Clinical methods for studying neurological patients
Any patient’s visit to a doctor should begin with a thorough examination and history taking. The same applies to a neurologist: in order to diagnose the disease and its cause, the doctor conducts a clinical examination. As a rule, 90% of successful diagnosis and subsequent treatment depends on this initial stage of diagnosis.
Features of clinical diagnostic methods in neurology
The task of a neurologist during a clinical examination of a patient is to assess the functions of brain systems. Each patient’s complaint must be taken into account, which gives the specialist the opportunity to suggest a problem in a certain anatomical and functional system of the brain.
The doctor must also determine, by analyzing the totality of symptoms, the pathogenesis and etiology of the lesion, that is, identify which disorders of the nervous system and of what nature cause certain symptoms.
At the appointment, the doctor may decide on the need for additional examinations using instrumental or laboratory diagnostic methods.
In his practice, the neurologist uses the following clinical diagnostic methods:
- Studying the patient's medical history and considering his complaints.
- General examination of the patient.
- Assessment of neurological status, in which various systems and functions of the body are examined.
Let's consider each of the methods in a little more detail.
How is the history and complaints of a neurological patient studied?
When a patient presents with neurological complaints, the doctor must first carefully examine the patient’s medical history, clarify passport details, profession, presence of other diseases, etc.
The neurologist must take a proactive approach by questioning his patient.
Considering the patient's complaints, the doctor, during a subsequent examination of the neurological status, analyzes and systematizes the information received, drawing a conclusion about a possible disruption in the functioning of certain anatomical and physiological systems of the brain and nervous system.
Depending on the complaints, the neurologist can clarify the presence of such symptoms in the patient:
- Loss of consciousness, fainting, epileptic seizures.
- Periodic darkening of the eyes, general weakness, dizziness.
- Headache – its location, nature, duration, most frequent manifestation at a certain time of day (night, morning or daytime hours).
- Visual disorders.
- Nausea, vomiting, intestinal disorders (tendency to constipation).
- Low blood pressure, etc.
When studying the patient’s symptoms, the doctor finds out the sequence of its development (chronology).
Possible precipitating factors that contribute to the manifestation of specific symptoms are also discussed.
Additionally, the neurologist clarifies some important details of the medical history:
- the presence of birth injuries, infections during the perinatal period;
- features of the sexual sphere: in women - facts of pregnancy, childbirth, menstrual cycle; in men – sexual function;
- clarification of family history (if necessary);
- the presence of neurological diseases in the past, how they were treated and what is its effectiveness.
The neurologist may, at his discretion, clarify some more details of the medical history.
What is included in a general examination of a neurological patient?
As a rule, during a general examination of a patient, a neurologist is guided by standard instructions for a neurological examination. However, some nuances of the examination can be changed individually depending on the patient’s complaints.
The examination begins with an assessment of the activity of various body systems: respiratory, cardiovascular, endocrine, urinary, digestive, musculoskeletal. Then the patient is asked to undress to his underwear and is examined according to the following scheme:
- Body type – normasthenic, hypersthenic, asthenic, nature of subcutaneous fat distribution.
- Condition of the skin - temperature, color, moisture, presence of spots and neuruses, hair, injection marks.
- Examination of the head - size, shape, symmetry. Assessment of the condition of the skull, temporal arteries, eyeballs, etc.
- Examination of the neck - tilt and rotation of the head, neck mobility, palpation and auscultation (listening) of the carotid arteries, lymph nodes, thyroid gland, tone of the occipital muscles, etc.
- Examination of the chest - palpation of the cardiac impulse and auscultation in the heart area.
- Palpation of the abdominal organs - liver, stomach, spleen, intestines.
- Examination of the spine - assessment of lumbar mobility, the presence of curvatures (scoliosis, kyphosis, chest deformity), condition of the hairline.
They also evaluate the condition of the back muscles and pay attention to the soreness of certain areas of the body.
Why is status determination important?
Many people ask the question: “Why is status determination necessary?” First, when diagnosing, the doctor must pay attention to the person’s behavior, his reaction and his overall state of mind. Especially if the patient has injuries or other complex diseases. It is also necessary to find out the state of the brain’s performance.
