Stages of development of myocardial infarction
There are 3 stages of development of myocardial infarction:
- acute
- subacute
- cicatricial
Acute stage
In the acute stage, the acute phase is distinguished, which lasts from several hours to 2-3 days.
Subendocardial damage occurs with signs of subendocardial ischemia. ST segment elevation is possible, resulting in a large area of damage. A pathological Q wave appears, i.e. the damage zone begins to partially move into the necrosis zone, and ST segment elevation remains - a monophasic curve.
Further, during the acute stage, the deepest Q wave is formed, and the ST segment begins to approach the isoline. The T wave begins to form.
Rice. 1. Q-myocardial infarction
Subacute stage
Lasts 14 days following the acute stage.
The acute stage turns into subacute - the ST segment approaches the isoline. The maximum changes occur on the part of the QRS complex, the ST segment is on the isoline with the deepest T wave formed (3-4 weeks from the onset of the disease).
Next, the negative dynamics of the T wave occurs. T wave inversion begins to decrease.
Video 1. Echocardiography. Scar changes in the lower wall of the left ventricle.
Scar stage
The R wave grows due to compensatory hypertrophy.
Causes
Hydrocephalus can be congenital or acquired. Congenital hydrocephalus debuts in childhood. Acquired hydrocephalus occurs under the influence of various provoking factors.
Depending on the mechanism of development of the disease, there are 3 main forms of hydrocephalus:
- occlusive hydrocephalus (ICD 10 code - G91.8);
- communicating (open, disresorptive) hydrocephalus (code G91.0);
- hypersecretory hydrocephalus (code G91.8 - other types of hydrocephalus).
Disruption of the flow of cerebrospinal fluid in occlusive (closed, non-communicating) hydrocephalus occurs due to the closure (occlusion) of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways by a blood clot, a voluminous neoplasm, or an adhesive process that develops after inflammation. If the blockage occurs at the level of the ventricular system (Aqueduct of Sylvius, foramen of Monroe, foramina of Magendie and Luschka), proximal occlusive hydrocephalus occurs. If the block in the path of cerebrospinal fluid flow is at the level of the basal cisterns, a distal form of occlusive hydrocephalus develops. Communicating (open, disresorptive) hydrocephalus occurs when the processes of reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid are disrupted, due to damage to the structures involved in the resorption of cerebrospinal fluid into the venous bed (Pachionian granulations, arachnoid villi, cells, venous sinuses). Hypersecretory hydrocephalus develops due to excess production of cerebrospinal fluid.
Based on the rate of progression of the disease, there are 3 forms of the disease:
- acute hydrocephalus, when no more than 3 days pass from the first symptoms of the disease to severe decompensation.
- subacute progressive hydrocephalus, developing within a month from the onset of the disease;
- chronic hydrocephalus, which develops within a period of 3 weeks to 6 months.
Depending on the level of cerebrospinal fluid pressure, hydrocephalus is divided into the following groups: hypertensive, normotensive, hypotensive. In hypertensive hydrocephalus, intracranial pressure is increased, in the case of hypotensive hydrocephalus, it is decreased. Normal pressure hydrocephalus (ICD code 10 – G91.2) is accompanied by normal values of cerebrospinal fluid pressure.
Hydrocephalus can develop after traumatic brain injury and various diseases. Hydrocephalus is formed due to the following diseases of the central nervous system:
- brain tumors localized in the brain stem or ventricles;
- acute cerebrovascular accidents;
- subarachnoid and intraventricular hemorrhages;
- encephalopathy of various origins (chronic hypoxic conditions, alcohol intoxication).
Elderly people often develop replacement hydrocephalus. Its cause is atrophy of brain tissue. When the volume of the brain decreases, the vacated space is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. Background diseases that provoke the development of hydrocephalus are arterial hypertension and diabetes mellitus. In case of thrombosis of cerebral vessels, the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is blocked and hydrocephalus occurs. Intracranial pressure increases and hydrocephalus develops with instability of the cervical spine.
At the Neurology Clinic of the Yusupov Hospital, priority is given to the problems of diagnosis and treatment of acute and chronic hydrocephalus in non-traumatic subarachnoid hemorrhages due to disruption of arteriovenous connections and rupture of arterial vascular aneurysms, post-traumatic hydrocephalus.
Small focal infarctions
ECG changes are minimal. Clinical and laboratory diagnostics are required.
Repeated infarction develops after the formation of a post-infarction scar. Recurrent infarction develops within 1-1.5 months before the formation of cardiosclerosis.
Rice. 3. Acute inferior myocardial infarction, subendocardial ischemia of the anterolateral wall of the left ventricle (continuation of Fig. 4).
