The ventricles of the brain are peculiar cavities in the brain tissue that are designed to deposit cerebrospinal fluid (CSF). Under the influence of certain pathological factors, they can increase in volume. The lateral ventricles are the largest in this system. The third ventricle of the brain is connected to the lateral ones through the interventricular foramina. The lateral ventricles consist of a central part, a frontal horn, and an occipital and temporal horn. They are located slightly below the corpus callosum, on the sides, with the left one considered first, and the one on the right considered second.
Between the cerebellum and the medulla oblongata there is another important element - the fourth ventricle. It has a diamond-shaped shape and therefore another name has been established - the diamond-shaped fossa. It contains the spinal canal. These anatomical formations perform storage and formative functions - they take an active part in the formation of cerebrospinal fluid. In a normal state, in a healthy person, the cerebrospinal fluid thus formed is removed into the subarachnoid space. However, sometimes this process goes wrong and hydrocephalus develops. Asymmetry of the ventricles is an enlargement of one of them or both cavities to varying degrees.
Causes of asymmetry
At the moment, it is reliably known that the size of the lateral ventricles can change during a person’s life. So, it gradually increases with age. Some diseases (mainly those resulting in hydrocephalus) can cause these cavities to enlarge. The lateral ventricles also dilate in people with schizophrenia or bipolar disorder.
If a newborn has a suspicion of asymmetry of the ventricles of the brain, there is no need to immediately panic: this condition can also be caused by physiological reasons. For example, this can only mean that the child’s head size is slightly smaller than normal. This condition is not uncommon in newborns. Enlarged ventricles can occur in babies born prematurely. Their cavities are larger in size than in newborns born at term.
Asymmetry of the lateral ventricles of the brain can develop in one of two types:
- hypertension;
- atrophic.
In the vast majority of cases, about 99%, the cause of the increase in the volume of the brain ventricles is hypoxia. The remaining one percent comes from very rare diseases and infections. A lack of oxygen in the brain in a healthy person inevitably causes increased production and accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid - intracerebral fluid. This causes intracranial hypertension, which is increased intracranial pressure. It expands the cavity of the ventricle and the resulting asymmetry becomes clearly visible on ultrasound.
Atrophic type hydrocephalus most often develops due to severe hypoxia. It can also be caused by metabolic diseases, which are quite rare, or infections and hemorrhages. In this case, they talk about direct damage to the brain, which promises the future occurrence of neurological pathologies or the threat of cerebral palsy.
What it is
Ventriculoasymmetry is a pathological condition in which the lateral ventricles are asymmetrical in relation to each other. Normally, they have a symmetrical arrangement and the same volume, however, due to external or internal factors, their relative position changes.
Ventricular asymmetry is considered a pathology only if it leads to dysfunction of the nervous system, deterioration of the body’s functioning and the development of symptoms. If the violation of symmetry is minimal and does not lead to disorders, this is considered an anatomical feature of the brain.
In the medical classification there is no such nosological unit (independent disease) as ventricular asymmetry, however, their asymmetry can lead to disruption of the circulation of cerebrospinal fluid, which in turn determines the clinical picture.
Lateroventriculoasymmetry is often latent (hidden) and does not cause symptoms. As a rule, the pathology of this system is determined by chance, by neuroimaging on computer or magnetic resonance imaging during a routine examination or after a head injury.
The change in symmetry itself is not dangerous to humans. The consequences that asymmetry can lead to are dangerous. For example, impaired liquor dynamics (fluid outflow), compression of cranial nerves, increased intracranial pressure. All consequences trigger a chain that develops its clinical picture.
Asymmetry is mainly diagnosed at an early age (up to one year) and in children.
Interhemispheric asymmetry with asymmetry of the cavities is not disturbed.
Diagnostics
It is quite difficult to determine reliably whether the ventricle of the brain is enlarged in a child. Even nowadays it is not always possible to make an accurate diagnosis. Diagnosis of this condition includes a complex of such measures.
- Estimated head growth monthly. The study is performed by a local doctor or the child’s mother. This method is incredibly simple, but provides reliable information about the degree of progression of hydrocephalus.
- Ultrasound examination of the brain clearly and reliably reflects the size of the brain cavities.
- Examination by a neurologist. It should be noted that in children under three months of age, such an examination is not informative.
- Examination of the fundus, detection of vascular edema, spasm or hemorrhage.
- Determination of the size of the cerebral ventricles using the neurosonography method.
If the doctor, having analyzed the data obtained from these studies, has concluded that the situation is serious, he can refer the patient for more detailed examinations: magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography of the brain. One of the most reliable research methods is lumbar puncture, which provides information about the pressure of the cerebrospinal fluid.