This is what further treatment and therapy depends on. Only after the person’s neurological status has been examined can the doctor begin therapy: prescribe medications, and so on. As a rule, medications are necessary to improve the functionality of the brain, which allows you to quickly achieve a positive effect.
It should be noted: the reaction of the pupils to light is not always an indicator of poor brain function. At the moment, there is a special diagnostic scheme that allows you to quickly and easily assess the condition of the main organ. The status can be found out by contacting special medical centers. Next, we will consider how it is installed and what points the doctor should pay attention to.
First of all, when communicating with a patient, the doctor must pay attention to his behavior, reaction and general mental state. Especially if the patient was admitted with some kind of injury or emergency assistance was called by relatives. The doctor determines, first of all, the condition of the brain, since the therapy prescribed in the future largely depends on this.
The reaction of the pupils to light is not sufficient to establish the neurological status. A scheme has now been developed that evaluates brain function based on certain neurological symptoms. You can establish the status by contacting a specialized diagnostic center. Let us consider further how status is established.
How is an appointment with a neurologist?
- arachnoiditis;
- Alzheimer's disease;
- insomnia in its various manifestations;
- cerebral palsy;
- stroke;
- Parkinson's disease;
- severe headaches;
- sciatica;
- lumbago pain;
- migraine;
- myopathy;
- polio;
- tunnel syndrome;
- hyperactivity;
- cerebrovascular accident;
- Willis disease;
- neuropathy.
To what a neurologist treats, you can add tuberculous meningitis, encephalitis and meningitis. In fact, these infectious diseases are the specialty of an infectious disease specialist. However, after these diseases, serious consequences can occur that affect the functioning of the brain and spinal cord. All this affects the coordination of movement, speech and memory. This specialist is engaged in eliminating such consequences.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytpolicyandsafetyru
This is a very capacious science. Neurology is a discipline that studies the connection between a patient’s well-being and the state of his nervous system. The following treatment methods are used here:
- medicinal – involve taking medications;
- non-drug (acupuncture, diets, reflexology, herbal medicine);
- physical (magnetic therapy, myostimulation, laser therapy);
- surgical.
In our country there is no difference between these terms. Until recently, a specialist dealing with these pathologies was called a neurologist. However, the list of tasks assigned to such a doctor was revised. At the same time, the name of the specialization also changed. In European countries, neurologist and neuropathologist are two different names.
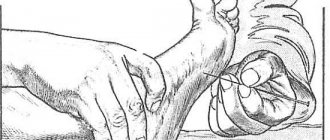
At the first visit, the doctor will carefully listen to the patient’s complaints. This will allow you to collect an anamnesis of the disease. A consultation with a neurologist also involves a tactile and visual examination. During the appointment, the specialist will check your basic reflexes. Special tools may be used to test some of them. To assess individual reflexes and muscle condition, the doctor may ask the patient to remove part of his clothing.
It is important for the patient to know what will happen in the doctor's office in order to prepare. An appointment with a neurologist involves the following manipulations:
- Using a special hammer, the doctor will check the condition of the optic nerve. The patient needs to follow the instrument without turning his head.
- The doctor will be able to check some reflexes by facial expressions. In this case, you will need to wrinkle your forehead, say “A” or stick out your tongue.
- The doctor uses a needle to test facial sensitivity. During this procedure, the neurologist asks the patient what sensations he experiences.
- To draw a conclusion about the state of muscles and reflexes, the doctor will ask the patient to bend his arm at the elbow. Based on the results of what he saw, the doctor gives a rating from 1 to 5.
- To determine the condition of the spinal nerves and pain points, drawing on the skin of the back is used.
- To test the deep reflexes of the legs and arms, the doctor will tap the tendons with a hammer.
- Movement coordination is tested with the Romberg pose.
Neurologist's diagnoses
To correctly prescribe treatment, the doctor will recommend that the patient undergo a full examination. Thanks to this procedure, the doctor can make an accurate diagnosis. Instrumental and laboratory tests can be used. More often, a neurologist’s diagnosis is established after the following research procedures:
- electroencephalography;
- x-ray;
- electroneuromyography;
- MRI;
- Dopplerography;
- CT;
- laboratory tests.
