Tunnel syndrome (tunnel neuropathy)
– damage to one of the peripheral nerves as a result of its compression in a narrow tunnel formed by musculoskeletal and tendon structures. This happens with the development of an inflammatory process in the canal through which the nerve passes, traumatic injury, and also due to other factors.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can significantly impair a person’s ability to work and cause a lot of inconvenience. Therefore, if pain appears and you suspect carpal tunnel syndrome, you should immediately consult a doctor (orthopedist, neurologist) to prevent its development and progression and begin treatment as early as possible.
In what places does it develop most often?
- Interscalene gap (brachial plexus neuropathy or anterior scalene syndrome)
- Carpal tunnel on the wrist
- Cubital canal in the elbow joint
- Guyon's canal at the wrist (ulnar nerve neuropathy)
- Leg tunnel syndrome
- the most common is neuropathy of the peroneal nerve (compression in the knee joint), less often - compression of the external cutaneous nerve of the thigh (under the inguinal ligament) and other nerve trunks.
Thus, most often with tunnel neuropathies, the elbow and wrist joints are involved in the process, less often – the shoulder, knee and ankle.
Factors causing pathology
A variety of reasons can lead to the development of the syndrome. They concern both the whole organism and a specific anatomical formation. The most commonly affected nerves are the median nerve of the wrist, ulnar and radial nerves. Pathology of the suprascapular and nerves of the lower extremity - piriformis, femoral, peroneal and tibial - is less commonly observed. The following may cause compression of any of these nerve endings:
- Family predisposition. There is a disease in which people are born with narrow canals - in this case, the development of pathology is almost inevitable.
- Increased amount of fluid in the interstitial space. This usually manifests itself as swelling. This happens during pregnancy, kidney and heart failure, and prolonged fasting.
- Diabetes. In this case, the pathology develops through several mechanisms: - deterioration of the trophism of the ligaments and the nerve itself; - water retention during orgasm and the development of edema.
- Endocrine disorders. Menopause, taking COCs, and hypothyroidism also affect the tone of the ligaments.
- Connective tissue diseases. Any hereditary pathologies, rheumatism, arthritis, arthrosis, severe obesity and injuries - all this affects the ligamentous apparatus and the tissue that surrounds the nerve. Such conditions can be complicated by vitamin deficiencies (especially lack of vitamin C).
It is worth considering in more detail why the carpal tunnel narrows, since carpal tunnel syndrome occurs most often in this section (55-60% of visits to the doctor):
- Constant monotonous movements of the hand or its being in an awkward position. This most often occurs in people who spend most of the day at the computer. Builders, musicians, seamstresses, and carpenters are susceptible to the disease. The wrist is constantly in an uncomfortable position, which is why the ligament is damaged over time - it swells, and then thickens and begins to put pressure on the nerve.
- Sports activities. Constant microtrauma to the wrist or surrounding tissues leads to their thickening. This category includes people who engage in martial arts, tennis, javelin and hammer throwing.
Causes
Carpal tunnel syndrome develops when the size of the carpal tunnel decreases or the volume of tissue inside it increases. The main role in the development of compression-ischemic neuropathy is given to injuries at home, at work or during sports.
Reasons for such processes:
- 1. sprains, dislocations and fractures of the wrist,
- 2. pregnancy and associated swelling of soft tissues,
- 3. long-term use of oral contraceptives,
- 4. lactation period,
- 5. diabetes,
- 6. dysfunction of the thyroid gland or its removal,
- 7. obesity,
- 8. water imbalance,
- 9. hormonal imbalance,
- 10. acromegaly,
- 11. kidney failure,
- 12. sudden weight loss,
- 13. amyloidosis,
- 14. rheumatoid arthritis,
- 15. gout,
- 16. hematological diseases,
- 17. tumors deforming the wrist,
- 18. hereditary predisposition.
In rare cases, neuropathy develops as a result of acute infectious diseases: typhus or typhoid fever, tuberculosis, syphilis, brucellosis, herpes. Carpal tunnel syndrome can be caused by vascular pathology. Spasm or thrombosis of a blood vessel leads to ischemia of the tissues supplied by it, swelling and compression of the nerve in the canal.