Anatomy of the ventricular system of the brain
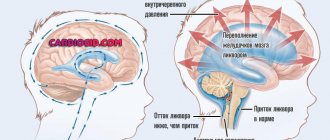
The ventricles of the brain are a cerebral system of cavities communicating with each other, the subarachnoid space and the spinal canal. Their inner surface is lined with ependyma. Under this layer are the choroid plexuses, which produce cerebrospinal fluid.
The lateral (or lateral) ventricles are the most voluminous. They are localized on both sides of the midline and have pairs of anterior, posterior and lower horns that are symmetrical relative to each other. The lateral ventricular cavities communicate with each other with the third ventricle, located between the thalami, through the foramen of Monroe. Between the cerebellum and the brain stem is the fourth ventricle. From it, the cerebrospinal fluid enters the subarachnoid space through the foramina of Luschka (paired) and Magendie (unpaired).
Causes of ventricular dilatation
An increase in the size of the lateral ventricles is formed as a result of impaired circulation of the cerebrospinal fluid. This picture emerges when:
- overproduction of cerebrospinal fluid;
- impaired adsorption of cerebrospinal fluid;
- difficulty in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid.
Changes in liquor dynamics due to overproduction and slower reabsorption of cerebrospinal fluid occur as a result of irritation of the ventricular choroidal plexuses and the arachnoid membrane of the brain by a pathological process (most often as a result of neuroinfection).
Difficulty in the outflow of cerebrospinal fluid is caused by blockage of the cerebrospinal fluid pathways by neoplasms and cysts.
The main reasons for the expansion of the lateral ventricles are:
- neuroinfections (meningitis, meningoencephalitis);
- skull injuries;
- brain tumors;
- idiopathic hydrocephalus;
- formed hematomas;
- hemorrhagic stroke;
- thrombosis of cerebral vessels;
- atypical embryonic anlage of the ventricular system.
Clinical signs
Manifestations of asymmetry of the lateral ventricles in an adult are often absent. In this case, such a structure of cerebral structures is not considered a pathology; it is revealed as a finding during neuroimaging. Along with this, a pronounced disturbance of liquor dynamics leads to the following clinical symptoms:
- headaches;
- feeling of heaviness and fullness in the head;
- dizziness;
- nausea;
- vomiting that does not bring relief;
- anxiety-phobic syndrome;
- apathy.
In addition, the clinical picture of ventricular asymmetry is complemented by symptoms of the disease that forms the basis of this condition. Paresis, pathology of cranial nerves, sensitivity disorders, cognitive decline, and cerebellar disorders may occur.
Symptoms
The development of symptoms occurs in accordance with the severity of intracranial pressure. Along with general discomfort, signs such as regurgitation (they may not exist), the appearance of postural reflexes (the child throws his head back, etc.) may be observed. A possible manifestation of the disease may be an increase in head size. Very often, the pathology does not manifest itself at all, but is detected only with the help of ultrasound.
Possible symptoms may also be: refusal of breastfeeding, restlessness, crying, trembling of the upper limbs, decreased muscle tone, decreased grasping and swallowing reflexes, squint. You can notice the divergence of the sagittal cranial suture, tension and swelling of the fontanelles. During a doctor's examination, the so-called rising sun syndrome may be observed - when the child's iris is slightly covered by the lower eyelid. During examination of the fundus, swelling of the optic discs is revealed.
What diagnoses are most often made using ultrasound and MRA?
Arterial hypoplasia
Options for the development of the circle of Willis, an open circle, asymmetry of the venous sinuses, and slight tortuosity of the arteries are the norm.
Minor and moderate arterial stenosis
Up to 50-60% in most cases does not manifest itself at all. In case of stenosis or occlusion, atherosclerosis, arterial dissection, arteritis, and cardiogenic embolism are excluded.
Vertebrobasilar insufficiency
Diagnosed on the basis of repeated strokes in the vertebral artery basin. Do you have recurrent strokes? Forget about vertebrobasilar insufficiency.
Vertebral artery syndrome
There is the concept of “dissection of the vertebral artery”, “occlusion of the vertebral artery” - in most cases this again manifests itself as strokes.
Possible consequences
What consequences can result from asymmetry of the cerebral ventricles? Not very pronounced pathology threatens only with the manifestation of some of the listed symptoms and a slight delay in the motor sphere, which passes over time. As a rule, this cannot lead to serious consequences, such as cerebral palsy. However, in cases where intracranial pressure is too high and fluid accumulation progresses, damage to brain matter can occur. Under the influence of constantly expanding ventricles, the brain changes its properties, which leads to a failure of nervous regulation. In childhood, the bones of the skull are elastic and are not yet connected to each other by rigid connections, this somewhat improves the condition and reduces cerebral pressure.
What is asymmetry of blood flow in the vertebral arteries
The most common ailments that disrupt the blood supply to the brain are asymmetry of blood flow through the vertebral arteries or vertebral artery syndrome.