A pediatric neurologist examines such problems in a child as increased excitability, sleep disturbances and behavior disorders. It treats seizure disorders and traumatic brain injuries.
A pediatric neurologist is responsible for the child’s brain, which must function normally and have good nutrition and blood supply.
When consulting, a neurologist acts according to the following scheme:
- Examines the baby according to the disease (collecting a life history - this is childbirth and pregnancy), as well as (anamnesis of the disease - these are complaints and the onset of the disease).
- Examine the child and, if necessary, the doctor prescribes additional examination. This is an examination of the fundus, ECHO-EG, ultrasound, EEG, ultrasound of the brain, MRI, etc. Then, based on the research, effective treatment and monitoring of the course of the disease are prescribed.
A neurologist conducts preventive examinations of a child from birth to one year, and then scheduled consultations once a year. These examinations are extremely important because they allow timely identification of all kinds of pathologies of the central nervous system and provision of therapeutic measures, if necessary.
The list of organs dealt with by a pediatric neurologist includes:
- Brain and spinal cord, spine, thalamus and nerves.
A doctor in this specialty deals with neurological lesions, including:
- Hereditary (genetic).
- Infectious.
- Those that appear as a result of toxic disorders and traumatic lesions.
- A large percentage of CNS lesions are hypoxic.
- Post-traumatic or hereditary (epilepsy).
- Specific syndromes.
Diseases, including:
- Tics, stuttering.
- Enuresis and epilepsy.
- Cerebral palsy (cerebral palsy).
- Vegetative-vascular dystonia.
- Alzheimer's disease, aphasia.
- Parkinson's disease, herpes zoster.
- Hyperhidrosis, meningitis.
- Brain injury.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytadvertiseru
Newborn age (when to see a doctor):
- The child often wakes up, sleeps heavily and restlessly, and sleep is very superficial.
- If he cries or in a calm state spits up a lot and often, if the child’s arms and chin shake when excited.
- If your fingers curl when leaning on your tiptoes.
- If twitching or convulsions are noticed when the temperature rises.
Preschool and school age:
- When a child complains of frequent fatigue and headaches, and also if he is irritated and does not want to play with toys and peers.
- At school, irritable, distracted and behind in school.
- He sleeps poorly, is reluctant to study, and faints.
- Complaints of headache, dizziness, tinnitus and nervous tics.
A pediatric neurologist can correct the disorders listed above in a timely manner. Many problems are resolved in a positive way. Sometimes it is enough to introduce a child psychologist, and sometimes the help of a qualified child neurologist is required; the main thing is to notice in time and consult with a specialist.
Analyzes:
- Complete blood test and for TORCH infections, STIs.
- Biochemical, oncological and bacteriological studies.
- Hormonal levels, analysis for diabetes.
- Allergological and immunological studies.
- General clinical, cytological and hematological studies.
- Test for osteoporosis.
- Toxicological and cardiorheumatological studies.
Diagnostics:
- EEG, ECHO-EG, ultrasound.
- Brain ultrasound, MRI.
- CT, X-ray.
- MRS (magnetic resonance spectroscopy).
- PET (positron emission tomography).
- SPECT (single photon emission computed tomography).
- Cerebral angiography, myelography.
- Cisternography.
Follow your daily routine. Sleep at least 8-10 hours, engage in active physical sports, reduce school loads, reduce watching TV and computer.
Children are recommended to engage in general strengthening sports activities in a health group, ride a bike, play table tennis and swim.
In the menu, limit the consumption of fatty meats, salt, flour and sweets. Increase the body's intake of magnesium and potassium, which are found in buckwheat, beans, peas, apricots, raisins, carrots, onions, eggplants, etc. The child should eat foods containing polyunsaturated fatty acids in the form of corn, sunflower and olive oil.
It is necessary for the child to undergo electrophoresis, water procedures, electrosleep, therapeutic massage, which stimulate the nervous system. Hardening is very useful, as it trains the entire body.
Pediatric neurologists resort to medicinal methods in extremely advanced cases when dystonia poisons the life of a child or teenager. And she is being treated together with doctors such as a cardiologist and gastroenterologist.
