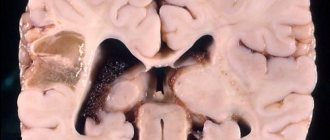
A brain cyst is a benign neoplasm. It looks like a cavity filled with cerebrospinal fluid.
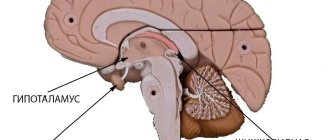
A lacunar cyst of the brain is located between the gray matter of the brain and its membranes; it can also be located in the hemisphere of the cerebellum or in the pons. According to observational data, it occurs in 4% of the population; men are more likely to suffer from the disease than women.
The danger of developing this type of cyst is that this formation can asymptomatically reach significant sizes.
Classification
By origin, cystic neoplasms are:
- congenital (primary) – arise even at the stage of intrauterine development;
- acquired (secondary) - their causes are pathological processes (bleeding, inflammation, traumatic injuries) occurring in the meninges.
Depending on the characteristics of the morphological structure, cavity arachnoid formations are divided into two types:
- simple - their cavity is lined with cells that produce cerebral fluid;
- complex (retrocerebellar) - their structure includes various tissues (arachnoid membrane cells, neuroglia).
According to the characteristics of the clinical course, the following are distinguished:
- frozen - they are characterized by a latent course, lack of growth;
- progressive - accompanied by a gradual increase in neurological symptoms, which is associated with an increase in the size of the formation and compression of brain structures.
Consequences and forecasts
In the absence of adequate therapy, the development of a lacunar cyst can have a number of adverse consequences, such as impaired coordination of movements, damage to vision and hearing, inflammatory processes in brain tissue, and death.
Children may develop hydrocephalus - accumulation of cerebrospinal fluid in the ventricles, leading to compression of brain structures.
However, with the correct diagnosis and timely treatment, it is possible to completely get rid of the signs of the disease and prevent the formation of new cysts.
To prevent the disease, you should undergo a preventive examination at least once every 2 years and, if necessary, consult a doctor.
Causes
Primary neoplasms
Congenital cerebrospinal fluid cysts are associated with anomalies in the structure of the brain that form even at the stage of intrauterine formation of the organ. Factors that can provoke their development include negative effects on the body of a pregnant woman and the developing fetus:
- intoxication (taking drugs with teratogenic effects, drug addiction, smoking, alcohol abuse, occupational hazards);
- infections (cytomegalovirus, herpes, rubella, toxoplasmosis);
- overheating (frequent visits to baths, sunbathing);
- radioactive exposure.
The appearance of arachnoid formations is often diagnosed in patients suffering from hypogenesis of the corpus callosum and Marfan syndrome.
Secondary neoplasms
The causes of secondary liquor cysts are:
- traumatic brain injuries (bruises, concussions);
- neurosurgical interventions;
- meningitis;
- meningoencephalitis;
- arachnoiditis;
- subdural hematoma or subarachnoid hemorrhage.
The principle of formation of lacunar cysts
Cysts are divided according to the nature of their origin into: congenital, acquired .
The congenital variety is formed in the womb as a result of the influence of various processes, the natural development of which was disrupted by painful factors. Sometimes genes mutate, affecting pathologies suffered by a girl during pregnancy, the effects of alcohol and cigarettes, and other psychotropic drugs.
Secondary cysts refer to the results of a previous illness; several pathologies differ. The patient’s immunity takes part in the formation of lacunar cysts. Today, the formation of a lacunar cyst in the head is promoted by: diabetes, meningitis, hypertension, skull trauma, connective tissue disorder, etc.
