of the reflected wave. Echo is a significant interference in audio recordings. Therefore, the walls of rooms in which songs, radio reports are recorded, as well as the texts of television reports are read, are usually equipped with sound-absorbing screens made of soft or ribbed materials that absorb sound. The principle of their operation is that a sound wave hitting such a surface is not reflected back and is attenuated inside due to viscous friction of the gas. This is especially facilitated by porous surfaces made in the form of pyramids, since even reflected waves are re-emitted deep into the cavity between the pyramids and are further attenuated with each subsequent reflection.
In what cases should the procedure be performed?
Children are referred for Echocardiography in several cases:
- Shortness of breath.
- Headache.
- During the examination, the pediatrician discovered a heart murmur.
- If a parent feels that the child's heart is not working as it should.
- If this is a newborn and he is not feeding well, you should pay attention to the color of the skin around the mouth. If there is blueness there, an urgent examination is necessary.
- Loss of consciousness of a child indicates a possible disease of the cardiovascular system, in which case it is also necessary to consult a specialist.
- Problems with weight gain, poor sleep.
- If a child becomes overtired for no apparent reason.
- Frequent illnesses, pneumonia.
- If anyone in the family suffered from heart disease.
Thus, if a child has any of the symptoms listed above, you should not delay, you should immediately contact a specialist.
The heart is the main organ that ensures the functioning of the entire body, and it must work like a clock!
In our country there are certain norms and standards according to which children under one year of age must be examined by a heart doctor. Before visiting a specialist, it is necessary to do an ECHO, KG and ECG.
Literature[ | ]
- Gezekhus N. A.,.
Echo, in physics // Encyclopedic Dictionary of Brockhaus and Efron: in 86 volumes (82 volumes and 4 additional). - St. Petersburg, 1890-1907.
| This is a draft article on physics. You can help the project by adding to it. |
To improve this article it is desirable:
Please, after fixing the problem, remove it from the list of parameters. After eliminating all the shortcomings, this template can be deleted by any participant. |
Echo kg for newborns
Usually ECHO KG of a newborn in case of possible investigative transmission from relatives or if the doctor during the examination discovered any disturbances in the functioning of the baby’s heart.
Checking a child's heart using echocardiography is done at any age, whether it is a newborn child or a schoolchild, it makes no difference, it is absolutely safe. There is no irradiation or the like, since in this case it is not laser beams that are used, but mechanical vibrations. The most important thing for parents is not to have any conversations with the doctor in front of the child and discuss all illnesses separately. Don't upset your baby.
Where to do ECHO KG?
Nowadays, in the age of high technology and the developed structure of medical institutions, ECHO CG can be done in almost any clinic.
There are also specialized medical institutions that specifically treat the heart and cardiovascular system. Most of them have their own websites, so you can find out all the information right at home, which is very convenient. Every city has such a center, plus there are general diagnostic centers. By contacting a state institution, ECHO CG can be done for free, but in private clinics you will most likely need to pay a certain amount for this.
Ultrasound examination or echocardiography of the heart is a diagnostic method that allows one to recognize pathologies of the heart and blood vessels around it. Such a study takes no more than twenty minutes, but shows fairly accurate results.
Quite often, doctors prescribe cardiac echocardiography for children. Having learned this, parents are very worried because they do not know how safe such a study is. Mom and dad immediately have many questions: why did the doctor order a diagnosis, what can it show and how, and, most importantly, when to do an ultrasound of the heart of a newborn child?
Order of conduct
No special preparation is required for echoencephalography. You can lead your usual lifestyle, there are no restrictions on diet or medication.
The procedure is performed in a lying or sitting position. It is important to keep the head still, so when examining the child, parents can be present in person and help the baby not move. A special gel is applied to the scalp to improve the conductivity of the ultrasound signal, then the doctor installs the sensors.
Depending on the tasks, a specialist can install one sensor or use two located on both sides of the head. The result of this diagnostic method is a graphic image that shows whether the midline structures of the brain are displaced or whether there is an expansion of the cerebrospinal fluid spaces.
Pathologies detected using EchoEG
Echoencephalography is effective in diagnosing tumors arising in the brain and determining their location. Using this research method, specialists also diagnose injuries, hydrocephalus, and various inflammatory diseases.
Neoplasms and hematomas
To make a diagnosis, the distances to the M-echo on the left and right sides are measured. In adults, they are almost equal to each other and amount to 65-80 mm. Differences can be no more than 2 mm.
If there is a volumetric neoplasm in one hemisphere, the following occurs:
- the pineal body and the third ventricle are shifted towards the normal hemisphere;
- the distance to the M-echo increases on the affected side and decreases on the healthy side.
With large displacements, specialists suspect malignant neoplasms.