When choosing a doctor, it is important to take into account his qualifications, experience, and find out patient reviews
Common kidney diseases:
- (in bean-shaped organs);
- spicy and;
- - metabolic problems that provoke the formation of amyloid;
- toxic damage to natural filters after consuming nephrotoxic drugs, surrogate alcohol, poisons, contaminated water and food;
- and hypertension affecting the bean-shaped organs;
- - damage to the renal glomeruli. The pathology is of an immuno-allergic nature;
- - the disease develops when;
- . The inflammatory process against the background of the penetration of harmful microorganisms and opportunistic flora occurs in the parenchyma and pyelocaliceal system;
- . This category includes pathologies of an inflammatory nature;
- tumor process in renal tissue. The formations are benign; in some patients, the doctor detects malignant tissue damage. Common pathology - . The surgical intervention is performed by a surgeon in a urological hospital; if cancer is detected, the patient is observed by a urological oncologist;
- . A dangerous condition with severe symptoms. The main symptom is a pronounced pain syndrome that develops with glomerulonephritis, infectious lesions of the bean-shaped organs. The pain spreads to the abdomen, groin, legs, the patient feels nauseous, vomiting is possible, blood pressure rises, painful shock often develops, and blood clots appear in the urine;
- . As a result of a sharp decrease in the fat layer, with injuries, congenital disorders, the bean-shaped organs are located incorrectly: it provokes problems with the functioning of natural filters. The nephrologist performs the diagnosis, and the problem is eliminated in the urology hospital by another doctor.
https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ytdevru
A specialist observes patients after bean-shaped organ transplantation, if it is detected.
Algorithm of work of a nephrologist:
- interviewing the patient, studying complaints and anamnesis;
- clarification of the clinical picture of the pathology, assessment of the test results with which the patient came to the appointment;
- determination of a possible list of pathologies of natural filters, referral for diagnostics: urine collection, blood test, instrumental studies;
- assessment of diagnostic test data, determination of the type and form of the disease;
- selection of treatment methods, if necessary, referral to a urological hospital for conservative therapy (severe forms of pathologies) or surgical treatment;
- advice on drinking regime, lifestyle changes, diet selection, indication of restrictions in everyday life and professional activities to prevent complications or relapses;
- recommendations for the prevention of renal pathologies, scheduling follow-up appointments.
Pediatric nephrology
What does a pediatric neurologist treat?
The nervous system is one of the most complex and multifunctional structures in our body and, unfortunately, the number of diseases associated with it is also very diverse. The most common reasons for visiting a neurologist are: migraines, neuralgia, sleep disorders, depression, spinal osteochondrosis, intracranial hypertension and vegetative-vascular dystonia.
In addition, a neurologist diagnoses and prescribes treatment for diseases characteristic of old age, such as Alzheimer's disease, Parkinson's disease, senile dementia (senile dementia). Also, the scope of activity of a neurologist includes the treatment of such serious diseases as epilepsy, multiple sclerosis, and encephalopathy.
A neurologist (a modern version of the name of the more familiar neurologist) is a specialist who prevents, diagnoses and treats diseases caused by damage to the central or peripheral nervous system.
This is especially important in childhood, when any disruptions in such a specific area are fraught with the development of conditions that can leave an indelible mark on the child’s subsequent life. A pediatric specialist should routinely examine infants in the first weeks after birth, at 3, 6, 9, and 12 months.
After this, visits to a specialized doctor must be made every year.
Problems with the functioning of the nervous system can begin during the period of intrauterine development of the fetus, and they are not always obvious to a lay person. This is why a pediatric neurologist should examine a newborn immediately after birth or in the first weeks of his life.
Damage to the nerves, spinal cord and brain are often the result of fetal hypoxia, placental abruption, prolonged or rapid labor, and the need for general anesthesia for delivery. The condition of the mother in the last month of pregnancy is no less important.
Toxicoses, the need to take a number of medications, smoking, and infectious diseases are the primary risk factors.
Only timely contact with a specialist, development of the correct treatment plan and its implementation can prevent inhibition of the work of one of the most important systems of the body.
Also, refusal of specialized therapy can lead to the development of attention deficit disorder, inappropriate behavior, emotional instability and problems with the development of basic social skills.