Stages of clinical course
Clinically, liquor formations begin to manifest themselves only as their size increases. This is due to the fact that the volume of the cranium is limited. The growing tumor begins to compress the structures of the brain, which leads to increased intracranial pressure and the appearance of neurological symptoms. In accordance with this, there are several stages of the clinical course of the disease, which are presented in the table:
| Stage | Description |
| Clinical compensation | There are no signs of brain damage, despite the presence of a tumor in the cranial cavity |
| Clinical subcompensation | A person experiences the first signs of brain dysfunction |
| Partial clinical decompensation | Characterized by persistent neurological impairment |
| Severe clinical decompensation | Dislocation (displacement of structures) occurs, wedging into the foramen magnum of the brain. Against this background, the patient begins to show initial signs of impairment of basic vital functions |
| Terminal | Disorders of respiratory regulation and cardiovascular activity increase, which ultimately becomes the cause of death |
Forecast
The prognosis for such a disease depends on the size and location of the cyst. If the formation rapidly increases in size, and this problem is noticed and treated on time, then the prognosis will be favorable. If severe neurological disorders develop, brain function cannot be restored. Of particular danger is the rupture of the cyst, which leads to the death of the patient.
In the absence of timely treatment and the growth of cystic cavities, serious disorders will occur, which will lead to loss of hearing and vision, impaired motor function, mental disorders and other problems.
Symptoms
Clinical manifestations of cerebrospinal fluid cystic formation include general cerebral and focal symptoms:
| Group of symptoms | Description |
| General cerebral | Their development is associated with an increase in intracranial pressure. The patient develops persistent headaches that are bursting in nature. They usually get worse at night and early in the morning. At the height of a painful attack, nausea occurs, and there may be repeated vomiting. Mental disorders may develop (psychomotor agitation, impaired critical abilities). When examining the fundus, congestion is revealed. |
| Focal | Caused by local damage to certain brain structures. When the formation is localized in the area of the frontal lobes, motor function suffers to a greater extent and the patient develops muscle hypertonicity, instability appears when walking, and speech disorders may occur. Lesions of the parietal lobe are characterized by disturbances of perception and sensitivity. Signs of damage to the temporal lobe are hallucinations, seizures, and defects in auditory perception. Localization of the cerebrospinal fluid cyst in the region of the occipital lobes causes dysfunction of the visual analyzer. With this form of the disease, the patient experiences symptoms such as cortical blindness, visual agnosia, and visual illusions. |
Why do lacunar cysts appear in the brain?
A scalp cyst is dangerous to human health. With weak development, there are no signs of the disease. Below is information about what a cerebral lacular cyst is.
Causes
This disorder can be congenital or acquired. In the last example, the disorder manifests itself during fetal development. This is due to:
- Smoking and drinking alcohol and other psychotropic drugs.
- Pregnant mother distress.
- Mutations at the gene level.
These are the causes of acquired disorders that develop against the background of other negative factors. This applies to post-ischemic lacunar cyst. There is fluid in the parietal and temporal region. After injury and disease, it can collect in the damaged area. Liquid is formed instead of tissue. If a lot of this fluid accumulates, a cystic lacunar tumor appears.
Patient immunity has a significant impact on such disorders. Taking into account the results of such studies, we can say that the disease manifests itself for the following reasons: arterial hypertension, skull trauma, diabetes mellitus, meningitis.
A heart attack often causes such anomalies, venereal disorders, and endocrinological disorders. Age-related changes contribute to the formation of cysts. They gradually develop in the brain in humans.
Cysts are divided according to the nature of their origin into: congenital, acquired.
The congenital variety is formed in the womb as a result of the influence of various processes, the natural development of which was disrupted by painful factors. Sometimes genes mutate, affecting pathologies suffered by a girl during pregnancy, the effects of alcohol and cigarettes, and other psychotropic drugs.
Secondary cysts refer to the results of a previous illness; several pathologies differ. The patient’s immunity takes part in the formation of lacunar cysts. Today, the formation of a lacunar cyst in the head is promoted by: diabetes, meningitis, hypertension, skull trauma, connective tissue disorder, etc.
Symptoms of the disease
The fact that patients develop a lacunar cyst of the head is not always realized during their lifetime. The neoplasm does not give any signs of itself. It is possible to detect a cyst only in 25% of cases.
When the tumor reaches large volumes, patients experience central nervous system disorder in several manifestations: the functioning of some organs is significantly weakened.
Vision is greatly affected by this disorder.
A lacunar cyst of the brain is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Nausea.
- Vomiting.
- Convulsive syndrome.
- Hallucinations.
- There is a noise in my ears.
- Sensitivity problems arise.
- Sleep gets worse.
- There is a throbbing sensation in the skull.