Localization of myocardial infarction
4 walls:
Front wall
- direct changes - V2,V4
- anterior septal - V1, V2
- anteroseptal anterior – V1-V4
- infarction dependent artery - anterior descending artery
- reciprocal changes - in the inferior leads
Side wall
- direct changes - I, AVL, V5, V6
- high side – I, AVL
- infarction dependent artery - circumflex or diagonal branch of the anterior descending artery
- reciprocal changes - II, III, aVL
Video 2. Echocardiography. Cicatricial changes in the middle segment of the lateral wall of the left ventricle.
Bottom wall
- direct signs - III, aVF, II
- infarction dependent artery - right coronary or circumflex artery
- reciprocal signs - I, aVL, V2-V4
Back wall
- there are no direct manifestations, or leads dorsalis - V7-V9
- reciprocal - V1, V2 (high R waves)
Right ventricular infarction
With a right ventricular infarction on the ECG, changes will occur along the lower wall of the left ventricle. Further, the clinical picture becomes more severe, and circulatory failure occurs in a large circle. To determine right ventricular infarction, it is necessary to remove additional leads V3r, V4r. And in case of right ventricular infarction in these leads there will be an elevation of the ST segment by 1 mm.
Rice. 4. Acute inferior myocardial infarction, subendocardial ischemia of the anterolateral wall of the left ventricle (continuation of Fig. 3)
Tags: non-Q myocardial infarction, Q myocardial infarction, side wall, Myocardial infarction, Right ventricular infarction, Small focal infarction, lower wall, acute stage of infarction, acute coronary syndrome, anterior wall, subacute stage of infarction, scar stage of infarction, heart, ECG
What kind of pathology is this?
Hydrocephalus has another name - hydrocephalus
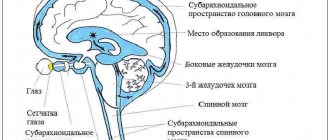
Hydrocephalus is a term that refers to an increase in the volume of cerebrospinal fluid within the skull. It's called cerebrospinal fluid.
Occlusive hydrocephalus occurs due to a violation of the outflow of fluid, which is why it lingers in the skull. According to statistics, every 450th child is born with this defect. There are significantly fewer acquired diseases in adults.
In a healthy person, the cerebrospinal fluid is always in balance and does not cause an increase in intracranial pressure. That is, in a normal state of health, the outflow of fluid is always controlled and absorbed in the required volume.
Science knows many types of hydrocephalus and they all depend on the cause and severity of the manifestation.
Occlusive is the type of cerebral hydrocele that occurs directly due to a violation of the movement of cerebrospinal fluid. Impaired patency leads to bilateral enlargement of the brain (due to excess fluid).
In turn, occlusive hydrocephalus is divided into several subtypes:
- monoventricular, which is manifested by dilatation of only one ventricle
- biventricular – bilateral hydrocele
- triventricular – enlargement of three ventricles
- tetraventricular – enlargement of all four ventricles
The reasons for its occurrence
There are many reasons for the occurrence of the occlusive form of hydrocephalus, and a doctor can accurately determine them after a series of tests and examinations.
Occlusive hydrocephalus is the most dangerous type of hydrocephalus
The most common among them:
- Congenital brain anomalies (Dandy-Walker syndrome, congenital stenosis, Arnold-Chiari malformation, etc.). Most often, such pathologies occur in children whose mothers’ pregnancies were not very favorable. They arise as a result of an infectious disease affecting a pregnant woman, as a result of which medications or pathogenic microorganisms themselves worsen (slow down) the development of the fetus. These include influenza, chlamydia, toxoplasmosis and others. Antibacterial drugs, which are necessary for treating the mother during pregnancy, also have a negative effect on the fetus.
- An intracerebral hematoma can block the channels for the movement of cerebrospinal fluid, which is why the development of dropsy begins. With a traumatic brain injury, a hematoma occurs, which becomes the direct cause of blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid channels.
- Cerebral tumors, that is, neoplasms in the ventricles that reduce their volume. In addition, the channels are compressed and the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid is disrupted, resulting in excess fluid in the ventricle.
- Brain hemorrhages that occur as a result of injury or excessive high blood pressure.
To eliminate the cause, you need to undergo several types of examination by specialists to establish an accurate diagnosis.
Main signs and symptoms
Pathology has two forms - distal and proximal
It is impossible to recognize occlusive hydrocephalus on your own. To establish a diagnosis, you need to take a series of tests and undergo certain examinations. The disease can be suspected by a regular increase in blood and intracranial pressure.
During this, headaches, redness and swelling of the eyes occur, swelling of the face, decreased visual acuity, and double vision are possible.
Disturbances in the functioning of the central nervous system, insomnia, weakness, drowsiness, irritability, fatigue after sleep, vomiting, and nausea may also occur. If such symptoms occur, you should immediately seek medical help.
If treatment against dropsy is not started in a timely manner, serious complications may occur.
This is due to the fact that fluid accumulation disrupts the functioning of the brain and central nervous system. In addition, the accumulation puts pressure on vital organs, which sooner or later can lead to their dysfunction.