Statistics mercilessly show that 50% of cases of childhood disability are associated with pathologies of the nervous system. Of these, about 70% of diagnoses are the result of problems during pregnancy and the newborn period (28 days after birth). Practice shows that a pediatric neurologist can cope with a significant part of these problems if a diagnosis is made in time.
The first signs of pathology in the development of the nervous system may appear in a child immediately after birth or after some time. In the case of infants, a pediatric neurologist must necessarily examine infants with the following symptoms:
- When crying or the slightest excitement, the little one's hands shake and his chin trembles. Sometimes this phenomenon occurs even in a calm state.
- The baby is characterized by restless, shallow sleep, which is easily disturbed by external factors.
Advice: If a baby can be awakened by even a conversation between parents, you should not try to create the most comfortable conditions for him.
A darkened room, closed doors and windows, walking on tiptoe and talking in a whisper will not help, but will only aggravate the situation and delay the start of diagnosis and treatment.
No matter what additional symptoms this condition is accompanied by (even if there is nothing else), contacting a specialist is necessary.
- The baby burps frequently and profusely, even if he does not eat much food at one time.
- Even with a slight increase in body temperature, the baby experiences convulsions, which necessitates the use of antipyretics.
- If, while supporting the baby, you “put” him on his feet or tiptoes, his toes become very tight.
As for children of older and more conscious age, a neurologist should be contacted when they experience the following manifestations:
- Frequent or persistent headaches.
- Shooting or piercing pain in the back.
- Problems with focusing and memory.
- At different levels of the spine, disruptions in the performance of usual functions are noted.
- Development of panic attacks.
- Fatigue, lethargy, lack of interest in surrounding objects.
- Damage to peripheral nerves (neuralgia, neuropathy).
- Visible delay in the rate of development of speech, writing, and intelligence.
Any neurologist will tell you that severe lesions of the nervous system are much easier to detect than mild ones.
At the same time, prolonged and missed development of the disease is no less dangerous than its more serious counterpart.
Only if parents contact doctors in a timely manner with their suspicions, without waiting for a scheduled examination, can they count on effective prevention of common pathologies.
In addition to the traditional examination and collection of information on existing complaints, the neurologist must clarify the list of all diseases suffered since birth. In addition, attention is drawn to the following points:
- The course of pregnancy, especially in the last weeks, and specific moments during childbirth are analyzed. The specialist clarifies whether the mother suffered any diseases in the third trimester of pregnancy.
- If suspicious or alarming points are detected, the pediatric neurologist can refer the child for an ultrasound, fundus diagnostics, MRI and other additional manipulations.
After the results of all procedures are received, the specialist compares the data, makes a diagnosis and prescribes a set of therapeutic procedures. It is worth considering that a good neurologist not only monitors the process of providing the child with the necessary services, but also actively treats him.
Thanks to the rapid development of medicine as a science, modern doctors have acquired many tools, drugs and devices that significantly improve the quality of treatment of neurological diseases. Today, a pediatric specialist treats children with chemical components only when absolutely necessary. First, the following procedures and manipulations are used:
- Manual therapy aimed at restoring the normal functioning of organs and restoring their mobility.
- A special technique of gentle children's manual therapy, based on working with ligaments and muscle fibers. All actions are carried out at a very slow pace, which allows you to relieve spasms from tense areas.
- Craniosacral technique. It is aimed at aligning the bones of the skull, as a result of which normal blood flow is restored, the movement of cerebral fluid improves, and intracranial pressure decreases. Most often, a neurologist treats very young children in this way, eliminating headaches and improving brain function.
- Emotional techniques are very relevant today. They are used for neuroses of various etiologies and behavioral disorders.
- Therapy is rarely complete without muscle relaxation. It includes several different techniques, each of which leads to relaxation of the fibers, which has a positive effect on the condition of bones, vertebrae and internal organs.
In addition to the listed conditions, a pediatric specialist identifies and treats infectious and traumatic lesions of the nervous system, the consequences of tumor growth, cerebral palsy, and convulsive conditions (including epilepsy). A neurologist identifies the connection between hereditary, endocrinological, psychiatric and orthopedic pathologies with lesions of the nervous system.