Types of pathology, symptoms and complaints
In addition to the classic type, there are two more forms of the disease that are associated with the median nerve of the wrist:
- pronator teres syndrome - often occurs when the pronator teres is working monotonously (for example, when holding a long, narrow instrument - a drill, etc.) or prolonged compression. In this case, the muscle ligaments compress the nerve;
- Strother's band syndrome is a congenital condition caused by the presence of an additional process on the radius that puts pressure on the nerve, making it more vulnerable.
Often, people who expose their hands to monotonous or constant heavy loads develop disturbances in other canals - the cubital and radial.
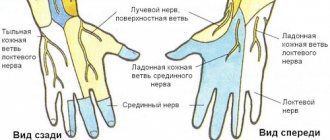
The median nerve innervates the thumb, index, middle, and about 1/3 of the ring finger, as well as most of the dorsum of the hand. Carpal tunnel syndrome is characterized by the following symptoms:
- Pain. It gets worse during work and at night (often interfering with sleep). There are two types of pain: - inflammatory - constant or wave-like, the strength can vary; - neuropathic - burning, sensation of electric current passing through a nerve.
- Numbness of a limb.
- Atrophic changes - a decrease in the elevation of the thumb in volume, muscle weakness, the phalanges are difficult to fully straighten.
- Tingling on fingertips.
- Local decrease in temperature and cyanotic skin;
Lower limb tunnel syndromes
Narrowing of the nerve canals of the lower limb is observed much less frequently. The symptoms are similar, the only differences are in the location and severity of the symptoms:
- femoral nerve – when compressed, the entire anterior edge of the lower limb suffers;
- tibial tunnel - symptoms appear on the entire back of the leg;
- fibular tunnel - tingling and numbness will be observed in the lower leg area.
Possible complications
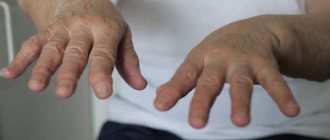
If you do not pay attention to the symptoms, the disease can take a complicated course. Degenerative processes will begin in the nerves. This is dangerous, as it can permanently deprive a person of his ability to work. In severe cases, contractures develop, the limb begins to resemble a primate’s paw, and the fingers in the area of innervation stop bending. The arm decreases in volume, weakness develops, and the inability to perform even simple actions develops. For people who mainly work with their hands, this condition means loss of ability to work.
Complications of the pathology lead to sleep problems and a deterioration in quality of life. A sick person cannot hold a spoon for a long time or lift a glass of water. In such cases, surgical treatment is usually indicated.
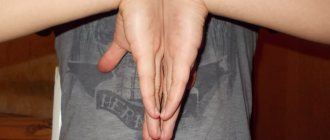
The photo shows the hand of a person with advanced carpal tunnel syndrome (“primate hand” or “claw hand”).
Categories of the population included in the risk group:
- 1. persons who, due to the nature of their work activity, make the same type of hand movements;
- 2. older people;
- 3. patients with endocrinopathies - dysfunction of the thyroid gland, pancreas or pituitary gland;
- 4. patients with diseases of bones and joints;
- 5. people with incurable diseases - vasculitis, rheumatism, psoriasis and gout.
The pathology that develops against the background of a systemic disease leads to loss of elasticity of articular cartilage, their aging, and cracking. Over time, the affected cartilage dies, and the articular surfaces grow together. Such deformations completely disrupt the anatomical structure of the hand.
Diagnostics
To clarify the diagnosis, in addition to questioning, the doctor conducts a series of tests:
- Tinel - when tapping the area of innervation, an increase in pain is observed;
- Phalena - the hand is bent and held in this position for about a minute. The test is considered positive if pain appears in the innervated fingers;
- Durkana – squeezing the hand leads to increased pain;
- Raising the limb - the arms are straightened above the head and held in this position for a minute. The appearance of pain and “pins and needles” indicates pathology.