This disrupts the supply of nutrients and oxygen to the cells of the main organ.
Disruption of blood flow to the human brain leads to irreversible changes in its structure, which often results in extremely serious consequences.
Several large vascular trunks are responsible for transporting the required amount of blood to the head, and any pathology that arises in them can disrupt the normal functioning of the brain. The consequences of this pathology can be the most severe - from a deterioration in general health to the development of ischemic stroke and brain failure.
Prevention
To avoid recurrence of problems with cerebral blood flow, a person who has undergone treatment needs to evaluate and, if necessary, radically change their lifestyle.
First of all, you will need to diversify your daily life with feasible physical exercises, which will increase blood flow through the vertebral cerebral vessels. Quit smoking and frequent drinking, follow a healthy diet and monitor your own body weight.
You will also need to regularly take vitamin supplements and medications that normalize the chemical composition of the blood.
Source: https://sheia.ru/sosudy/156-asimmetriya-krovotoka-po-pozvonochnym-arteriyam.html
Treatment
Treatment for this pathology is carried out by a neurologist together with a neurosurgeon. In order to minimize the likelihood of complications, a child with this diagnosis should be under constant medical supervision. The main methods of treating cerebral ventricle asymmetry are: taking diuretics that reduce the production of cerebrospinal fluid, taking nootropics that help improve blood supply to the brain, and taking sedatives. In addition, a course of special massage and gymnastics is required. Newborns and infants up to six months are treated on an outpatient basis. Treatment is quite long and takes up to several months. Older children are treated in accordance with the cause of the pathology. So, if the condition is caused by an infection, then the treatment program includes antibiotics or antiviral drugs. In case of a tumor or head injury, surgery may be performed.
Signs of asymmetry of blood flow in the vertebral arteries, diagnostic methods and treatment of pathology
Asymmetry of blood flow through the vertebral arteries is a rather unpleasant ailment. It appears due to improper blood supply to the human brain, as a result of damage to the main arteries.
It also has another name - vertebral artery syndrome, as well as vertebrobasilar syndrome. This disease has become quite widespread lately. Previously, it affected the elderly population, but now this syndrome increasingly affects people between 20 and 30 years of age.
Symptoms of the disease
Hypertension, vestibular disorders, headache are signs of vertebral artery syndrome
Without proper diagnosis, it can be quite difficult to recognize the symptoms of asymmetry of blood flow in the vertebral arteries. This is not due to the fact that such a disease does not manifest itself in any way. On the contrary, the symptoms of vertebrobasilar syndrome are very similar to other diseases.
This begins with osteochondrosis, which is very common among different groups of the population, and ends with diseases that the patient can hardly somehow associate with the spine. That is why, as soon as at least one of the symptoms listed below is detected, you should immediately contact a medical facility for examination.
Very often, people with vertebrobasilar disease may experience a headache. It manifests itself either in attacks that occur with the same frequency or has the same basis. Mostly pain is concentrated in the occipital region.
But besides this, they can spread to the temporal region and even the forehead. Vertebrobasilar syndrome very often begins to increase over time. On the skin, in places where hair grows, the discomfort increases with touching this area.
All this can come together with a burning sensation.
Another symptom of the vertebrobasilar symptom is a strong crunching of the vertebrae in the neck with any turn of the head.
If a patient has this pathology, then first of all, doctors recommend that such patients change their lifestyle to a more active one. It is largely thanks to this method that the majority of those who have asymmetry of blood flow through the vertebral arteries can easily overcome such an unpleasant illness.
Other signs:
- blood pressure rises
- there is a strong noise and ringing in the ears
- the patient periodically vomits
- my heart hurts
- constant feeling of overwork
- dizzy, up to a state similar to fainting
- the patient loses consciousness
- severe neck tension or pain in that area
- vision is impaired
- eyes and ears hurt
Sometimes, in addition to this syndrome, VSD may develop, as well as increased pressure inside the skull. In addition, very often the arms or legs, especially the fingers and toes, go numb.
Among other things, signs such as mild psychological abnormalities in the patient may appear.
But it should be remembered that all these symptoms do not appear immediately, so some patients may delay the treatment of such an unpleasant illness.
Causes of occurrence and risk groups
There are many factors that can cause vertebral artery syndrome
The causes and risk groups for this disease can be completely different:
- The most important reason for this disease is the not entirely uniform development of a pair of arteries, which leads to asymmetry in blood flow. This type of pathology cannot be cured by modern medicine. Often the patient lives with such an illness until death, without feeling the slightest inconvenience.
- Not very stable vertebrae in the cervical spine can also cause this syndrome. They gradually lead to the destruction of the discs in it and to their weakening. It can develop either as a result of an injury in the patient (for example, after an accident) or gradually, due to lifestyle. In the second case, the cause of blood flow asymmetry is a sedentary lifestyle, without sports or regular physical activity.