What developmental features should you pay attention to in the behavior and development of a child up to 1 year and later? What symptoms can serve as signals to contact a specialist? And which ones, on the contrary, are not a sign of pathology? These and other questions are answered by neurorehabilitation specialists: neurologist, neurophysiologist Igor Zhdanov and clinical psychologist Natalya Morozova.
What should you pay close attention to in a child’s life in the first year of life?
The most important thing is the child’s sleep and appetite. How a child eats and sleeps determines his development. Secondly, you should pay attention to certain developmental milestones.
- With regard to motor development: at 2 months you should observe holding your head in a supine position, at 3 months - rolling over onto your stomach, by 5 months - rolling over from your stomach, in the interval from 6 to 8 months - sitting up, standing on all fours, crawling on all fours , 8-10 months - the child stands near a support, in the interval from a year to a year and four months - independent walking. If you observe certain delays in musculoskeletal development, the child should be shown to a neurologist.
- Symptoms indicating increased intracranial pressure may be the following: poor sleep, constant restlessness and screaming, tearfulness, frequent regurgitation, trembling of the arms, legs and chin, protrusion of the fontanelle, as well as a rapid increase in head circumference in size.
- After birth, physiological tone usually lasts up to 3-3.5 months, then gradually returns to normal. Children with increased tone (hypertonicity) are very restless, often cry, are capricious, their arms and legs seem to be drawn towards the body and do not straighten.
Babies with hypotonia, on the contrary, rarely cry, sleep a lot, often skip feedings, and move their unusually flexible limbs little.
As for mental development, you need to pay attention to the pre-speech component: the child’s reaction to toys, to loved ones, as well as to sound in general. A rare pathology, but one that affects development, is hearing impairment. Therefore, if parents have the impression that the child does not respond to sound, this is a signal that they need to have their hearing checked.
At an older age (after 1-2 years), what symptoms may be a reason to contact a neurologist or psychologist?
Taste sensitivity
Taste irritations are perceived by taste buds, which are located in the mucous membrane of the back of the tongue, soft palate, the anterior surface of the epiglottis and vocal cords, the posterior wall of the pharynx and the upper part of the esophagus. In the oral mucosa, taste buds are found as separate inclusions.
There are four types of basic taste sensations - sweet, salty, sour and bitter. With prolonged exposure to any flavoring substance, sensitivity to it gradually decreases due to taste adaptation.
Different parts of the mucous membrane of the tongue are unequally sensitive to the main irritants. The sensation of sweet and salty is more pronounced at the tip of the tongue. The leaf-shaped and roll-shaped papillae are most sensitive to bitter.
To study disorders of taste sensitivity, the patient is asked to rinse his mouth for 3-5 seconds (the intervals for bitter are 3 minutes, and for other irritants 2 minutes) with 10 ml of a certain solution (temperature 20-250C). For the study, a 20% sugar solution, 10% sodium chloride solution, 0.2% hydrochloric acid solution and 0.1% quinine sulfate solution are used.
Receptors
In order to perform a thorough examination, it is necessary to understand the performance of deep and superficial receptors. In addition, the doctor evaluates autonomic functions by interviewing the patient. It is based entirely on his complaints. In order to perform a deep analysis of the nervous system, the doctor does special research. The person is in a sitting position, and his blood pressure is artificially reduced. After this, you need to check your heart rate and conduct deep breathing tests. Next, the doctor, as a rule, takes a test for the reaction and pressure in the eyeball. It is also necessary to palpate the skin to determine the state of sweating. We need to find out whether iodine can be used in therapy. If there are problems with urination, then it is necessary to further examine the abdomen. And if there is a need for this, then treatment of the disease should begin.
2. Inadequate methods of treating pathological processes of the dental system:
- traumatic (complicated) tooth extraction;
- the phenomena of galvanism in the manufacture of prostheses from different metals;
- improperly manufactured dentures that injure the oral mucosa and disrupt the height of the bite;
- galvanism phenomena when using fillings made of different metals.
Clinical picture. Persistent pain with severe pain syndrome and autonomic disorders predominate. The pain is localized in the area of the pathological focus, intensifies in paroxysms, lasts from several hours to several days, gradually decreasing in intensity.