In addition to tests, ultrasound, MRI, thermal imaging, and electroneuromyography are used in diagnosis. These methods always complement the basic research and help establish an accurate diagnosis and cure the disease in a short time.
Treatment
Treatment of carpal tunnel syndrome is aimed at preventing further entrapment of the median nerve. Patients are given anti-inflammatory and decongestant therapy to relieve pain and discomfort. Treatment of the underlying disease, manifested by carpal tunnel syndrome, is a mandatory condition, failure to comply with which can lead to frequent relapses and the development of complications.
When the first signs of pathology appear, it is necessary to fix the wrist. Patients are advised to apply cold to the lesion. If the cause of the pathology is work activity, it must be changed.
Therapeutic measures
Carpal tunnel syndrome can be easily treated in the early stages even without drug therapy (with the exception of anesthetics) and surgery.
Lifestyle correction
The first thing to do is to temporarily stop any stress on the affected limb. The doctor prescribes wearing a special fixator - a device that holds the hand in the correct position. It is worth paying attention to the following recommendations:
- The posture and position of the hand when working matter. A comfortable place will reduce the strain on your wrist;
- breaks during work and exercise for 30–40 seconds will relax the ligaments and muscles, increase blood flow, this will avoid excessive stress;
- if it is impossible to reduce the load in any way, use additional means, for example, warm hand baths with chamomile or oak bark.
Drug and physical therapy
If a patient suffers from carpal tunnel syndrome for a long time, then drug treatment is necessary. For this purpose, the following drugs are used:
- Anti-inflammatory drugs (including NSAIDs) are effective for inflammation of joints and ligaments, and for swelling. It is usually used topically in the form of ointments, in severe cases - orally or by injection. Provide pain relief and anti-inflammatory effects. Usually Ibuprofen, Diclofenac, Dimexide are used.
- Antineuropathic therapy - this includes drugs such as Lidocaine (in the form of plates), Gabapentin and weak antidepressants. Such conservative therapy is aimed specifically at the neuropathic component, so relief may not occur immediately, but after a few days.
- Hormonal drugs - for severe pain are prescribed - "Dexamethasone", "Prednisolone";
- Local anesthetics - also used in the form of injections - "Lidocaine", "Novocaine". If the pain is severe and interferes with sleep, a novocaine blockade is performed.
Along with drug treatment, physiotherapy should also be used:
- wrist massage. Can be done at home. The main thing is regularity and not dosed effort;
- warming up;
- electrophoresis of medicinal substances - NSAIDs, hormones, vitamins.
Surgery
Surgical intervention is resorted to in difficult cases and in the absence of effectiveness from the use of other methods. The operation is simple, usually performed under local anesthesia. The surgeon alternately cuts through the layers of skin, muscle and then cuts the transverse ligament, which puts the main pressure on the nerve. Stitches are applied, and after 2–3 weeks the patient returns to everyday life. There is a risk of developing another condition - severe separation of the little finger and thumb, but such a complication occurs rarely.
Drug treatment
To eliminate the symptoms of carpal tunnel syndrome, experts prescribe:
- NSAIDs – “Ibuklin”, “Diclofenac”, “Nimesil”,
- corticosteroid hormones - “Betamethasone”, “Prednisolone”, “Diprospan”,
- diuretics - Furosemide, Lasix, Hypothiazide,
- vasodilators - Cavinton, Piracetam, Vinpocetine,
- muscle relaxants – “Sirdalud”, “Mydocalm”,
- neurometabolites - B vitamins, Neostigmine, Nicotinic acid,
- injection of the anesthetic “Novocaine” into the place of compression,
- warming ointments and a fixing bandage on the wrist to relieve symptoms at night,
- compress of Dimexide, Lidocaine, Hydrocortisone and water,
- Methotrexate and other cytostatics are prescribed to suppress the activity of the immune system,
- chondroprotectors for joint restoration - “Rumalon”, “Alflutop”,
- thyroid hormones for hypothyroidism,
- diabetics are prescribed insulin or glucose-lowering drugs,
- for hypertension, ACE inhibitors or calcium antagonists are prescribed.