- Problems with coordination of movements.
Symptoms vary depending on the location of the disease. In some situations, the cyst causes problems with the central nervous system. In such situations, seizures occur.
When significant anomalies are achieved, limbs become paralyzed and visual function deteriorates. The skull is compressed. If a cyst appears in or near the cerebellum, the work of the vestibular apparatus becomes difficult, the gait changes, and balance is lost.
If such symptoms occur, a large, painful tumor develops. For these purposes, it is necessary to provide people with urgent medical care, which leads to the death of people.
This section is responsible for the contraction of muscle tissue, so when a cyst forms in this place, motor function is impaired. This is often characterized by involuntary contraction of muscle tissue on the face, convulsions and epileptic seizures appear. The clinical picture develops quickly; there are no prerequisites for the development of epilepsy.
If a cyst appears in the occipital region, vision problems occur. The patient manages to lose vision completely or partially. A sharp deterioration in the condition is observed in neurological blindness without any particular cause or injury.
Diagnostics
In modern medical practice, there is a research method that allows one to determine the presence of lacunar tumors in people.
Let's list the main ones:
- MRI.
- Spiral CT.
- Morphological examination of biopsy samples of brain structures.
- Electrocardiography can detect heart failure.
- Head biopsy, determination of the state of the histological structure of the brain and the properties of the tumor.
- Blood tests for cholesterol and clotting. High levels indicate blockage of blood vessels. This causes the appearance of a lacunar cyst.
- Blood pressure monitoring throughout the day. Pressure changes can cause strokes.
- Checking for the presence of pathogenic microbes in the blood if there is a suspicion of an infectious origin of the cyst.
All of the above methods allow doctors to determine the nature of the development of the disease, the cause of the formation of a cyst, or a tumor in the patient’s head.
Pathological disorders in the head in people are indicated by a blood test that reveals the level of glucose and the concentration of cholesterol in the blood. When patients are diagnosed with a head tumor, specialists can determine the differential diagnosis.
A biochemical blood test may indicate developing disorders in this organ of the patient. Such examinations make it possible to determine glucose and cholesterol levels. When identifying a tumor in a patient's head, doctors advise using a differential diagnosis.
Treatment
When the size of the cyst is small and the patient is not bothered by symptoms, treatment is not performed. People advise conducting an examination of the development of neoplasms. Developing asymptomatic kitties are not diseases, but anomalies. Other experts are convinced that small formations stimulate dementia in old age and the development of neurological diseases.
It is necessary to treat diseases that appear due to the cyst. For this purpose, antibiotics, antiviral agents, and antihypertensive drugs can be used, taking into account the etiology of the disease.
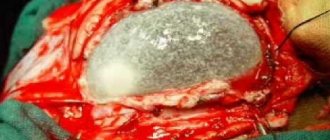
If neoplasms appear after a cerebral hemorrhage or signs develop that worsen the patient’s quality of life, surgery is performed. Today this is the only way to eliminate lacunar cysts.
We list the treatment methods:
- Shunting. To do this, a drainage tube is implanted through which fluid drains from the cyst. The increased risk is considered a disadvantage of the method. The shunt is used for a long time.
- Endoscopy involves eliminating a tumor through a puncture in the skull using an endoscope equipped with a video camera. This is the most painful and least traumatic method. There are contraindications for its use.
- Trepanation is a highly effective procedure that helps eliminate cysts of various locations. There is a possibility of brain damage.
Today, the bypass procedure is resorted to in exceptional cases. Only with the help of surgery can the method of getting rid of the disease be corrected. The check is carried out according to the following indicators: convulsions, increased symptoms, formation of lacunar cysts during hemorrhage.
Before surgery, doctors assess the condition of the heart. Today, neurologists perform minimally invasive surgeries. Rarely, shunting and drainage of lacunar cysts are performed.
Consequences
If therapy is not carried out normally, negative consequences appear in the form of problems with coordination of movements, hearing and vision disorders, inflammation, and death.
In babies, hydrocephalus may occur, where cerebrospinal fluid collects in the ventricles, causing the brain to shrink. If the disorder is correctly diagnosed and treated, it will be possible to get rid of the signs of the disease and prevent the appearance of new cysts. For preventive purposes, it is necessary to undergo preventive procedures less than every 2 years.