A distinctive feature of odontogenic neuralgia is its long course, despite the elimination of the etiological factor of the disease.
Treatment.
1. Identification and elimination of the etiological factor.
acetylsalicylic acid 0.25-0.5 g 3-4 times a day after meals;
quversalin, 1-3 tablets 3-4 times a day before meals;
b) pyrazolone derivatives:
- antipyrine 0.25-0.5 g 3-4 times a day;
- amidopyrine 0.3 g 3-4 times a day (for people with hypertension, amazol 1 tablet 3 times a day is preferable);
- analgin 0.5 g 2-3 times a day (for very severe pain, analgin is administered intramuscularly or intravenously, 1-2 ml of a 50% solution 2-3 times a day);
- butadione 0.1-0.15 g 4-6 times during or after meals;
c) aniline derivatives:
- phenacetin 0.25-0.5 g 2-3 times a day;
- Sedalgin 1 tablet 3 times a day;
d) indole derivatives:
- indomethacin, starting from 25 mg. 2-3 times a day, bringing the daily dose to 100-150 mg (can be combined with salicylates); ibuprofen 0.2 g in the morning before meals, washed down with tea, and 3 times a day after meals.
3. Antihistamines:
- diphenhydramine 0.03-0.05 g 2-3 times a day;
- diprazine 0.025 g 2-3 times a day;
- suprastin 0.025 g 2-3 times a day;
- diazolin 0.1 g 2 times a day;
- tavegil 1 mg morning and evening.
History taking
At the first appointment, the doctor gets acquainted with the patient, his passport data, type of activity and collects anamnesis. The active position here is given to the specialist, not the patient.
First, the neurologist listens to the patient's complaints. Each complaint presented is a symptom of the disease. History plays an important role in making a diagnosis. It is very important to listen carefully to the patient.
The doctor asks questions about the patient’s complaints:
- when did the first symptoms of the disease appear;
- disease progression;
- duration of pathology;
- rehabilitation period;
- frequency of exacerbations.
The specialist also finds out all the patient’s chronic pathologies, the presence of hereditary factors, and what infectious diseases he has previously suffered. An experienced doctor immediately evaluates the patient’s gait, movements, and facial expressions during examination and history taking. All of the above indicators play a leading role in making a diagnosis.
Standard optimal neurological examination:
- examination of the neck and head;
- palpation of the abdominal organs;
- study of brain functions;
- testing for the presence of twilight consciousness.
Tranquilizers:
- Chloridiazepoxide initially 5-10 mg per day. Gradually the dose is increased to 100-120 mg per day, then gradually reduced;
- diazepam 2.5-5 mg 2-3 times a day;
- oxazepam 0.01 g 2-4 times a day.
5. Neuroleptics:
- Aminazine 0.025 g per dose 3 times a day after meals;
- thioridazine 0.05-0.15 g per day;
- haloperidol 0.0015 g 3 times a day.
Inspection. Evaluated:
- facial configuration;
- facial skin color (pallor, hyperemia, play of vasomotors on the face and chest, marbling, greasiness, dryness, increased sweating);
- the presence of elements of damage;
- the presence of hyperkinesis (character, localization, amplitude, rhythm, tempo, constancy, degree of severity, variety or stereotyping, disappearance or intensification during sleep).
Additional research methods: electroodontometry, electromyography, tests with adrenaline and histamine, radiography of the skull, maxillofacial region and cervical spine, electroencephalography, ultrasound encephalography, study of facial blood flow.
Movement and reflex assessment
Of course, the doctor must evaluate muscle function. He must examine the lower leg, shoulder girdle, determine their tone and the process of contraction. This will make it clear how developed the muscles are. As a rule, special and special tasks have been developed for such tests. They allow you to study the neurological status to the maximum.
It is imperative to take time to coordinate the patient. To determine this indicator, as well as to find out the performance of motor function, it is necessary to pay attention to the patient’s gait. In addition, a popular diagnosis is also used: you should touch the tip of your nose with your finger with your eyes closed.
Reflexes should also be assessed. They are divided into deep and regressive.