The difference between the right and left sides may exceed normal values for hematomas. If the displacement is 4-8 mm and increases gradually, neurosurgical intervention is performed. A slight displacement (less than 3 mm) can be observed with brain contusion and swelling. In such cases, the displacement disappears after a couple of days. In addition to echoencephalography, an EEG may be prescribed.
EEG of the brain
Meningoencephalitis
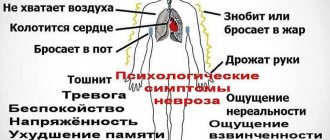
This disease is characterized by inflammation of the substance and membranes of the central nervous system organ. Meningoencephalitis develops due to the entry of certain bacteria, viruses and protozoa into the body. Patients develop symptoms such as headache, nausea, chills, vomiting, and body temperature rises.
If a sick person has meningoencephalitis, then during an Echo EG a significant displacement of the M-echo will be noticed. With large values of the indicator (more than 7-8 mm), the development of a brain abscess (focal accumulation of pus in the substance of the organ) may be suspected.
Hydrocephalus (dropsy)
This term refers to the excess accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the cranial cavity. The disease develops:
- due to increased fluid formation;
- violations of its circulation;
- decreased fluid absorption, etc.
Signs of dropsy in newborns include a rapid increase in the size of the head, a displacement of the eyes to the bottom, a bulging, tense fontanel, and the appearance of round, pulsating protrusions in areas where the bones of the skull have not fused normally. In adults, walking is impaired, balance disorders progress, dementia occurs, and urinary incontinence occurs.
When conducting a study of the central nervous system organ (with hydrocephalus), a splitting of the M-echo into a pair of teeth is noticed. The degree of discrepancy can be from 5−6 mm or more. In addition to the splitting of the M-echo, on the echogram one can see a large number of additional high-amplitude signals located between the initial, middle and final complexes.
Intracerebral hemorrhages
Cerebral hemorrhage not associated with trauma most often occurs due to arterial hypertension (due to rupture of perforating arteries of the organ). More rare causes are atherosclerosis, inflammatory changes in cerebral vessels, blood diseases (for example, leukemia, anemia, thrombocytopenia, other disorders of the coagulation system).
The leading research method for intracerebral hemorrhages is computed tomography of the head. It is also possible to conduct an Echo EG. The study reveals a large shift in the M-echo. Also in the affected hemisphere of the organ, additional multiple echo signals are noted.
In conclusion, it is worth noting that the echoencephalography method, like EEG, is quite simple and accessible for examining sick people on an outpatient basis. Diagnostics carried out using this method allows obtaining highly informative results. After analyzing them, a conclusion is written, which indicates all the found parameters and indices, interprets the necessary information, and notes the presence and severity of the identified changes in the brain of a particular patient.
What is a heart echo?
Echo of the heart: what is it? This diagnostic method is a special study using pulsed ultrasound (ultrasound). With its help, you can see the structure of the organ, its size, the condition of not only the heart muscle, but also the heart valves, as well as in real time look at the work of the heart, the characteristics of blood flow in the organ.
Using reflected ultrasound waves, the doctor creates a moving image on the screen that can be recorded and copied. The image can be tilted, looked at from different angles, at a three-dimensional image, sections of organs. Echocardiography tells about the volume of the heart chambers, their sizes, wall thickness, muscle mass . This diagnosis is non-invasive, completely safe and very effective.
How to properly prepare for the procedure
No special preparation is required for the echocardiography procedure. Need to:
- Take the results of previous echograms with you (to compare the results).
- If it is planned to administer a contrast agent, the patient should be tested for allergies.
- On the day of the echocardiogram, you should wear comfortable clothing (especially when planning a stress echocardiogram).
- When performing a procedure with stress tests, physical activity should be stopped 3 hours before the examination.
- If it is necessary to conduct a transesophageal ultrasound of the heart, you should not eat or drink 4–5 hours before the procedure.
How is an ultrasound of a child's heart performed?
Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) is performed on a child in exactly the same way as an ultrasound scan was performed on you during pregnancy. A gel is applied to the chest and a sensor is moved over it. During the procedure, the child can speak, move, fidget - this will not affect the results of the study.
During cardiac ultrasound, the child does not need any preliminary preparation.
The duration of the procedure is about 15 minutes. The result must be deciphered by a qualified doctor. Along with the results of echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart), the cardiologist also needs to show the results of an electrocardiographic study (ECG), fresh urine and blood tests.
The Echocardiography (ultrasound of the heart) procedure is not painful.
Contraindications to echoencephalography in M-mode
Echoencephalography of the brain in children and adults is a safe procedure. It does not require the use of painkillers (or any other pharmacological drugs) and has no physiological contraindications. However, it should be postponed during acute respiratory diseases accompanied by a runny nose and/or cough. It is not used if the patient has open wounds or suffers from psychological disorders in the areas where the sensors need to be installed. The latter can cause hysterics due to the unfamiliarity of the situation.