If a lacunar cyst of the head is not identified in a timely manner, the patient does not receive proper treatment, which leads to disastrous results. Postischemic lacunar cyst is fraught with the following disorders: problems with coordination of movements, difficulties with auditory and visual analyzers, hydrocephalus, death, encephalitis.
Prevention
Small cysts do not manifest themselves in any way. Their presence is present thanks to diagnostics. Large cysts must be removed surgically.
If such a diagnosis is detected in a patient, you need to quickly seek help from a specialist. Hypothermia should not be allowed, it is better to avoid stress, increase blood pressure, and protect yourself from viruses.
In most cases, the cyst forms after birth. There is a type of porencephalic lacunae. This neoplasm is formed during intrauterine development. Rarely does an obstetrician's mistake lead to the formation of cavities with fluid. Pressure may be put on the baby's head.
The proencephalic cyst is large. The area of damage to nerve cells is very high. Uncontrolled growth of the tumor provokes problems in the development of the child’s body.
Diagnostics
The presence of an intracranial space-occupying lesion can be determined based on a neurological examination and the results of a primary examination, which includes the following methods:
- echoencephalography (Echo-EG);
- rheoencephalography (Rheo-EG);
- electroencephalography (EEG).
In order to clarify the location and nature of the space-occupying neoplasm, MSCT and MRI of the brain with contrast are indicated. The use of a contrast agent allows for differential diagnosis between a cerebrospinal fluid cyst and another formation, since the contrast can accumulate in the liquid contents of the cystic cavity.
Based on the diagnostic results, a decision is made on the need for surgical treatment of a cystic neoplasm.
Treatment of ovarian cystoma with folk remedies
- Infuse a tablespoon of dry cinquefoil herb in boiled milk or water for a couple of hours. Drink half an hour before meals three times a day.
- A decoction of this plant will also work. You just need to boil the herb for a quarter of an hour over low heat, then let it brew for two hours and strain. You need to drink a quarter glass three to four times a day.
- Chamomile, taken in equal proportions with lemon balm, has proven itself to be excellent. Pour this mixture with just boiled water and let stand for four hours. Must be drunk hot.
- Pour three tablespoons of corn silk with a glass of boiling water and boil for 10 minutes over low heat. After straining, drink 50 g three times a day.
- Take one tablespoon each of calendula, celandine and chamomile. This collection is poured with half a liter of boiling water, and the container is well wrapped in a warm blanket for the whole night. Drink the resulting infusion three times a day, half an hour before meals, with a dose of half a glass.
- A decoction of mantle made with grape wine is suitable for douching.
Our great-grandfathers advised starting treatment with folk remedies in the first phase of the lunar calendar. They believed that in this case the therapy would be more effective.
Treatment
If a patient is diagnosed with a frozen cerebrospinal fluid cyst with clinical compensation, then treatment is not indicated for him. In this case, the patient must be monitored by a neurologist with a mandatory annual MRI.
With a progressive cyst in the stage of clinical subcompensation, the patient is prescribed conservative therapy aimed at reducing intracranial pressure. If it is ineffective, surgical intervention is indicated. The choice of surgical method in each specific case is made by a neurosurgeon, taking into account the characteristics of the disease, the patient’s age, and the presence or absence of concomitant pathology.
Currently, the following surgical techniques are most commonly used:
- Complete excision. The indication for surgery is capsule rupture or hemorrhage into the cavity of the formation. The intervention is quite traumatic, and the recovery period is long.
- Endoscopic fenestration. A small hole is made in the bones of the skull using a milling cutter. Through it, puncture and aspiration of the liquid contents of the neoplasm are performed, followed by the creation of holes between its cavity and the subarachnoid space or ventricles of the brain. After this, the cavity in the arachnoid membrane is no longer filled with fluid and therefore the disease does not progress.
- Cystoperitoneal shunting. The essence of this operation is that a path is created for the outflow of cystic contents into the abdominal cavity, where it is absorbed into the blood.
What is a cerebral lacunar cyst?
A cyst is a benign cavity neoplasm.