- Another reason for the occurrence of this disease is associated with extravasal compression. And she, in turn, appears due to hernias and injuries. Also, this pathology can develop into other diseases.
- Trauma received during childbirth is another factor that causes vertebrobasilar disease.
- Osteochondrosis is a very common cause of vertebrobasilar symptoms.
Torn arteries of the spine can also be the beginning of the development of such a disease. This pathology is quite dangerous, and in many cases can lead to strokes.
It is for this reason that patients who have been diagnosed with this syndrome can almost instantly become at risk.
This category of sick people should definitely monitor their health with special scrupulousness. An active lifestyle is especially recommended for them.
If you have any of the pathologies listed above, you should start playing sports or at least exercising. In addition, it is necessary to undergo examination and diagnosis once every few years to identify such a disease at the initial stage.
General information about the disease
Asymmetry in the area of vertebral blood vessels is a general concept that includes vertebrobasilar syndrome, that is, a violation of the blood supply to the brain as a result of dysfunction of the vertebral arteries.
Of the four major streams that provide blood supply to the brain, vertebrates realize a relatively small percentage of the total amount of blood circulated. The remaining more significant part falls on the share of sleepy ones.
Asymmetry of the vertebral arteries, resulting from exposure to a negative etiology, is caused by obstruction and uneven blood flow in the vertebral arteries. It occurs as a result of a decrease in the diameter of one or more of them. Reducing the lumen leads to the inability to supply the brain with oxygen and nutrients. As a result, negative symptoms appear.
The signs of vertebral artery syndrome are similar to those of other diseases, so recognizing it requires a careful diagnostic process. The danger is that the syndrome is only part of a general pathological process, which can be:
- osteochondrosis with accompanying negative manifestations,
- atherosclerosis,
- neoplasms,
- bone and cartilaginous pathologies of the spinal column, leading to compression, narrowing of the lumen and significant deterioration of a person’s condition.
Some of the pathologies that cause impaired blood flow and accompanying negative symptoms can be life-threatening. They require emergency surgery.
The signs that accompany vertebral artery syndrome are often similar to those of other diseases. The patient may experience sudden changes in pressure (increase or decrease), high intracranial pressure, pain in the ears and eyes, blurred vision and hearing, and a burning sensation in the neck.
Along with the progression of the lesion, dizziness, lightheadedness, sometimes fainting, nausea, and less often vomiting, numbness of the fingers and psycho-emotional disturbances may appear. Few people associate all the symptoms, so contacting a doctor occurs already at a late stage of development, when the diameter of the vessel is significantly narrowed.
Any negative symptoms indicating the presence of pathology in the body should not be ignored. Very often attributed to overwork and physical exertion, poor health is a signal from the body about a serious illness.
The prerequisites for the occurrence of pathology are conventionally divided into congenital and acquired. The second principle of division is vertebrogenic or non-vertebrogenic. Vertebrogenic are a direct consequence of diseases of the spine (Bechterew's disease, tumors, injuries, osteochondrosis). Nonvertebrogenic suggest:
- external compression (muscle spasm, postoperative scars),
- vascular diseases leading to changes in their natural course (kinks, tortuosity),
- systemic diseases that cause vascular pathologies in the form of thrombosis, atherosclerosis, inflammatory arteritis.
A study of the causes of cerebral ischemia has shown that the largest number of cases occur due to pathologies of the blood vessels that supply it. Vertebral arteries, compressed due to pathological causes, can cause vegetative-vascular dystonia, high intracranial pressure and mental disorders.
The risk group for the disease includes both those who have congenital developmental anomalies and those who neglect their health. Most of the possible provocateurs of asymmetry arise from systemic disorders of the body’s vital functions, which lead to the appearance of chronic, often incurable diseases. Destructive processes, metabolic pathologies, and immune system failures also lead to the appearance of vertebral artery syndrome.
At the initial stage of the disease, in addition to speech and hearing disorders, a malfunction of the vestibular apparatus may occur. In an advanced state, without proper treatment, attacks of angina pectoris appear, leading to myocardial infarction. The prevalence of the disease and its appearance at an increasingly younger age make it necessary to prevent its occurrence.
The resulting dysfunction of the pharyngeal reflex can cause suffocation and spasmodic blockage of the airways. Pathology of brain stem cells causes seizures, drop attacks and loss of consciousness with a sudden fall to the floor. The longer the visit to the doctor, the process of diagnosis and proper treatment are delayed, the worse the manifestations of the disease become.
It is generally accepted that abnormal functioning of the vertebral arteries is not dangerous, but this is an initially erroneous opinion. The forms of this syndrome in the spine, especially the asymmetry of the diameter of the intracranial segments of the vertebral arteries, can lead to loss of functionality of the organs of vision and hearing, as well as to complete disability of the patient.