Patient examination
Not in all cases it is possible to make a diagnosis based on clinical data. There is a need for additional studies that will provide detailed information about the patient's condition.
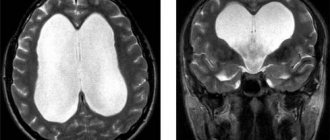
- CT scan. Identifies areas of hemorrhage, malformations of arteries or veins. Allows you to see tissue changes, swelling, softening during a heart attack or injury.
- Magnetic resonance imaging. More modern diagnostics provide more detailed and accurate data due to the greater resolution of the device and do not have such a detrimental effect on the patient.
- Angiography. A contrast X-ray examination that reveals pathologies and changes in blood vessels in the brain.
- Ultrasound. Using this study, a detailed image of the large vessels of the neck is obtained.
- Lumbar puncture or cerebrospinal fluid analysis. Conduct a study for meningitis, hemorrhages, tumors of the membranes.
- X-ray. Contrast is used to detect intervertebral disc herniations, proliferation of vertebral bodies, and tumor processes. The study gives a clear picture of the state of the subarachnoid space of the entire spinal cord.
- Electroencephalography. The main test prescribed for patients with suspected epilepsy.
And there are quite a lot of methods and studies that help in diagnosing diseases: biopsy of muscles, nerve tissue, genetic studies, blood tests.
Successful treatment requires finding out the cause of the pain and making the correct diagnosis. And for this you need to contact a neurologist. You shouldn’t let the disease get started; it’s much easier to defeat it in its infancy!
To carry out differential diagnosis and verify the diagnosis, the neurologist prescribes instrumental and laboratory tests. Some of them are performed on an outpatient basis, while others are performed in an inpatient setting.
In the presence of diseases of the brain and spinal cord, head injuries, spine and other neurological diseases, X-ray examination methods are used. Using a craniogram (x-ray of the skull), congenital defects of the skull bones, microcephaly, hydrocephalus, microcephaly, fractures or dystrophic changes in the bones of the skull are detected.
X-rays show changes characteristic of brain tumors and increased intracranial pressure. X-ray of the spine makes it possible to identify malformations of the spine, traumatic injuries and changes in the vertebral bodies due to tuberculosis.
X-ray contrast research methods include ventriculography and contrast myelography. A valuable examination method that allows one to obtain an image of the cerebral vessels after the introduction of a radiocontrast agent is angiography. Using this diagnostic method, the localization of the pathological focus is clarified, its nature and character are clarified. X-rays show images of veins, arteries, and venous sinuses.
Computed tomography is a research method that allows you to see precise and detailed changes in the density of brain tissue. Neuroimaging methods include magnetic resonance imaging.
Electroencephalography is a method of recording brain biocurrents. They are recorded on paper or on the screen of a cathode ray tube. Analysis of the electroencephalogram allows neurologists to identify waves that differ in vibration frequency, shape, amplitude, regularity and severity in response to external stimuli. During an ultrasound examination, the doctor receives information about changes in the blood vessels of the brain.
Neurologists at the Yusupov Hospital prescribe clinical and biochemical tests to patients. Laboratory technicians use the most accurate reagents for research. If indicated, genetic testing is performed.
Make an appointment with a neurologist by phone. The doctor will conduct an examination, prescribe the necessary tests and additional examination. Having received their results, after making a final diagnosis, he will prescribe individual treatment.
Doctor's specialization
In adult patients, the main organs examined are the brain and spinal cord.
Nerves and nerve plexuses become important elements of study. When the brain is damaged or pathological, other important organs and parts of the human body may suffer, so it is believed that neurology is closely related to the endocrine system, the activity of the gastrointestinal tract and the sensory organs.
It is worth visiting a doctor when you feel pain in the back, neck and head, chest and abdomen. In addition, you should consult a neurologist if depression has set in and neuroses, obsessive states and anxiety have appeared.
Neurological diseases can manifest themselves in the form of limb tremors and tics, which also becomes an important reason for quickly contacting a specialist.
It is necessary to consult a specialist if attention deficit disorder or a constant feeling of fear occurs. Such conditions contribute to the narrowing of blood vessels in the brain and disruption of its normal activity.