If it finds a place in the head, then its cavity is filled with cerebrospinal fluid - cerebrospinal fluid. There is a special type of such formation in the human brain. This is a lacunar cyst. It is so called because it begins to grow between the membranes around the gray matter in the lacunae from the displacement of tissues when they are damaged by inflammation.
note
These may be the hemisphere or pons, subcortical ganglia or visual thalamus.
The danger of this type is that the cyst grows to a significant size and only then makes itself felt. The course of the disease when diagnosed with a lacunar cyst of the brain is accompanied by headaches and dizziness (when the cyst fills with fluid and begins to put pressure on neighboring areas of the brain).
Existing types
So what is it - a lacunar cyst in the brain and in what form does it manifest itself? Lacunar cysts in modern neurology are classified as congenital and acquired. Congenital forms are considered the primary form of the disease, acquired forms are considered secondary.
A congenital lacunar cyst can form in the mother's womb if the expectant mother allows herself to smoke, take alcohol and take psychotropic drugs. They are undoubtedly pathological factors for the formation of the fetus in the womb.
The cause of primary lacunar formation in a baby may be a disease suffered by the mother that affects the structure of the nerve fibers and tissues of the fetus.
This happens due to a violation of the development of the unborn child or a pathology of the development of the central nervous system. The formation of a cystic cavity occurs at any stage of embryonic development, but doctors suggest that most often this happens in the first trimester of pregnancy.
A secondary lacunar cyst is formed as a result of a disease suffered by a person that affected the nervous system. The mother may suffer from several illnesses, which will weaken her immunity. To date, research has confirmed that a weak immune system can also cause the growth of lacunar tumors.
Unfortunately, most lacunar cysts of the brain grow asymptomatically, rarely manifesting themselves in the early stages. They may be seen by a doctor on a head scan that was done for another reason. But this is a rare accident.
And with active development, when the cyst reaches a large size and makes itself felt with severe pain and confusion, it is already difficult to determine the cause of the disease, since a lot of time passes from its onset.
Important
Interestingly, the size of the cyst can vary from a couple of millimeters to tens of centimeters, and the tumor does not show any symptoms of its growth.
Medical scientists have certainly proven that a lacunar cyst can be a consequence of certain somatic diseases:
- meningitis;
- diabetes mellitus;
- arterial hypertension;
- traumatic brain injuries;
- systemic connective tissue diseases;
- metabolic diseases;
- thrombosis.
After an ischemic stroke, a lacunar cyst in the brain forms in the place of dying glial cells and neurons. As a result of freeing up space, a free cavity is formed - a lacuna; it is filled with cerebrospinal fluid. In such a situation, the size and shape of the cystic formation depend on the location and degree of damage to the brain tissue.
You can easily live your whole life with a lacunar cyst and not know about it. In many cases, it does not make itself known to either the patient or the doctors. Some experts suggest that such a cystic formation should be considered not a disease, but a developmental anomaly.
However, based on some symptoms, the doctor may suspect the presence of a cystic node and offer the patient a directed examination.
As the cystic tumor grows, it compresses the tissues of neighboring areas of the brain, and, depending on its location, can give a certain clinical picture.
A large formation causes headaches that change when a person’s body position changes. Then the patient himself shows the doctor exactly where the headache hurts. In other cases, the symptoms may be such that a person does not associate them with head diseases:
- nausea;
- vomit;
- convulsions;
- hallucinations.
Depending on the location of the cystic neoplasm, the following manifestations occur:
- pressure on the basal ganglia causes difficulty performing complex coordination movements;
- when placed in the parietal region, a person experiences imbalance and coordination of movements;
- the cyst affects the parietal lobes - oral and written speech will regress.
Vision is especially susceptible to impairment; it can suffer primarily in any location of the cystic node. There are also other signs of the appearance of a lacunar neoplasm. The sense of smell and taste is lost when the temporal region is affected; facial expressions are distorted when the frontal lobe is affected.
A long and latent course of the disease is a characteristic feature of lacunar cystic tumors. This is the reason for the late onset of symptoms and referral to specialists for medical help.
Advice
If the neoplasm, due to vital reasons, does not grow to a large size and does not begin to put pressure on the tissues of neighboring areas of the brain, then it will not affect the functions of the main organ at all and will not give any clinical manifestation.