In what cases is a cardiac ultrasound indicated for a child?
Indications for ultrasound examination of the heart are the following situations:
- The pediatrician, examining your baby, listened to heart murmurs
- If you yourself can feel a tremor in the area of the projection of the child’s heart
- If a child has complaints of pain in the area of the heart of a pulling, aching or stabbing nature
- The baby is not eating well. But before you plan to conduct an echocardiogram in this case, rule out the possibility of improper breastfeeding - consult your pediatrician. It is imperative to look at the color of the skin around the baby’s mouth. As a rule, if he has heart problems, then when sucking or crying a characteristic symptom occurs - the skin in the area of the nasolabial triangle turns blue
- If you notice that your child’s legs and arms periodically become cool for no apparent reason.
- The child loses consciousness with or without intense physical exertion
- Fatigue, insufficient weight gain, excessive sweating may indicate heart problems
- If the child’s family has relatives with severe heart pathology, echocardiography should be performed at least once a year. This will help prevent the formation of hereditary pathology in time.
- Unreasonable frequent pneumonia in a baby may also indicate heart damage
- Each child, according to the standards adopted in our state, must be examined by a cardiologist before reaching 1 year of age as part of a routine medical examination, before which it is recommended to have an electrocardiogram and an ultrasound examination of the heart.
What abnormalities can be diagnosed during cardiac ultrasound?
Thanks to an ultrasound of the newborn's heart, the doctor will be able to confirm or refute the suspected diagnosis. Through echocardiography of the heart you can see:
- The presence of blood clots in the lumens or on the internal surfaces of the cavity of the heart or blood vessels.
- Congenital heart defect.
- Neoplasms.
- Deviation of heart size from the established norm.
- Various inflammatory processes in the heart and blood vessels.
- Ischemia, myocardial infarction and similar diseases.
In most cases, heart pathologies occur in newborns in the form of defects. This may be a hole in the interventricular septum. In this case, the walls of the heart and the size of its cavities can be increased.
Atrial septal defect may also be observed. In this case, an abnormal hole between the walls of the atria will be visible on the screen of the ultrasound machine.
Mitral valve defects involve an increase or decrease in the size of the opening through which blood circulates between the ventricles.
Another anomaly is narrowing of the aorta. In this case, enlargement of the walls of the atria and ventricle will be diagnosed.
What diseases can ultrasound of the heart diagnose?
- Acquired and congenital heart defects - aortic and mitral valve, ventricular septal defect, patent ductus arteriosus and others. Most often, congenital heart defects can be detected in the prenatal period during an ultrasound scan of the expectant mother.
- Enlargement of the heart chambers
- Causes of heart murmurs
- Hypo- and hypertrophy of the heart
- Ischemic disease
- Blood clots and other formations
- Changes in the walls of the myocardium, disruption of their work
- Other cardiac pathology
Thus, echocardiography is a safe and informative diagnostic method that can be performed on a child from the moment of birth.
Interpretation of results: norm and possible diseases
To make a correct diagnosis, the results of the Echo EG and the patient’s complaints are compared. The decoding is carried out either by a neurologist or a laboratory specialist. Only a doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. When interpreting data, the doctor’s experience and precise adjustment of the equipment are important.
To decipher Echo EG data, the doctor looks at three indicators of the echo signal:
- Initial complex. The signal is reflected from the bone, soft tissue, meninges and lateral ventricle on the side where the scanning occurs.
- Ultimate complex. This is the reflection of an ultrasonic wave from the bones of the skull and soft tissues of the head of the opposite hemisphere.
- Between them, a stable M-echo signal is recorded, which is reflected from the middle parts of the brain: epiphysis, pineal gland, septum pellucidum, and others. M-echo is essential for diagnosis.
Echoencephalography can be performed in two modes:
- M-method. One-dimensional scanning in which a graph is displayed on the screen
- Ultrasound scanning. 2D scanning. The brain is imaged in two planes.
Normally, the M-echo distance should be the same on one side and the other of the head. If the deviation is more than 1-2 mm (in children up to 3 mm), then this may be a sign of conditions such as hematoma, cerebral edema, abscess (accumulation of pus), intracerebral tumors, bruises and neoplasms. An increase in the volume of the lateral ventricles and the 3rd ventricle indicates the presence of hydrocephalus.
In a state of wakefulness, sleep, anxiety, the EG echo shows its rhythm: alpha, beta, delta or theta rhythm. Normally, the frequency of the alpha rhythm is 8-13 Hz, the beta rhythm is 13-30 Hz, the theta rhythm is 4-7 Hz, and the delta rhythm is 0.5-3 Hz.
In case of severe disorders, electroencephalography is used as a preliminary diagnostic method. Additional research methods, such as magnetic resonance imaging, may be needed.