Then the neoplasm may be accidentally detected during a head examination performed for completely different indications.
Lacunar formation can only be seen on CT, MRI or spiral computed tomography. The images clearly show the location, the affected neighboring areas, the shape and size of the neoplasm.
Dopplerography helps in clarifying the clinical picture: it reflects the speed of blood flow, the condition of the arteries, the presence of an aneurysm or atherosclerotic changes in blood vessels. These examination methods are non-invasive. However, when doctors need to clarify the histological structure of the cyst tissue, they resort to invasive methods.
The first and most revealing is a biopsy, which accurately determines the nature of the tumor, allowing for a morphological study of the biopsy sample taken.
Laboratory diagnostics give their results:
- cholesterol content and coagulability reflect the possibility of vascular blockage;
- Determination of pathogenic microorganisms in the blood indicates the infectious basis of the neoplasm.
As an additional examination, 24-hour blood pressure monitoring is performed. Pressure drops and extreme blood test values become indirect confirmation of the presence of pathology in the brain.
For small lacunar cysts, when clinical manifestations do not bother the patient and there are no disturbances in brain function, then supportive treatment and rehabilitation are carried out in sanatorium institutions. However, it is recommended to regularly monitor the condition of the cyst, changes in its position, shape and size, since scientists believe that even a small formation accelerates the aging process of the body.
The main treatment is aimed at the pathologies that caused the cyst to appear. Depending on the etiology, antiviral drugs or antibiotics, antihypertensive and immunomodulatory drugs are used.
Medicines used by neurologists for drug therapy of cysts:
- anti-adhesion agents;
- medicines to restore blood circulation;
- immunomodulators;
- antioxidants;
- nootropic drugs.
During drug treatment, cholesterol levels, blood clotting, and blood pressure are constantly monitored. To completely get rid of a lacunar cyst today means undergoing surgery, agreeing to surgical intervention. Patients whose quality of life sharply decreases take this risk.
Methods offered by modern medicine for removing lacunar cysts:
- bypass;
- endoscopy;
- craniotomy.
Today, the use of an endoscope is considered less invasive. Such equipment is used when the cyst is in an easily accessible place. But there are contraindications for endoscopy.
When shunting, a drainage tube is inserted into the cyst cavity by puncturing the skull, through which the fluid contained inside the formation flows out, and the walls of the cyst gradually grow together. This method has a risk of infection. Craniotomy today is the most highly effective operation, although the most difficult.
It makes it possible to remove cysts of any size, located anywhere. However, trepanation carries a high risk of damage to brain tissue.
Prevention
Prevention of congenital cerebrospinal fluid cysts is based on the prevention of congenital malformations and includes the following areas:
- eliminating the impact of teratogenic factors on a pregnant woman;
- rational management of pregnancy;
- careful delivery.
Prevention of acquired cerebrospinal fluid cysts is based on timely and complete treatment of vascular and inflammatory cerebral diseases, traumatic brain injuries.
How to diagnose lacunar tumor today?
A few decades ago, the conventional X-ray method was used to diagnose this type of disease. However, despite its effectiveness in the field of other diseases of the human body, this method is not capable of qualitatively identifying the symptoms of cysts in the brain. For this reason, most modern specialists use computed resonance tomography or MRI, which allows not only to scan the site of attachment of the cyst, but also to see the size, causes of the lacunar cyst, the nature of development and the presence of side effects that the tumor could cause during its growth.
In addition to magnetic resonance imaging, in the process of diagnosing a lacunar cyst, doctors also often use the method of spiral determination of the disease using tomography, as well as a biopsy of morphological tumor tissue, which allows one to study the characteristics of the formation and growth of the tumor, as well as analyze the tissue of its capsule for microbiological testing.
All of the above diagnostic methods today are the most effective, since they allow us to detect the presence of a cyst in the brain, as well as determine its size and prescribe the most effective course of treatment for post-ischemic lacunar cyst of the brain. Thanks to this scanning method, the doctor is able to track the speed and growth rate of the tumor, as well as understand the likelihood of it malignizing - turning into an oncological problem, cancer.